Fluorescent probe and application thereof in detection of autolysosome
A technology of fluorescent probes and stereoisomers, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as lack, and achieve the effects of good biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, and easy detection and operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. The synthesis methods of compounds (1)-(5) are as follows, wherein the reaction ratios and purification methods adopt conventional ratios or conventional purification methods in the art. In addition, the inventors have confirmed that the structure of the above-mentioned compounds is correct by analyzing the hydrogen spectrum, carbon spectrum and / or mass spectrum data of each compound, wherein the mass spectrum and mass spectrum of compound (2) 1 H-NMR spectra were referred to Figure 8 and Figure 9 shown.
[0042]
Embodiment 2
[0044] Compounds of formulas (1)-(5) have similar properties, and the following mainly describes their properties by taking the compounds of formulas (1)-(3) as fluorescent probes (1)-(3) respectively as examples.
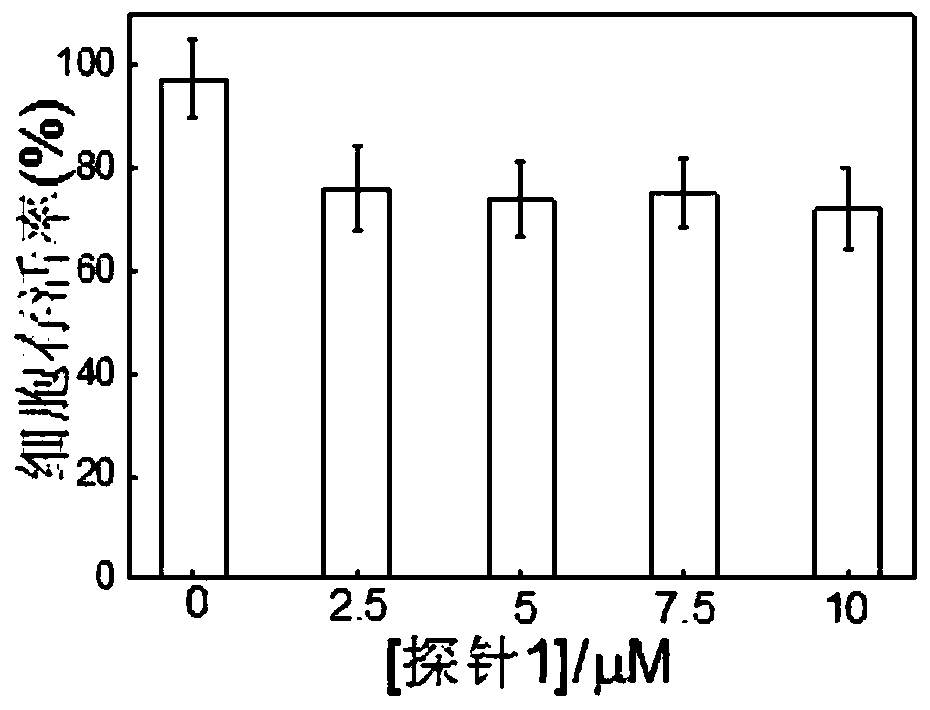
[0045] Utilize the fluorescent probe (1) of the embodiment of the present invention to carry out cytotoxicity experiment, specifically as follows:
[0046]
[0047] (1) Dissolving the fluorescent probe (1) with a small amount of methanol;
[0048] (2) The cultured HeLa and MCF-7 cells were added different concentrations of probe (1) solutions and continued to culture for 24 hours;
[0049] (3) Add 10% MTT solution after sucking up the culture medium, and continue culturing for 4 hours;
[0050] (4) After the culture medium was blotted dry, DMSO was added to dissolve it, and the absorbance at 559 nm was measured by a microplate reader. Take the absorbance value at 559 nm as the ordinate, and the concentration value of the probe (1) as the abscissa, and draw a g...
Embodiment 3
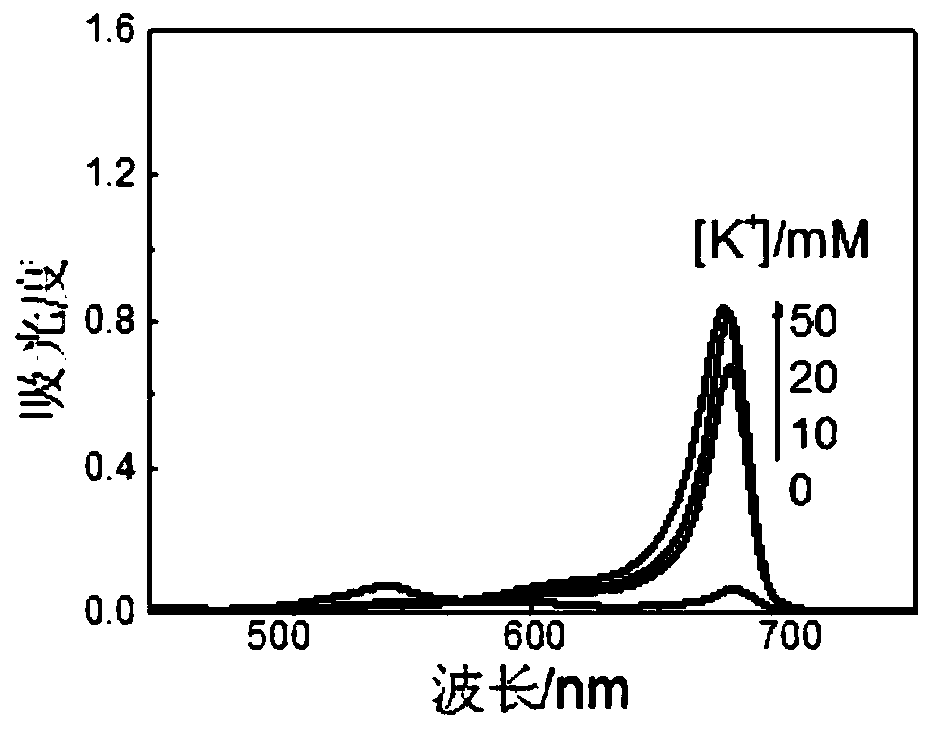
[0052] Utilize the fluorescent probe (1) of the embodiment of the present invention to assemble in an aqueous solution containing potassium ions to form supramolecular J-aggregates, as follows:
[0053]
[0054] (1) Dissolving the fluorescent probe (1) with a small amount of methanol;
[0055] (2) Dilute the fluorescent probe solution in step (1) with water containing different concentrations of potassium ions, and configure them into aqueous solutions containing the fluorescent probe (1) at a concentration of 4 μM;
[0056] (3) Utilize ultraviolet absorption spectrometer to detect the absorption spectrum of step (2) fluorescent probe (1) aqueous solution, the result is as follows figure 2 As shown, with the increase of potassium ion concentration, a new absorption peak was generated at 650nm, indicating that probe (1) formed supramolecular J-aggregates.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap