Patents
Literature
2494 results about "Block (data storage)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
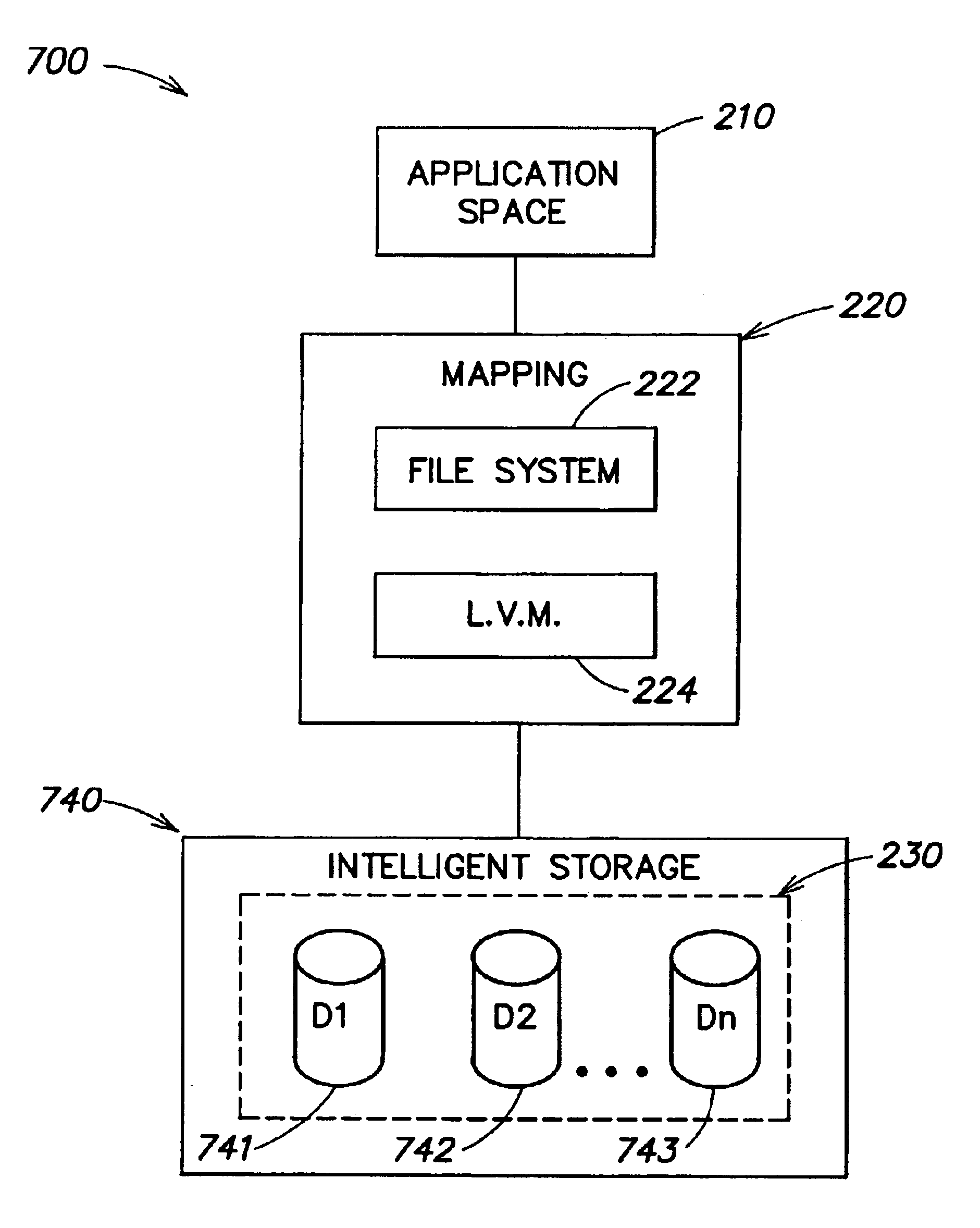
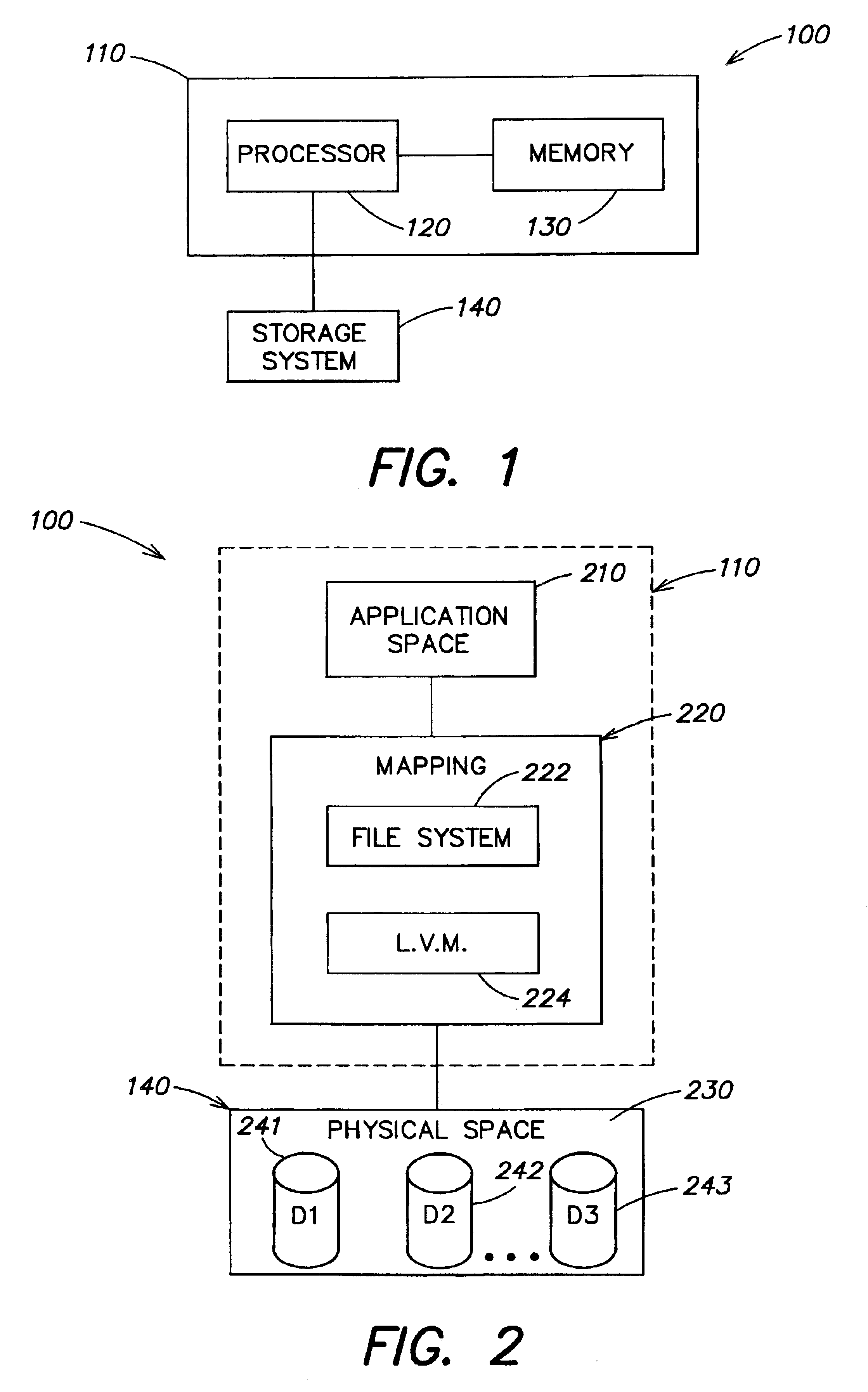
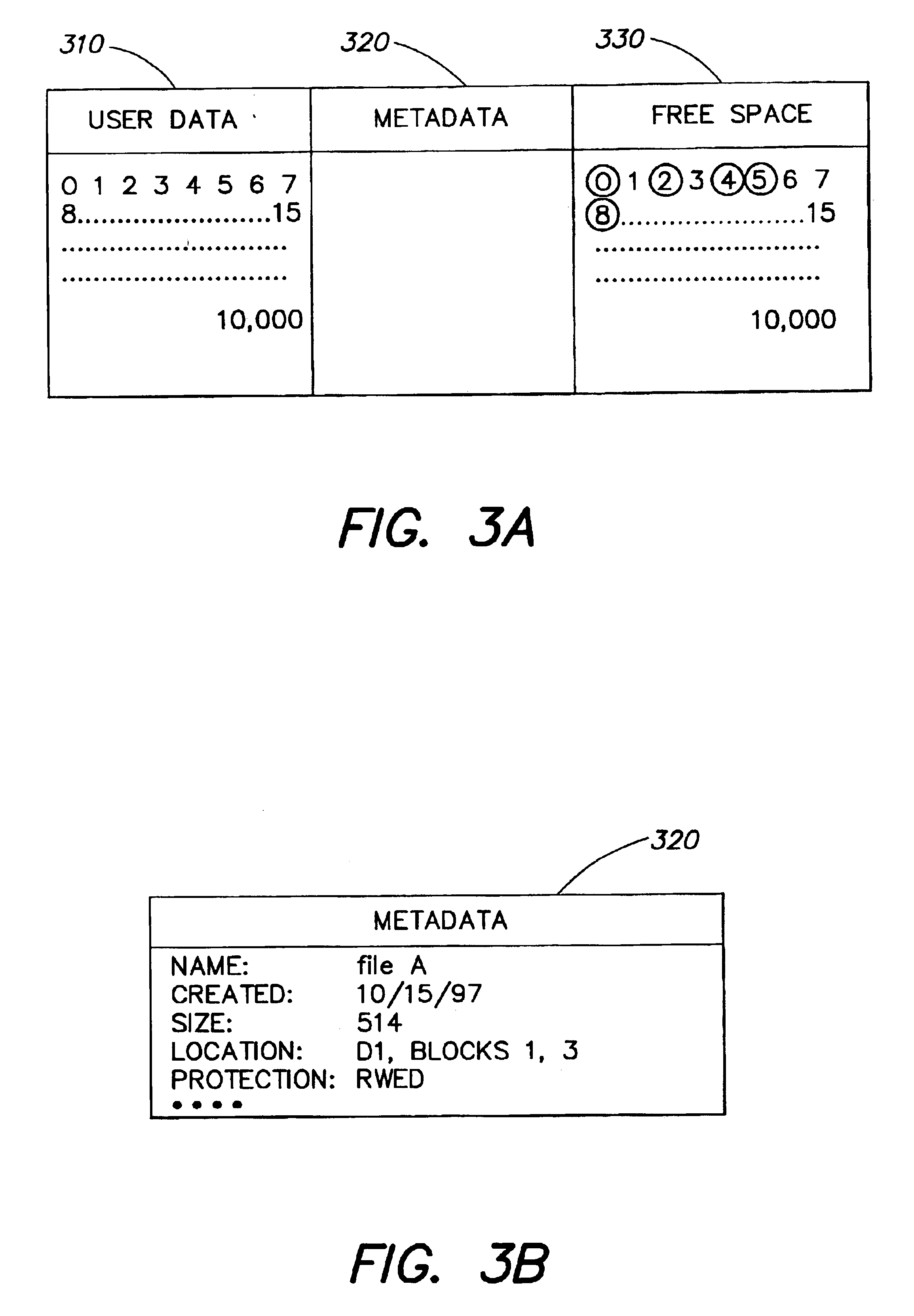
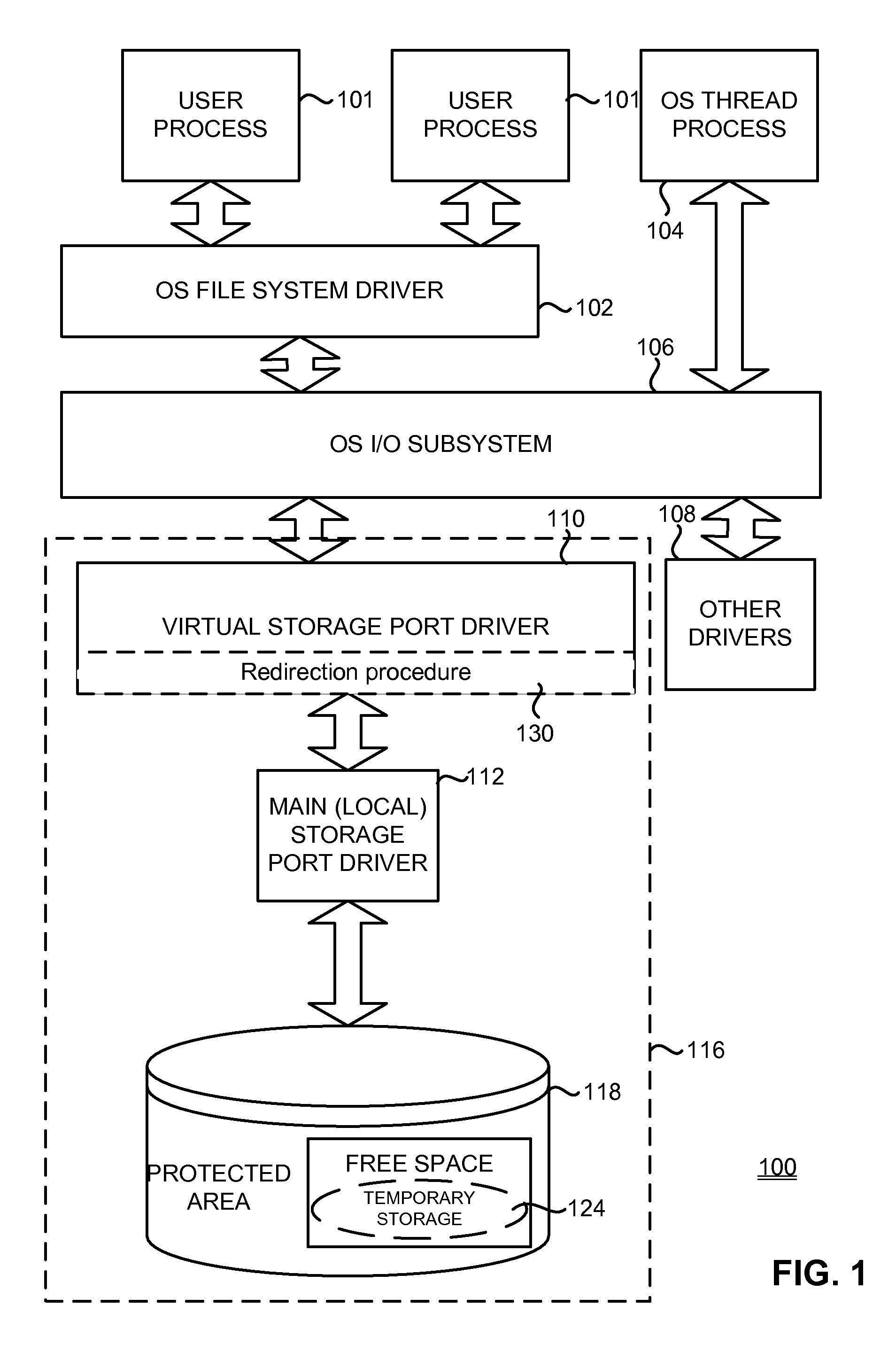
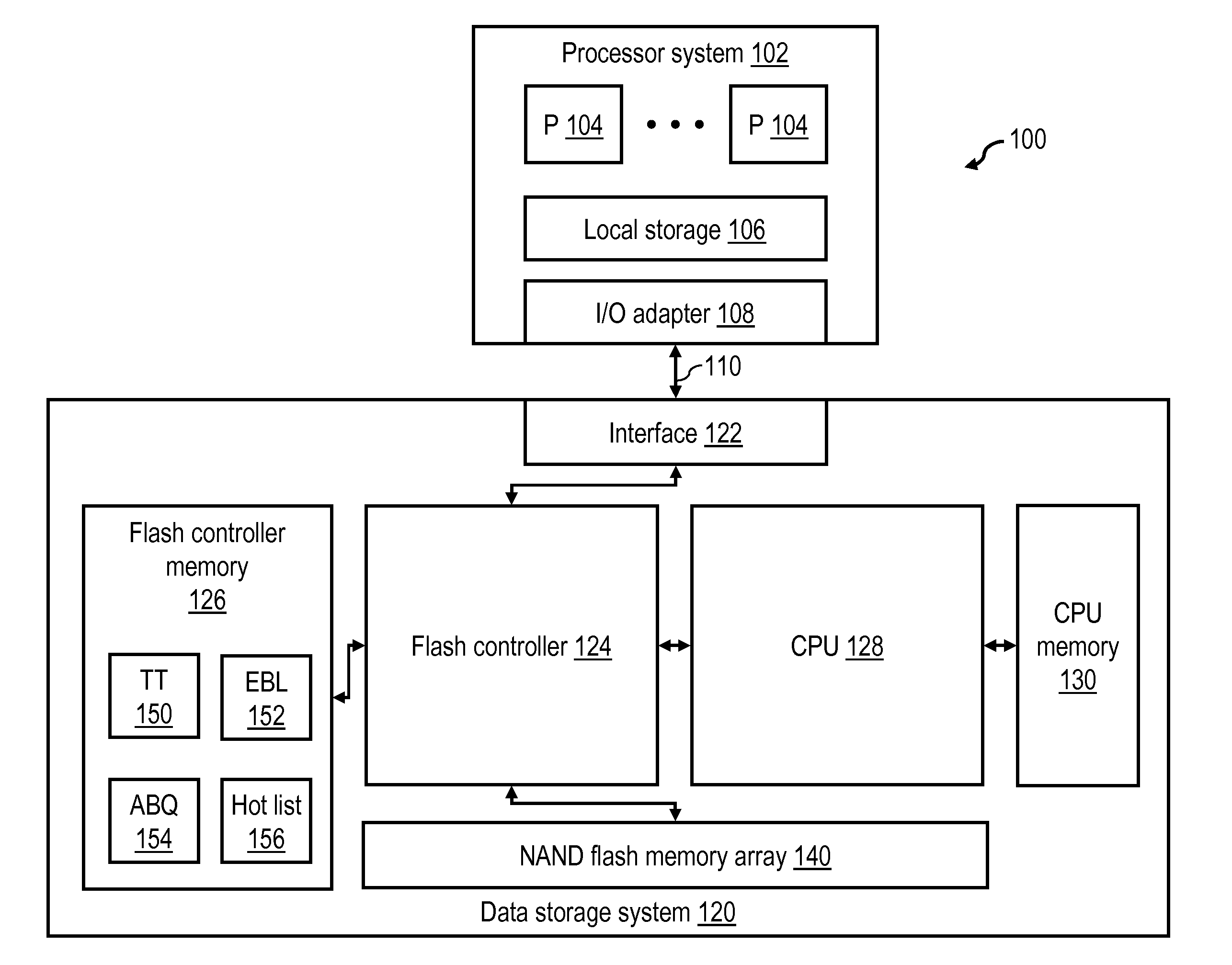
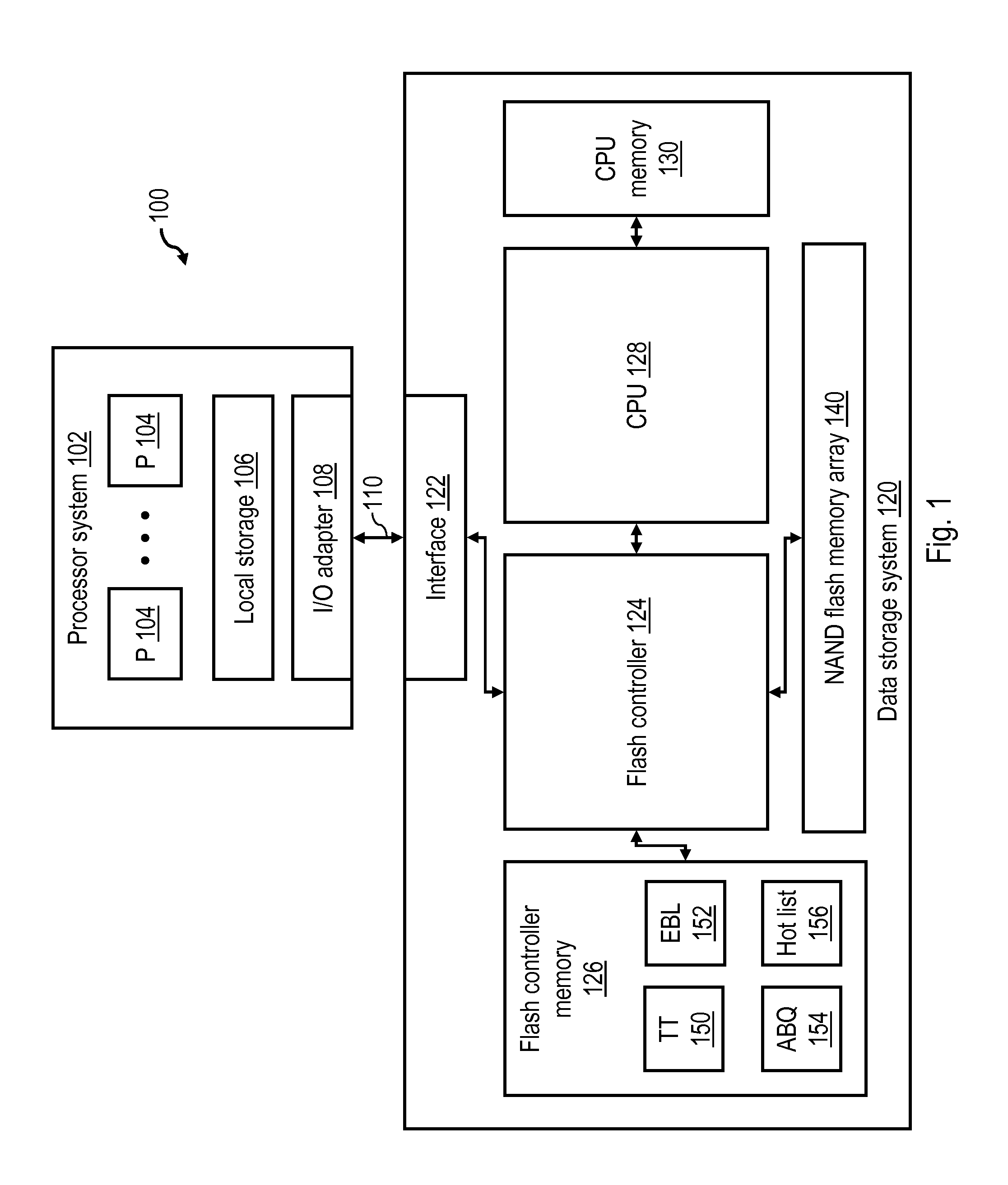
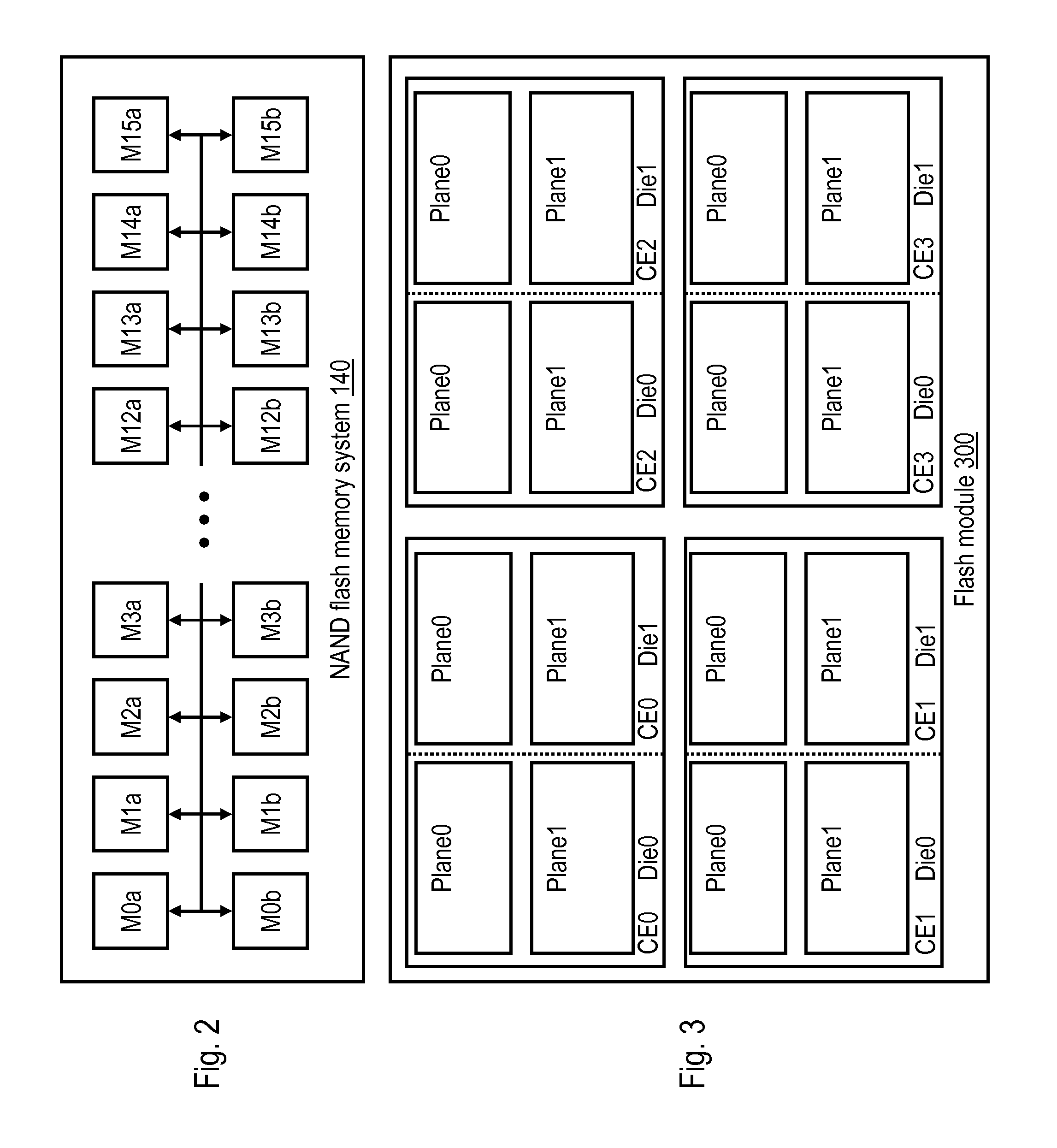
In computing (specifically data transmission and data storage), a block, sometimes called a physical record, is a sequence of bytes or bits, usually containing some whole number of records, having a maximum length, a block size. Data thus structured are said to be blocked. The process of putting data into blocks is called blocking, while deblocking is the process of extracting data from blocks. Blocked data is normally stored in a data buffer and read or written a whole block at a time. Blocking reduces the overhead and speeds up the handling of the data-stream. For some devices, such as magnetic tape and CKD disk devices, blocking reduces the amount of external storage required for the data. Blocking is almost universally employed when storing data to 9-track magnetic tape, NAND flash memory, and rotating media such as floppy disks, hard disks, and optical discs.
