Electricity storage device
A technology of power storage device and power storage element, which is applied to circuits, electrical components, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as easy volatilization, and achieve the effect of preventing or suppressing ignition and preventing the chain of overheating states.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
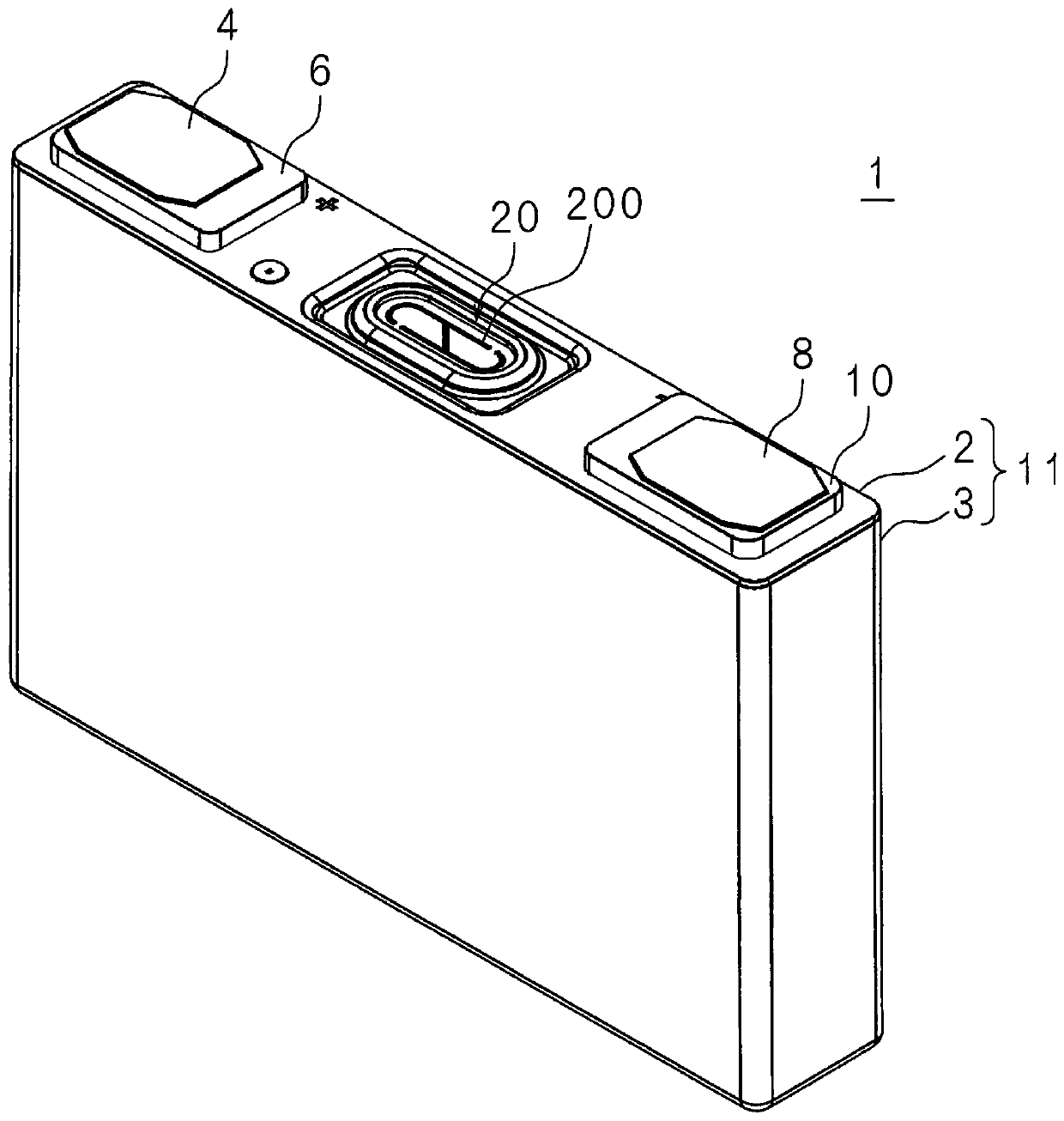
[0042] figure 1 It is a perspective view of the electricity storage element 1 . Although the case where the electricity storage element 1 is a lithium ion secondary battery is described below, the electricity storage element 1 is not limited to the lithium ion secondary battery.
[0043] The storage device 1 has a case 11 having a cover plate 2 and a case body 3, a positive terminal 4, a negative terminal 8, gaskets 6, 10, a burst valve 20, a current collector, and an electrode body (not shown).
[0044] The case 11 is formed of, for example, metal such as aluminum, aluminum alloy, or stainless steel, or synthetic resin, and is formed in a rectangular parallelepiped shape, and accommodates an electrode body and an electrolytic solution (not shown). Alternatively, the casing may also be a soft casing using laminated sheets.
