Block chain data storage method and device, equipment and medium
A data storage and blockchain technology, applied in the field of blockchain technology, can solve problems such as affecting local data and poor performance, and achieve the effect of saving storage space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
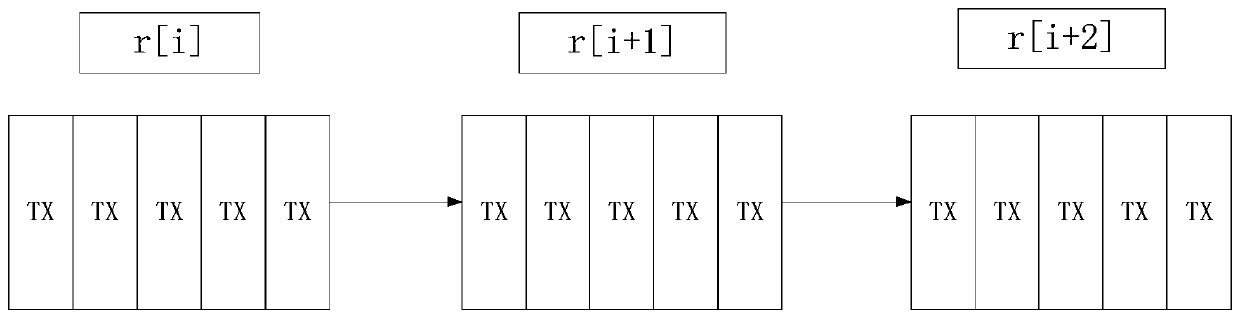
[0068] Figure 1A It is a flowchart of a blockchain data storage method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The method of this embodiment is applicable to the case where blockchain nodes store data locally. During the operation of the blockchain, many transaction requests that perform various functions will be initiated; the transaction requests are executed by nodes to form transaction data, which are packaged into blocks, and the blocks are connected in sequence, thus forming a blockchain. Blocks are recorded by all nodes in the blockchain network, thus preventing tampering.
[0069] In addition to storing transaction data in the blockchain, nodes generally store it locally, for example, to provide users with richer and more flexible data query services. Local data is the data generated according to the transaction request in the block and its execution result.
[0070] Based on different actual data access requirements, the local data storage methods adopte...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Figure 2A It is a flow chart of a blockchain data storage method provided in Embodiment 2 of this application. This embodiment specifically introduces the processing method when the blockchain is synchronized based on the aforementioned storage scheme.