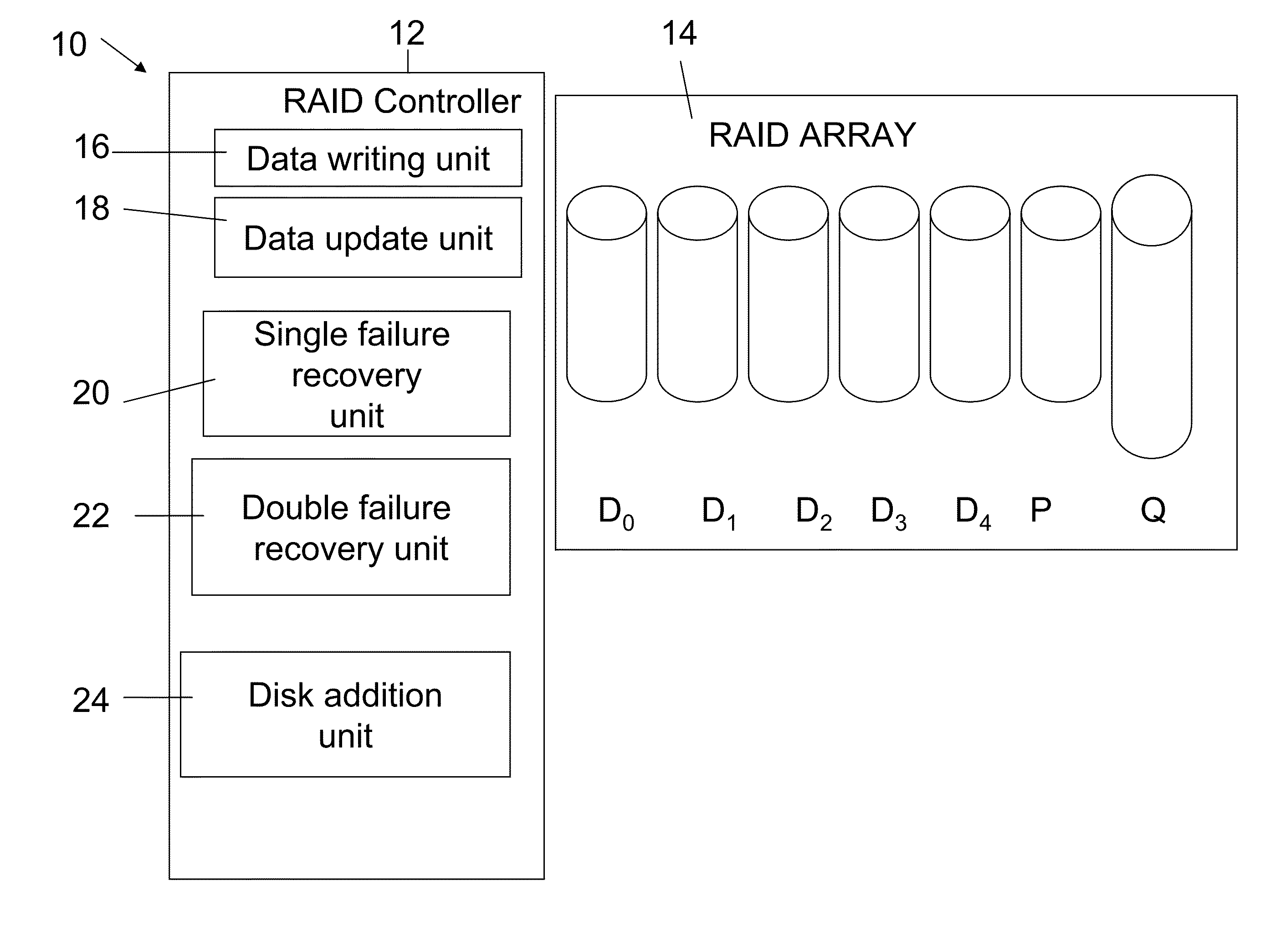
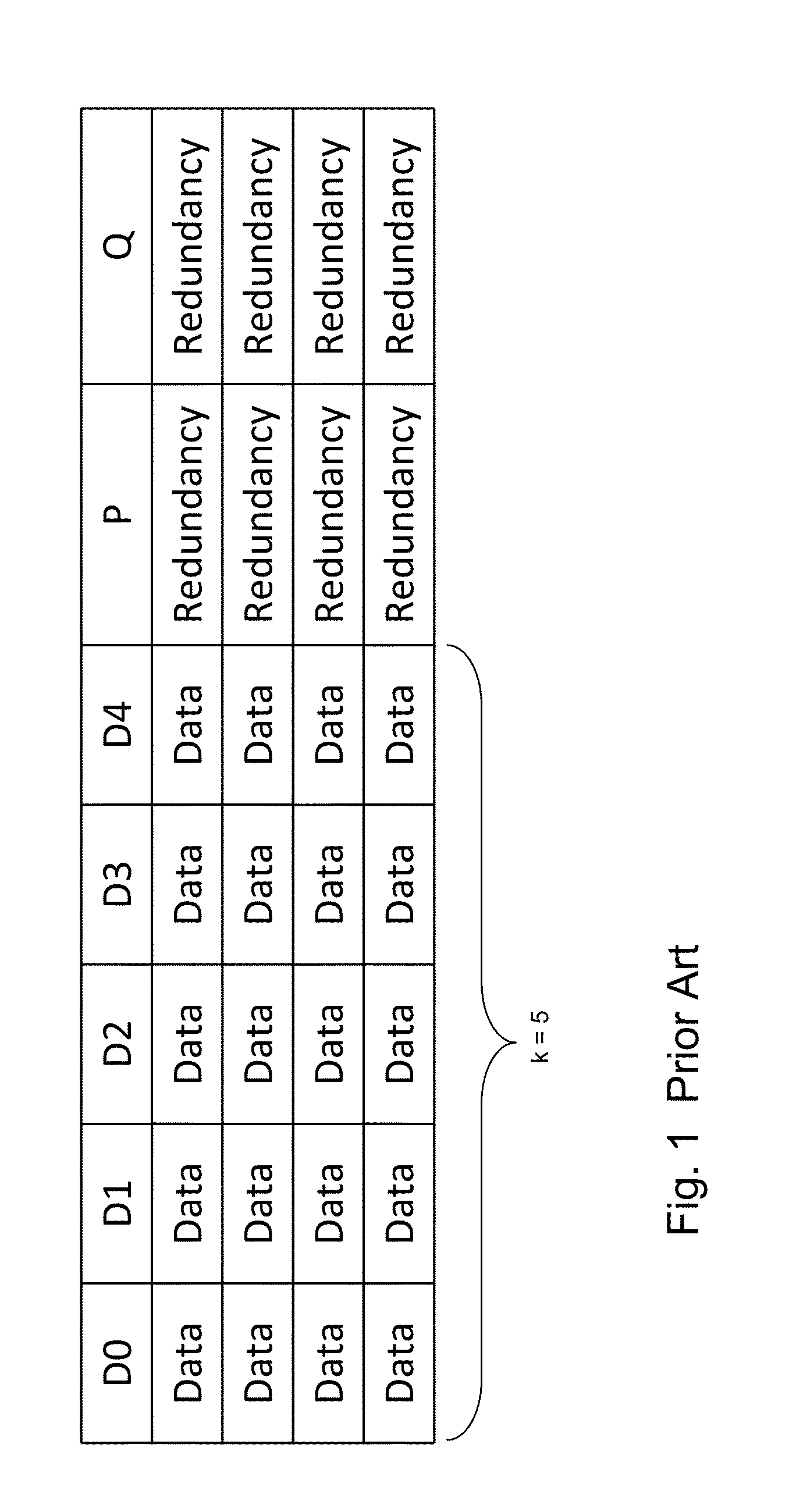
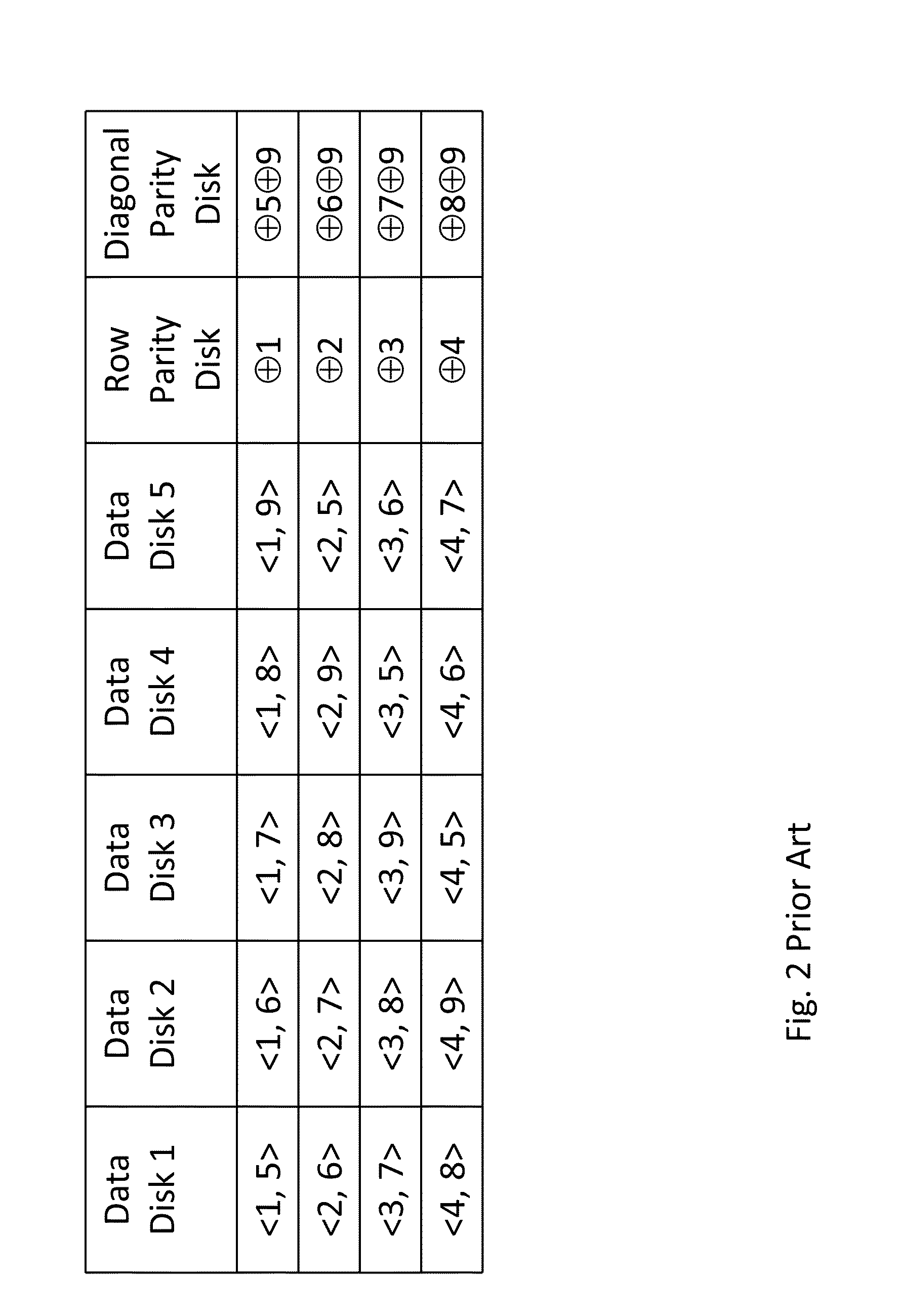
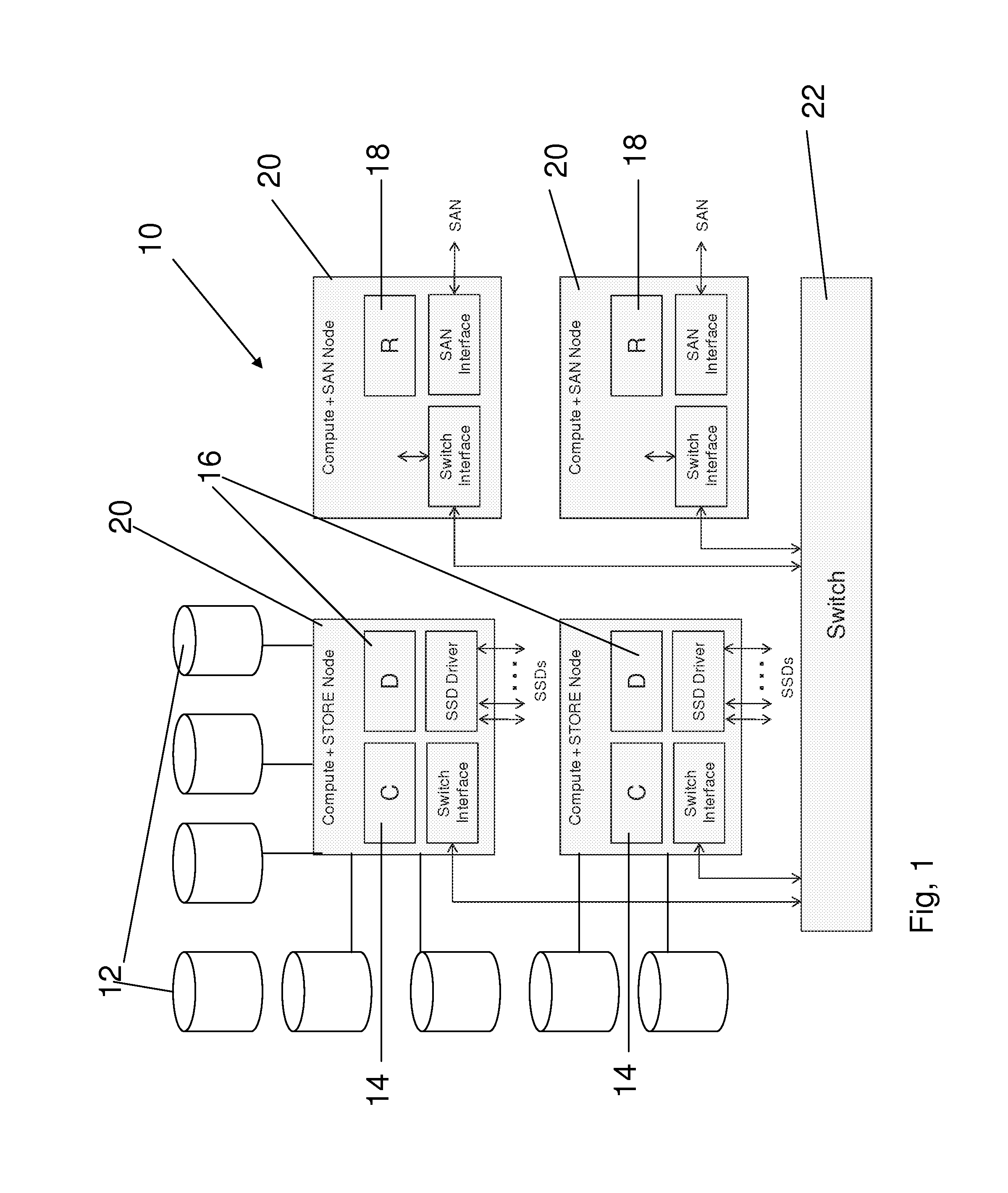
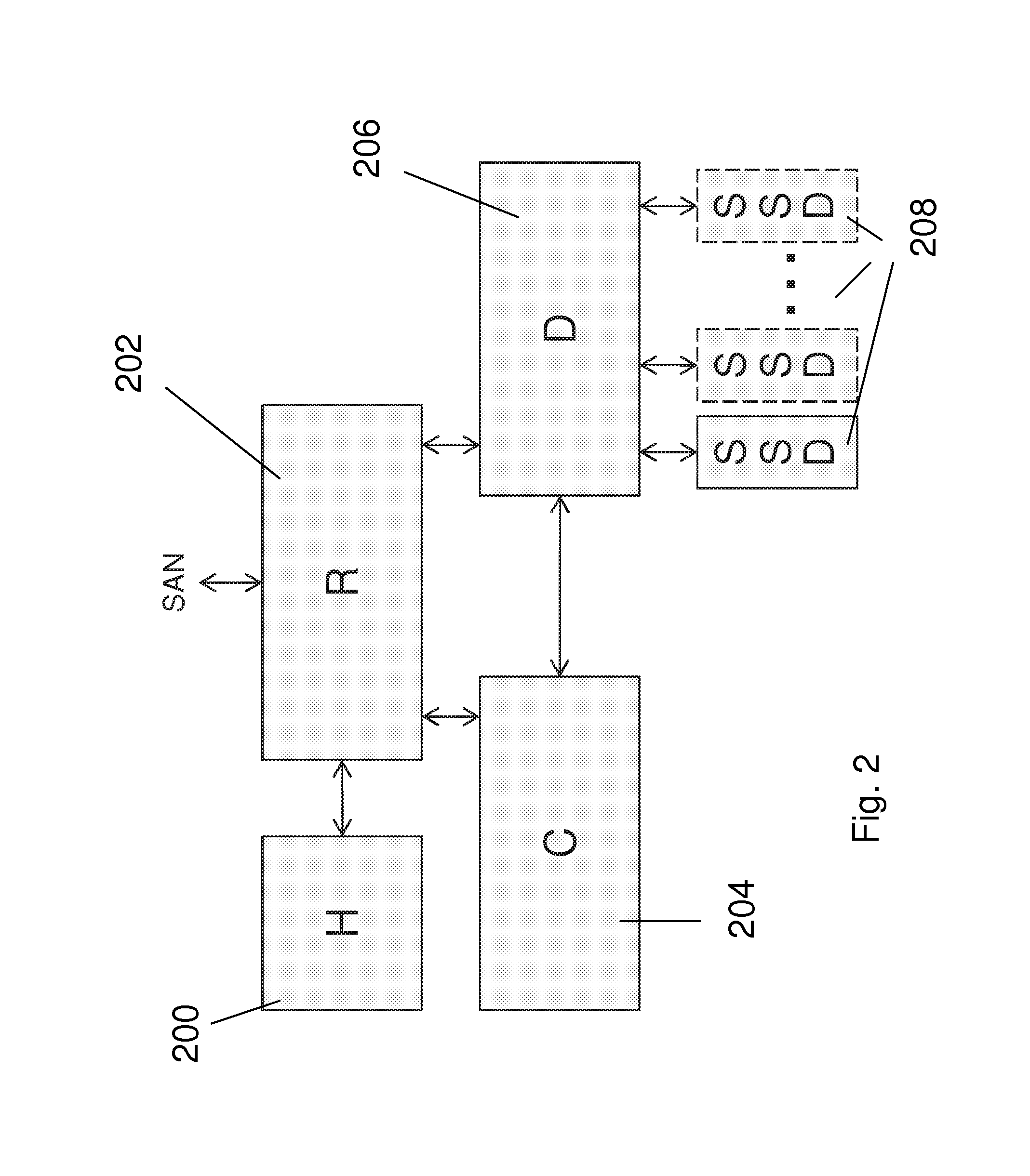
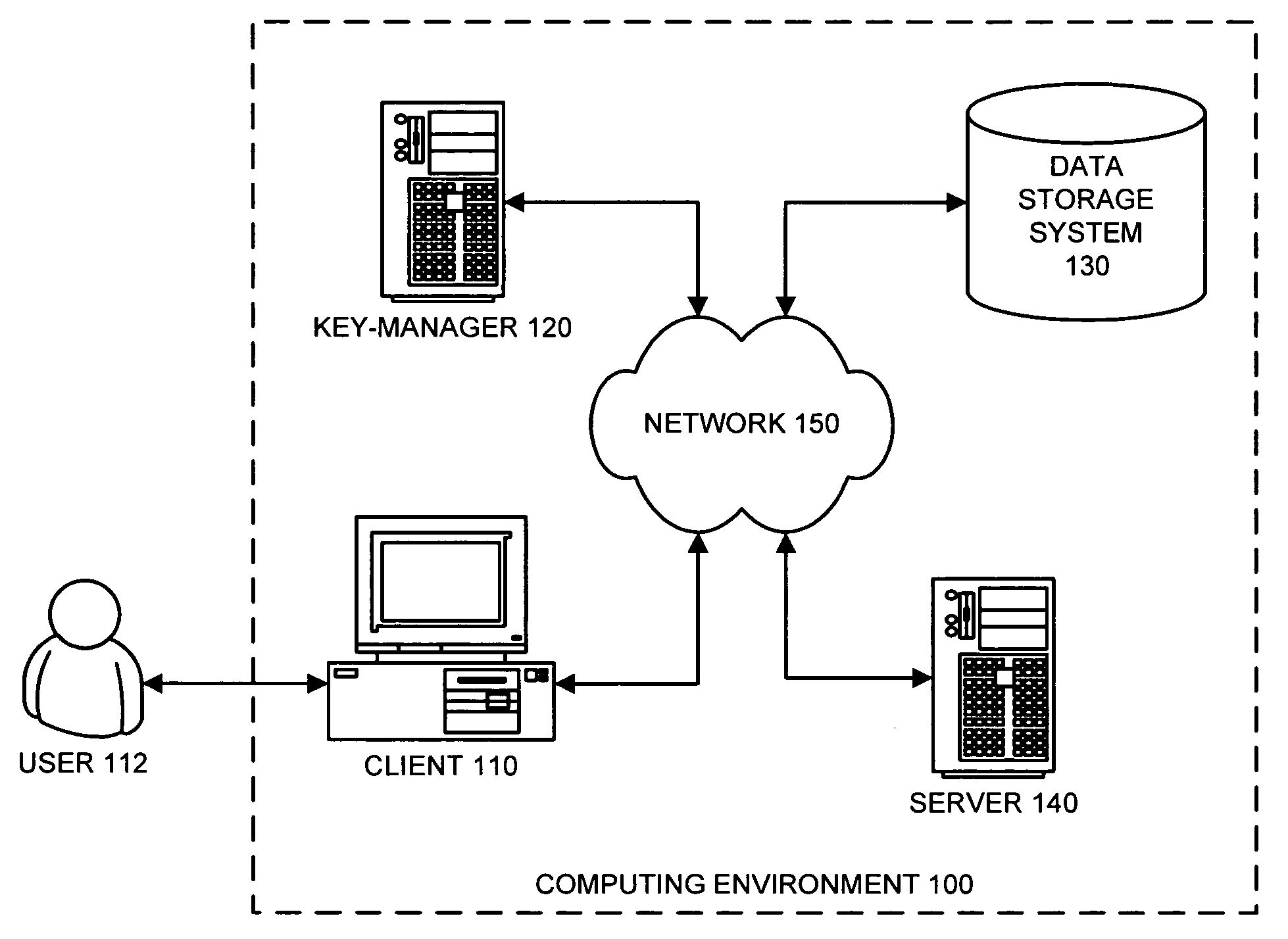
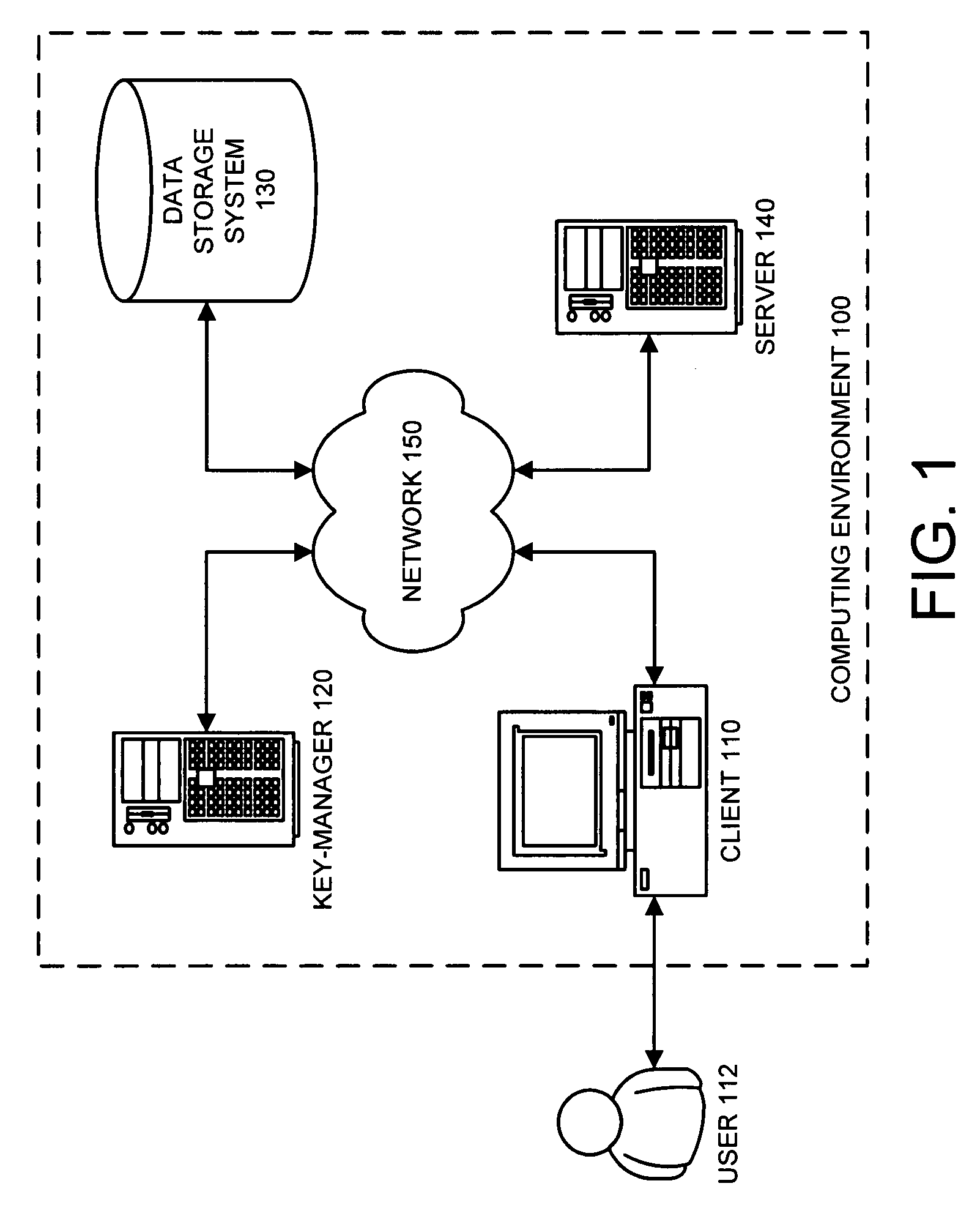
Secure data storage in raid memory devices
ActiveUS20130124776A1Reduce overheadUtility and advantageMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRAIDComputer architecture
A redundant array of independent disk (RAID) memory storage system comprising data storage blocks arranged in a first plurality of data rows and a second plurality of data columns, wherein parity data is stored in additionally defined parity blocks, and wherein numbers of data blocks in respective columns are different, to accommodate the additional diagonal parity data block that the geometry of the system requires. The system is suitable for an SSD array in which sequential disk readout is not required.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Scalable block data storage using content addressing
ActiveUS9104326B2Unlimited in capacityUnlimited in performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsComputer moduleDatapath
A device for scalable block data storage and retrieval uses content addressing. Data storage devices store data blocks, and are connected over a network to computing modules. The modules comprise control modules and data modules and carry out content addressing for both storage and retrieval. The network defines separate control paths via the control modules and data paths via the data modules.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
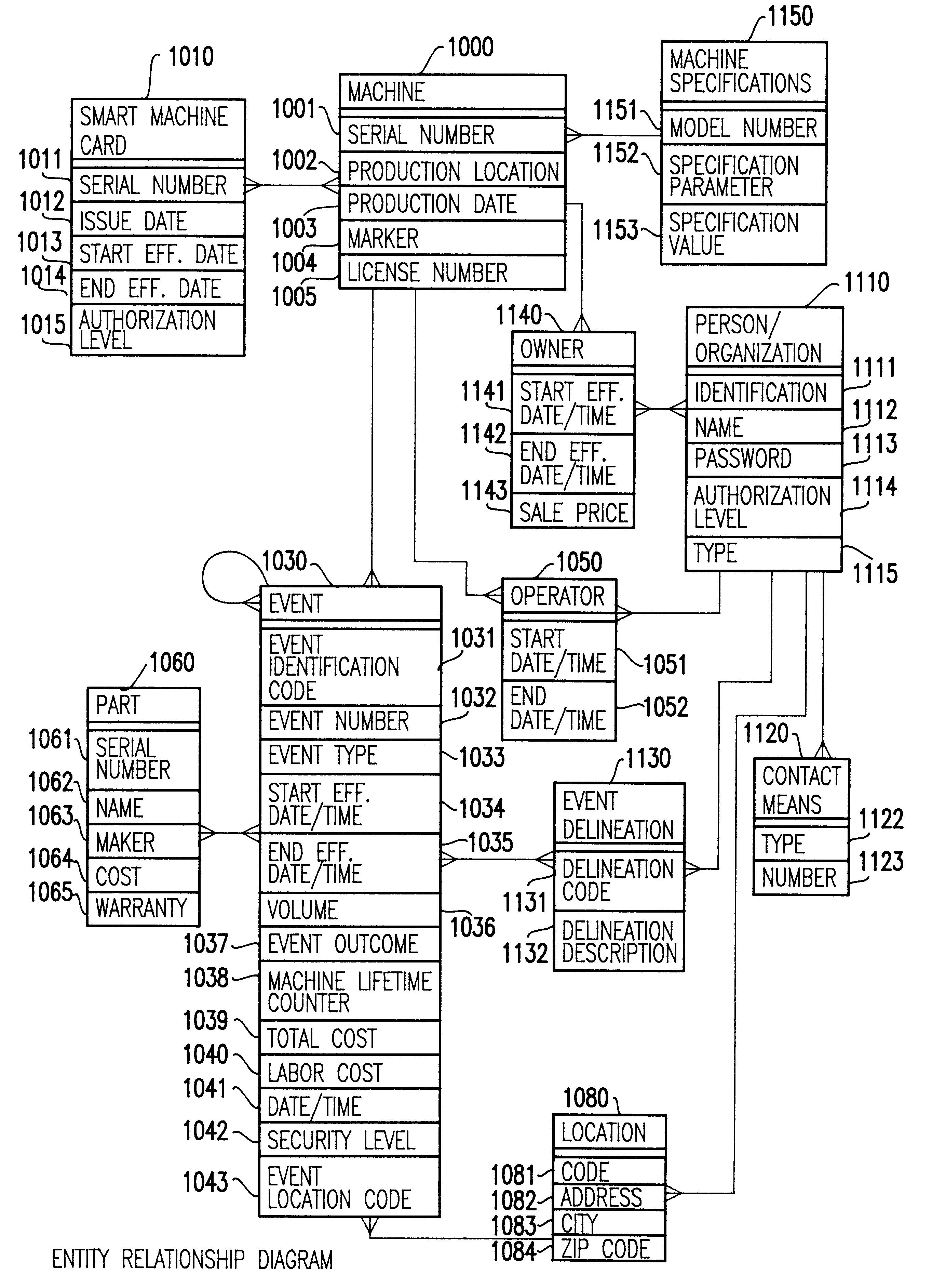
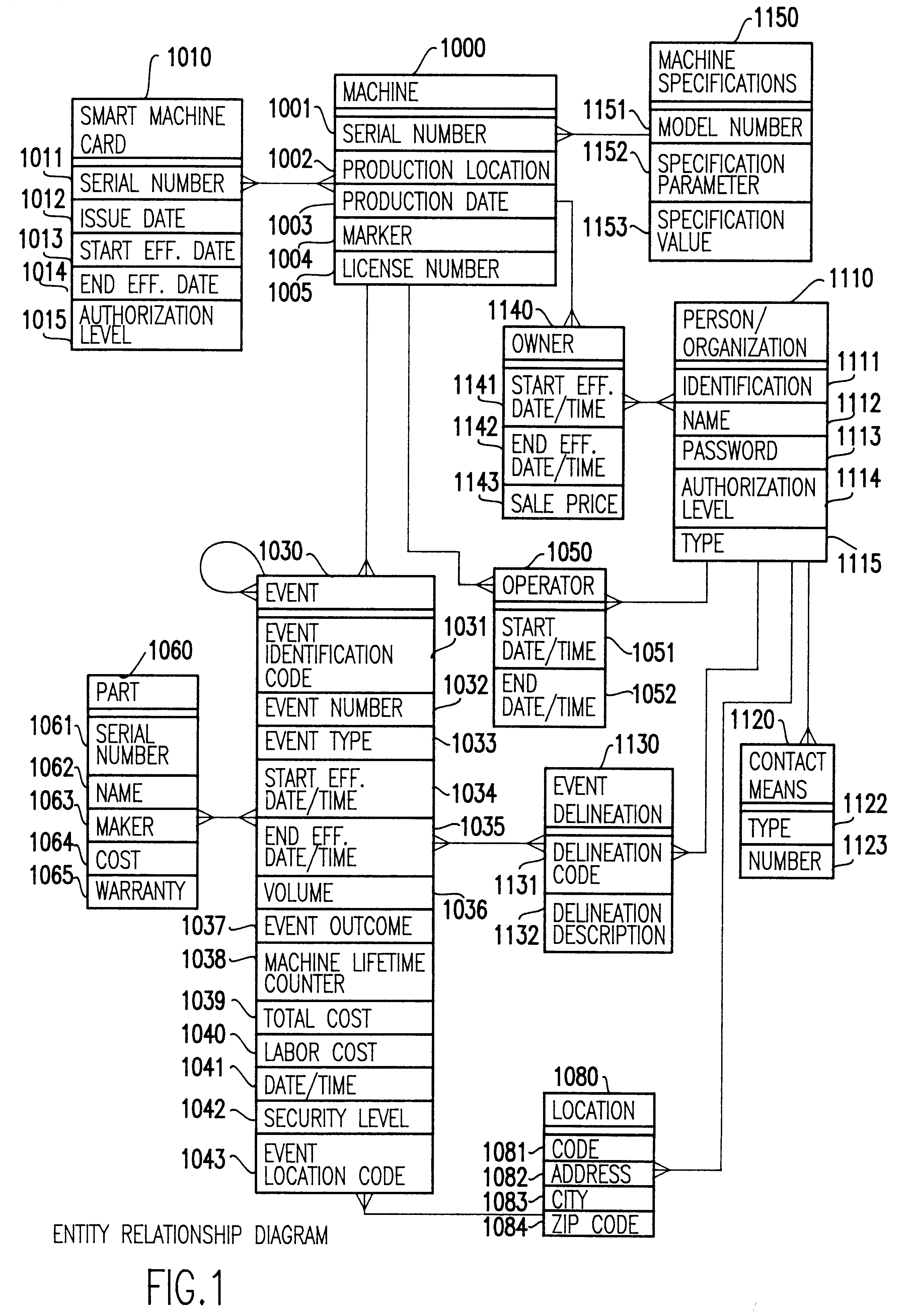
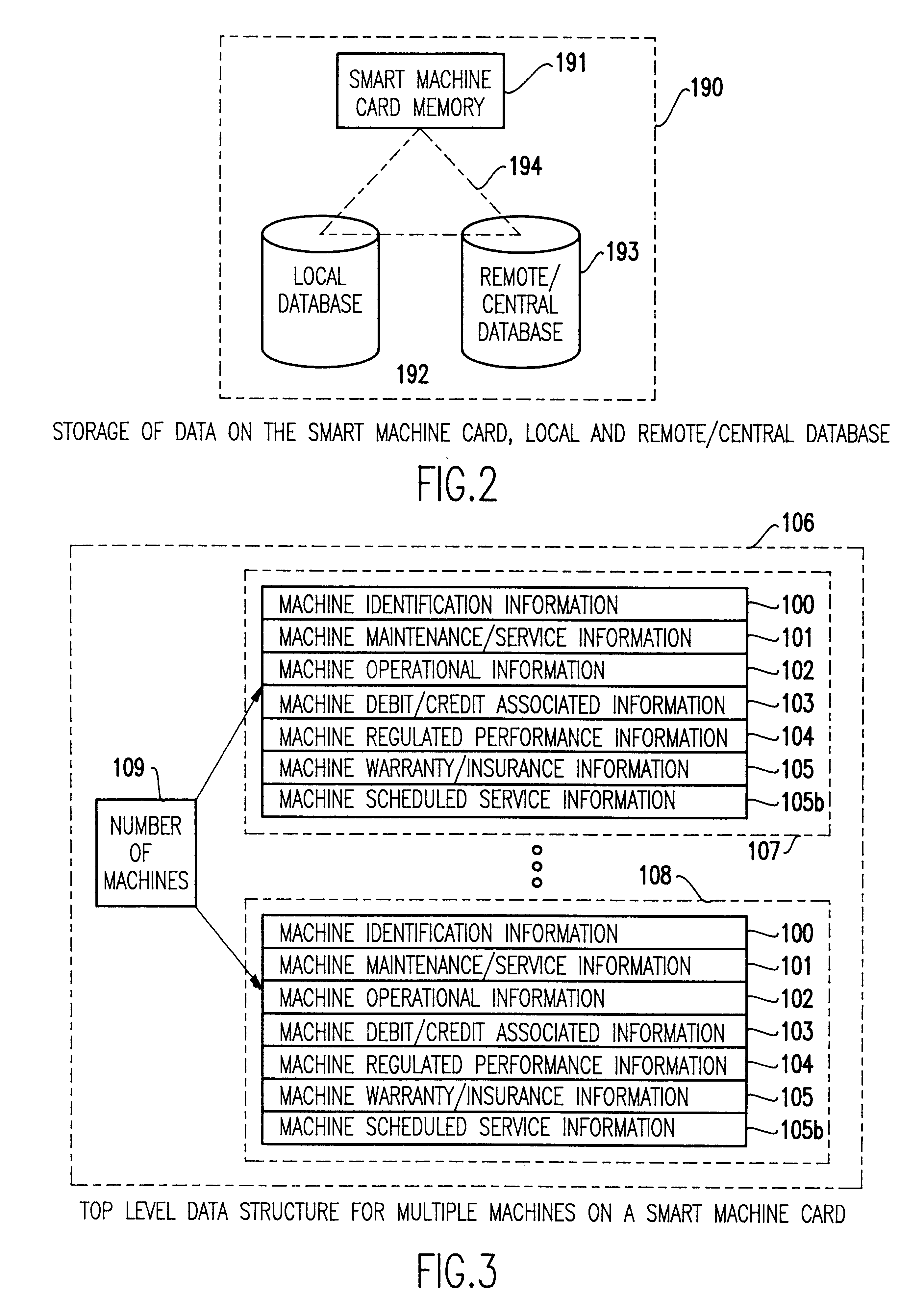
Method for using a smart card for recording operations, service and maintenance transactions and determining compliance of regulatory and other scheduled events
InactiveUS6170742B1Specific performanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRegistering/indicating working of machinesTelecommunications linkSmart card
A computerized "smart card" which has a read / write memory and formatted data storage blocks is used to track the life history of one or more associated machine(s) (e.g., vehicles, medical instrumentation and apparatus, business and copying machines, etc.). The smart card can store a variety of information including machine identification, hardware / software specifications, debit / credit, regulated performance, warranty / insurance, maintenance / service and operational transactions that might impact the hardware, software or the intended operation or performance of the machine. The smart card will be equipped to interact with any of a plurality of autonomous reader / writer smart card units and computer-based reader / writer smart card units that may be equipped to interact with any of the plurality of computer databases through the utilization of land or wireless communications links. Preferably, each smart card will be associated with one or more specific machines at the time of sale of the machines, and will be periodically updated at each transaction (e.g., repair, scheduled maintenance, transfer of title, etc.) using reader / writer units operated by service technicians, repair shops, insurance agents, or the like. The stored life history can be used for valuation, maintenance scheduling, problem trouble shooting, and other applications.
