Docked aptamer eab biosensors
A body-sensing and complex technology, applied in the direction of biomaterial analysis, biochemical equipment and methods, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to produce aptamers, time-consuming, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
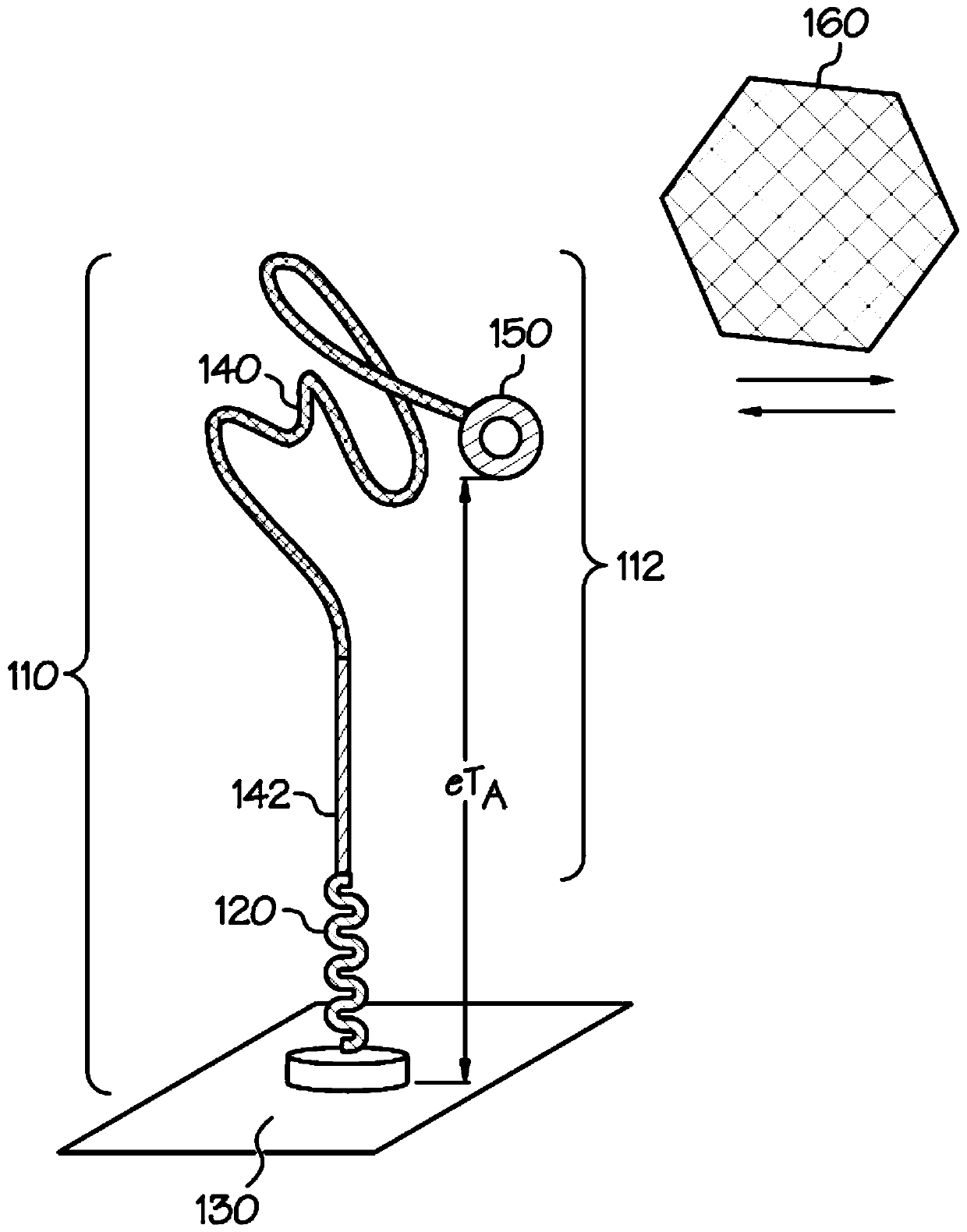
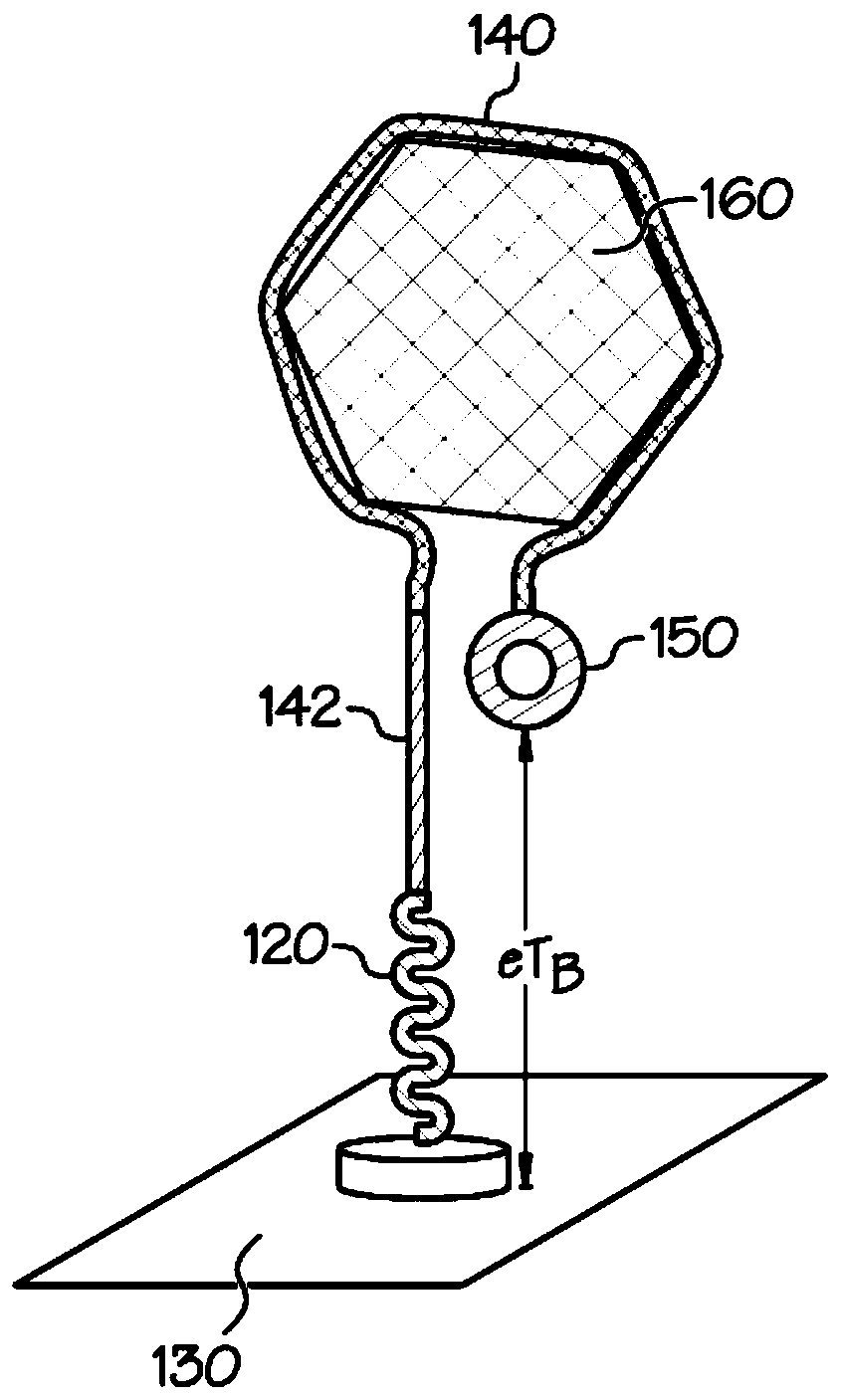
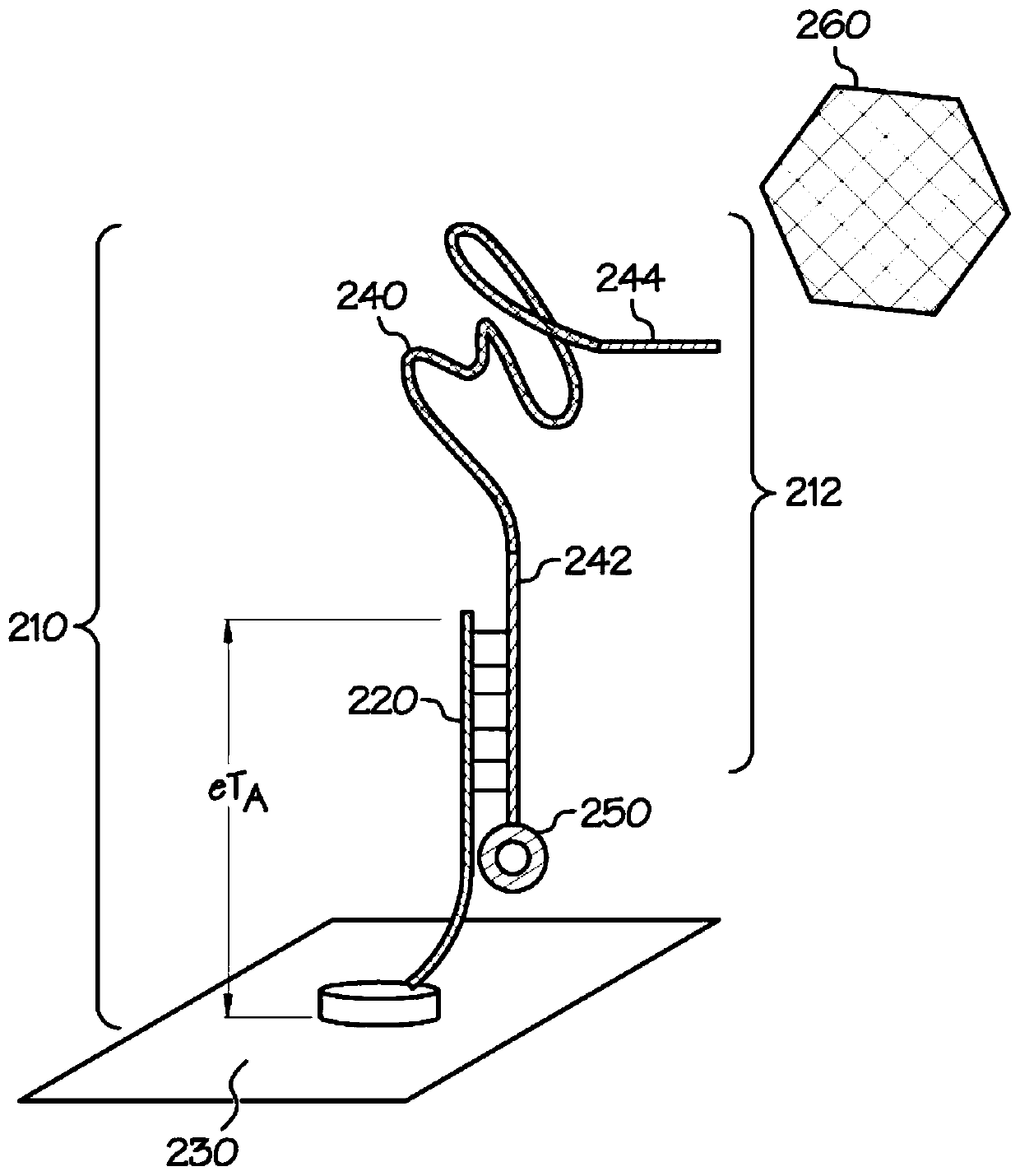
[0035] The embodiments described herein address the shortcomings of the SELEX process in biofluid sensor development by using docking aptamer EAB sensors. The disclosed sensors reduce the requirement to identify aptamers that not only preferentially bind the target analyte, but also exhibit a conformational change sufficient to generate an analyte capture signal that is distinct from an unbound signal. Specifically, docked aptamer sensors detect analyte capture using redox moiety position changes caused by the dissociation of bound aptamers from the docking structure. As described herein, a docking aptamer EAB sensor includes an aptamer initially bound to a docking structure. When bound to the docking structure, the redox moiety associated with the aptamer produces a first redox signal that can be measured by the sensing device. After interacting with the analyte, the aptamer changes shape to bind the analyte, causing the aptamer to disengage from the docked structure. Separ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com