[0094] In the blockchain network, due to various reasons, other nodes will synchronize the synchronization block to the local node. The synchronization block is a block that does not exist in the local node or an existing block. It may be a block or a block. May be multiple blocks of a branch.
[0095] Such as Figure 2A As shown, the method of the present embodiment includes:
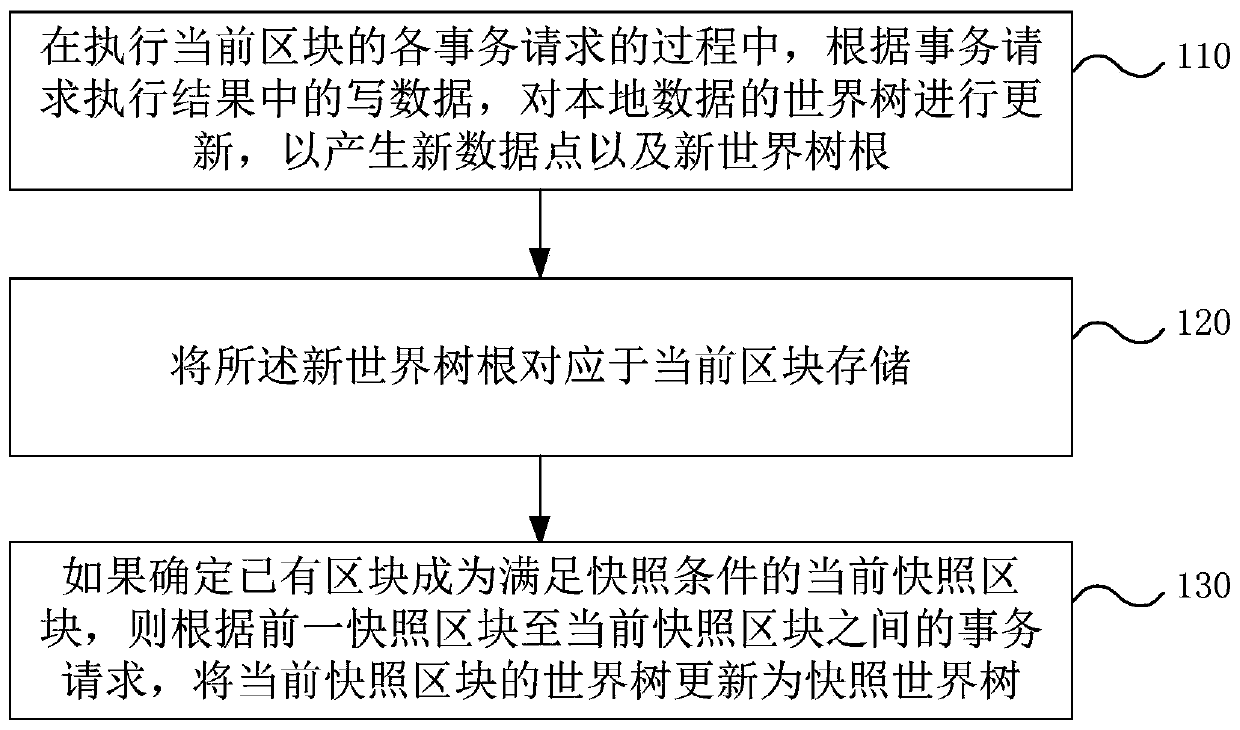
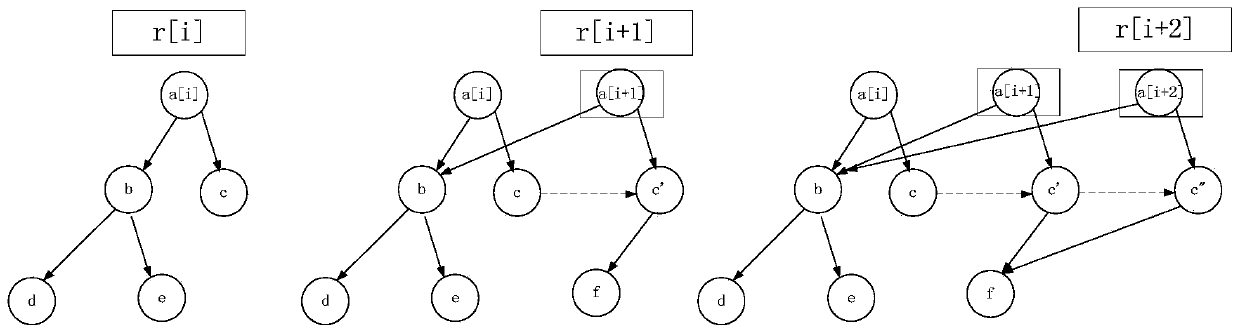
[0096] S210. In the process of executing each transaction request of the current block, update the world tree of the local data according to the write data in the execution result of the transaction request to generate new data points and a new world tree root, wherein the new The data point is an entity data point or a patch data point of ...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Figure 3A It is a flow chart of a blockchain data storage method provided in Embodiment 3 of this application. This embodiment specifically introduces the processing method when the blockchain is forked based on the foregoing storage scheme.
[0111] The so-called blockchain bifurcation is due to network communication, node failure and other reasons, which cause one or some nodes to generate different data from other nodes when processing blocks. But this inconsistency will not be discovered immediately, so new blocks continue to be generated on the basis of inconsistent blocks. Such as Figure 3B As shown, starting from block r[i-1], different nodes generate different blockchains, that is, a fork occurs. Until a fork is discovered based on the fork mechanism in the blockchain, the correct branch and the wrong branch will be determined at this time, for example, the long chain is the correct fork. Then, the node with the wrong branch will cancel the block of the wr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com