Owner:Q INT
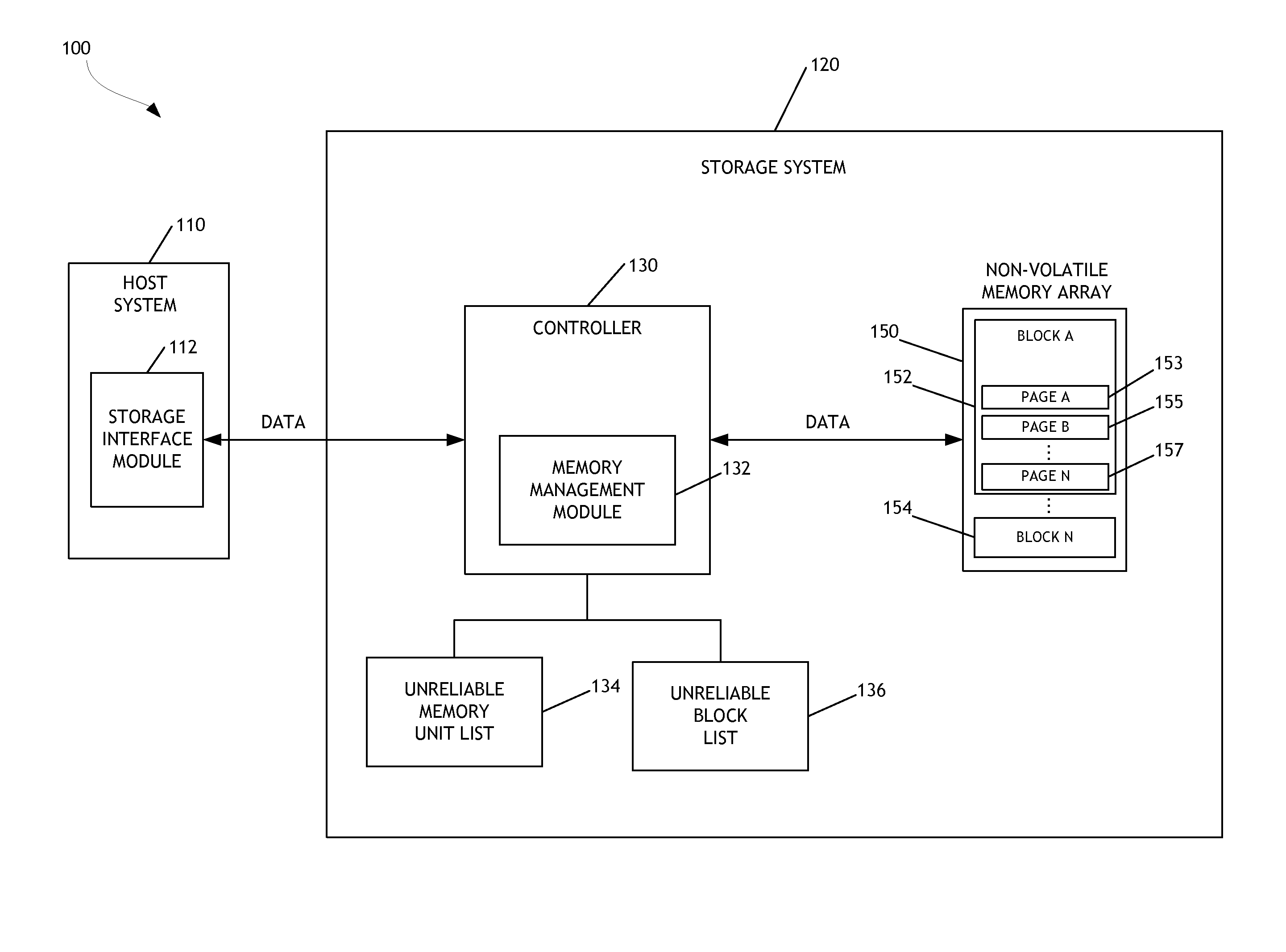
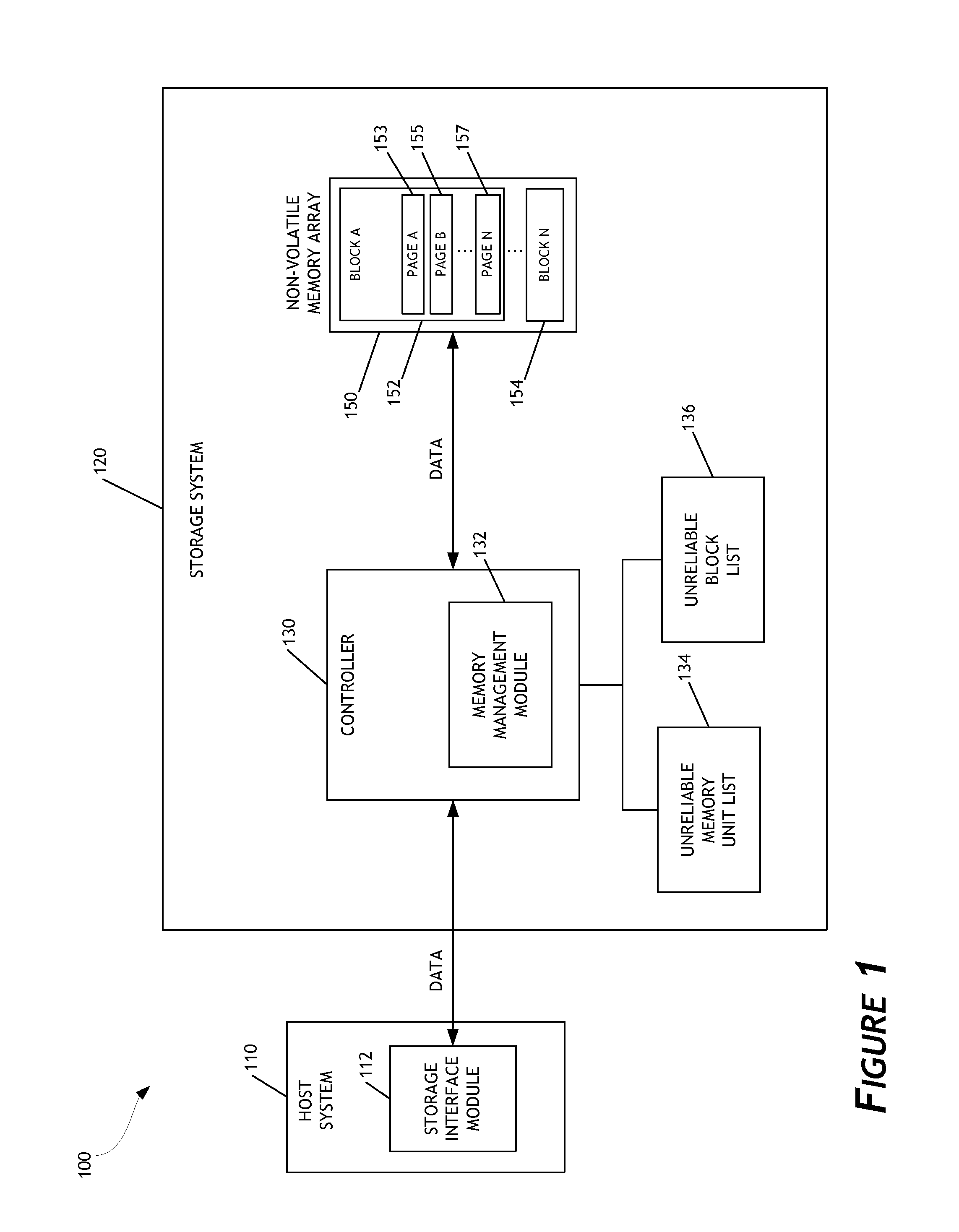
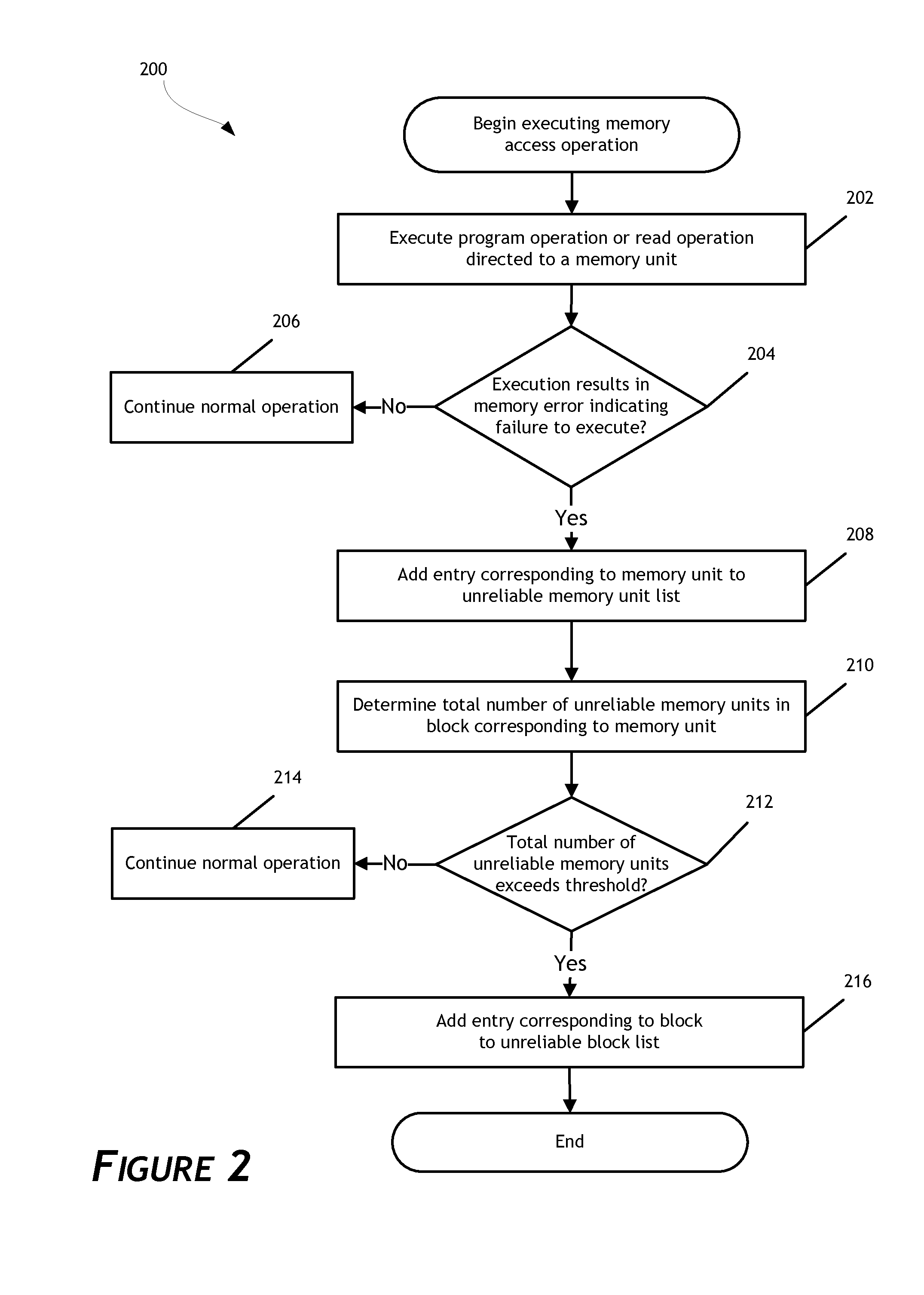
Managing unreliable memory in data storage systems
A data storage system configured to manage unreliable memory units is disclosed. In one embodiment, the data storage system maintains an unreliable memory unit list designating memory units in a non-volatile memory array as reliable or unreliable. The unreliable memory unit list facilitates management of unreliable memory at a granularity level finer than the granularity of a block of memory. The data storage system can add entries to the unreliable memory unit list as unreliable memory units are discovered. Further, the data storage system can continue to perform memory access operations directed to reliable memory units in blocks containing other memory units determined to be unreliable. As a result, the operational life of the data storage system is extended.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Three-dimensional non-volatile nor-type flash memory
ActiveUS20160086970A1High storage densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectricityEngineering
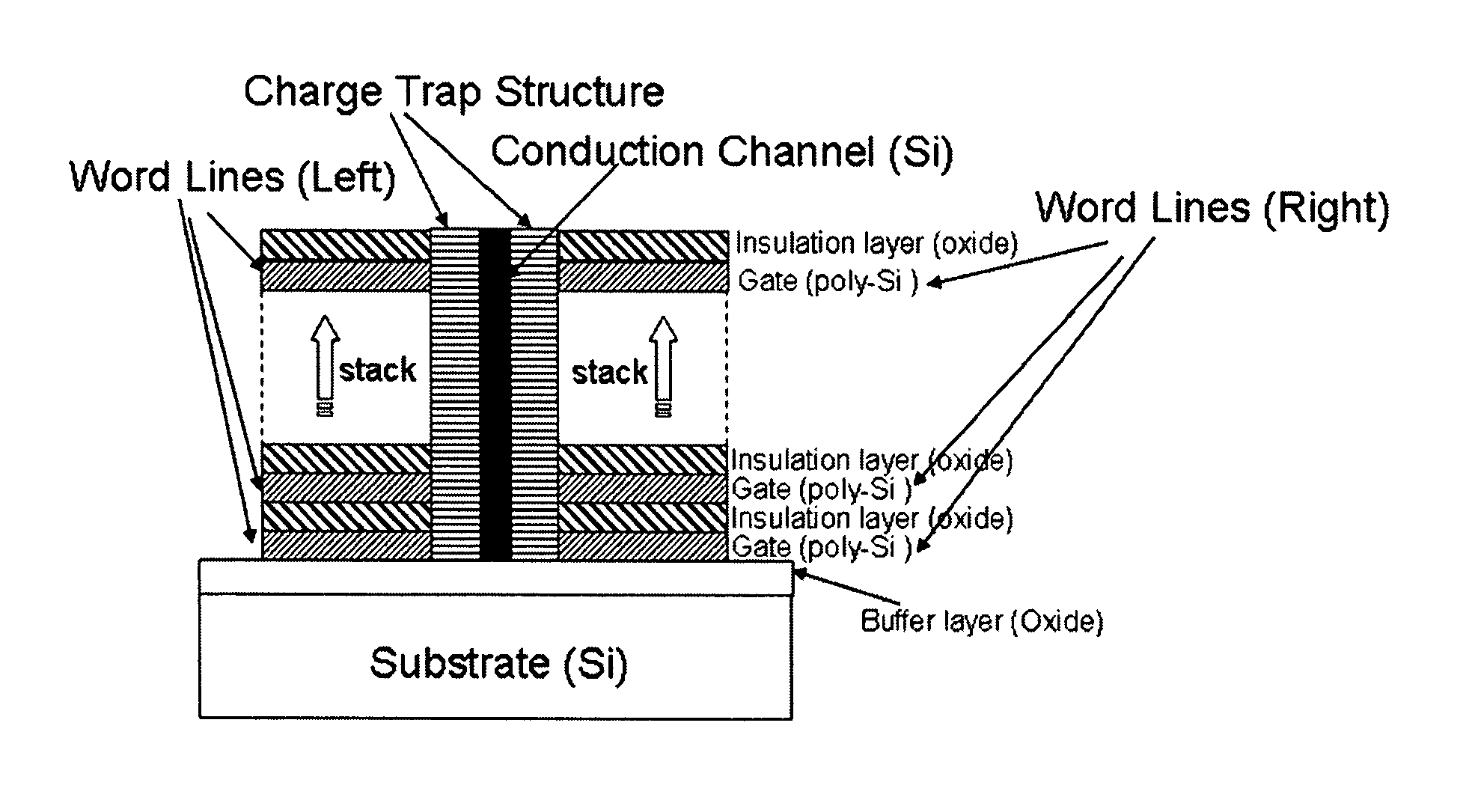
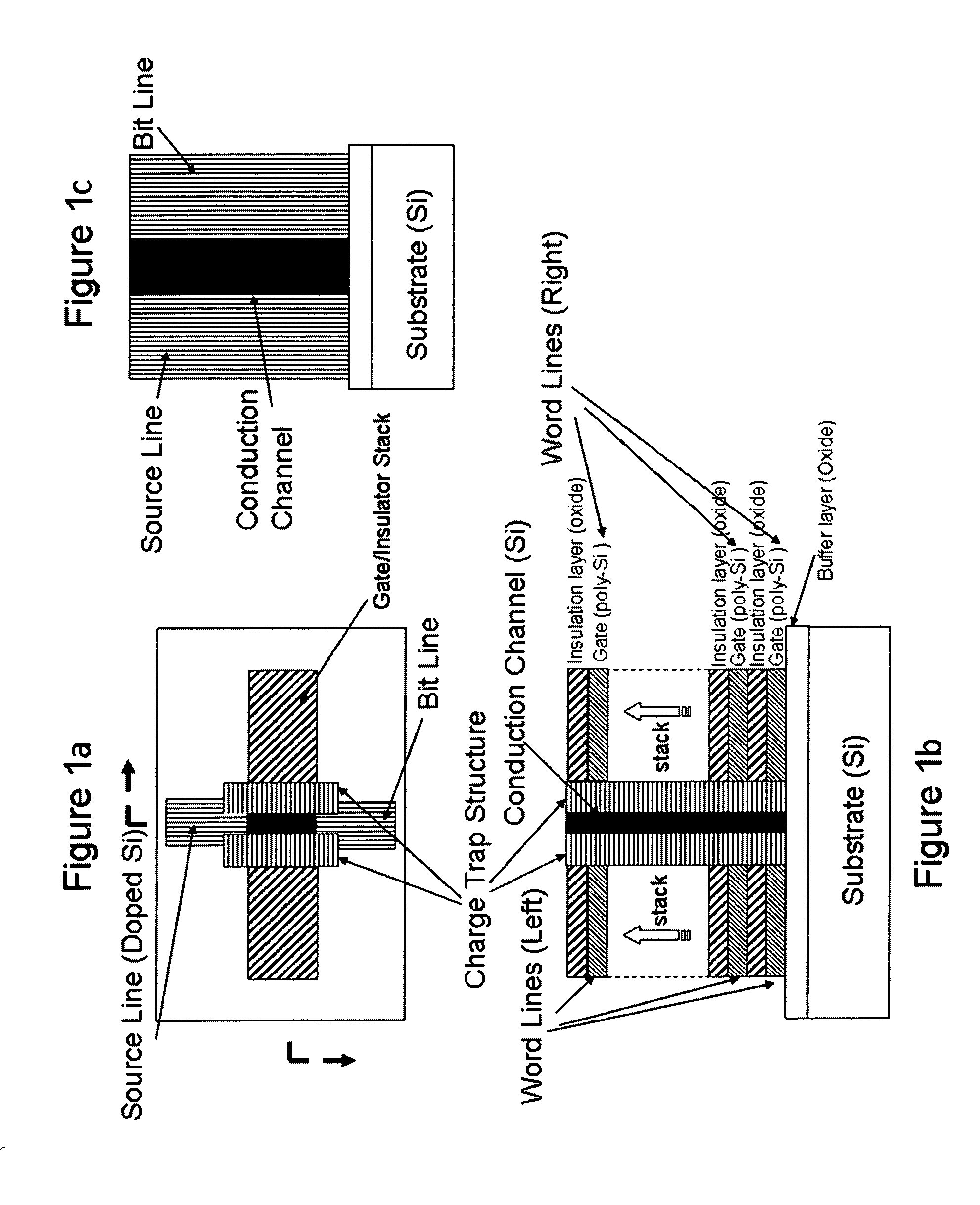
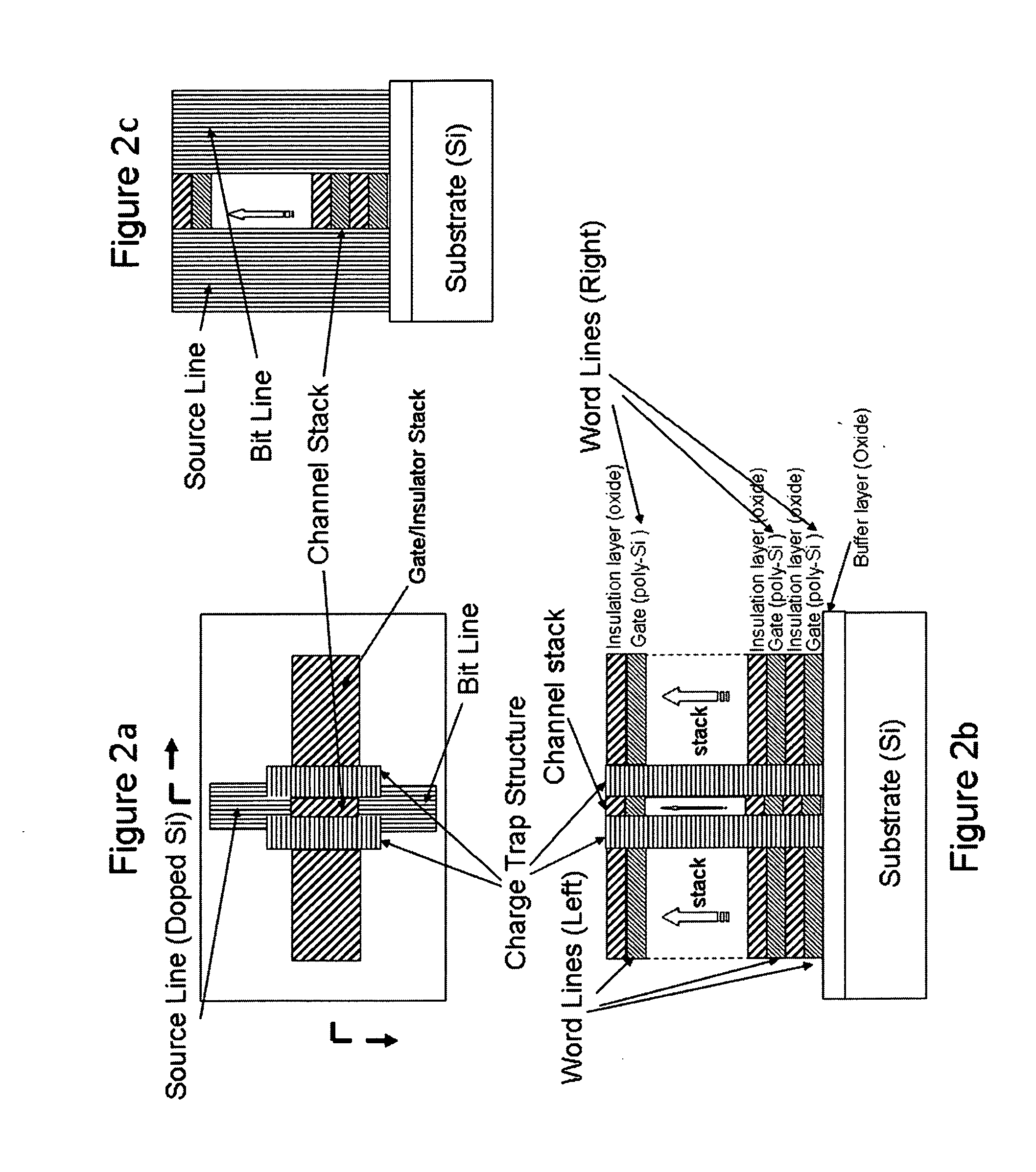
The present invention provides a design of three-dimensional non-volatile NOR flash memory devices consisting of arrays of basic NOR memory group in which individual memory cells (field-effect-transistors) are stacked along a direction (or directions) either out of or parallel to the plane of the substrate and electrically connected in parallel to achieve high storage densities approaching 1 TB with lower manufacturing cost. Offering full random access to every individual memory cells and also capability of parallel programming / erasing in blocks of memory cells, such three-dimensional non-volatile NOR flash memory can be widely used for both executable-code storage and mass data storage applications.
