Mechanical exoskeleton data acquisition control device
A technology of data acquisition and control device, which is applied in physical therapy, appliances to help people walk, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately collect motion information, high cost of acquisition devices, slow information acquisition rate, etc., and achieves high signal conversion efficiency and structure. Simple, low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
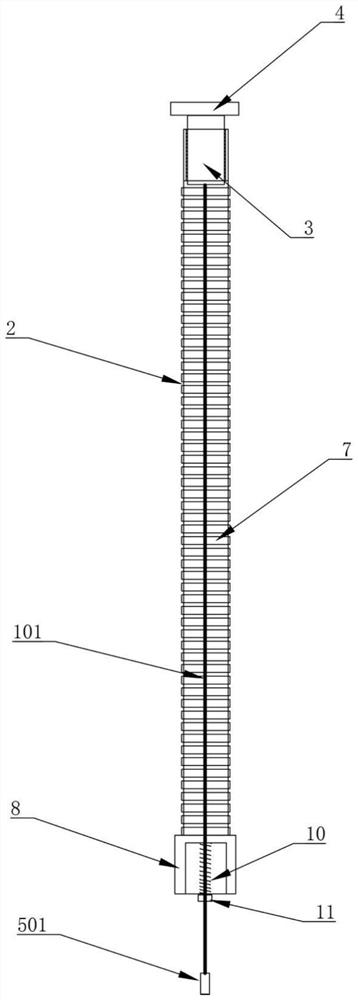
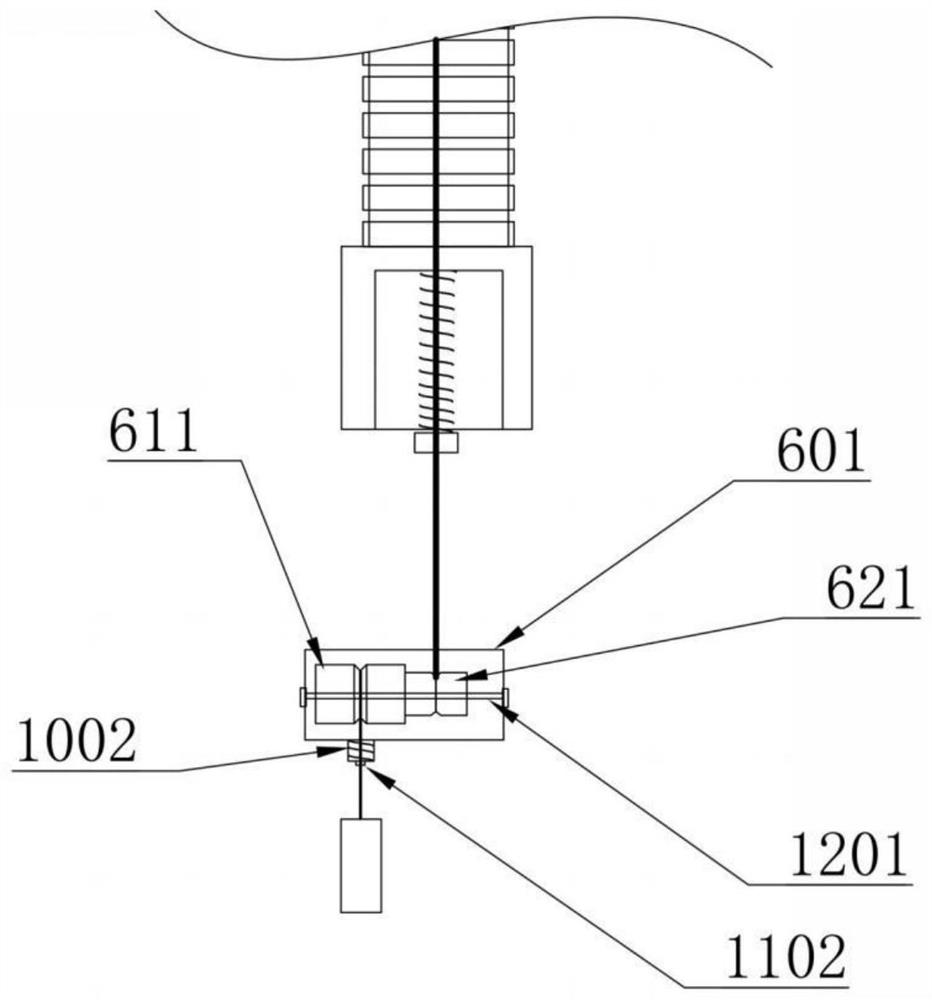
[0035] refer to figure 2 The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the first traction rope 101 is provided with a first amplifier 601, the first displacement sensor 501 is connected to the first traction rope 101 through the first amplifier 601, and the first amplifier 601 includes: The first coil 611 and the second coil 621, the first coil 611 and the second coil 621 are respectively arranged on both sides of the first amplifier 601, the first coil 611 and the second coil 621 are connected by the first rotating shaft 1201, the first displacement sensor One end of 501 is connected to the first coil 611, one end of the first traction rope 101 is connected to the second coil 621, the first amplifier 601 is provided with a second elastic member 1002 near the side of the first displacement sensor 501, and one end of the first displacement sensor 501 A second limit block 1102 corresponding to the second elastic member 1002 is provided. Specifica...