[0045] The positive terminal 4 has a shaft portion penetrating through the cover plate 2 and a plate portion provided at one end of the shaft portion. ...
no. 2 approach
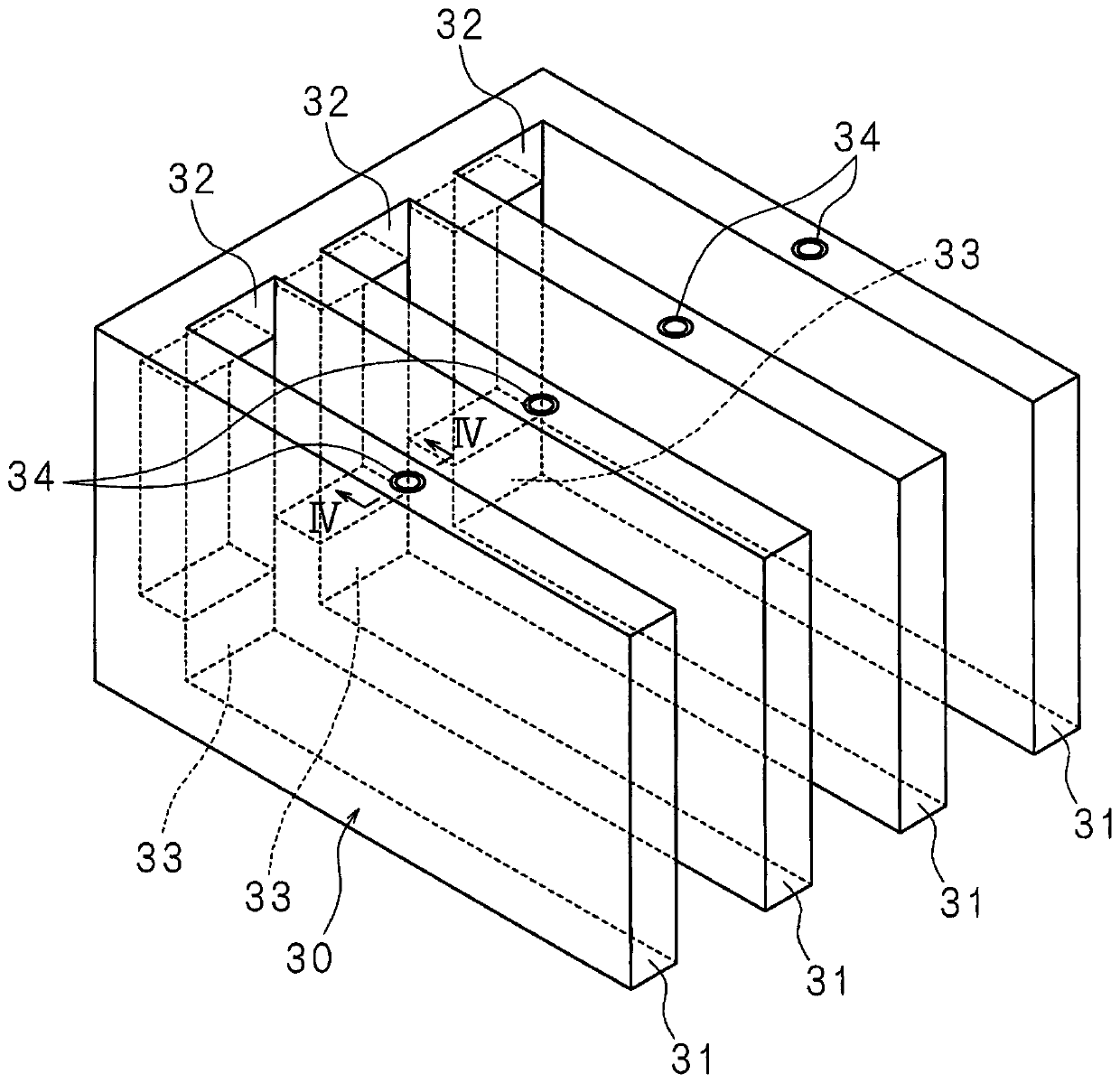
[0119] Figure 7 It is a perspective view of the cooling module 35 of the second embodiment. In the picture with image 3 The same symbols are used for the same parts, and detailed descriptions are omitted.
[0120] The cooling module 35 has four cooling sections 31 and cooling plates 36 .
[0121] The cooling module 35 is different from the first embodiment in which the four cooling units 31 are connected by the connection parts 32 and 33 , in that the end surfaces 31 a of the four cooling units 31 are in contact with the cooling plate 36 . The flame retardant L is accommodated in the cooling unit 31 in the same manner as in the first embodiment.
[0122] The internal spaces of the cooling unit 31 and the cooling plate 36 may or may not communicate with each other.