Owner:PENG HAIBING
Data storage and query method and device based on block chain
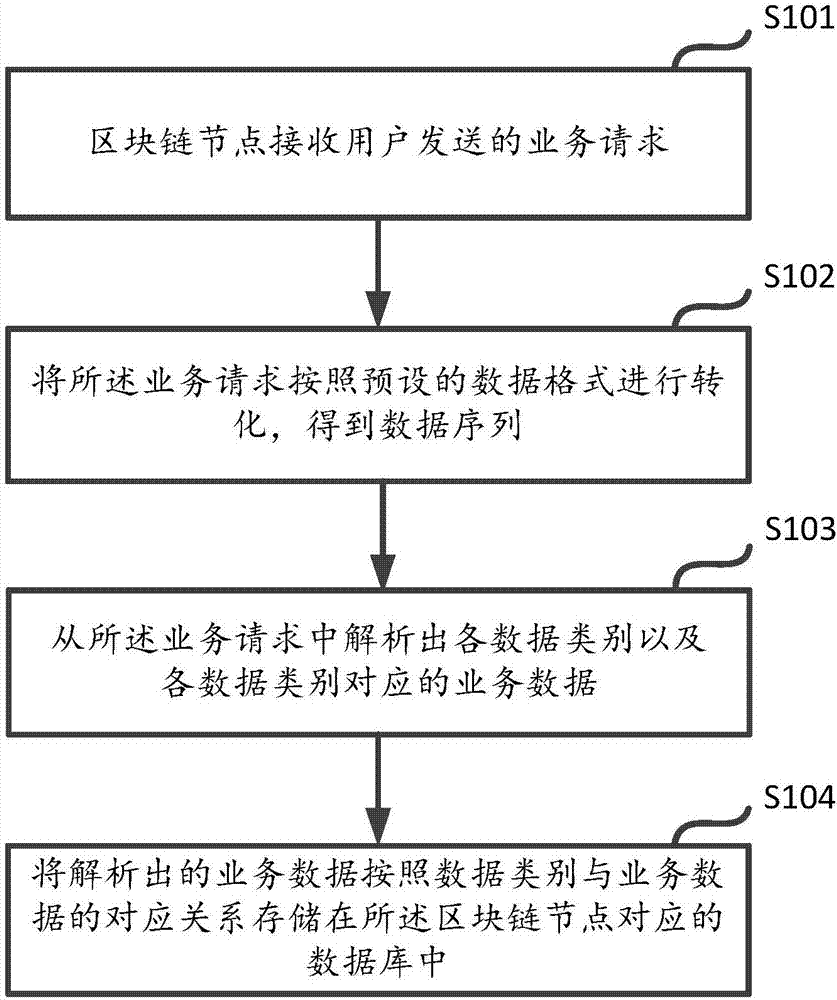
ActiveCN107239479AIncrease flexibilityImprove query efficiencyDatabase queryingDatabase distribution/replicationData queryData library
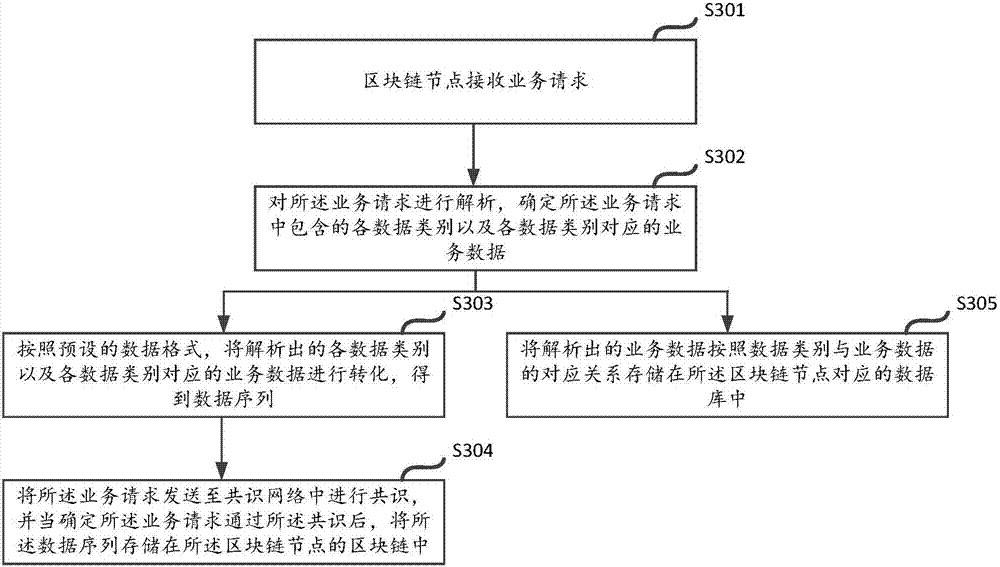
The application discloses a data storage and query method and device based on a block chain. The method comprises the following steps: after receiving a service request sent by a user, a block chain node can resolve each data category and service data corresponding to each data category from the service request, and stores the resolved service data in a database corresponding to the block chain node according to a corresponding relation of the data category and the service data. By resolving the service data, the service data can be stored to the database corresponding to the block chain node according to the corresponding relation between the data category and the service data; therefore, the user can realize the query based on the corresponding relation in the database when querying the service data, a problem existent in the query based on the query in the existing block chain is avoided, the flexibility of the data query in the block chain is increased, and the data query efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
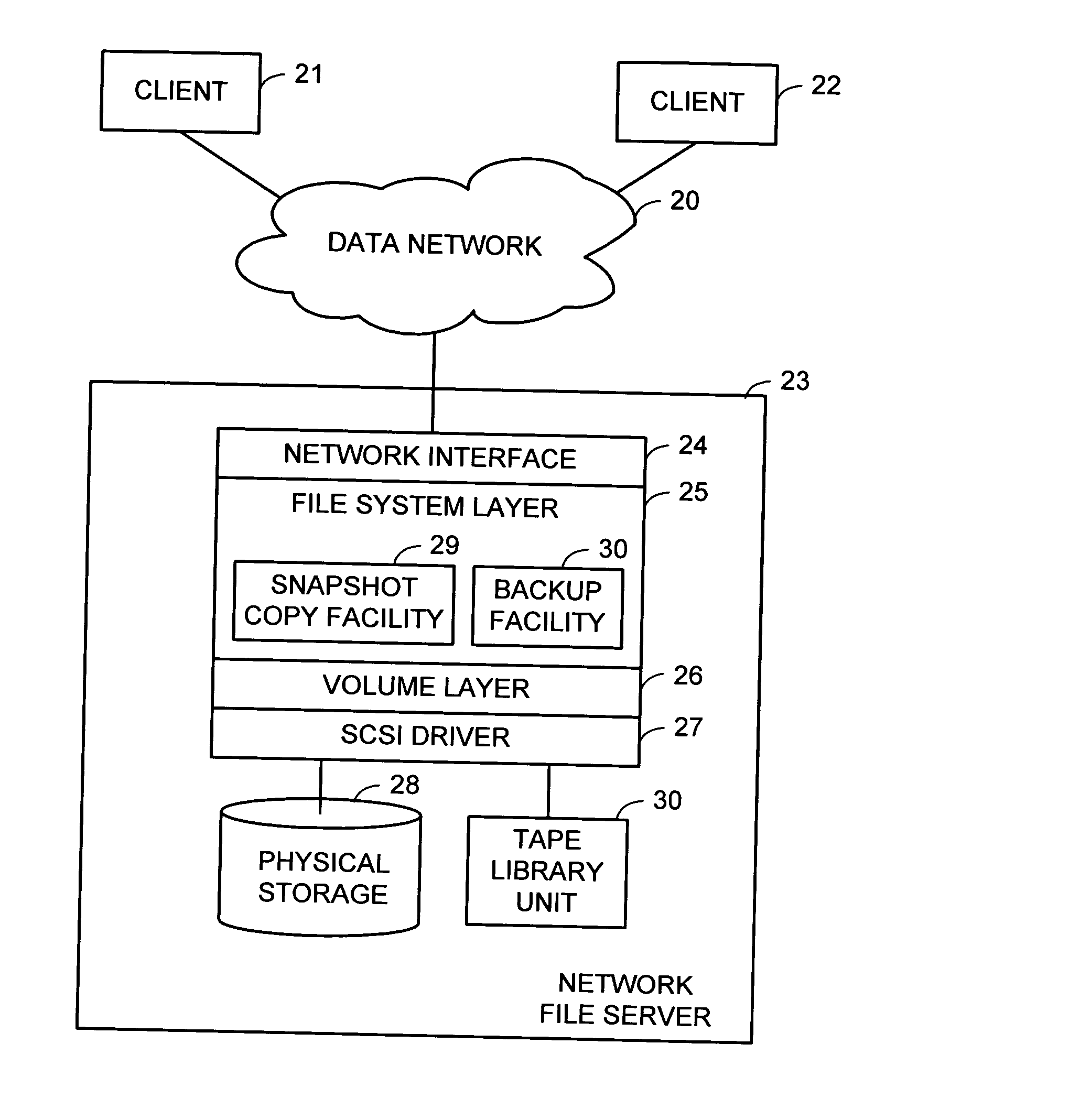
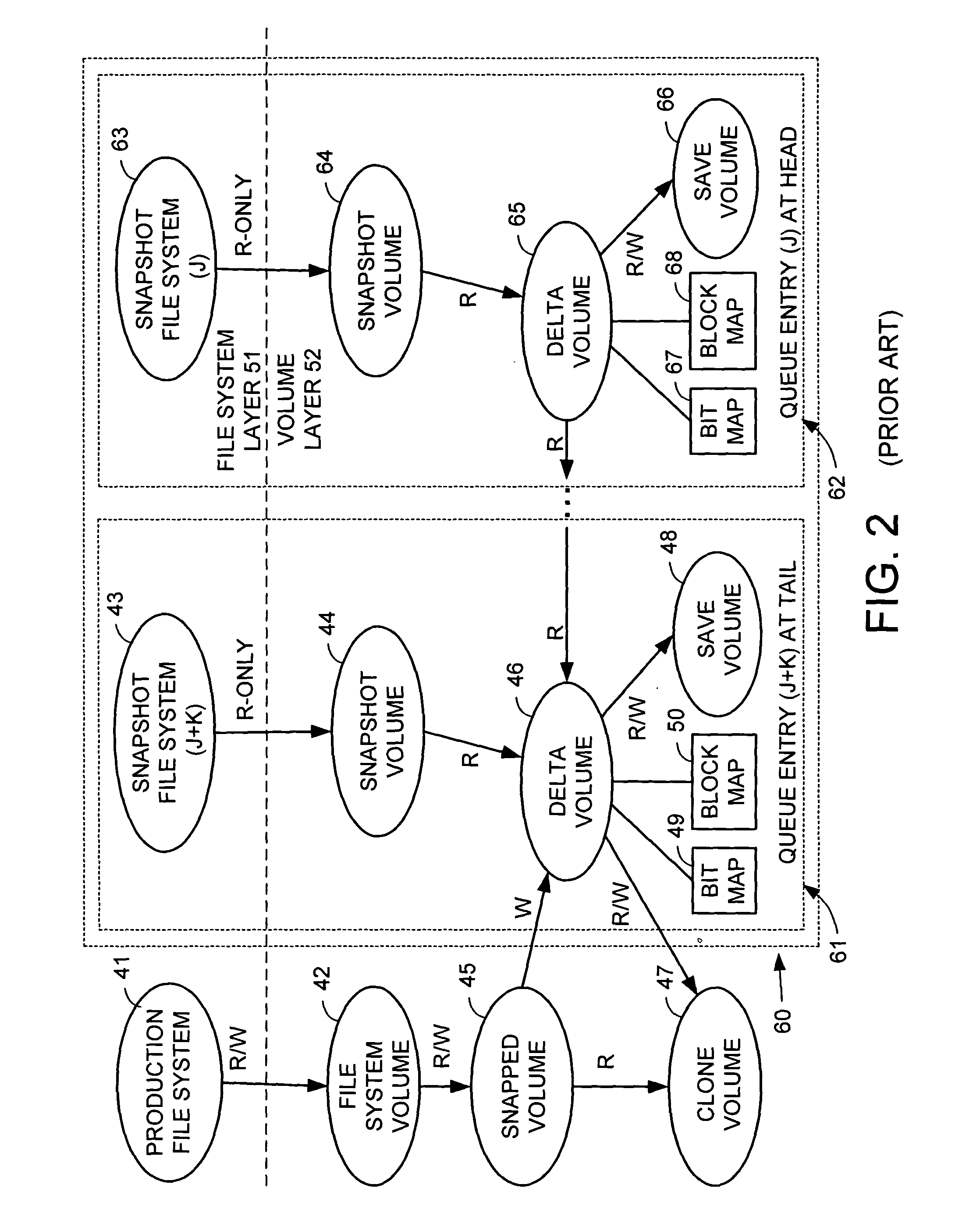
Organization of read-write snapshot copies in a data storage system
A file system maintains a series of read-only snapshot copies of a production file system. A read-write snapshot copy is created based on a selected read-only snapshot copy by maintaining a set of save volume blocks of new data of the read-write snapshot copy. A block of new data is written to the read-write snapshot copy by allocating a save volume block and writing to the save volume block. A specified block is read from the read-write snapshot copy by checking whether there is a respective save volume block allocated to the specified block, and if so, reading from the respective save volume block, and if not, reading from the read-only snapshot copy upon which the read-write snapshot copy is based. The read-write snapshot copy can be refreshed with a specified read-only snapshot copy. The production file can be restored with a specified read-write snapshot copy.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and apparatus for accessing multidimensional data
InactiveUS20050071349A1Shorten the timeDigital data processing detailsStatic storageData accessStorage model
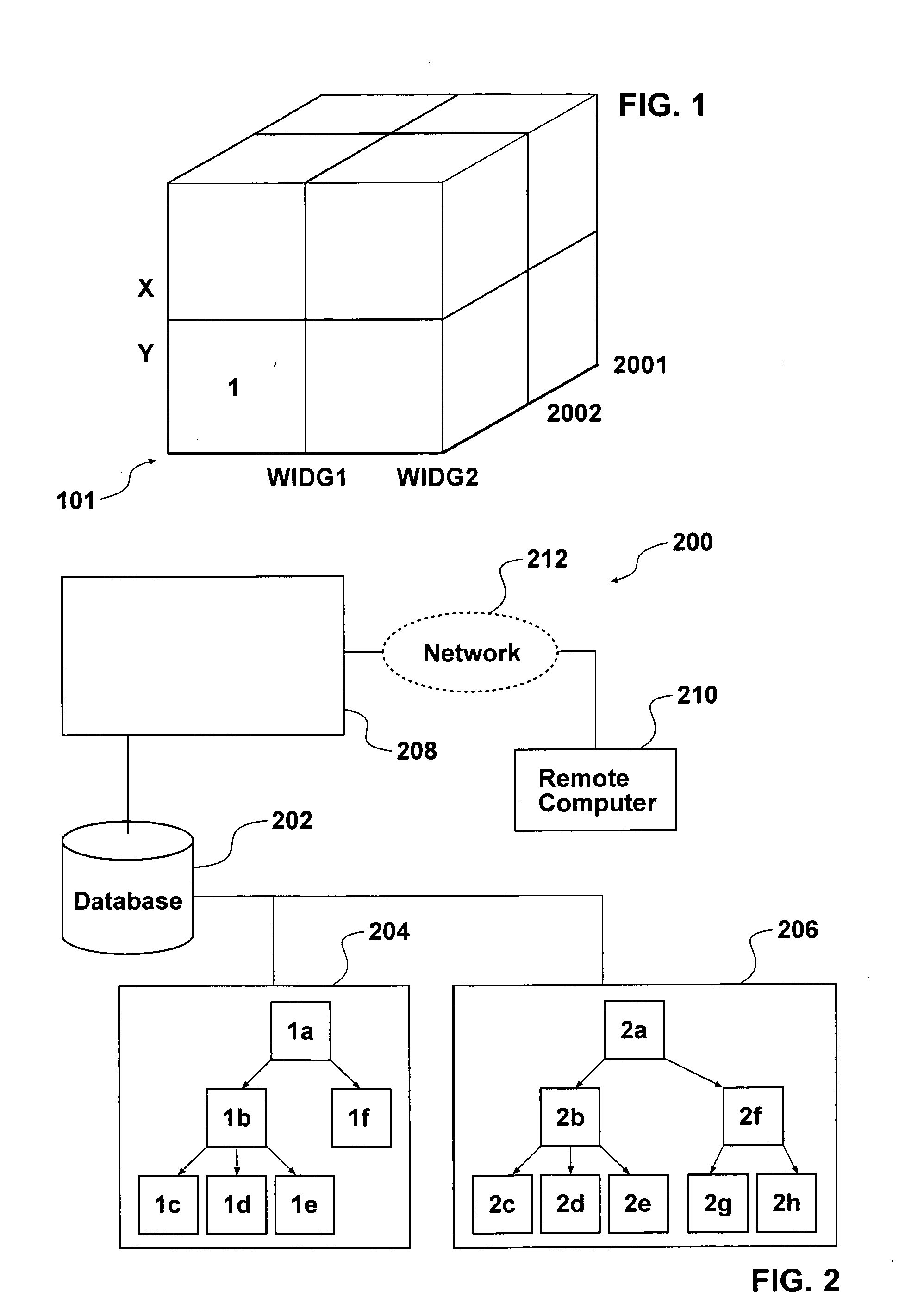
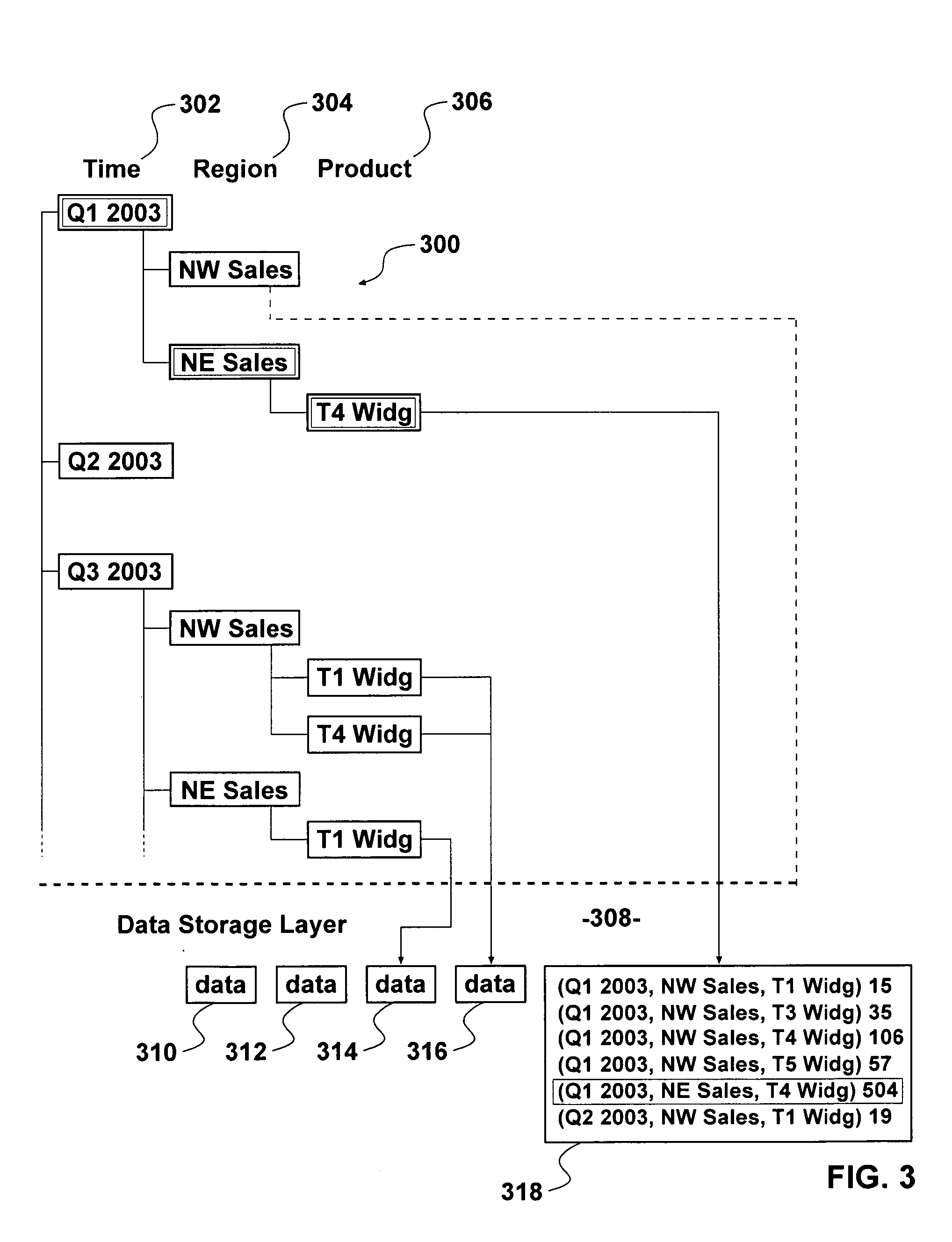
A method of indexing data in a multidimensional database includes creating a multidimensional logical access model, creating a multidimensional data storage model in which data is located in cells that are stored and retrieved in blocks, gathering data access information derived from one or more user queries of the database, and reorganizing one or more selected cells in the multidimensional data storage model based on the data access information to reduce the time taken to access the one or more selected cells in response to a user query of the database. A computerized apparatus in communication with a multidimensional database includes a program to perform the method. A computer readable medium contains instructions to cause a computer to perform the method.
Owner:DESCISYS
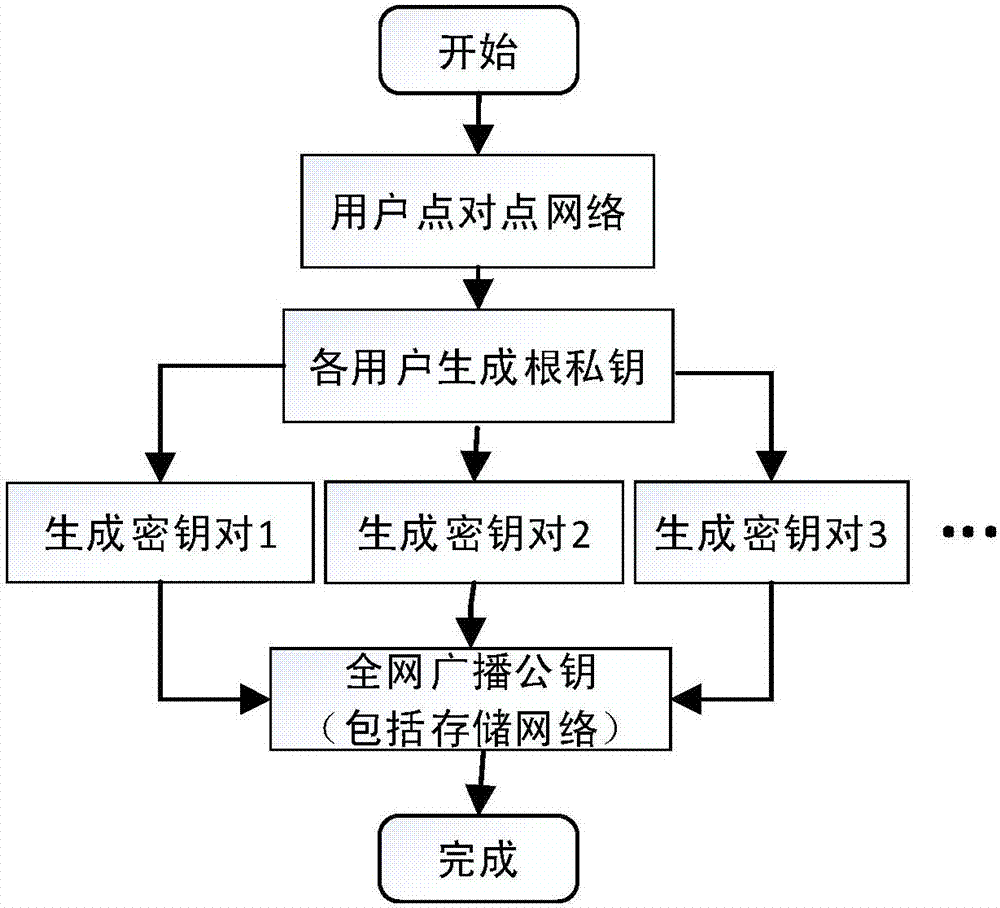
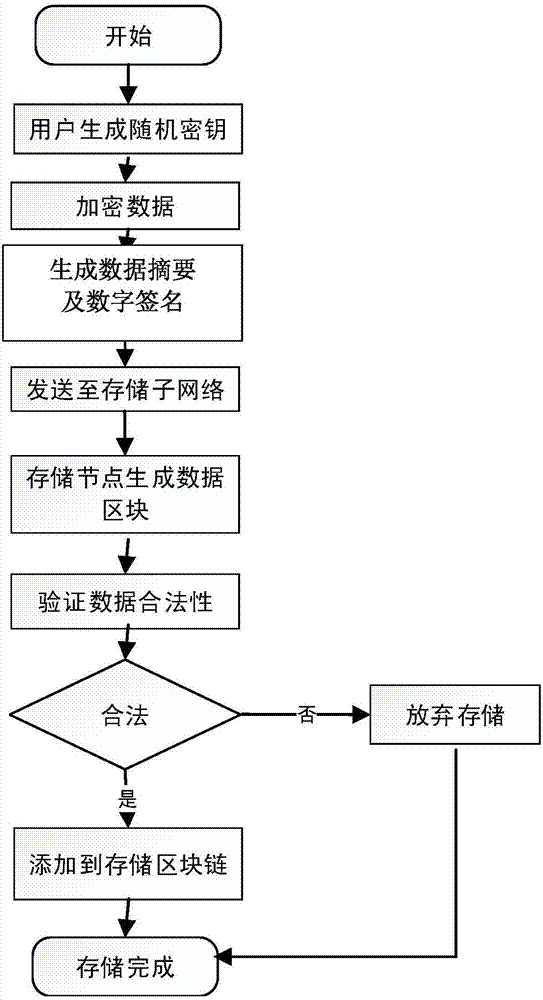
Routing position data secrecy storing and sharing method based on block chain
ActiveCN107181599AGood data protectionSolve workload bottlenecksKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationByzantine fault toleranceOriginal data
Provided is a routing position data secrecy storing and sharing method based on block chains. The routing position data secrecy storing and sharing method includes a data storing method and a data sharing method. The data storing method includes the steps of node configuration, data encryption sending, storage subnetwork verification storing, etc. The data sharing method includes the steps of demand generation, demand response, sharing achievement and the like. The effects of the invention are as follows: through a block chain technology, data sharing is realized through data encryption storage and a decentralized network to solve the problems that data storage parties have no right to use data and users do not have channels to selectively enable personal data to be accessed; local encryption sending is adopted during data storage, service parties store encrypted data, the users themselves save decryption secret keys, and the service parties have no access to original data, so a better data protection effect is achieved; and the block chain technology is adopted during storage, commonly recognized storage is realized through a practical Byzantine fault-tolerant algorithm, workload bottleneck problems of centralized storage are solved, and data is prevented from being tampered.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
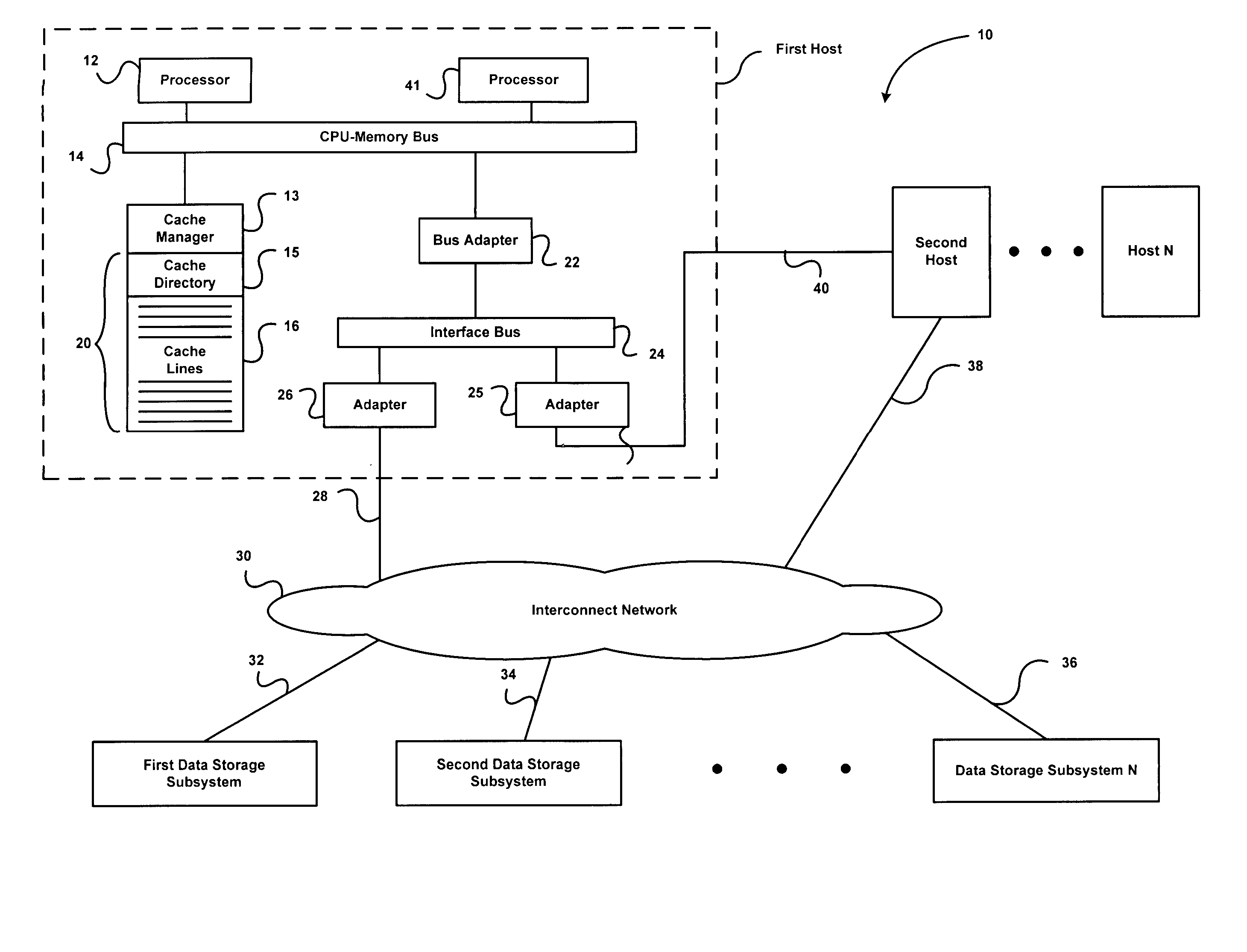
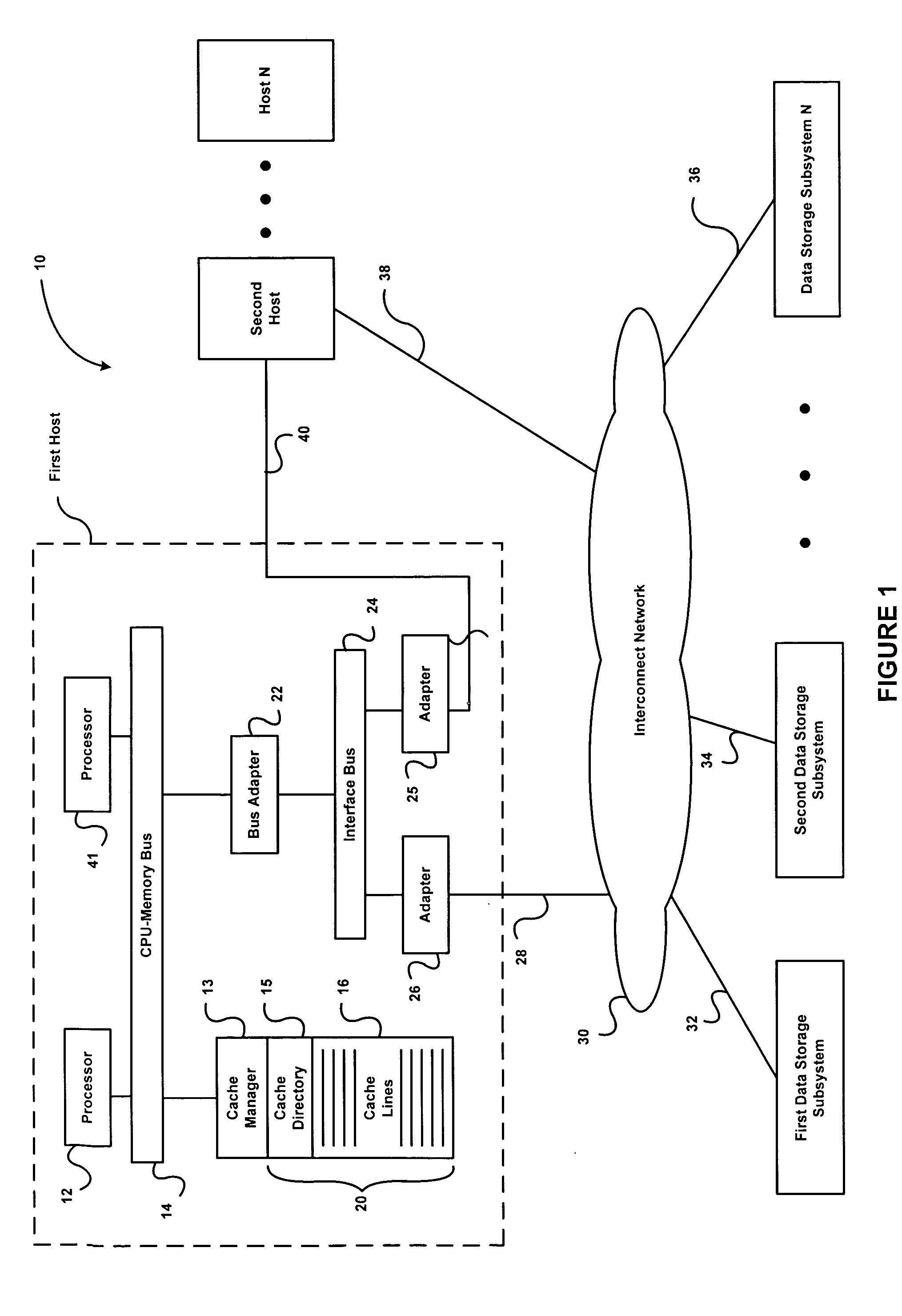
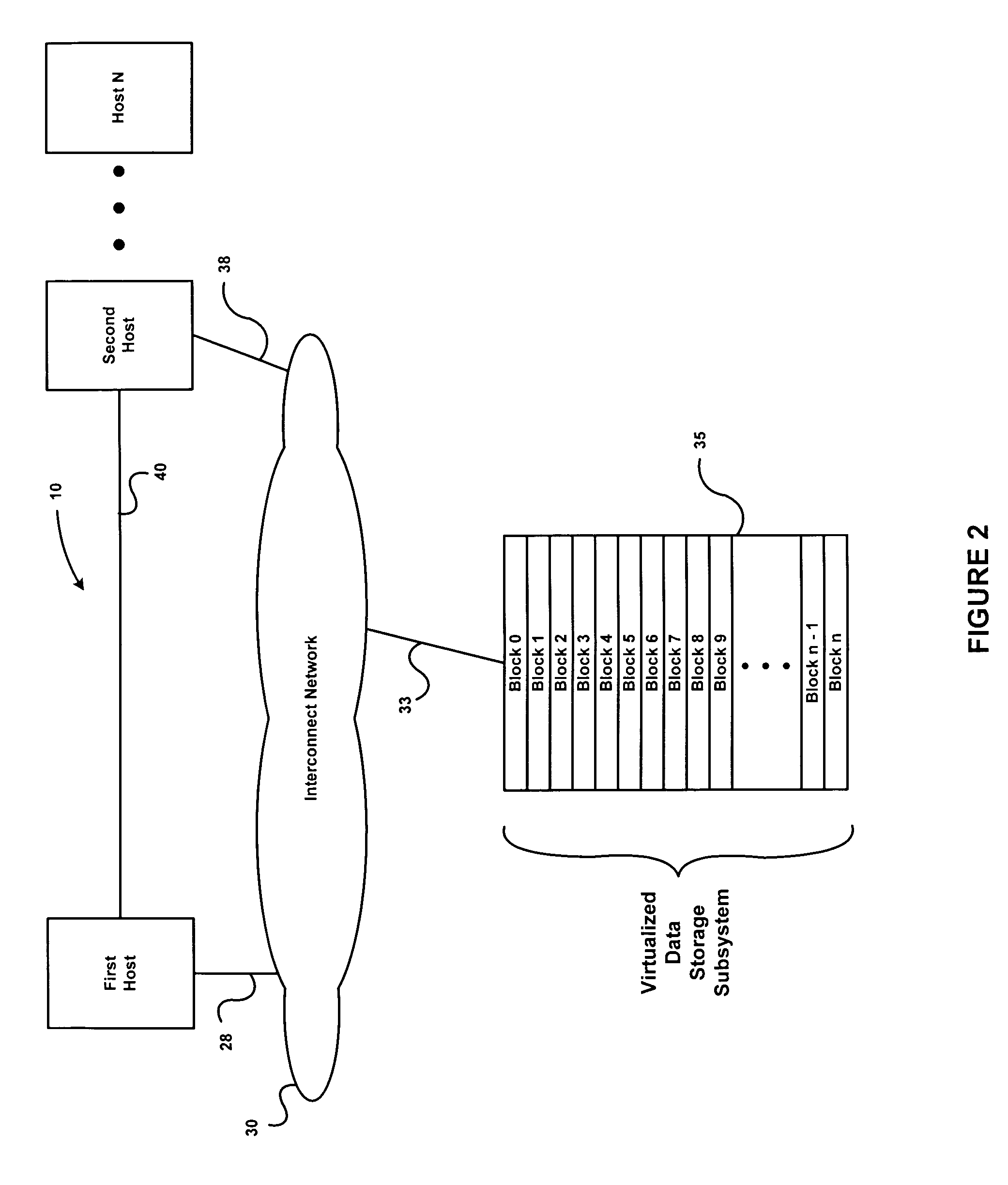
Data integrity for data storage devices shared by multiple hosts via a network
InactiveUS20090043971A1Digital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData integrityNetworked system
Owner:LEE HEON SU
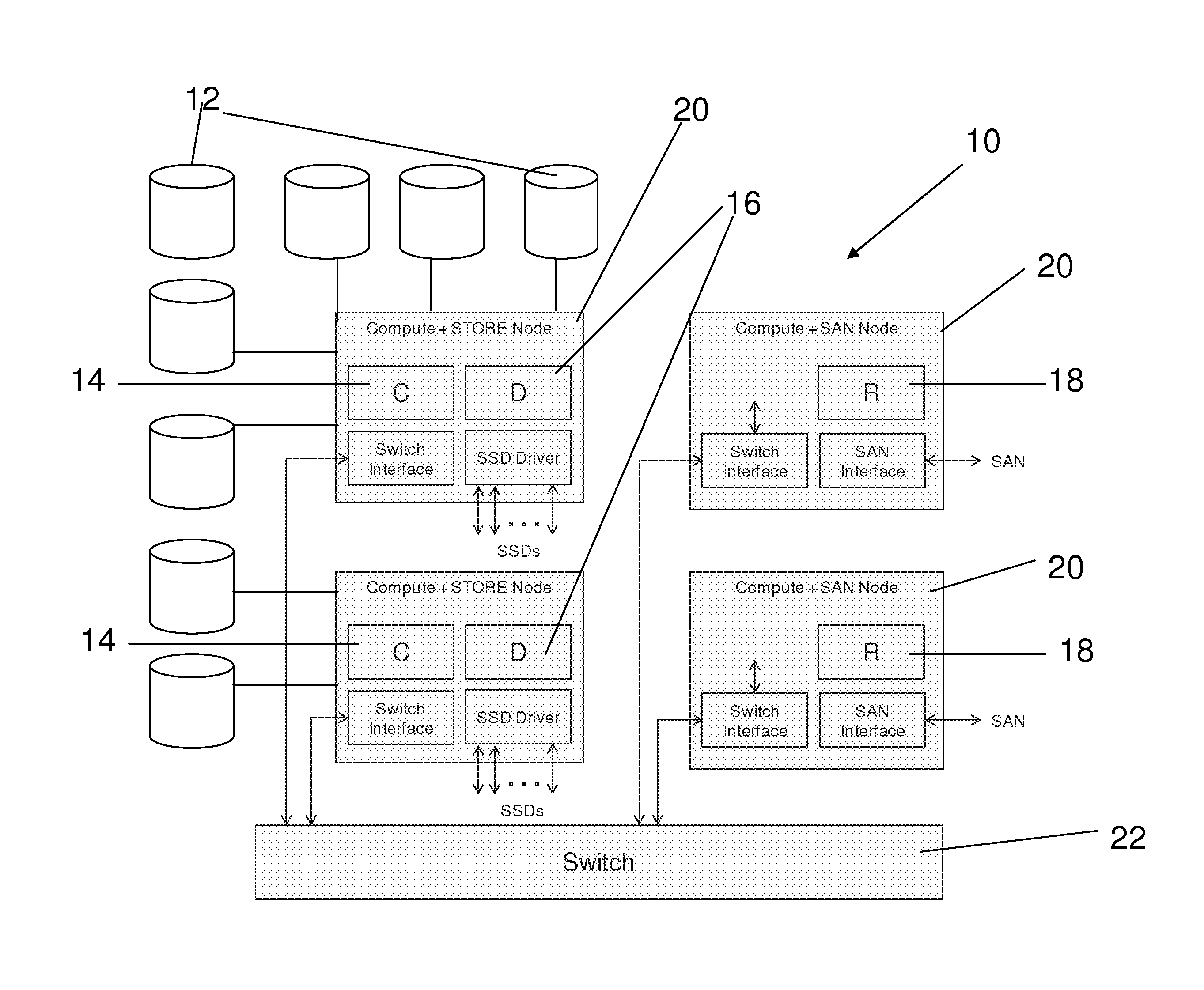
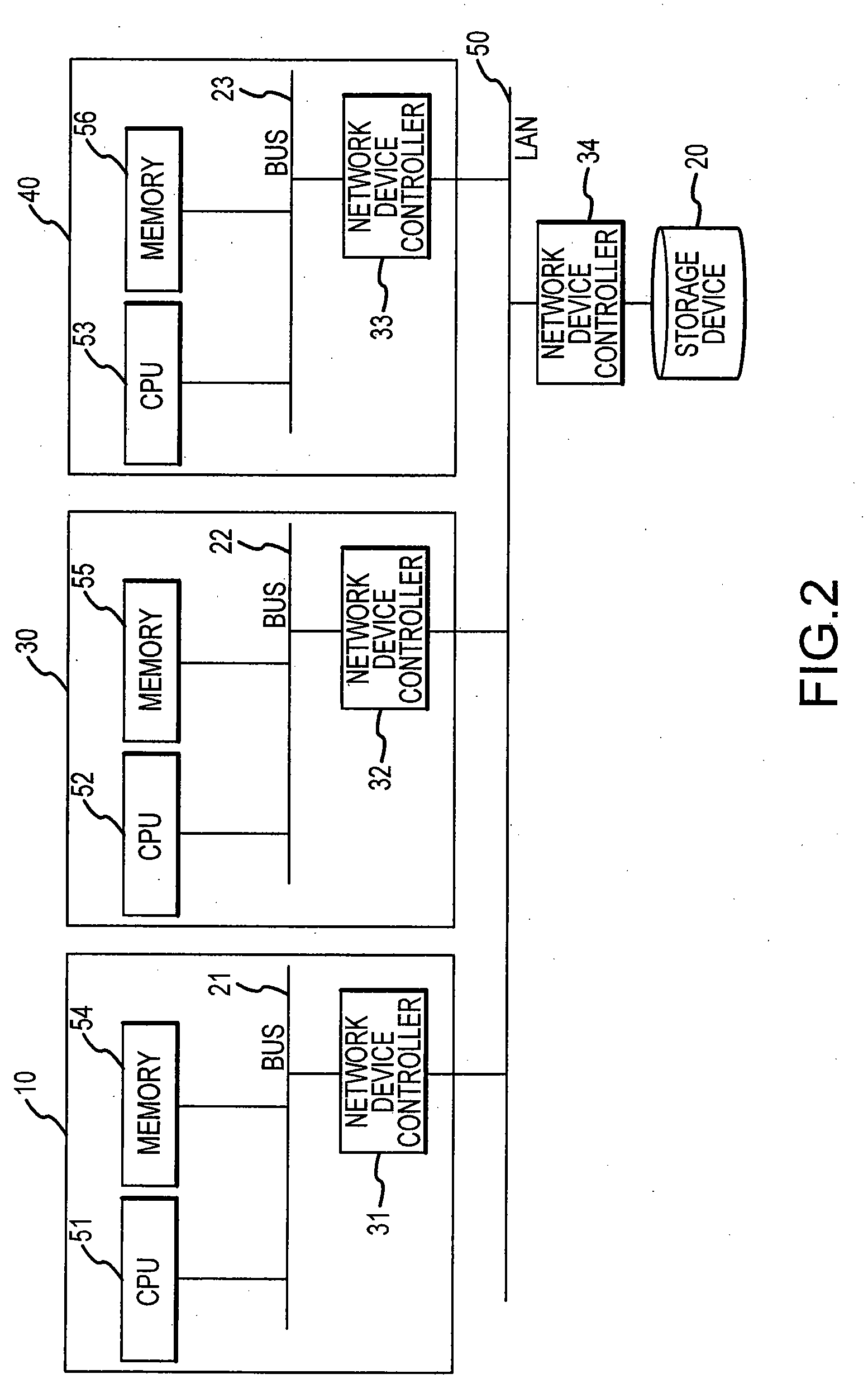
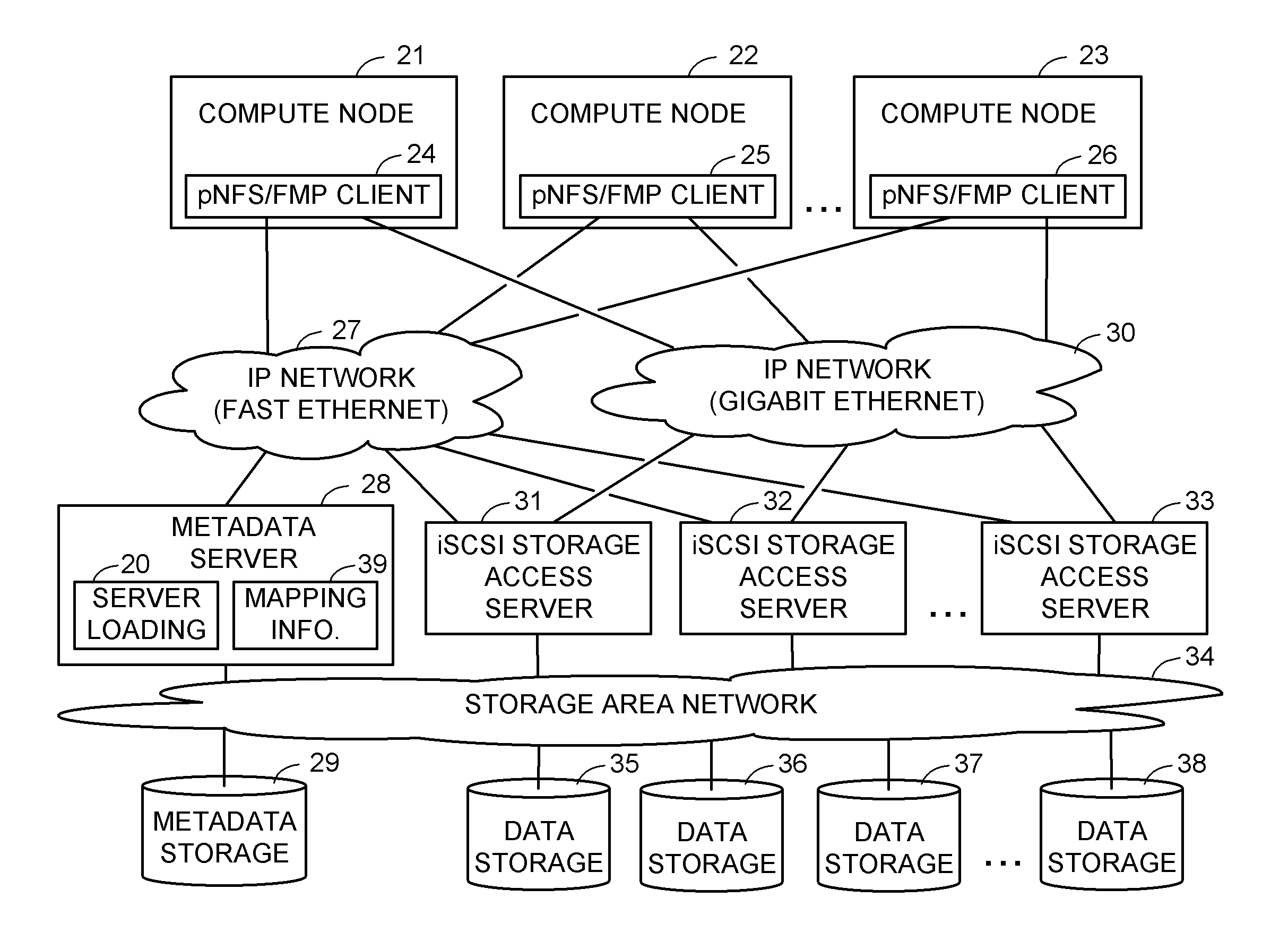
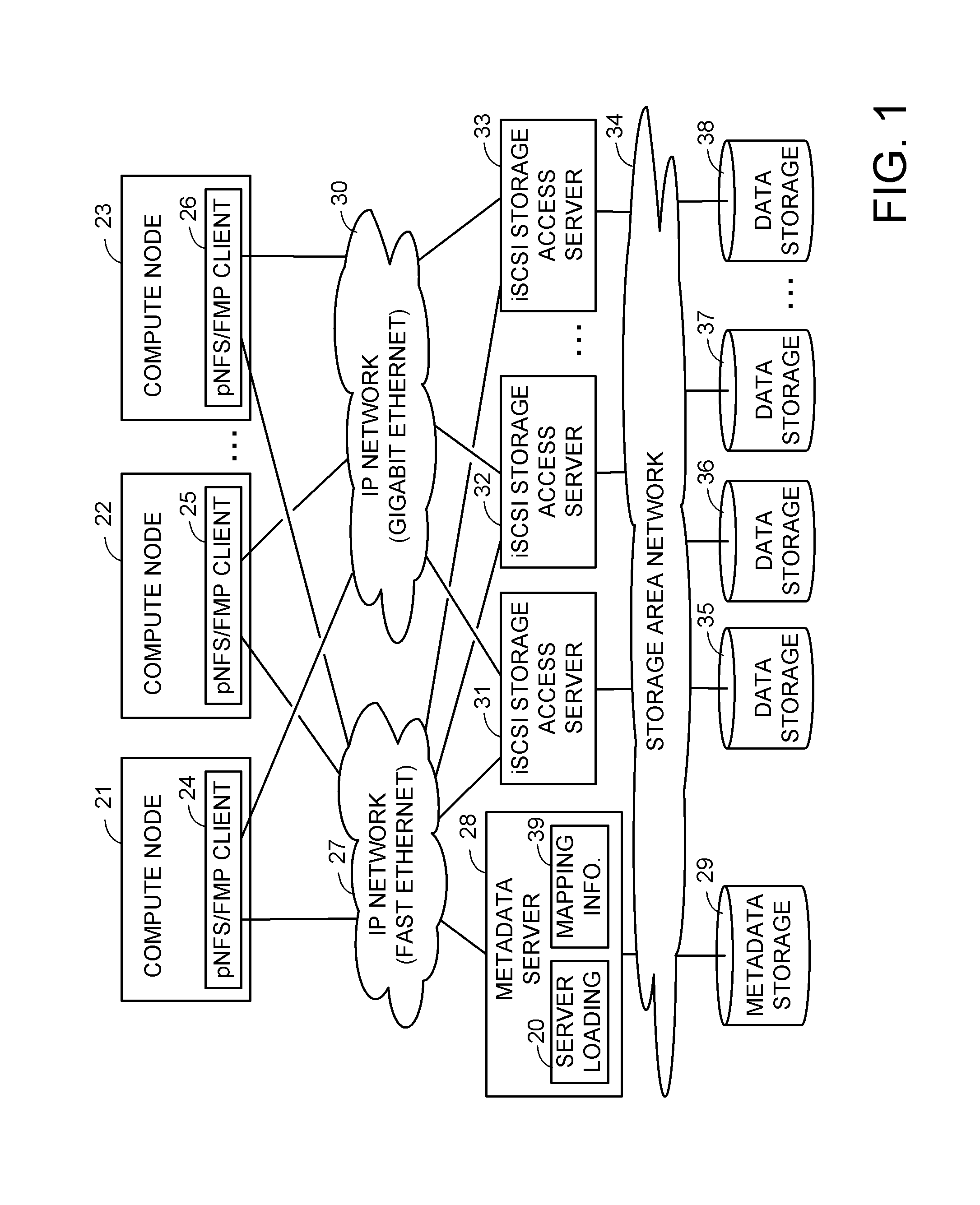
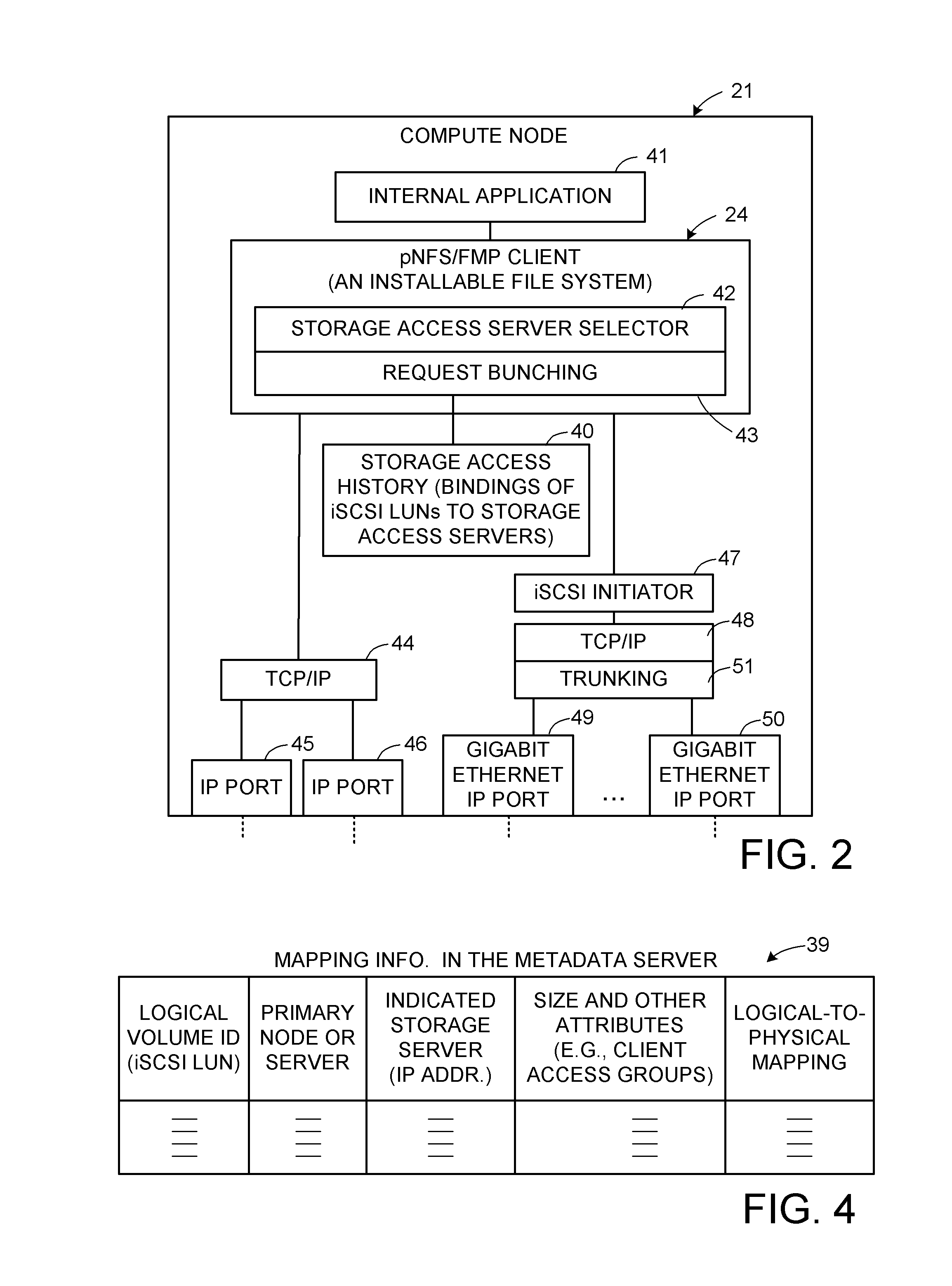
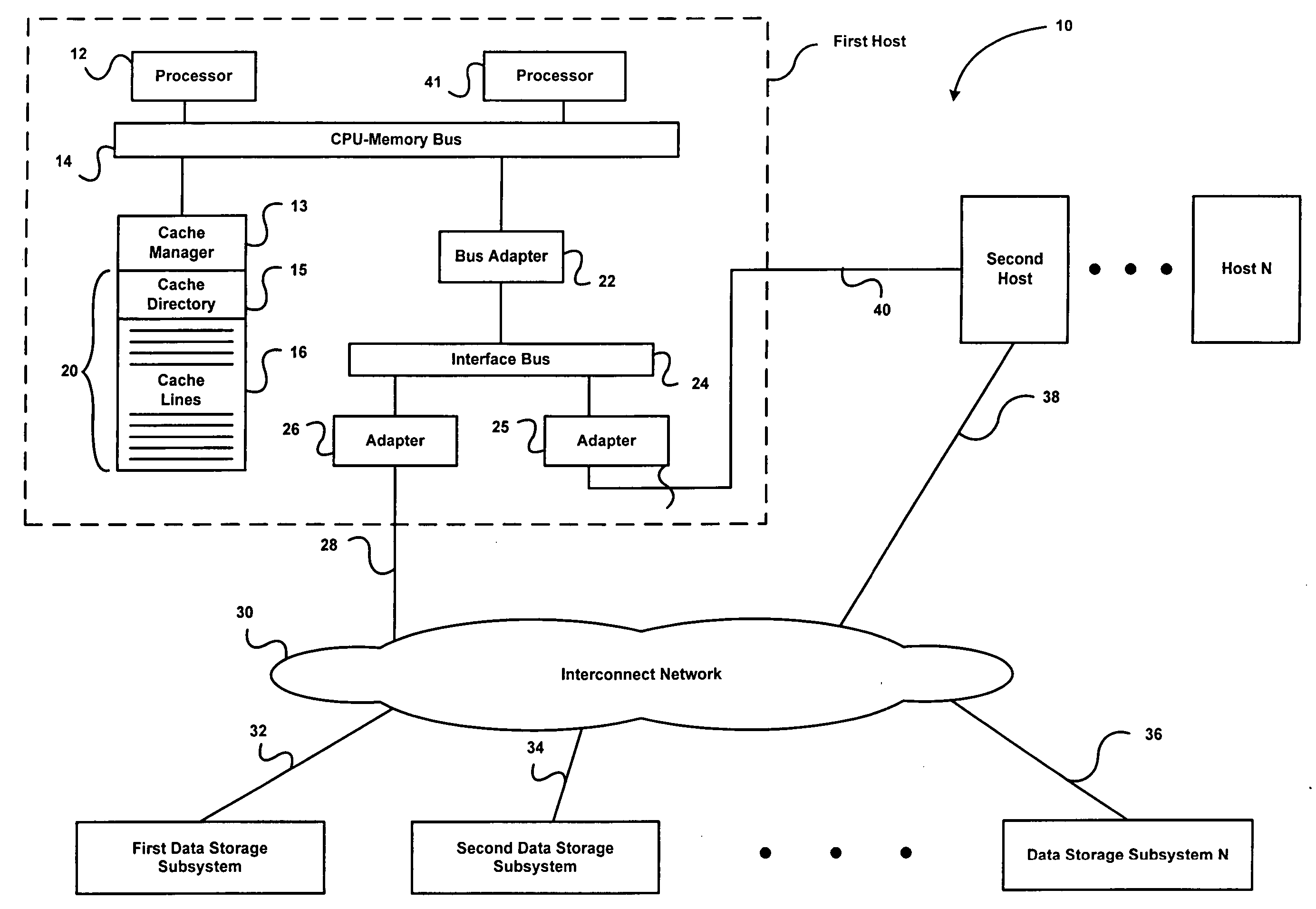
Asymmetric data storage system for high performance and grid computing
ActiveUS8589550B1Easy accessEnsure load balanceDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemData treatment
A data processing system includes compute nodes, at least one metadata server, iSCSI storage access servers, and data storage devices. The metadata server services requests from the compute nodes for file mapping information identifying iSCSI LUNs and logical blocks of file data. The storage access servers service iSCSI I / O requests from the compute nodes, and report server loading to the metadata server. A Gigabit Ethernet IP network transfers read and write data between the compute nodes and the storage access servers. The storage access servers are linked to the data storage devices for parallel access to iSCSI LUNs of the file data in the data storage devices. The metadata server is programmed for server load balancing by indicating to the compute nodes respective ones of the storage access servers that should be used for access to the iSCSI LUNs.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Snapshots of file systems in data storage systems
ActiveUS20050021565A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemData space
