Vomitoxin degrading enzyme DDH and application of DDH in detoxification of Trichothecenes
A technology of trichothecenes, vomitoxin, applied in the field of agricultural biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
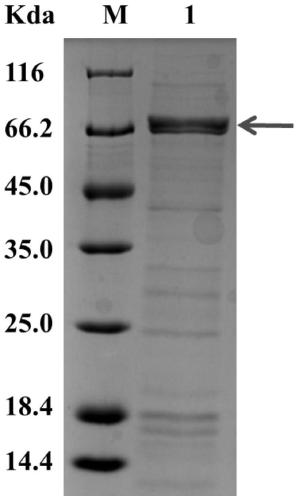
[0063] Example 1 Acquisition and expression of deoxynivalenol-degrading enzyme DDH protein
[0064] The DDH protein coding gene was amplified with the genomic DNA of M. halotolerant ANSP101 as the amplification template, and the recombinant expression vector containing the DDH protein coding gene sequence and its engineering bacteria were constructed to express the DDH protein. Specific steps are as follows:
[0065] 1. Cloning of DDH gene encoding deoxynivalenolase
[0066] 1.1 Extract the genomic DNA of M. halotolerant according to the following steps:
[0067] Take 50 μL of the preserved bacteria solution from the glycerol tube, inoculate and streak on the LB solid plate, and culture at 37°C for 12 hours.
[0068] Pick a single colony from the cultured plate and inoculate it in 5 mL liquid LB medium, culture at 180 r / min, 37°C for 12 h.
[0069] Aliquot the bacterial solution into sterilized 1.5mL microcentrifuge tubes, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 1min to collect the ba...
Embodiment 2
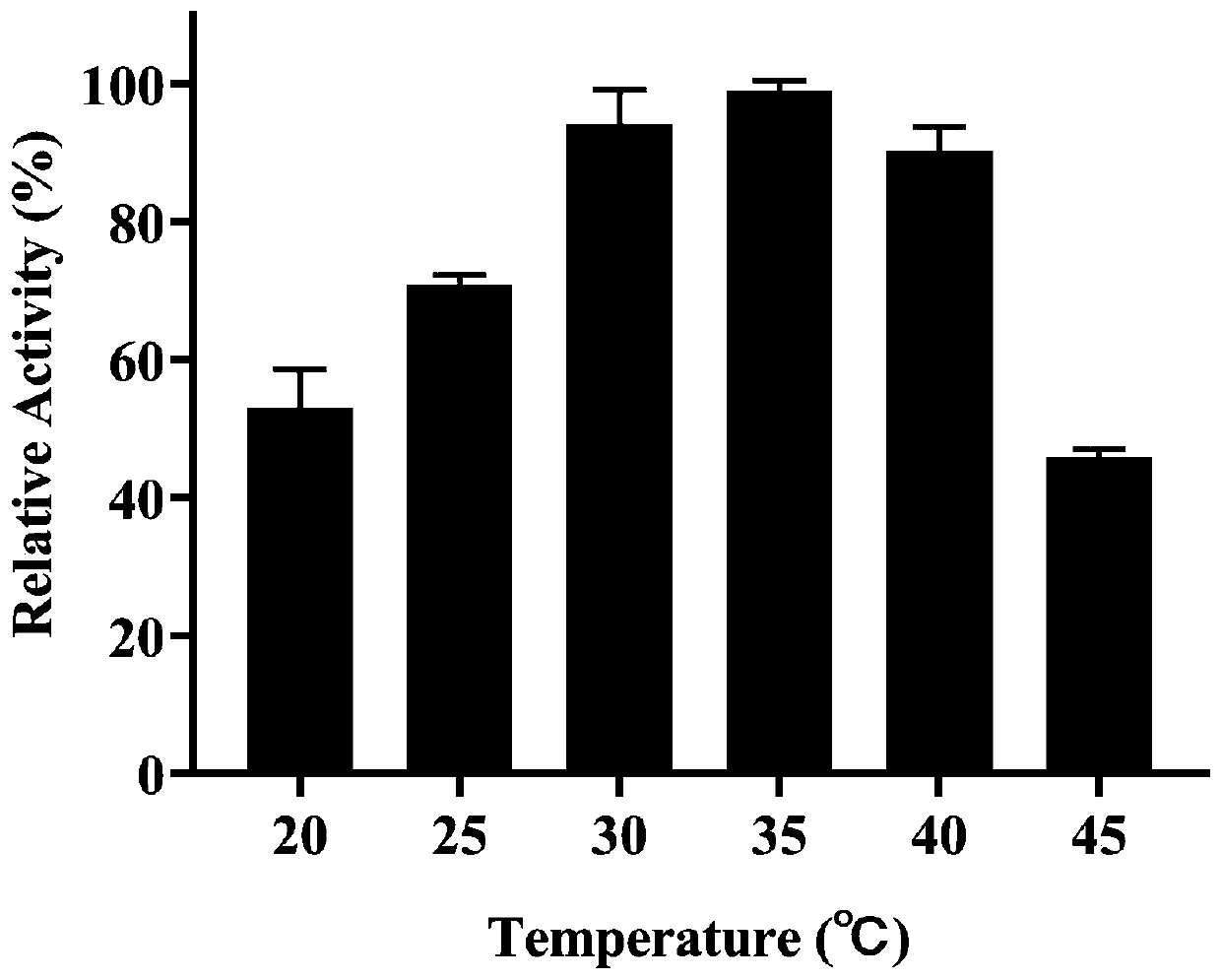
[0103] Example 2 Effect of temperature on activity of deoxynivalenol-degrading enzyme DDH degrading DON
[0104] Dissolve solid vomitoxin in acetonitrile to make a 500 μg / mL mother solution, and dissolve the prosthetic group PMS (phenazine methyl sulfate) in ultrapure water to make a 5 mM mother solution. The experiment is carried out according to the following 500 μL reaction system: 350 μL glycine-hydrogen Sodium oxide buffer (0.05M, pH9.0), 50 μL DDH protein (23.5 μg), 50 μL prosthetic PMS solution, 50 μL DON solution. The system without adding DDH protein was used as a control. The reaction was carried out at different temperatures (20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45°C) for 1 h, then 500 μL of methanol was added to terminate the reaction, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, and the supernatant was filtered with a Millex-GV filter membrane (0.22 μm). The residual DON content in the system was detected by liquid chromatography.