[0123] Figure 8 It is explanatory drawing of the case where internal spaces are connected in this embodiment. The power storage element 1 is inserted between the cooling parts 31 , and the flame retardant ...
no. 4 approach
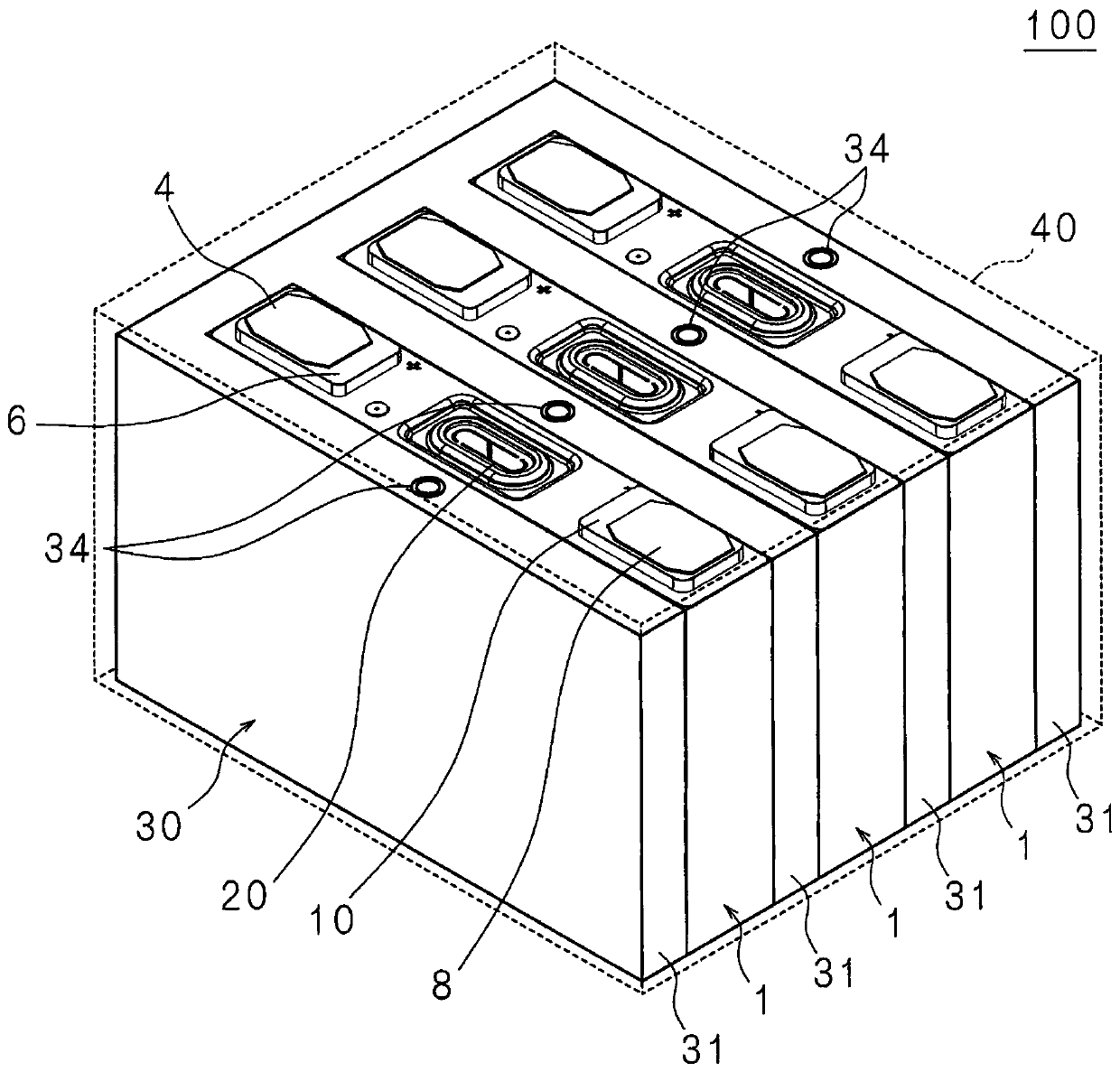
[0142] Figure 11 It is a perspective view of the power storage device 101 of the fourth embodiment. In the picture with figure 2 The same symbols are used for the same parts, and detailed descriptions are omitted.
[0143] Power storage device 101 is different from power storage device 100 according to the first embodiment in that it does not have connection parts 32 and 33 for connecting cooling part 31 . Cooling unit 31 is independently disposed between power storage elements 1 or between power storage elements 1 and the inner surface of case 40 . A flame retardant L (not shown) is accommodated in the cooling unit 31 .
[0144] When the energy storage element 1 generates heat, the flame retardant L in the cooling portion 31 in contact with the energy storage element 1 evaporates by taking away the heat of vaporization from the energy storage element 1 , and rapidly cools the energy storage element 1 . The generated gas is convected, cooled by the outside of power stora...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com