The present invention relates to methods and systems of snapshot management of a file system in a data storage system. To represent the snapshots, the invention maintains pointers to the root block pointer of each snapshot. When the active file system is modified, this invention avoids overwriting any blocks used by previous snapshots by allocating new blocks for the modified blocks. When the invention needs to put an established block in a new location, it must update a parent block to point to the new location. The update to the parent block may then require allocating a new block for the new parent block and so forth. Parts of the file system not modified since a snapshot remain in place. The amount of space required to represent snapshots scales with the fraction of the file system that users modify. To maintain snapshot integrity, this invention keeps track of the first and last snapshots that use each block in space map blocks spread throughout the file system data space. When users delete snapshots, this invention may use a background process to find blocks no longer used by any snapshot and makes them available for future use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
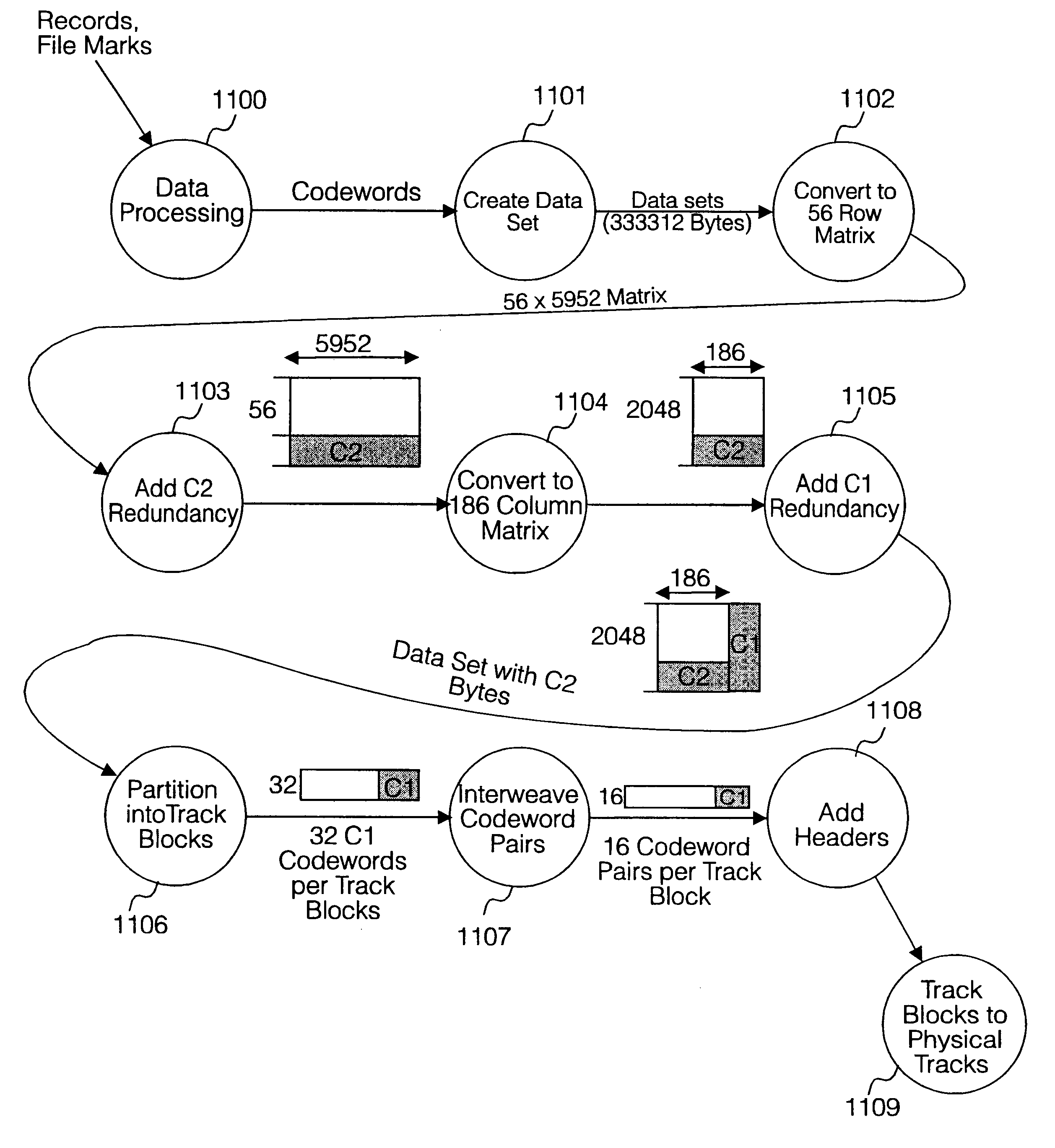
Scratch protection in tape data storage system
InactiveUS6282039B1Improve protectionEvenly distributedDigital data storage formatRecord information storageData setMagnetic tape
A method of redundancy coding of user data received from a host apparatus and storage of said coded data on a magnetic tape data storage medium comprises inputting a byte stream of user data into a buffer and assembling a plurality of data sets in the buffer; for each data set assembling a data set into a two-dimensional data array and (1103) applying a second redundancy coding algorithm (C2 parity) to the two-dimensional data set in a second dimension; applying (1105) a first redundancy coding (C1 parity) algorithm to the second redundancy coded data array in a first dimension to form a two-dimensional data frame having second and first redundancy coding in respective second and first dimensions, the two-dimensional data frame comprising a plurality of rows, each row comprising a first codeword and a plurality of columns, each column comprising a second codeword; partitioning the two-dimensional data frame into a plurality of logical track blocks (1106) each comprising a plurality of first codewords; and recording (1110) each logical track block to a corresponding respective physical track on the magnetic tape data storage medium. Redundancy coding of a data frame is distributed across a plurality of other data frames along the tape, and redundancy bytes of each data frame are distributed across a plurality of data tracks. Redundancy coding may be distributed diagonally across a width of the tape. Data obliterated due to damage to individual physical recorded tracks or sections of tracks on the tape may be recovered from redundant coding data distributed across other adjacent parallel physical tracks on the tape.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
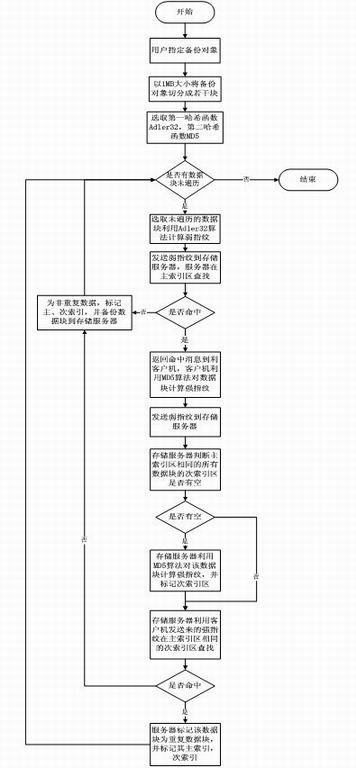
Method for deleting repeated data by using double-fingerprint hash check
InactiveCN102156727AAvoid parityReduce the amount of fingerprint calculationSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionComputer hardwareHash function
The invention provides a method for deleting repeated data by using double-fingerprint hash check. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing an object to be backed up into data blocks to be backed up with equal lengths; judging whether the weak fingerprint of one of the data blocks to be backed up is the same as the weak fingerprint of any data block in a server; if the weak fingerprint of one of the data blocks to be backed up is different from the weak fingerprint of any data block in the server, backing up the data block; if the weak fingerprint of one of the data blocks to be backed up is the same as the weak fingerprint of any data block in the server, judging whether the strong fingerprint of the data block is the same as the strong fingerprint of any data block in the server; if the strong fingerprint of the data block is different from the strong fingerprint of any data block in the server, backing up the data block; and performing the operation on all data blocks to be backed up. In the method for deleting the repeated data, a hash function with low calculation amount is adopted at the first time to perform weak check on every data block and a has function with high calculation amount is adopted then to perform strong check, so the problem that all the data are checked by the hash function with the high calculation amount is avoided, the fingerprint calculation amount during checking is reduced greatly, the series performance is enhanced, and the appreciable transmission performance is provided for data backup based on mass data storage.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
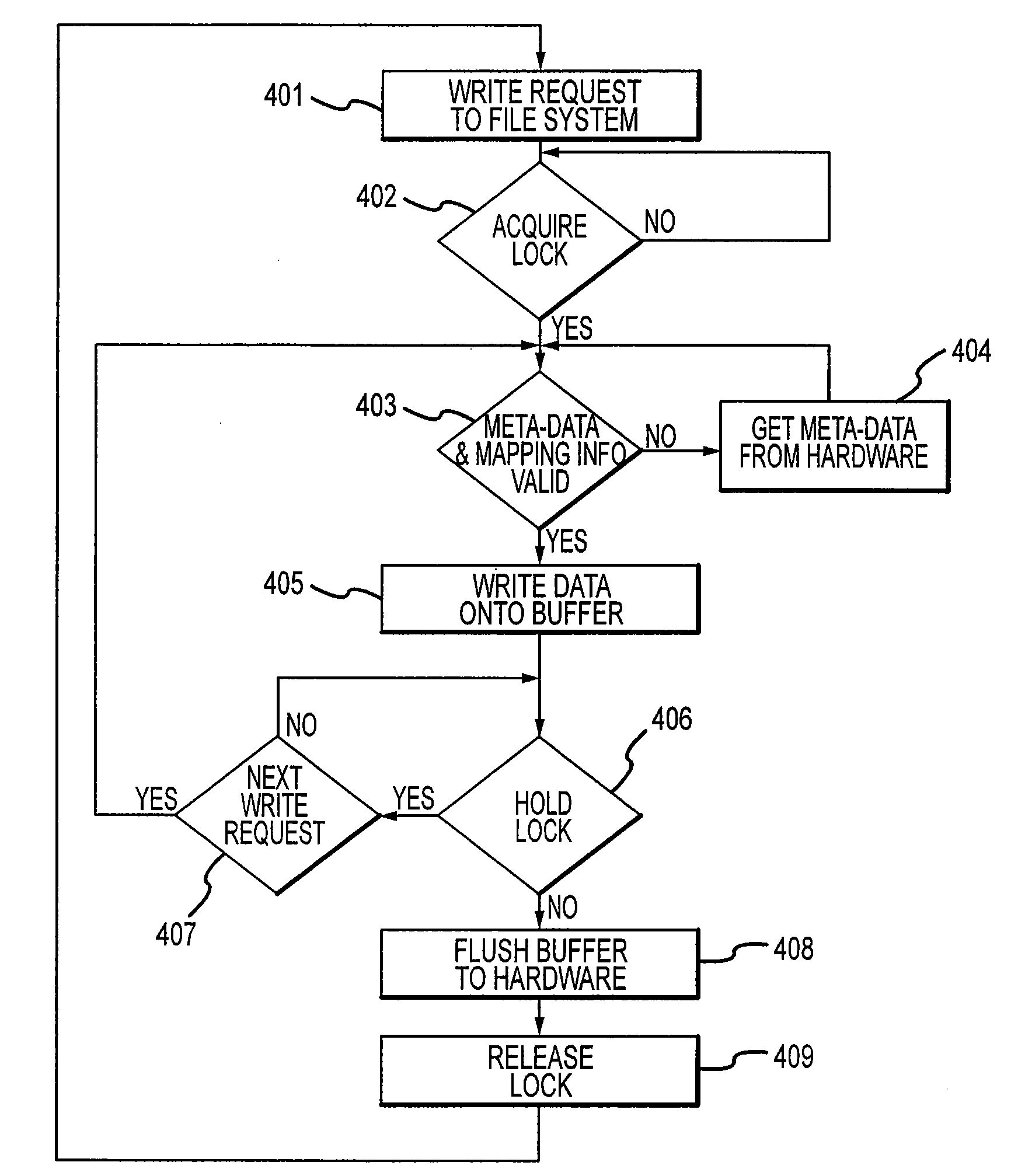
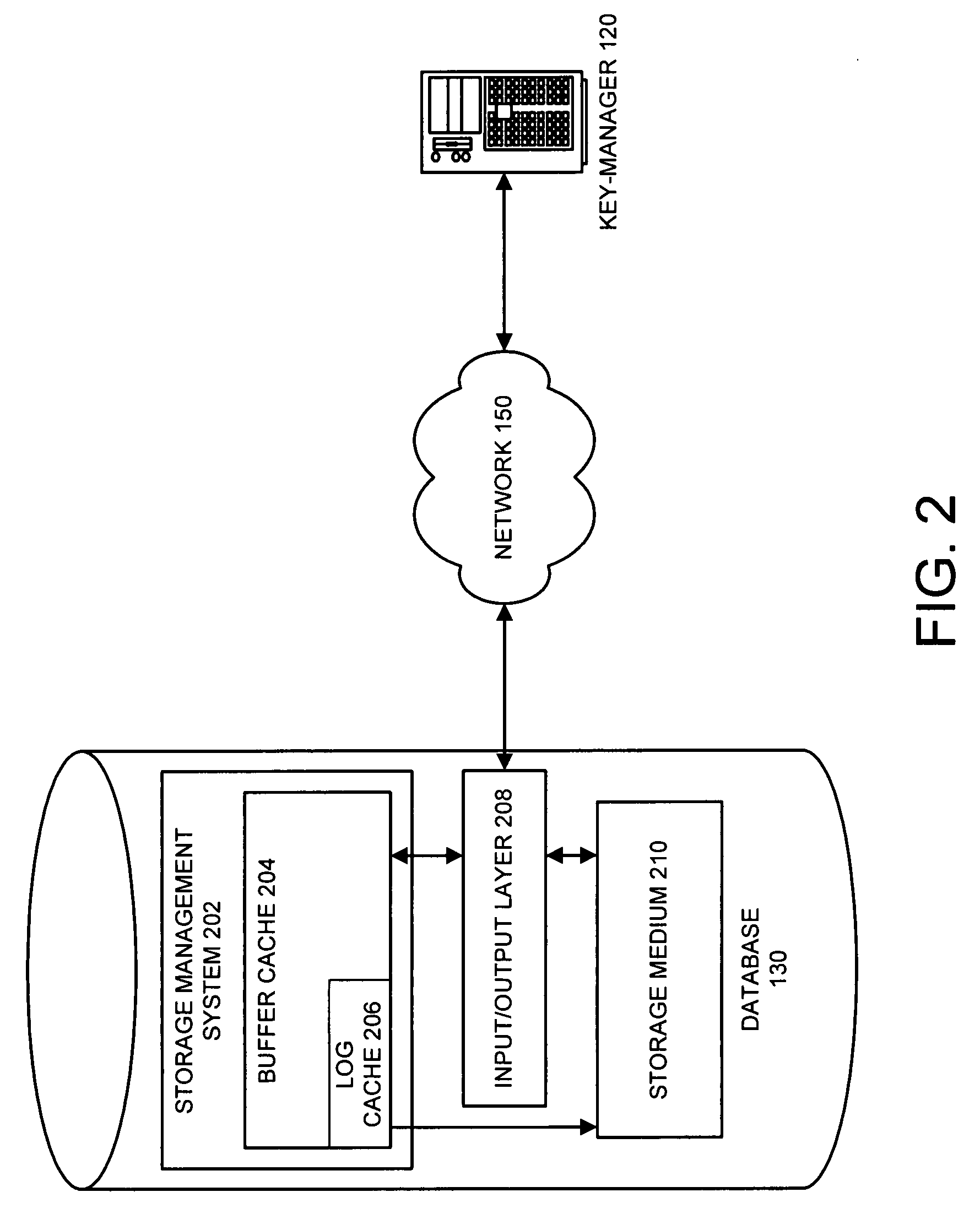
Method and apparatus for performing selective encryption/decryption in a data storage system
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for performing selective encryption / decryption in a data storage system. During operation, the system receives a data block from a storage medium at an input / output layer, wherein the input / output layer serves as an interface between the storage medium and a buffer cache. Next, the system determines whether the data block is an encrypted data block. If not, the system stores the data block in the buffer cache. Otherwise, if the data block is an encrypted data block, the system retrieves a storage-key, wherein the storage-key is associated with a subset of storage, which is associated with the encrypted data block. Using the storage-key, the system then decrypts the encrypted data block to produce a decrypted data block. Finally, the system stores the decrypted data block in the buffer cache, wherein the data block remains encrypted in the storage medium.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data storage structure of Flash memory and data manipulation mode thereof
ActiveCN102081577AExtended service lifePower-down resistantMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant data error correctionElectricityData operations
The invention relates to the field of a Flash memory, particularly a data storage structure of a Flash memory. A storage unit on each page comprises a data storage space for storing data and a spare space, wherein the spare space is defined into the following parts: a file name recording area, a page name recording area, a page storage state recording area, a page state recording area, a block erase counter recording area and a data check code recording area. The data manipulation mode of the data storage structure of a Flash memory specifically comprises a system initialization step and a data manipulation step, wherein the data manipulation step comprises storage space allocation and release operation, anti-power-down protection operation, abrasion balancing operation, bad block processing and data check operation. The invention optimizes the data storage structure of a Flash memory and the data manipulation control mode thereof, balances the Flash memory in the read-write operation, carries out anti-powder-down processing and designs an ECC (Error Correction Code) processing mechanism, thereby avoiding the defects of the existing Flash.
