Social message propagation range prediction method without topological structure
A technology of topology structure and prediction method, which is applied in the field of prediction of the spread range of social information, can solve problems such as problems that do not consider the mutual influence of information, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and accurate prediction results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0044] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, a method for predicting the spread range of social information without a topology structure is as follows:
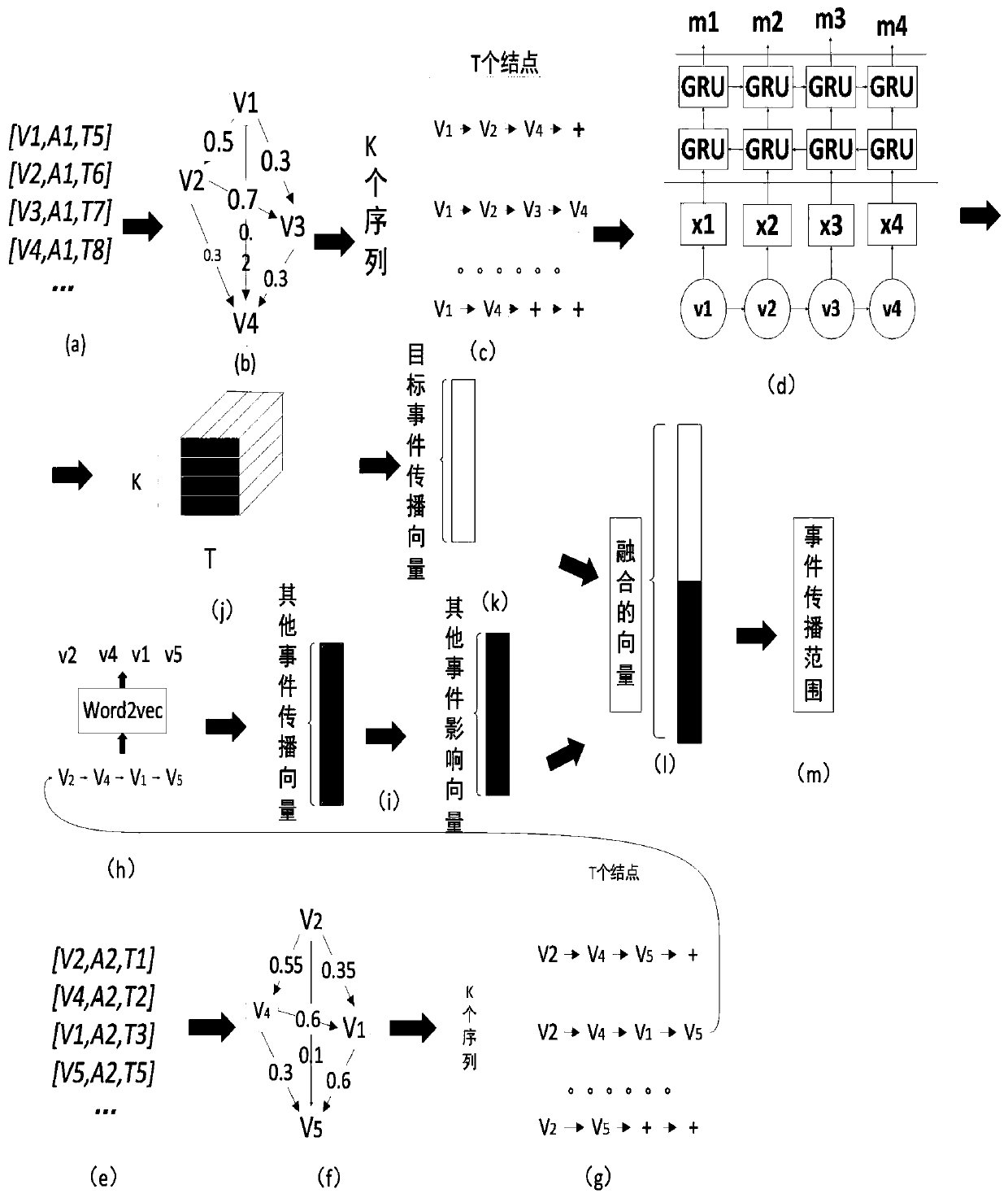
[0045] The invention studies the problem of predicting the range of message propagation under the condition of no topology structure, and proposes a method NT-EP for predicting the range of message propagation without topology structure. The method consists of four parts: (1) Construct a weighted propagation graph for each message by using the characteristics of message propagation decaying with time, use random walk strategy to obtain multiple propagation paths on the propagation graph, and then use the word2vec method to calculate each (2) replace the propagation path of the target message with the user’s feature vector sequence and input it to the Bi-Gate Controlled Recurrent Neural Network (Bi-GRU), and combine the attention mechanism to calculate the propagation feature vector of the target message;...
