Quantitative control method for carbon anode replacement in aluminum electrolysis process
A quantitative control, carbon anode technology, applied in the field of electrolytic aluminum, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of the quantitative control of the sedimentation depth of the carbon anode, the uncertainty of the subsidence depth of the carbon anode, and the large error of the sedimentation depth. Value and practical value, energy saving, effect of ensuring stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1. A quantitative control method for carbon anode replacement in an electrolytic aluminum process, comprising the following steps:
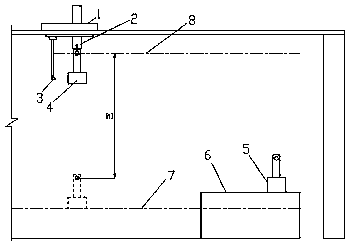
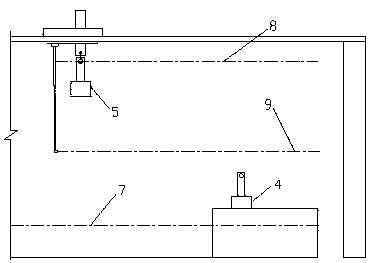
[0037] a. Set the zero point 8 and the reference point 9 in order from top to bottom above the liquid level 7 of the molten aluminum;
[0038] b. Record the height h1 at which the used carbon anode A4 moves up to the zero position 8, see figure 1 ;
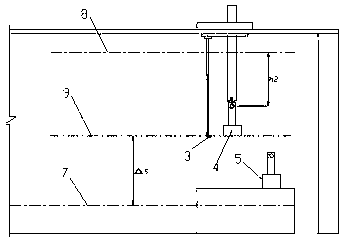
[0039] c. Record the height h2 when the bottom surface of the carbon anode A4 falls to be flush with the reference point 9;
[0040] d. Calculate the height △s from the reference point 9 to the liquid level 7 of the aluminum liquid,
[0041] △s= h1-h2;
[0042] e. Record the distance h3 from the carbon anode B5 to the zero point 8 when the bottom surface of the new carbon anode B5 that has been replaced is flush with the reference point 9;
[0043] f. Calculate the total height H that the carbon anode B5 should eventually drop,
[0044] H= h3+△s+△h;
[0045] Among them, Δh is th...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2. A quantitative control method for carbon anode replacement in an electrolytic aluminum process, comprising the following steps:
[0056] a. Set the zero point 8 and the reference point 9 in order from top to bottom above the liquid level 7 of the molten aluminum;
[0057] b. Record the height h1 at which the used carbon anode A4 moves up to the zero position 8, see figure 1 ;
[0058] c. Record the height h2 when the bottom surface of the carbon anode A4 falls to be flush with the reference point 9;
[0059] d. Calculate the height △s from the reference point 9 to the liquid level 7 of the aluminum liquid,
[0060] △s= h1-h2;
[0061] e. Record the distance h3 from the carbon anode B5 to the zero point 8 when the bottom surface of the new carbon anode B5 that has been replaced is flush with the reference point 9;
[0062] f. Calculate the total height H that the carbon anode B5 should eventually drop,
[0063] H= h3+△s+△h;
[0064]Among them, Δh is the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com