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
System for determining the mapping of logical objects in a data storage system
InactiveUS6938059B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData storage systemApplication software
A method and apparatus for manipulating data in a storage device that is coupled to a host computer. Manipulations that can be performed by the storage device include moving non-contiguous blocks of data between the host computer and the storage device in a single operation. Other manipulations can be performed directly by the storage device without passing data to or from the host computer and include copying data from one logical object that is defined on the host computer to another, initializing, backing-up, transforming, or securely deleting a logical object that is defined by the host computer with a single command. In one embodiment, an application programming interface is provided that allows a relationship between logical objects on a host computer and storage locations on a storage device to be communicated between the host computer and the storage device. By providing the storage device with knowledge of the relationship between a logical object and the storage locations corresponding to that logical object, data corresponding to the logical object can be manipulated directly by the storage device, rather than by the host computer. In another embodiment, a graphical visualization routine is provided that displays the global mapping of a logical object to a set of physical blocks on the storage device for each layer of mapping below the logical object.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
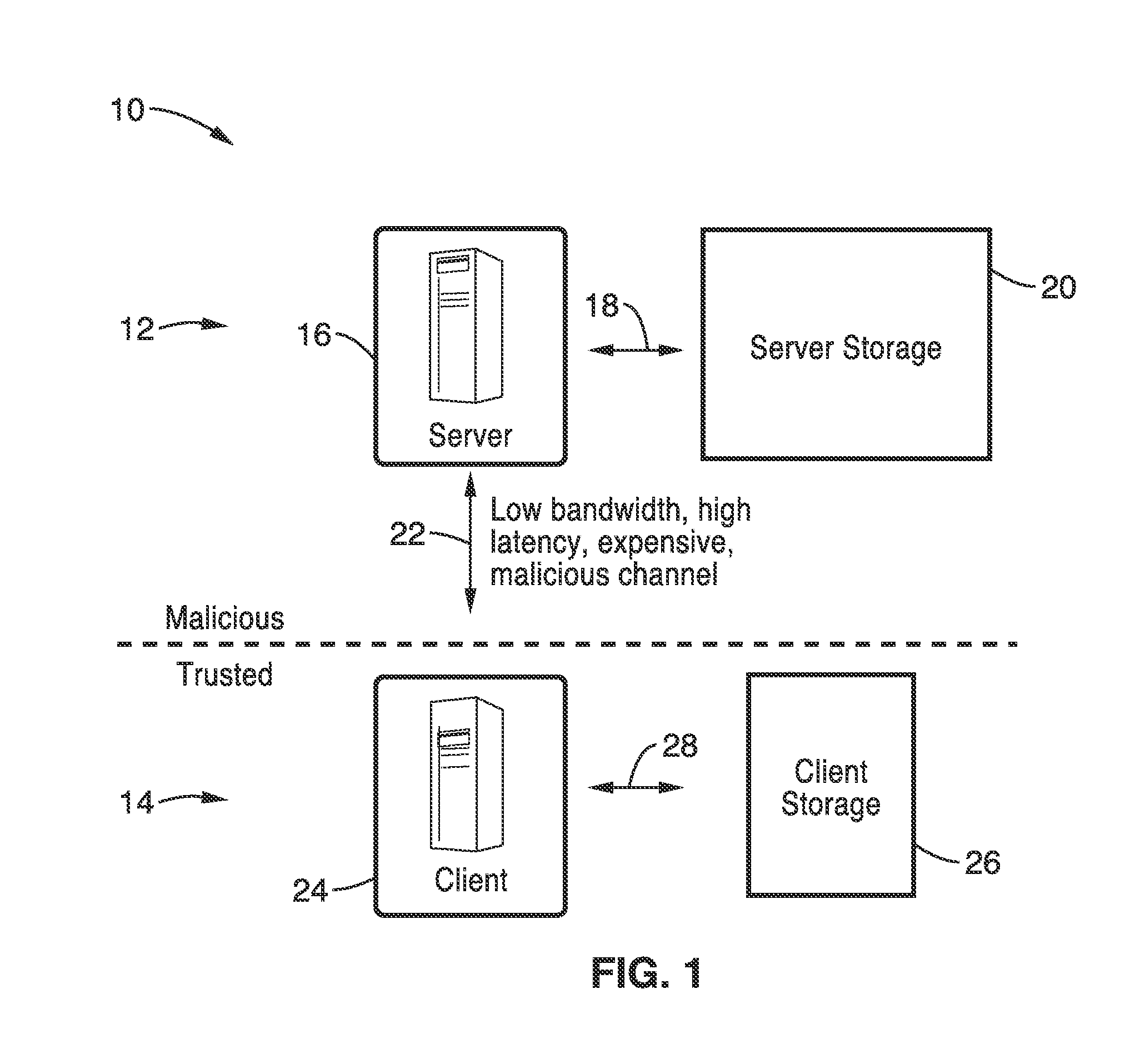
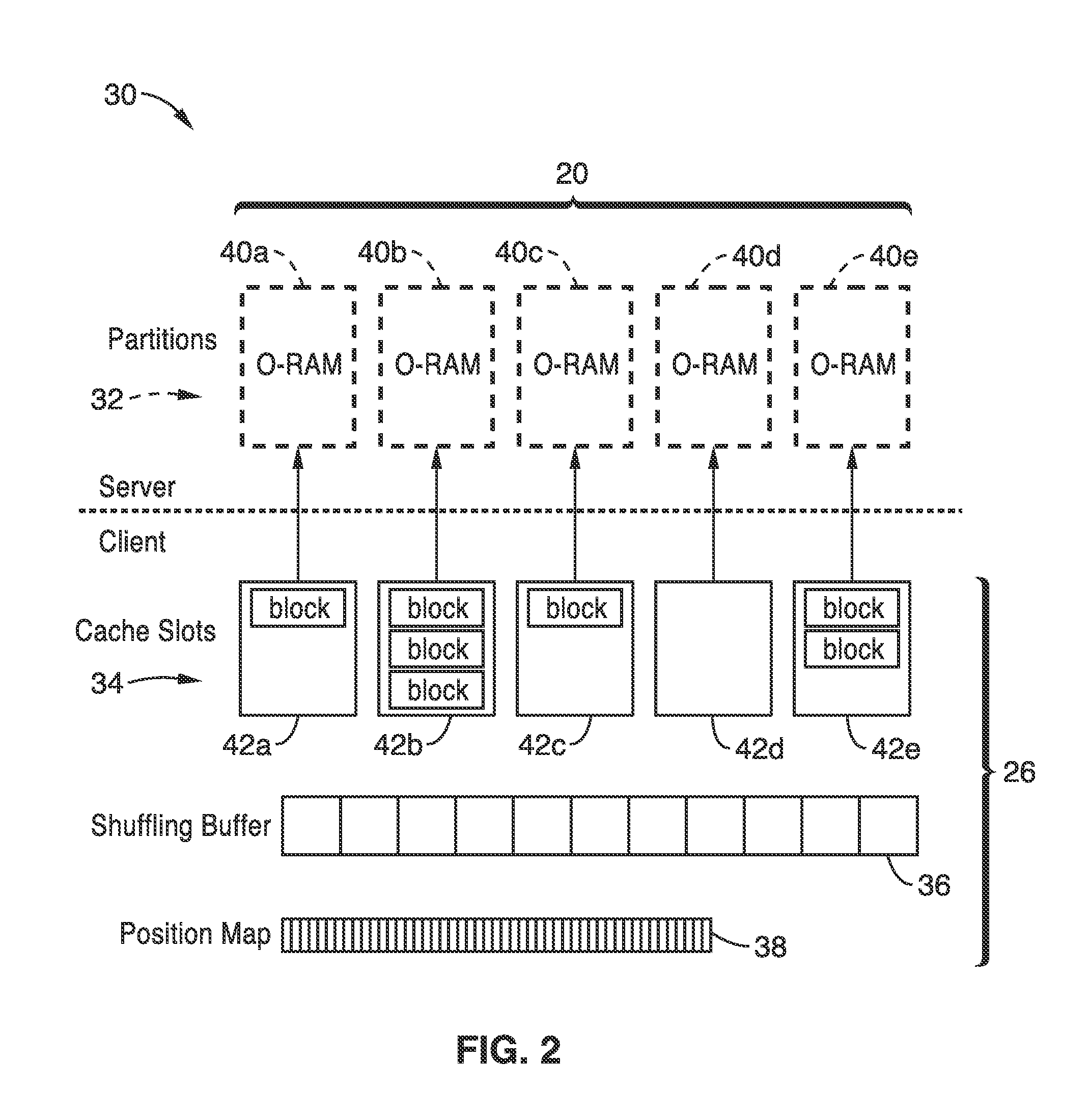
Concealing access patterns to electronic data storage for privacy
InactiveUS20140007250A1Easy to usePrivacy protectionDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsClient-sideData store
Methods and systems of concealing access patterns to data storage, such as within servers of a cloud computing environment are presented. Server data storage is securely partitioned into smaller electronic data storage partitions of predetermined size. The client side maintains a shuffling buffer and position map for these blocks as stored on the electronic data storage partitions of the server. Concealment is performed with respect to accesses from the client to server using an oblivious sorting protocol. Access operation is concealed with each block being randomly assigned to any of the data storage partitions, and whenever a block is accessed, the block is logically removed from its current partition and logically assigned to a fresh random partition selected from all partitions, while the client maintains tracking of which partition each block is associated with at any point of time.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
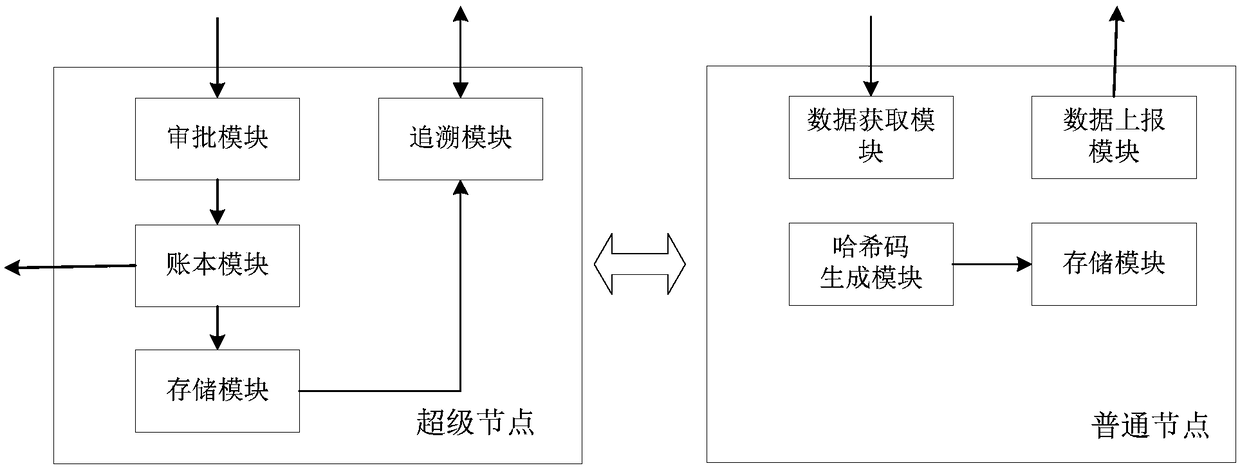
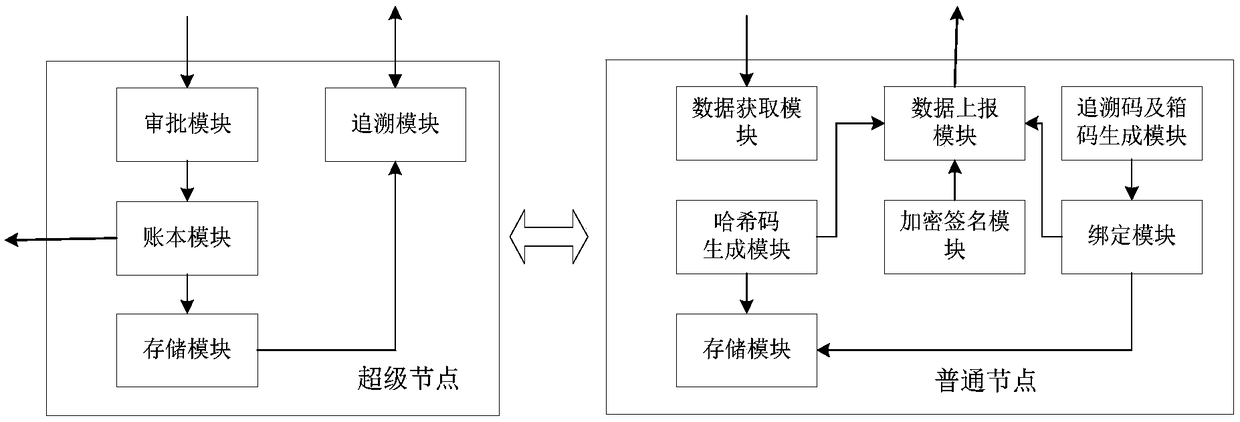
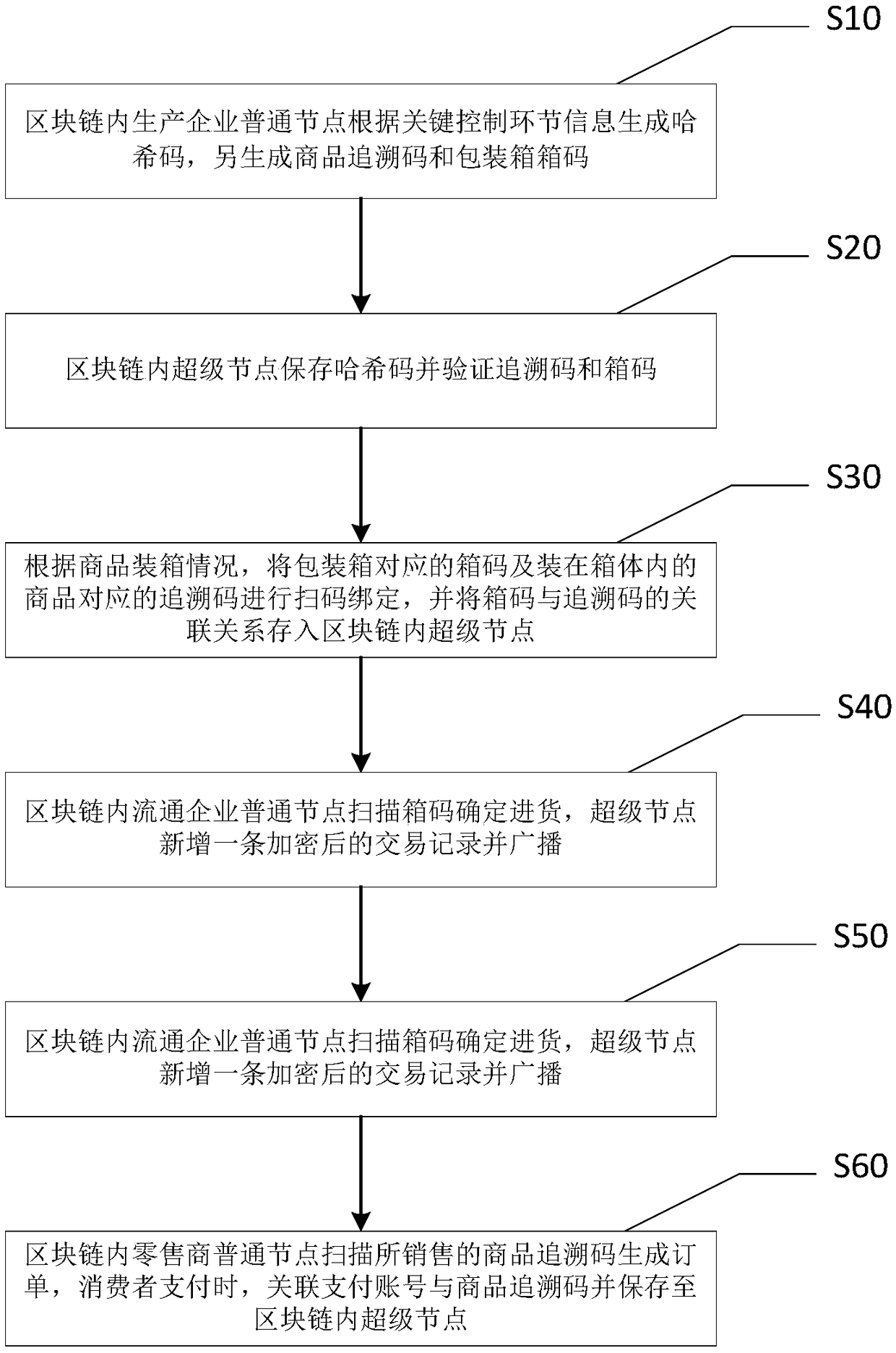
Data storage system, circulating method and tracing method of distributed commodities based on block chain
The invention discloses a data storage system, a circulating method and a tracing method of distributed commodities based on a block chain and relates to the field of data tracing. The system is deployed by adopting a league chain mode and comprises multiple super-nodes and multiple common nodes. The data storage system, the circulating method and the tracing method of the distributed commoditiesbased on the block chain solve the problem of non-transparent transaction data in current commodity production and circulation chains, reduce trust friction between enterprises and trust friction between enterprises and supervision departments by utilizing the characteristic that the block chain cannot be tampered, solves the problem of big storage pressure of a centralized tracing platform as thedetail information of the production and circulation links are stored in databases of each enterprise node dispersedly and guarantees the data to be not tampered arbitrarily by the enterprises through the Hash codes, solves the problem of tracing data incompleteness and responsibility positioning difficulty of a supply chain as all the information in the whole life cycle is recorded by regardingthe tracing codes as core and combining with means such as box code association and mobile payment, the responsible party can be positioned rapidly when a quality problem occurs and a recall notice can be sent to related enterprises and related consumers.