specific Embodiment approach 2
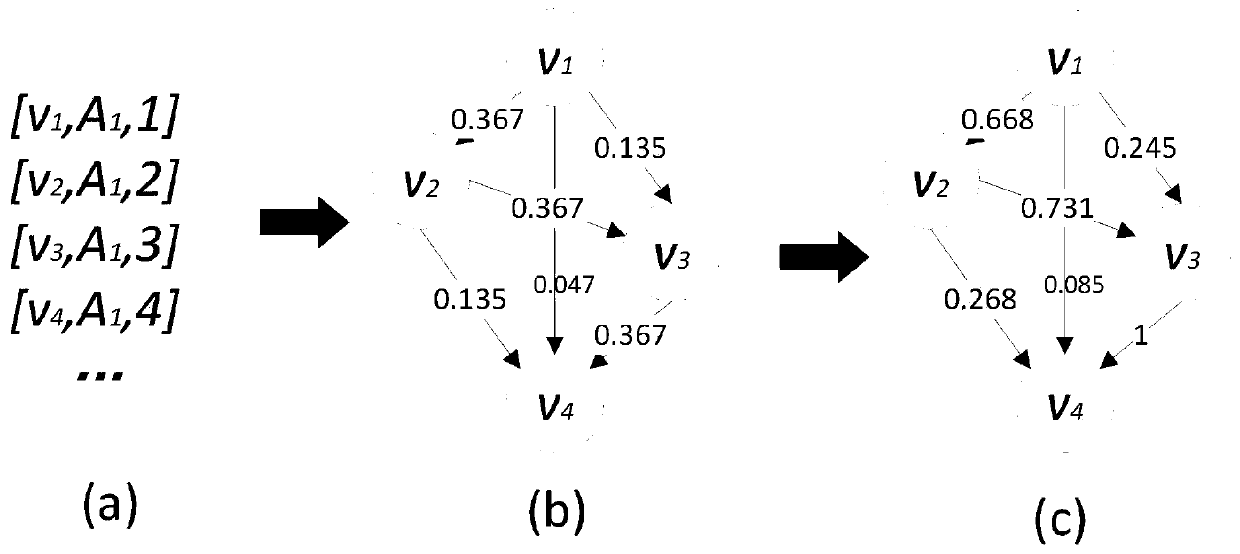
[0057] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 1, a weighted propagation graph is constructed for each message according to the propagation time difference in the message action log, as shown in figure 1 Shown in (a) and (b). The numbers on the side of the propagation graph represent the influence probability between users. After the propagation graph is constructed, use random walk to extract several possible propagation paths of the message from the propagation graph, such as figure 1 Shown in (c); the specific process is:
[0058] Transmission path selection
[0059] A given action log usually sorts the actions of each message according to the propagation time, such as figure 2 Shown in (a). User V 1 Received message A at time 1 1 , user V 2 Received message A at time 2 1 ,……. The real propagation track of the message cannot be obtained from the given action log. Because the real situation may be: use...