[0105] The chromatographic conditions for high perform...
Embodiment 3
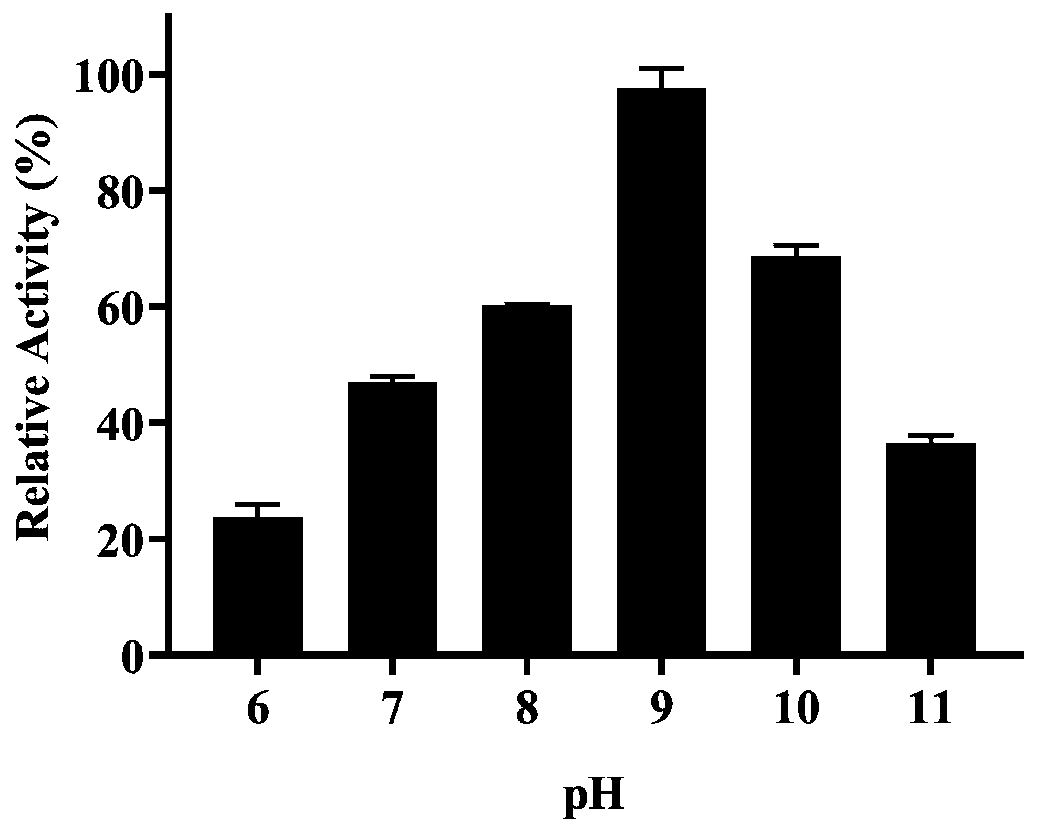
[0108] Example 3 Effect of pH on Degradation DON Activity of Deoxynivalenol-degrading Enzyme DDH
[0109] In order to test the effect of the deoxynivalenol degrading enzyme DDH on the DON degradation activity under different pH conditions, the reaction system used in case implementation 2 was adopted: 350 μL buffer (0.05M sodium phosphate buffer, pH6-8; 0.05M glycine-NaOH buffer, pH9-11), 50 μL DDH protein (23.5ug), 50 μL prosthetic PMS solution, 50 μL DON solution. After the reaction was carried out at 35°C for 1 hour, 500 μL of methanol was added to terminate the reaction, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 1 minute, and the supernatant was filtered through a Millex-GV filter membrane (0.22 μm), and the residual DON content in the system was detected by the method described in Case Example 2.
[0110] The result is as image 3 It was shown that the optimum pH for degrading DON by the deoxynivalenol-degrading enzyme DDH was 9.0.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com