Owner:广州中科易德科技有限公司
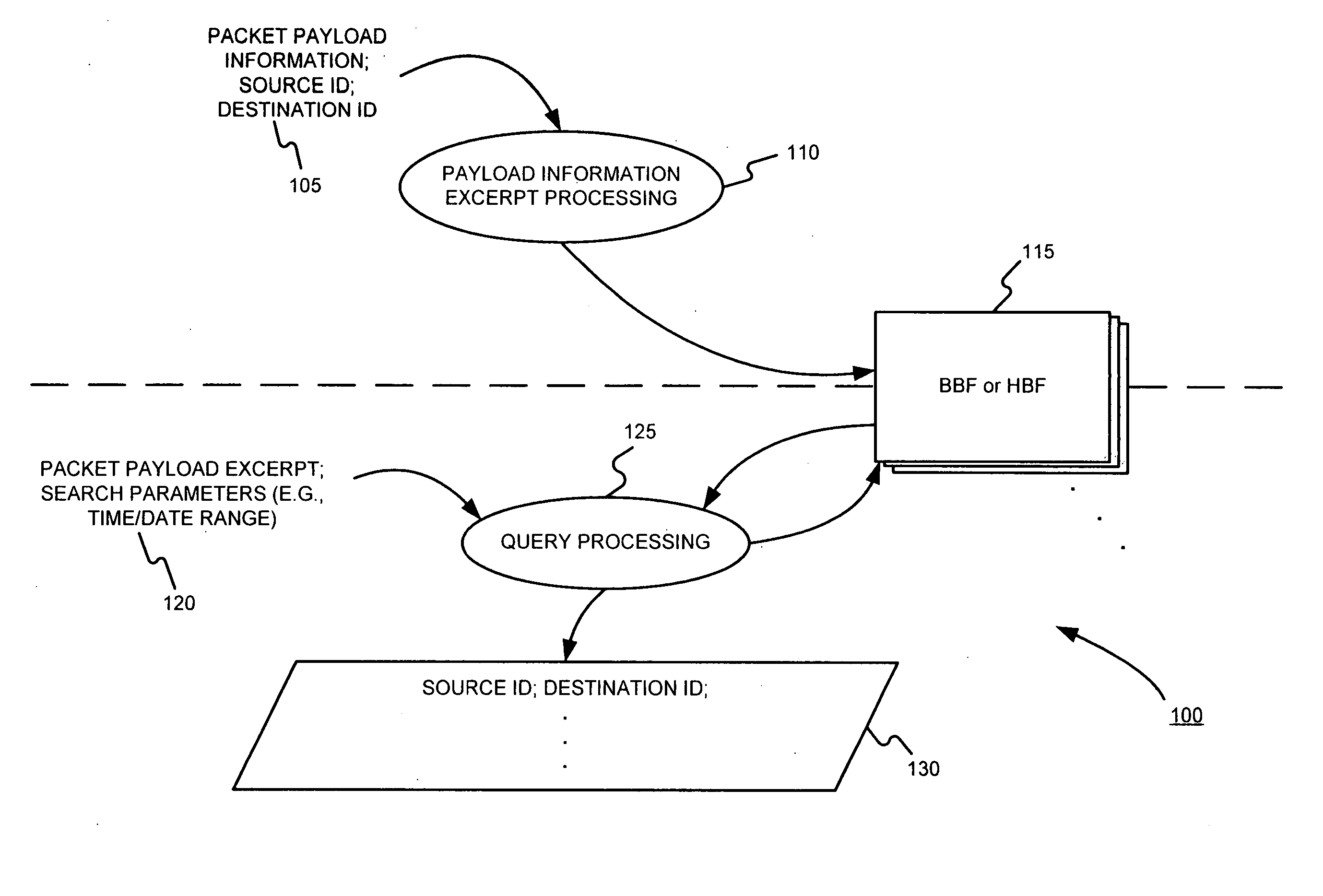
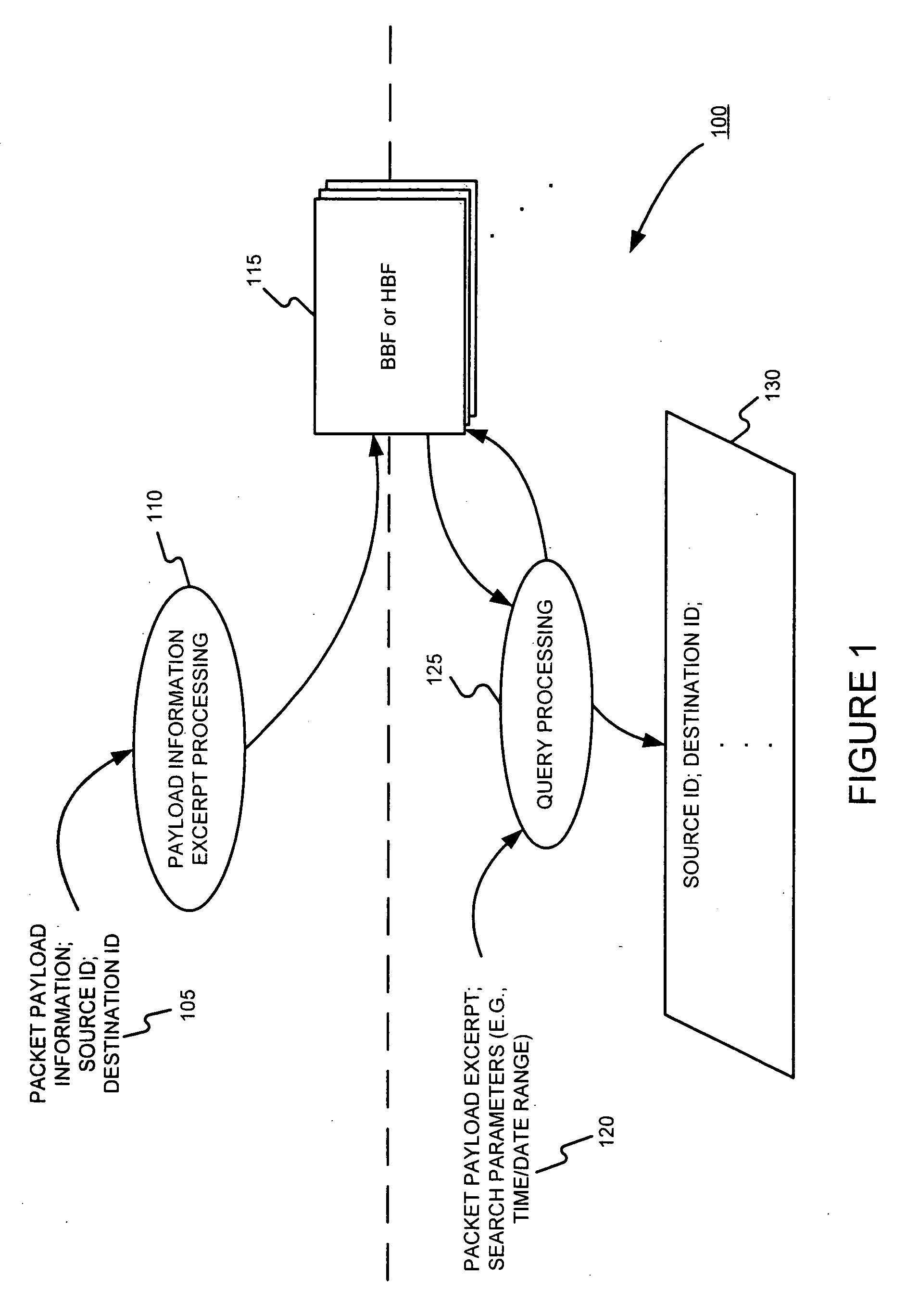
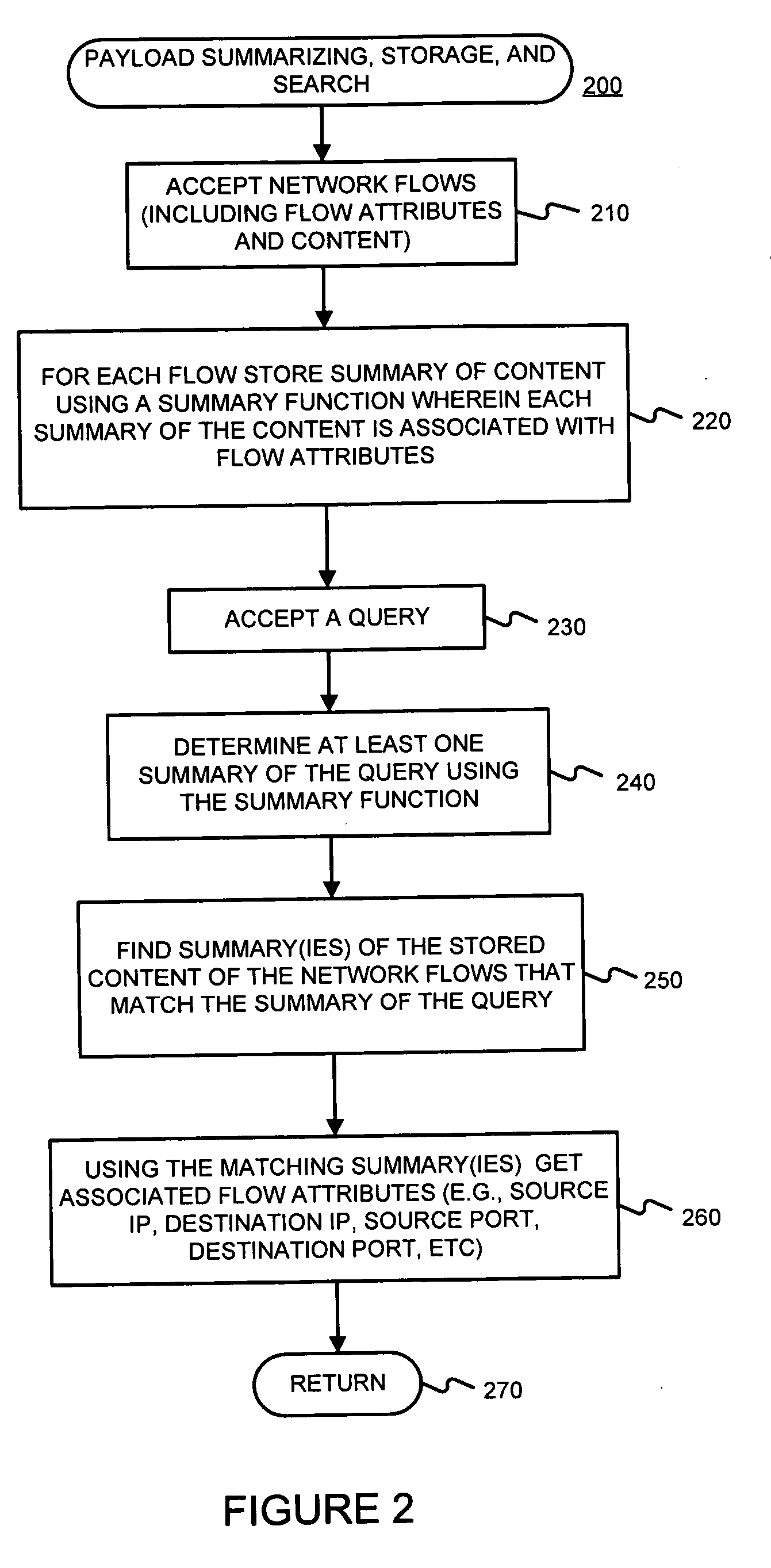
Facilitating storage and querying of payload attribution information
InactiveUS20060072582A1Solve the high false positive rateImprove accuracyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareBloom filter
A hierarchical data structure of digested payload information (e.g., information within a payload, or information spanning two or more payloads) allows a payload excerpt to be attributed to earlier network flow information. These compact data structures permit data storage reduction, while permitting efficient query processing with a low level of false positives. One example of such a compact data structure is a hierarchical Bloom filter. Different layers of the hierarchy may correspond to different block sizes.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
System and method for data protection on a storage medium
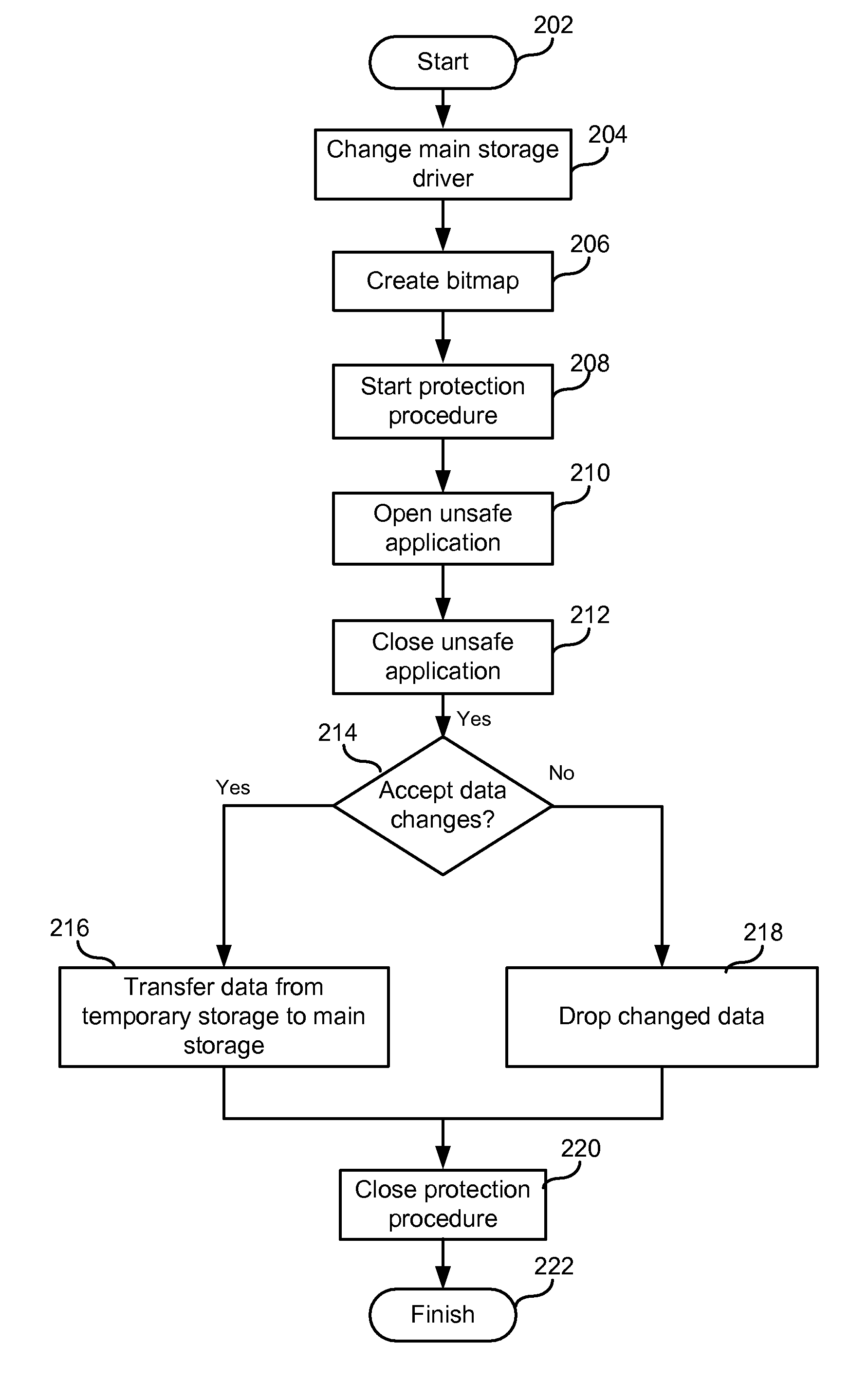
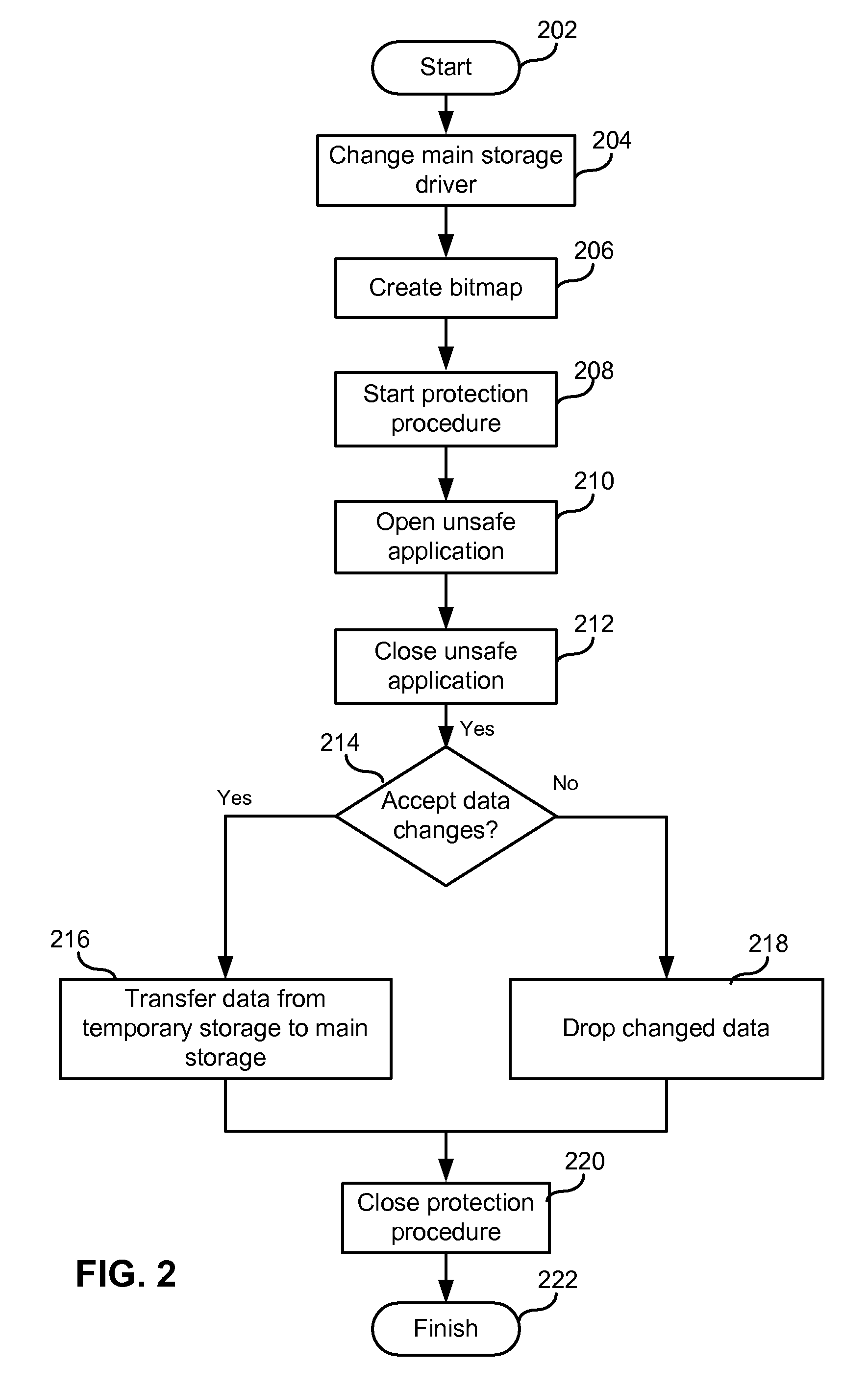
ActiveUS7953948B1Eliminate disadvantagesError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsData memoryVirtual storage
A method of and system for protecting a disk drive or other data storage includes mounting a virtual storage that combines a READ-only portion of a volume of the main storage and a full access temporary storage located on the same data storage, wherein the READ-only portion represents a protected area of the volume of the main storage; generating a bitmap for blocks of the virtual storage; redirecting virtual storage write requests to the temporary storage; marking, in the bitmap, blocks of the virtual storage corresponding to blocks of the temporary storage that are being written to; redirecting, to the READ-only portion, read requests for unmarked blocks; redirecting, to the temporary storage, read requests for marked blocks; upon an acceptance of a state of the virtual storage, merging the temporary storage with unmarked blocks of the READ-only portion of the volume of the main storage, to form an integral storage; and upon a rejection of a state of the virtual storage, terminating the redirecting. Optionally, data in the temporary storage can be archived.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
Snapshots of file systems in data storage systems
InactiveUS20050240635A1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemData space
The present invention relates to methods and systems of snapshot management of a file system in a data storage system. To represent the snapshots, the invention maintains pointers to the root block pointer of each snapshot. When the active file system is modified, this invention avoids overwriting any blocks used by previous snapshots by allocating new blocks for the modified blocks. When the invention needs to put an established block in a new location, it must update a parent block to point to the new location. The update to the parent block may then require allocating a new block for the new parent block and so forth. Parts of the file system not modified since a snapshot remain in place. The amount of space required to represent snapshots scales with the fraction of the file system that users modify. To maintain snapshot integrity, this invention keeps track of the first and last snapshots that use each block in space map blocks spread throughout the file system data space. When users delete snapshots, this invention may use a background process to find blocks no longer used by any snapshot and makes them available for future use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
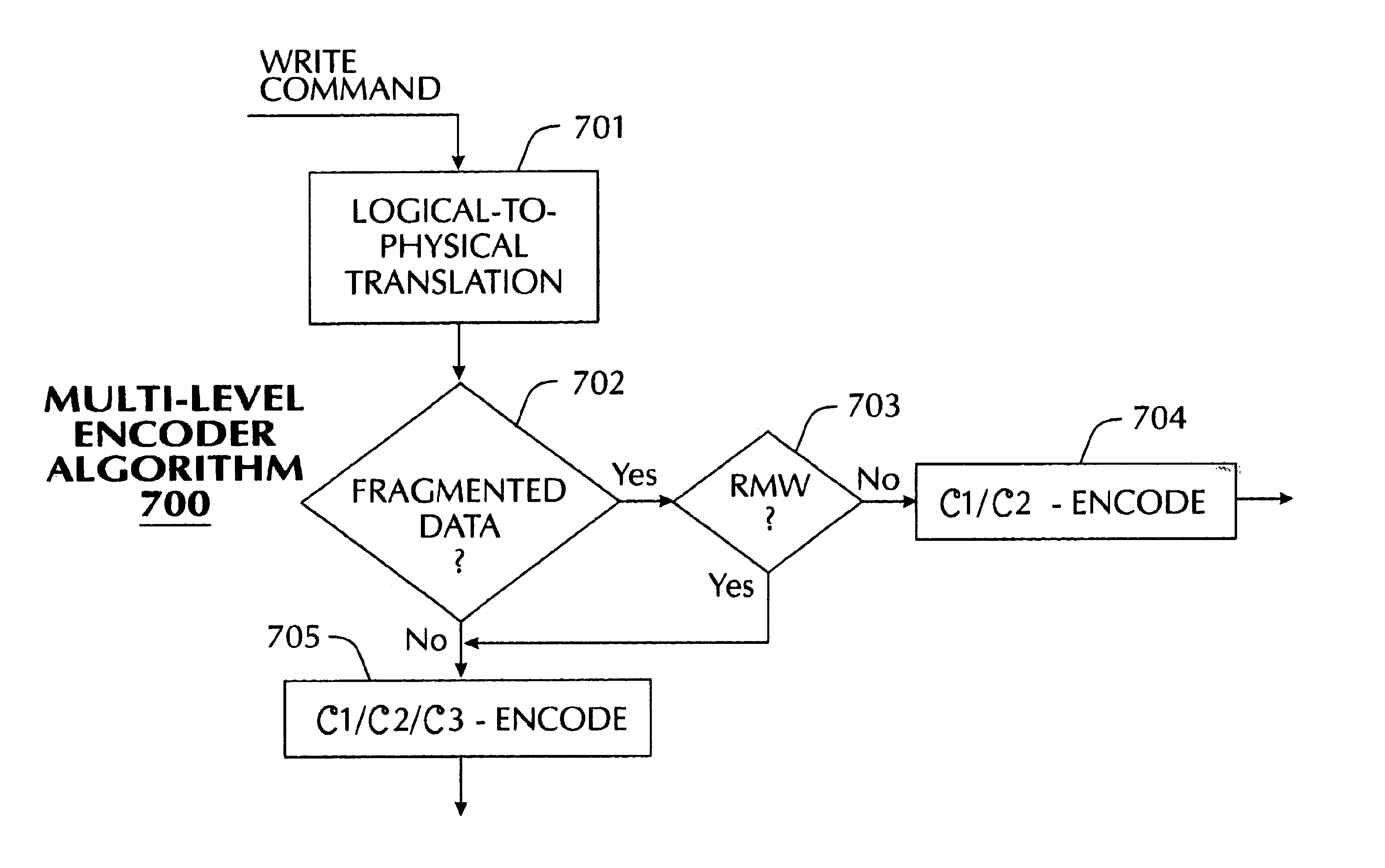
Multiple level (ML), integrated sector format (ISF), error correction code (ECC) encoding and decoding processes for data storage or communication devices and systems
A method and an apparatus encodes and decodes blocks having a predetermined number of sectors of data bytes to detect and correct data bytes in error in each sector of a block. The method and the apparatus generates sector level check bytes for each sector in the block responsive to the data bytes in each sector according to a first level of an error correction code, and generates block level check bytes for a predetermined sector in the block responsive to the sector level check bytes of various sectors, including the predetermined sector, according to at least a second level of the error correction code. The method and apparatus processes the block to detect and correct data bytes in error in each sector within the capability of the sector level check bytes, to detect and correct data bytes in error in the at least two sectors that exceed the correction capability of the sector level check bytes but within the correction capability of the block level check bytes, or to indicate that the data bytes in error in the at least two sectors exceed the correction capability of each of the sector level check bytes and the block level check bytes. The method and apparatus improves signal quality for long streams of information having multiple sequential physical blocks of data bytes, such as audio visual information, with a low check byte overhead while being compatible with conventional 512 data byte sized sectors and conventional single sector error correction code processes.
Owner:IBM CORP
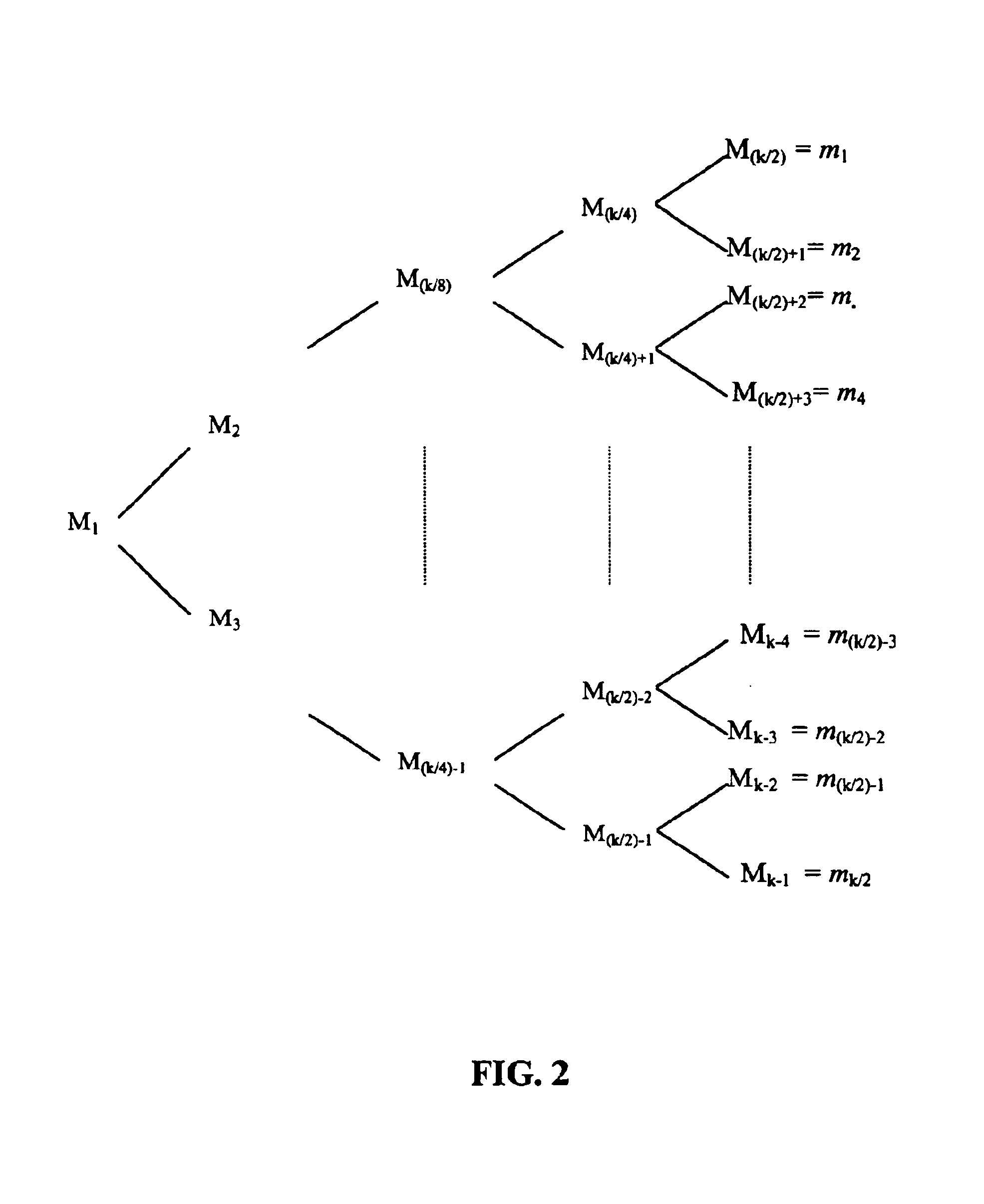
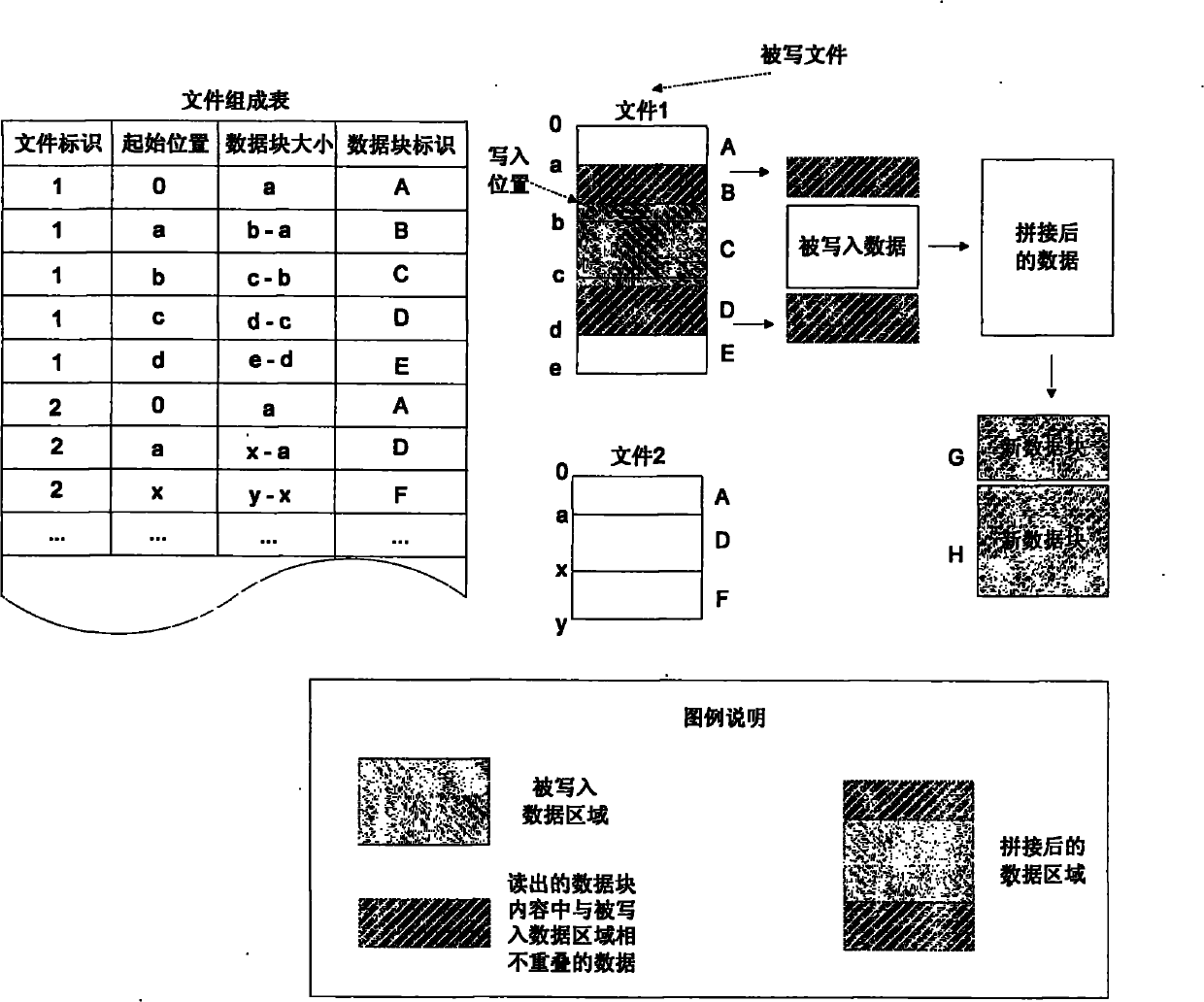
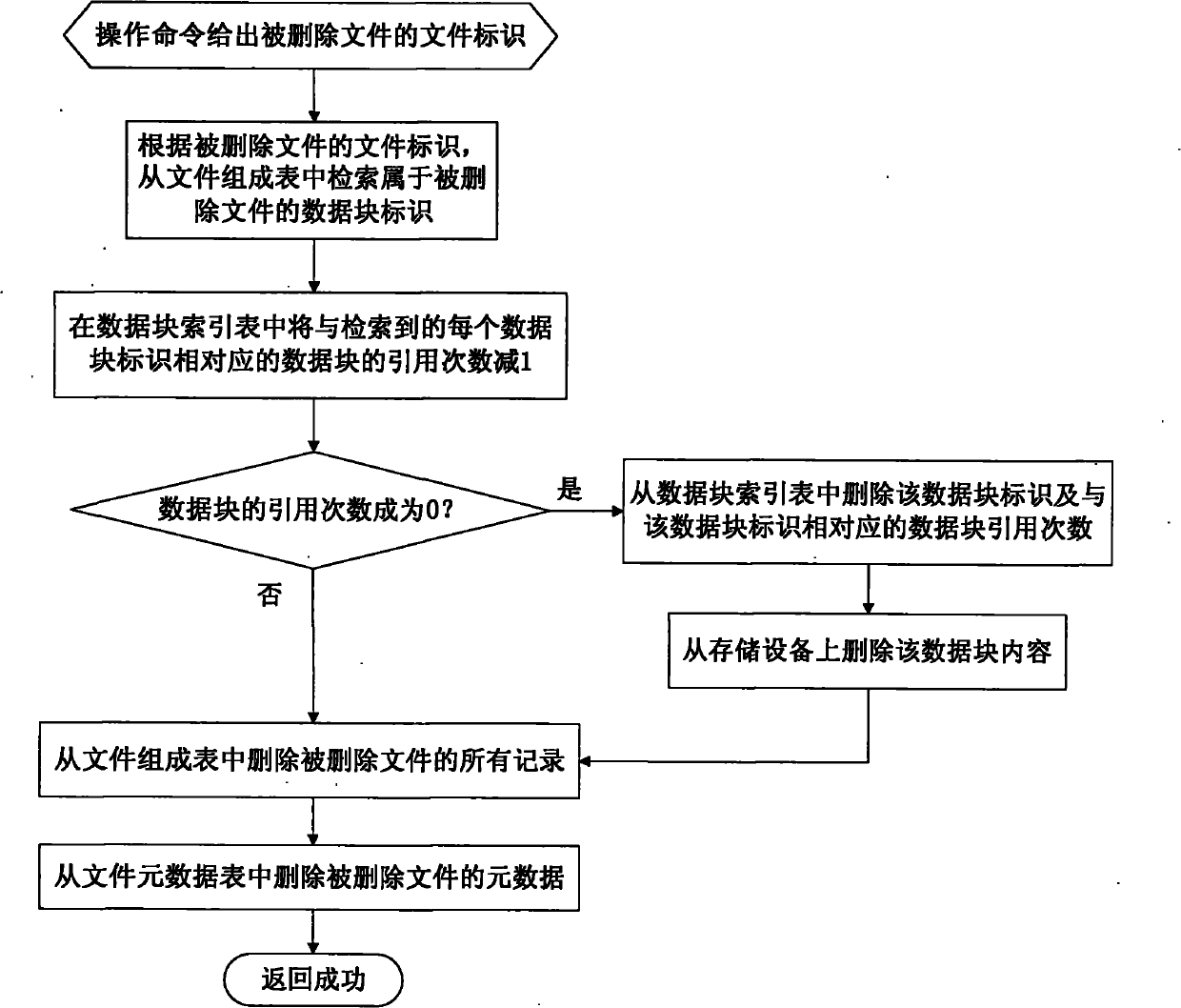
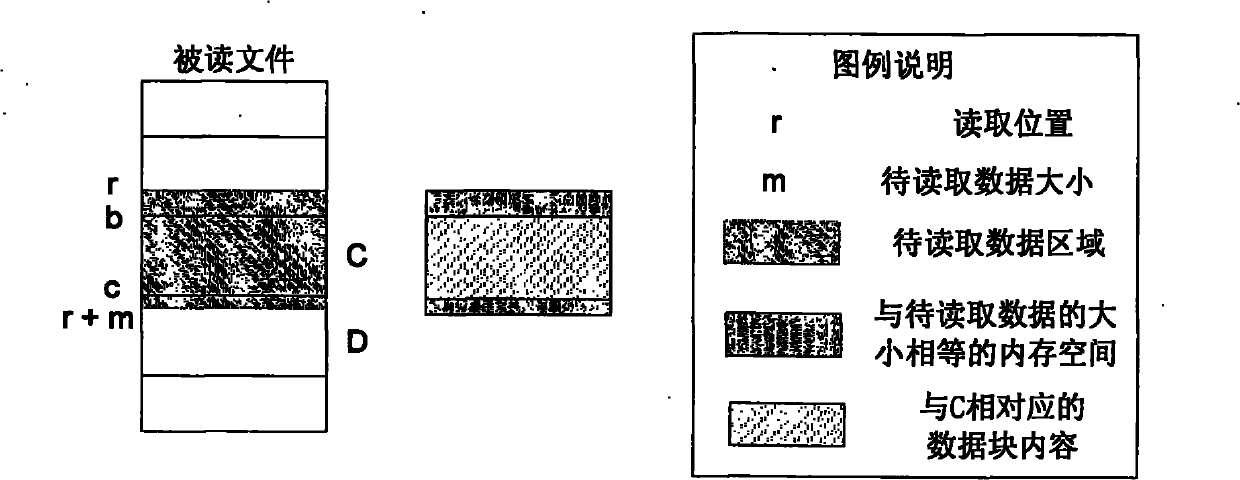
Method for deleting duplicated data in file system in real time
InactiveCN101908073ASave storage spaceImprove processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDatasheetEmbedded database
The invention relates to a method for deleting duplicated data in a file system in real time, and belongs to the technical field of computer data storage. In a file system establishment stage, a file metadata table, a data block index and a file constitution table are set in an embedded database; and in a file system operation stage, operating commands initiated to the file system by applications are received and responded through a file system driver, and include establishing a new file, writing data to an existing file, reading data from the existing file and deleting the existing data. The method simultaneously supports fixed-length and variable-length file blocking methods, and can delete the duplicated data in the file system in real time, save storage space and improve the utilization efficiency of storage equipment; and the process of deleting the duplicated data is completely transparent to the applications and a user, the file operation of various conventional applications is seamlessly compatible, and almost all negative effects on the user experience are avoided.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
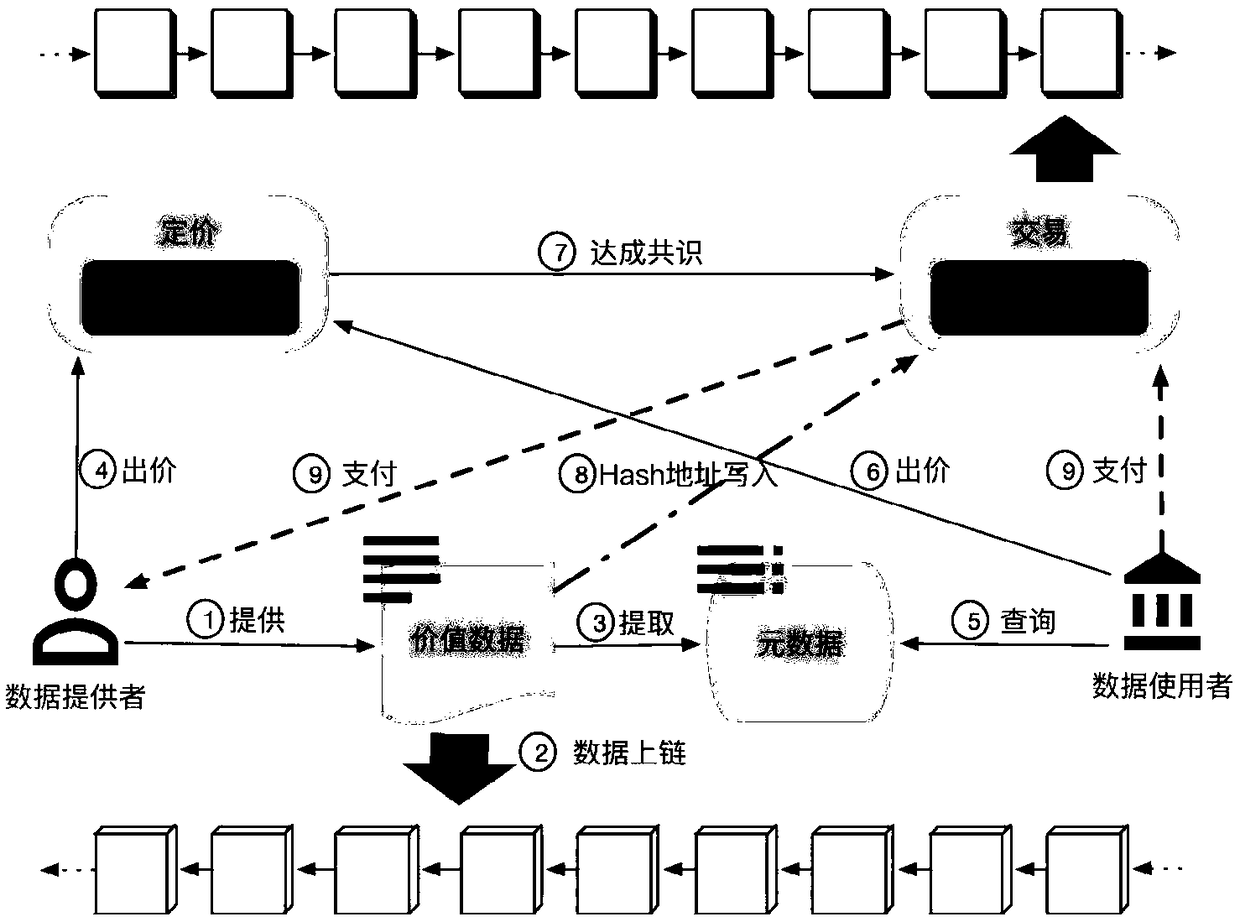
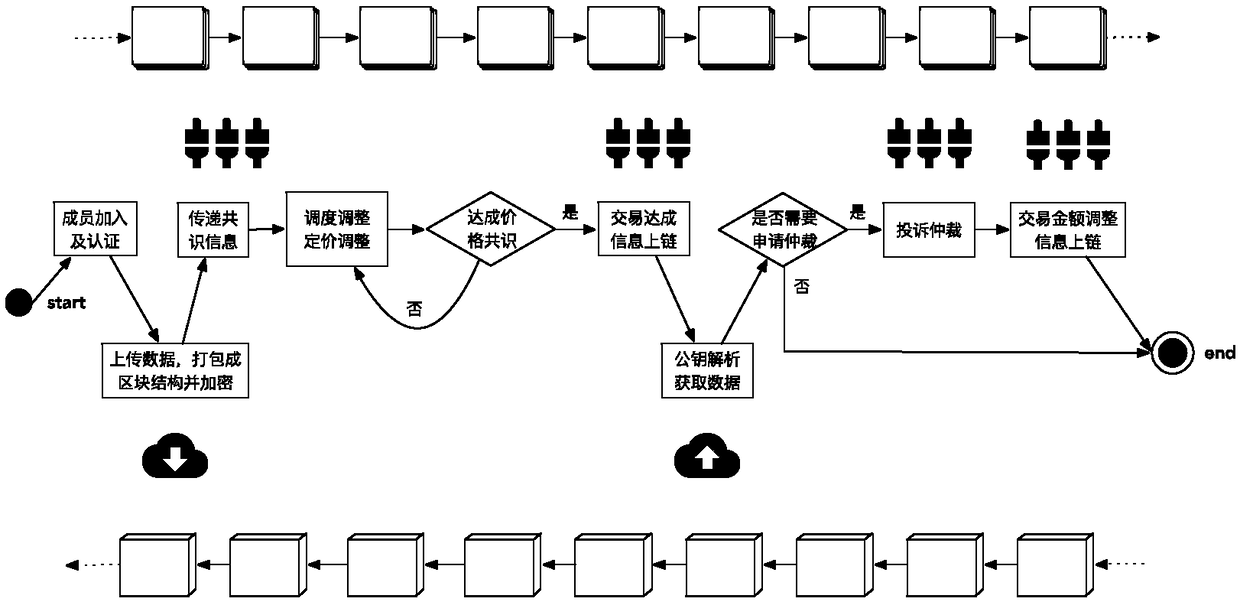
A data trading system based on a block chain and an implementation method thereof
InactiveCN109242636AData acquisition barriers are highLower barriers to accessFinanceDigital data protectionData providerData acquisition
The invention discloses a data trading system based on a block chain and an implementation method thereof. The invention comprises a data collector, a background application management module, a blockchain data storage module based on a federation chain, a block chain data transaction module based on a public chain, and a user display terminal. The data collector interacts with the background application management system, The block chain storage module stores the data obtained by the collector in a distributed manner, and the block chain data transaction module stores the information and transaction information exchanged between the data collector and the background application management system in a decentralized manner and controls the transaction flow, and the user operates the user display terminal. The invention can encourage data providers to participate in data flow and reduce data acquisition barriers, protect the rights and interests of data providers and make full use of data value. It solves the contradiction between the high efficiency of data transaction and the high cost of current block chain. Data pricing strategies are implemented in a more concise, efficient, and executable manner.