Embodiment 3
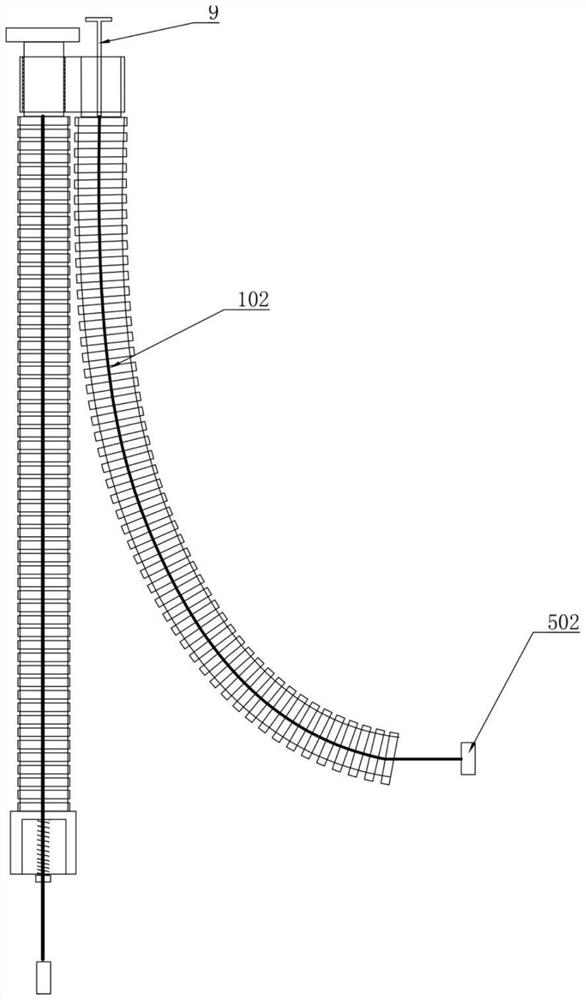
[0038] refer to image 3 The difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 is that: a mechanical exoskeleton data acquisition control device also includes a second traction rope 102, and one end of the second traction rope 102 is provided with an adjustment rod 9 connected to the External motor, the other end of the second traction rope 102 is provided with a second displacement sensor 502, specifically: the exoskeleton data acquisition control device is arranged on the user's limbs, when the user needs to rotate the limbs, it only needs to rotate slightly Rotate the limbs and stop, the second traction rope 102 will rotate under force relative to the housing sheath 2, at this time the second displacement sensor 502 detects the rotational displacement signal of the second traction rope 102, and transmits the rotational displacement signal to the The motor is used to drive the adjustment rod 9 to rotate, so that the second traction rope 102 can satisfy the mechanical exoskele...
Embodiment 4
[0041] refer to Figure 4 The difference between the fourth embodiment and the third embodiment is that: the first traction rope 101 is provided with a first amplifier 601, the first displacement sensor 501 is connected to the first traction rope 101 through the first amplifier 601, and the second traction rope 102 A second amplifier 602 is provided, and the second displacement sensor 502 is connected to the second traction rope 102 through the second amplifier 602. The second amplifier 602 includes: a third rim 612, the third rim 612 is rotated through the second rotating shaft 1202 and is arranged at the second On the second amplifier 602, one end of the second displacement sensor 502 is connected to the third rim 612, and one end of the second traction rope 102 is fixedly arranged on one side of the second amplifier 602, and the second amplifier 602 is close to the side of the second displacement sensor 502 A third elastic member 1003 is provided, and one end of the second ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com