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0068] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the word2vec method is used in the step two to calculate the initial feature vector of each target user on the propagation path of the message; the specific process is:
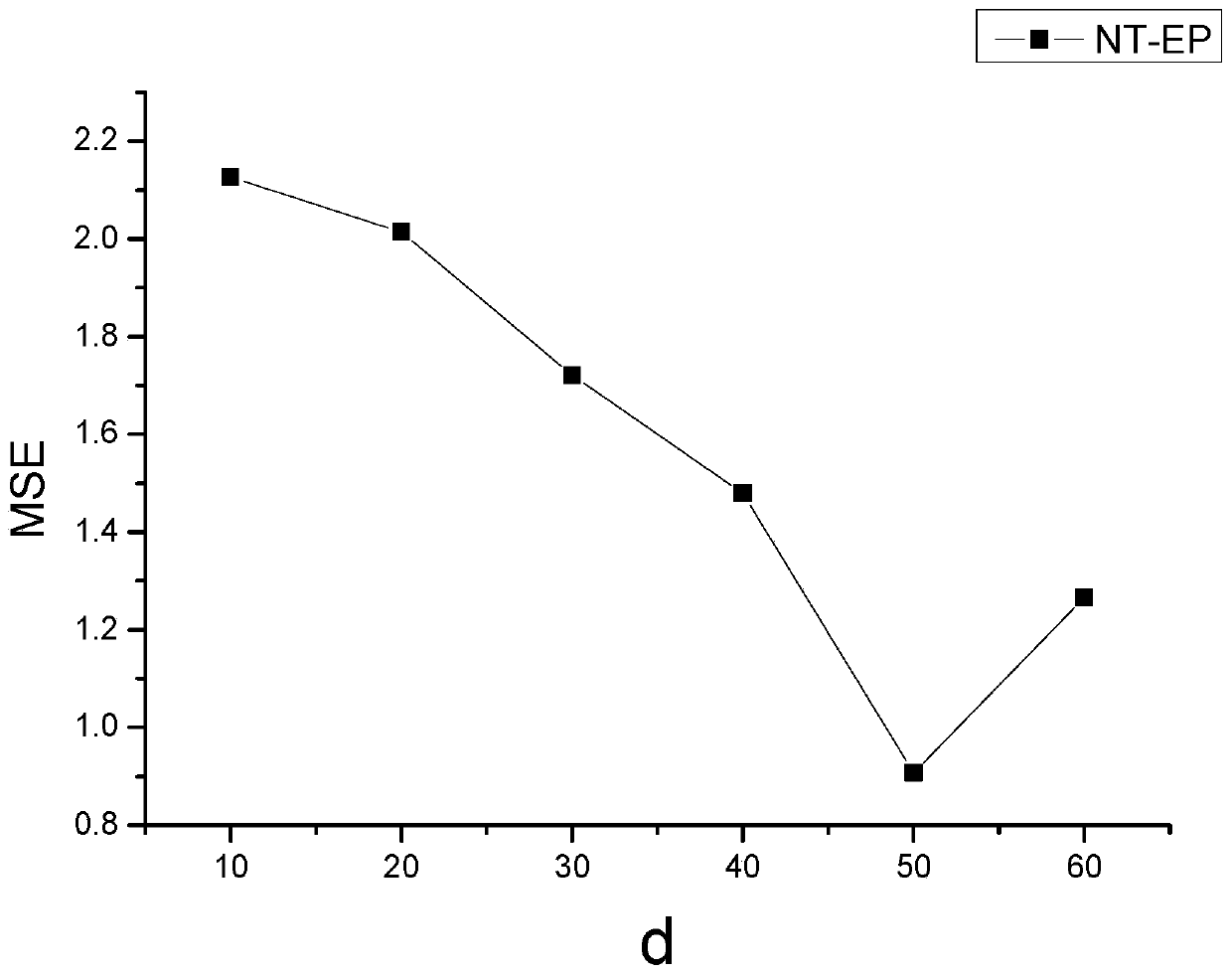
[0069] After extracting the propagation paths of all messages, treat each propagation path as a sentence, and each user on the path as a word in the sentence, input to word2vec [23] (Le Q,Mikolov T.Distributed representations of sentences and documents[C] / / International conference on machine learning.2014:1188-1196.) In the skip-gram model, the initial feature vector of each target user is obtained; assuming the user's initial The feature vector has dimension H.
[0070] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com