Owner:盈盈(杭州)网络技术有限公司
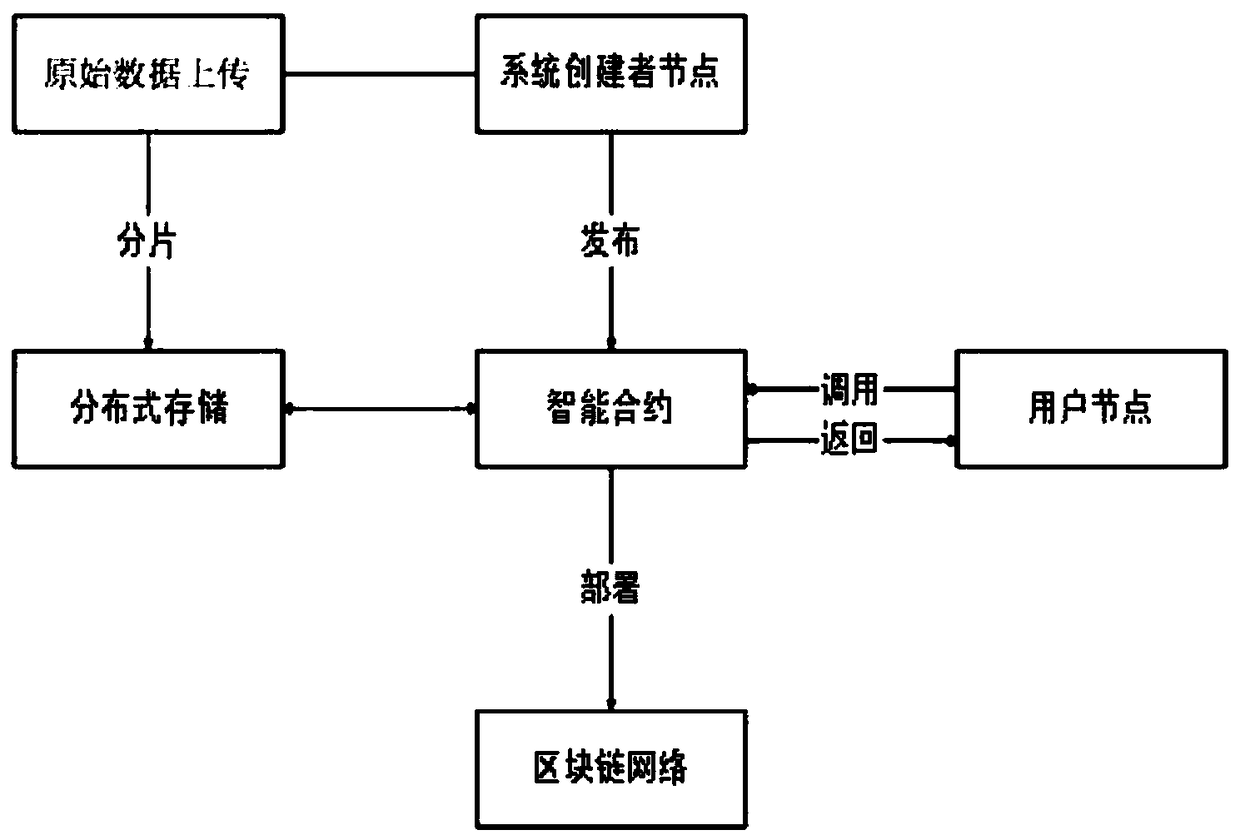
An electronic data storage method based on a block chain intelligent contract
InactiveCN109165190ASerious centralizationSolve complexityDigital data information retrievalFinanceOriginal dataSmart contract
The invention discloses an electronic data storage method based on a block chain intelligent contract, which comprises the steps of raw data uploading, slicing, storing, issuing, data structure defining, anchoring, writing, calling, returning and comparing and verifying. The method utilizes an intelligent contract and a block chain technology, and has features of decentralization, open transparency, unalterable properties, easy traceability and data trustworthiness. By slicing and storing the electronic data in a distributed way, the method solves the problems of serious centralization and long and complex data of an existing electronic data storage method, improves the security of the user data, records the electronic data stored in each customer certificate in the block, traces each electronic data, facilitates the user to supervise the data security, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for protecting and recovering continuous data based on time stick diary memory
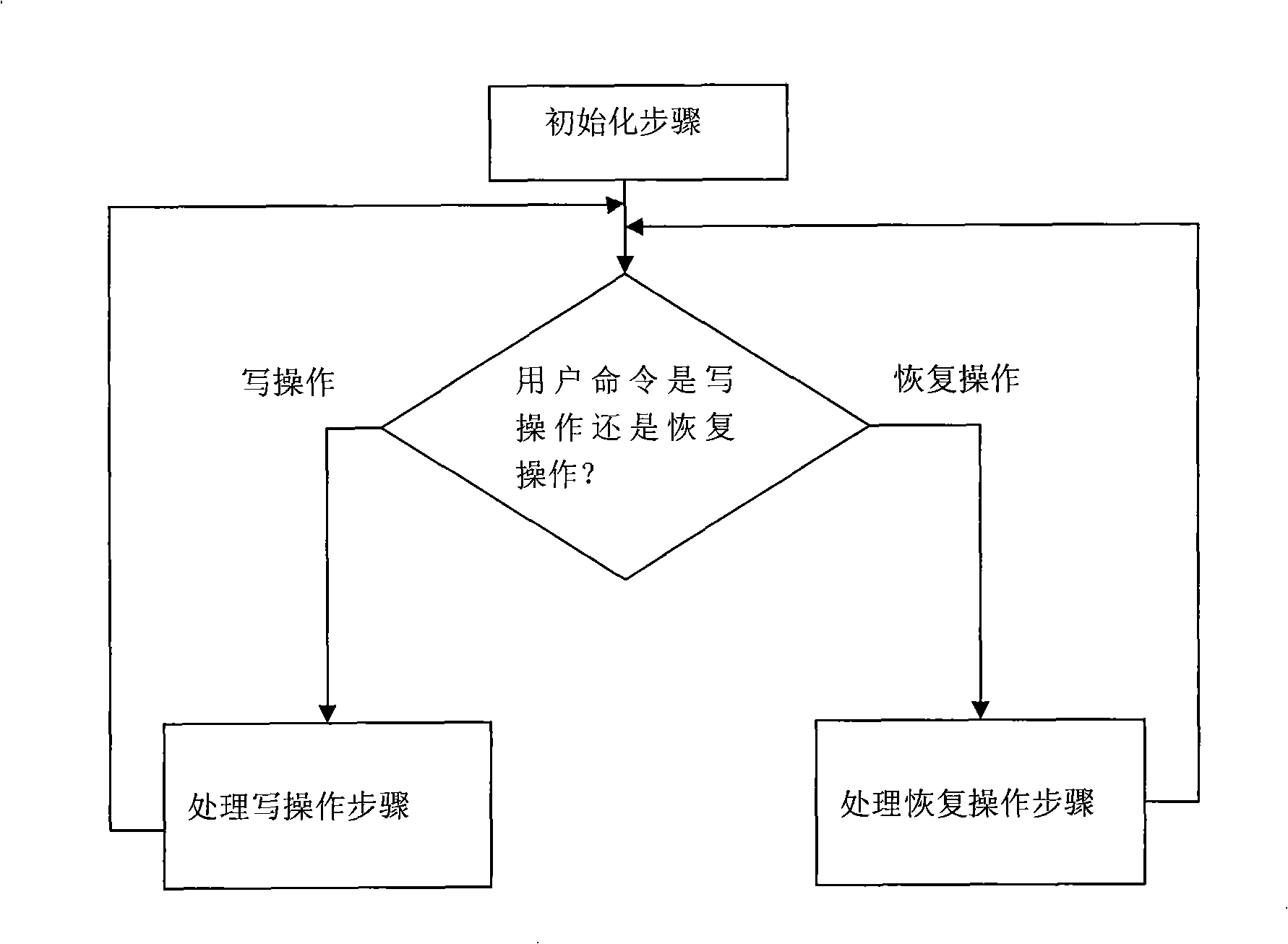
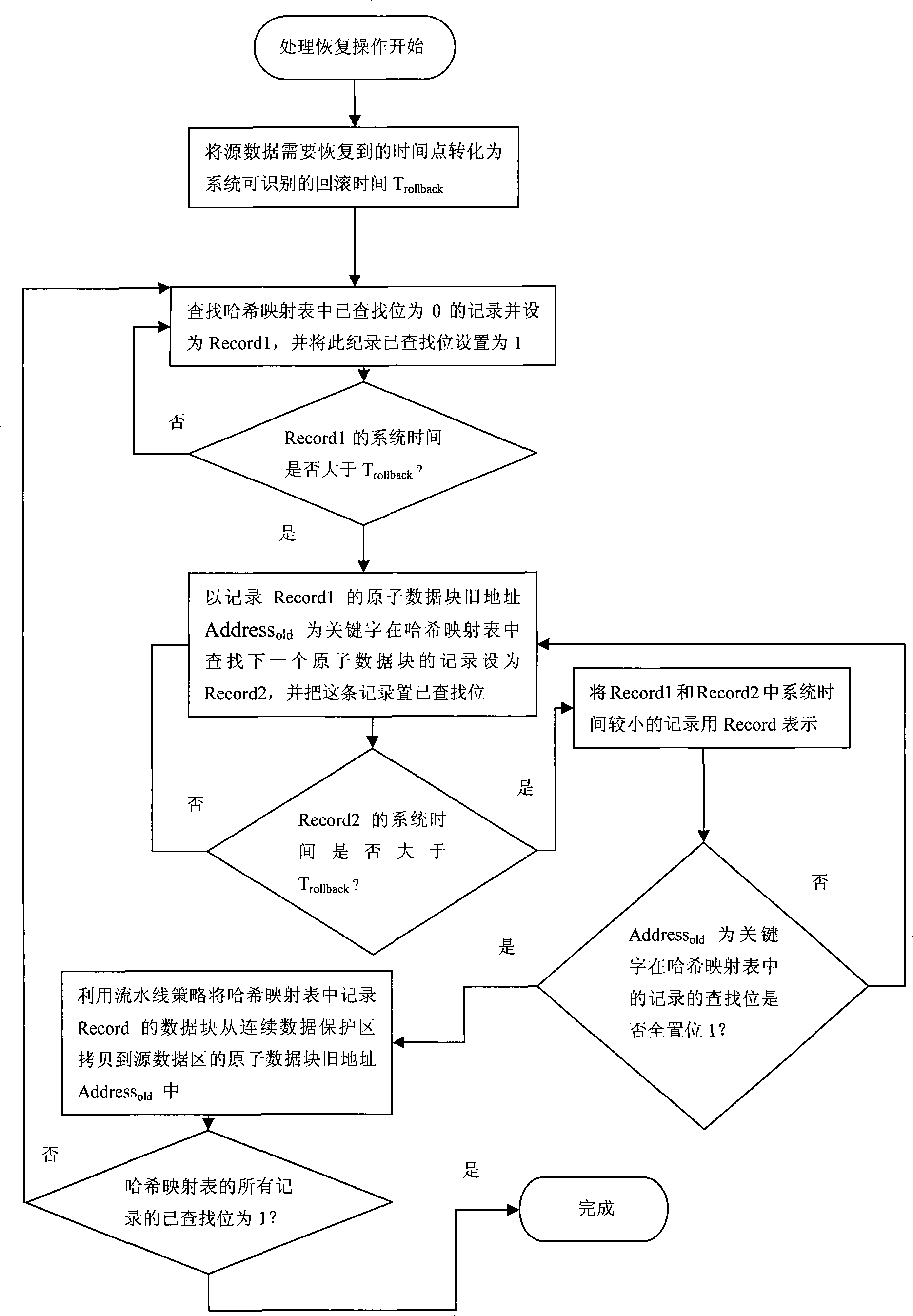
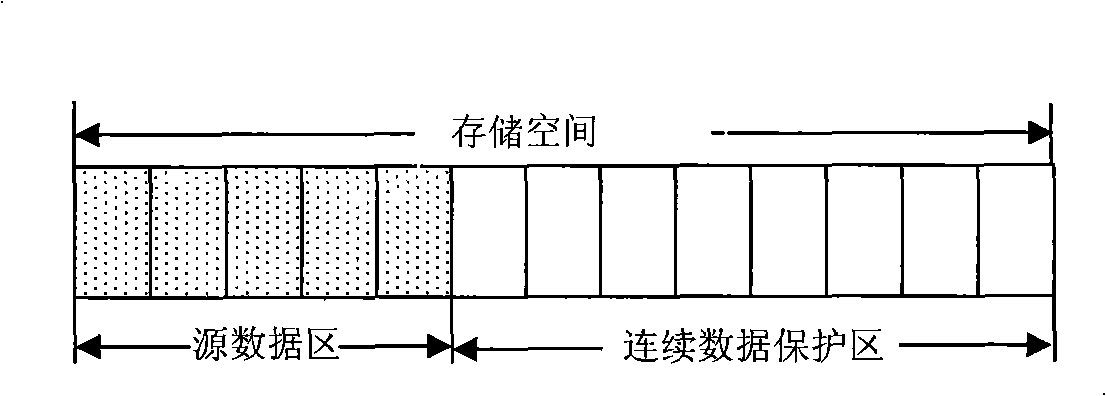
The invention relates to a method for the protection and recovery of continuous data stored in a time-stamp diary, which pertains to a computer data storage and backup method and aims at reducing the time of processing a write operation and a recovery operation and increasing processing parallelism. The method comprises the steps that: (1) a storage area is divided into a source data area and a continuous data protection area; a Hush mapping table is initialized; (2) a user command is judged, and the write operation is carried out sequentially; the recovery operation is carried out as the step (4); (3) the write operation is processed; by adopting a production line strategy, a copy operation and a new write operation are carried out in parallel; a source data record is inserted into the Hush mapping table; the step (2) is carried out; (4) the recovery operation is processed, and the source subdata block record needing copying is searched in the Hush mapping table; corresponding source subdata block record is written into the source data area by adopting the production line strategy; then the step (2) is carried out. The proposal of time-stamp diary storage is adopted in the invention; the production line strategy is adopted when the write operation and the recovery operation are processed; therefore, write operation processing time and target recovery time are shorter.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Programming non-volatile memory using a relaxed dwell time
InactiveUS20150161036A1Improve data integrityExtended service lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureEngineering
In at least one embodiment, a data storage system includes a non-volatile memory array including a plurality of blocks of physical memory, each including multiple pages. The data storage system further includes a controller that maintains a data structure identifying blocks of physical memory in the memory array that currently do not store valid data. The controller, responsive to receipt of a write input / output operation (IOP) specifying an address and write data, selects a particular block from among the blocks identified in the data structure prior to a dwell time threshold for the particular block being satisfied, programs a page within the selected block with the write data, and associates the address with the selected block.
Owner:IBM CORP
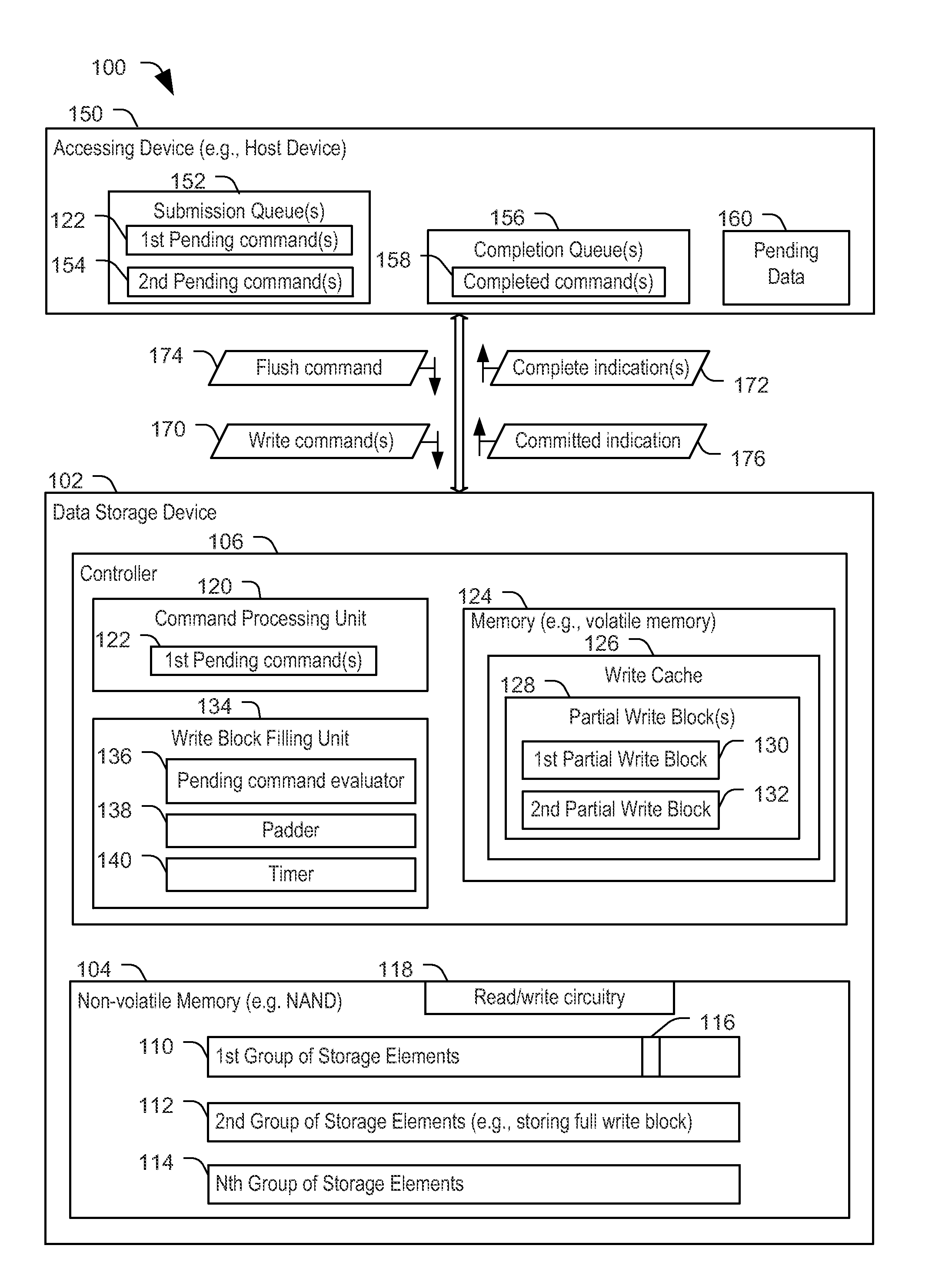
Systems and methods of write cache flushing
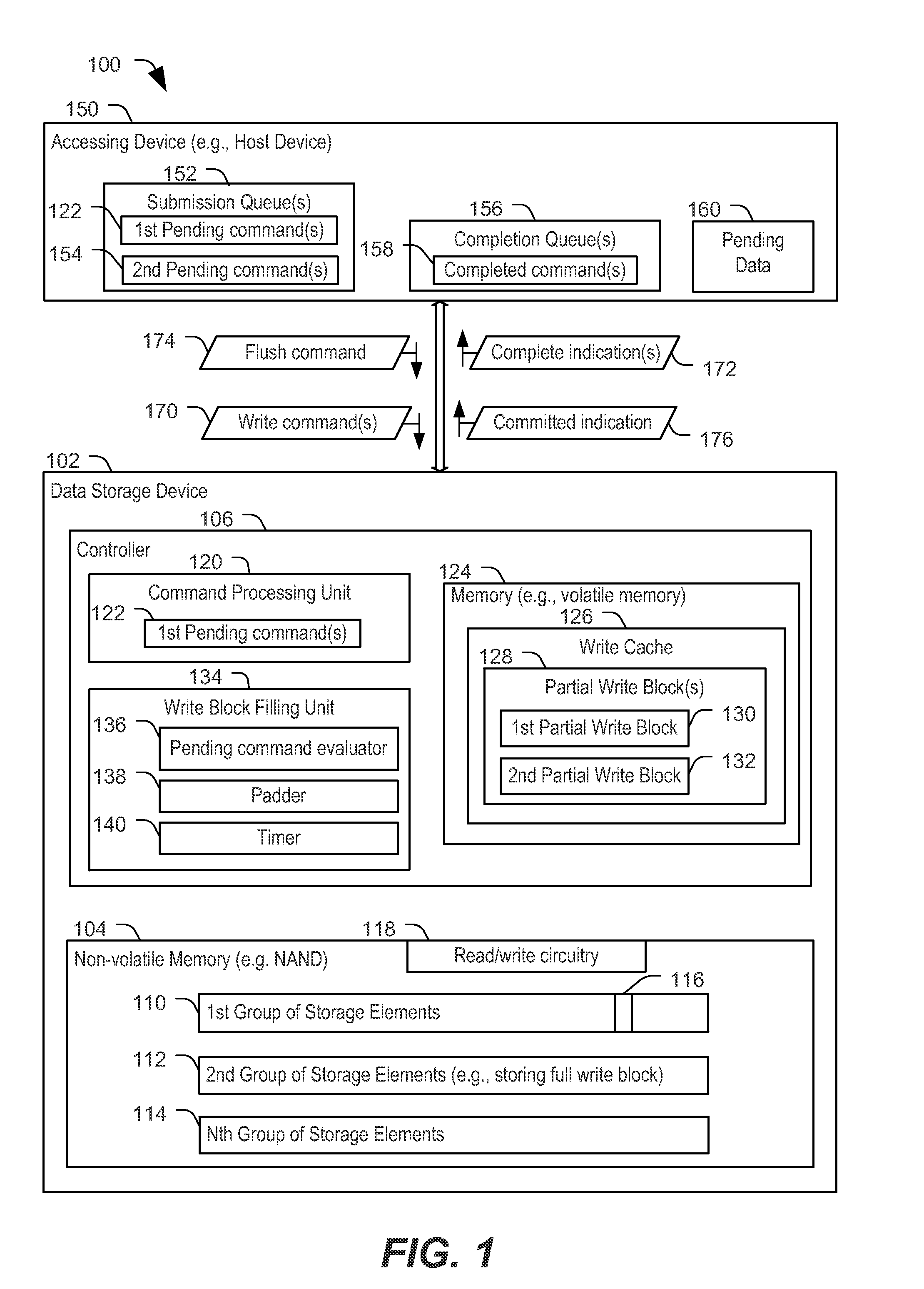
ActiveUS20160147671A1Improve efficiencyTo overcome the large delayMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationEngineeringData store
A data storage device includes a write cache, a non-volatile memory, and a controller coupled to the write cache and to the non-volatile memory. The controller is configured to, responsive to receiving a command to flush particular data from the write cache, attempt to fill a write block of data using the particular data and pending data obtained after receipt of the command.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for rebuilding data of magnetic disk array
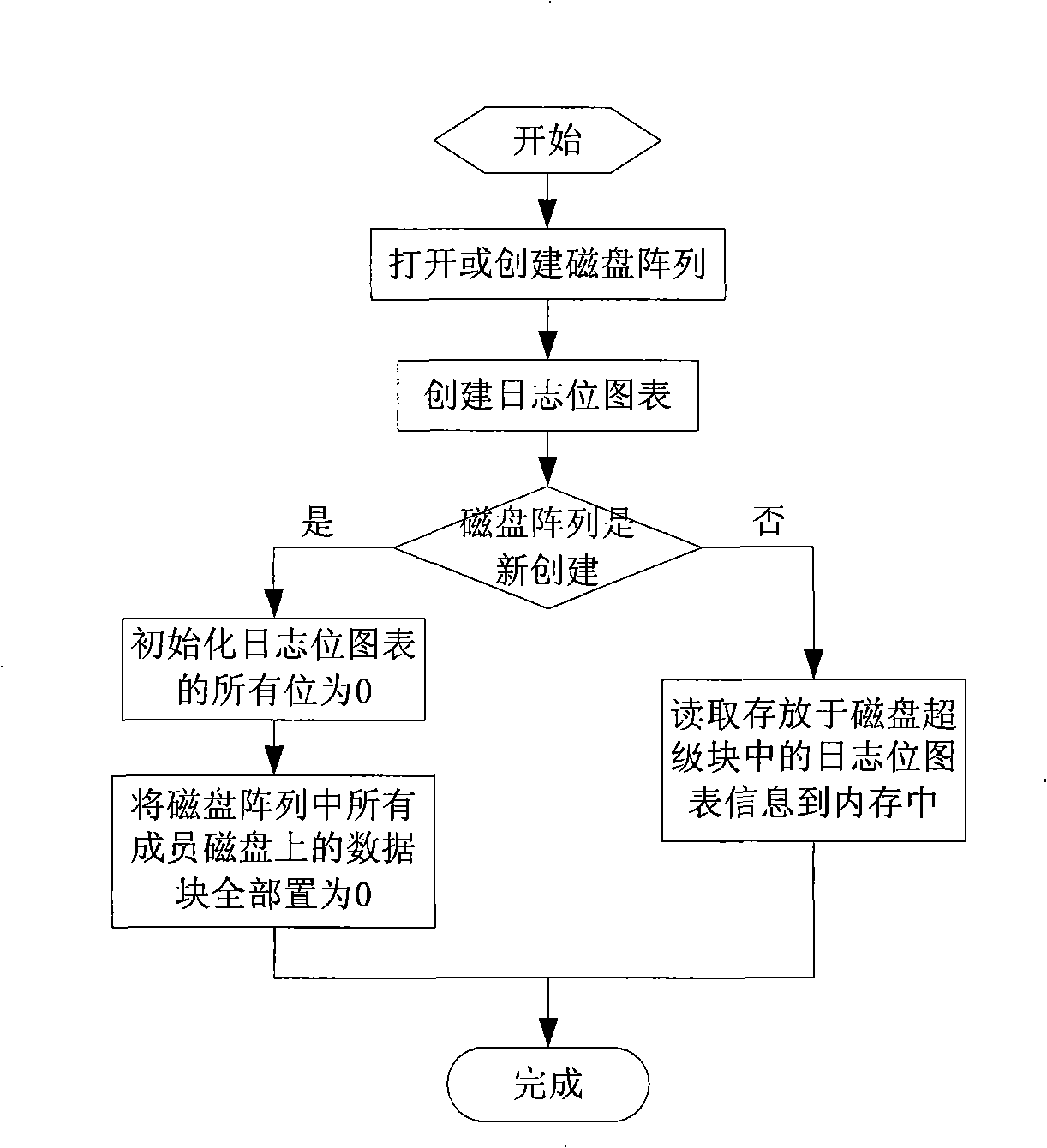
InactiveCN101329641AImprove performanceImprove usabilityRedundant operation error correctionVisit timeReconstruction method
The invention relates to a disk array data reconstruction method which pertains to a computer data storage method and solves the problem that the existing disk array data reconstruction method takes too much time and affects the reading and writing performances and reliability of a storage system. A disk array of the invention is provided with a main control module, reading and writing processing modules and a reconstruction module and comprises the steps of initialization, diary pot diagram update, reconstruction based on diaries and finishing. The method instructs data reconstruction process by the real-time monitoring of disk space using status of the disk array; when space that is not accessed is reconstructed, the only requirement is to write 0 in all corresponding data blocks newly added into a disk, thus greatly reducing physical disk visiting time brought by reconstruction, increasing reconstruction speed and reducing the response time of user access; the reconstruction method does not change the reconstruction procedure or the distribution manner of disk array data, can conveniently optimize various traditional disk array data reconstruction methods and is applicable to the construction of storage systems with high performance, high usability and high reliability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com