Mutation sequence annotation method
A variation and sequence technology, applied in the field of annotation of variation sequences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0070] (1) Determine the variant sequence information (call variants)
[0071] (1.1) Obtain the variant sequence
[0072] Using probe capture technology, next-generation sequencing of human exons is performed to obtain the sequence to be analyzed. Using the variant sequence analysis software (GATK, https: / / gatk.broadinstitute.org / hc / en-us), compare the sequence to be analyzed with the reference genome to obtain the variation information (call variants).
[0073] (1.2) Integrate reference sequence information
[0074] Obtain hg19 reference genome sequence and hg19 reference genome annotation file, which includes gene name, transcript name, physical location, positive and negative strands, information of each element (elements include UTR, Intron, CDS), etc. Among them, the download address of the hg19 reference genome sequence is ftp: / / hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu / goldenPath / hg19 / bigZips / hg19.fa.gz; the access address of the hg19 reference genome annotation file is: ftp: / / hgdownlo...
example 1
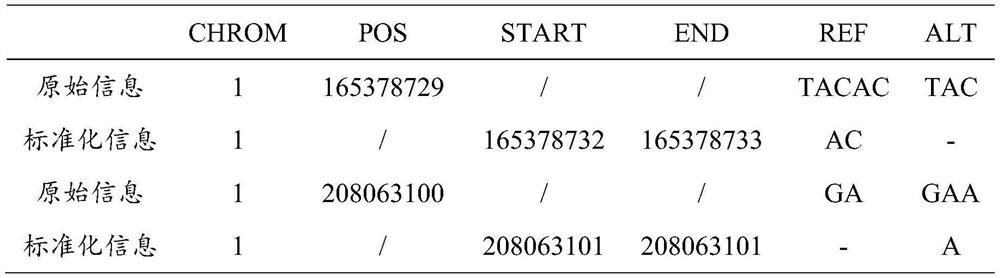
[0130] Mutation site: A mutation at position 69511 of chromosome 1 to G (step 1.3 standardized variation information, 1:69511:69511:A:G)
[0131] Amino acid sequence variation annotation results:
[0132] Comparative example: OR4F5:NM_001005484:exon1:c.421A>G:p.T141A
[0133] Example: OR4F5:NM_001005484:exon1:c.421A>G:p.Thr141Ala
[0134] The annotation results are consistent, but the abbreviation of amino acid used by ANNOVAR in the comparative example does not conform to the specification.
[0135] Nucleic acid sequence variation annotation results:
[0136] Comparative example: Symbol: OR4F5
[0137] Example: Symbol: OR4F5, EntrezID: 79501
[0138] The annotation results are consistent, but ANNOVAR has no EntrezID information in the comparative example.
[0139] Functional area notes: both exonic; results consistent.
[0140] Variation type annotation: all are nonsynonymous SNV; the results are consistent.
example 2
[0142] Variation site: Chromosome 9 70176769 G deletion (step 1.3 standardized variation information, 9:70176769:70176769:G:-)
[0143] Nucleic acid and amino acid sequence variation annotation results:
[0144] Comparative example: FOXD4L5:NM_001126334:exon1:c.1215delC:p.W406Gfs*21
[0145] Example: FOXD4L5:NM_001126334:exon1:c.1215_1215del:p.Trp406Glyfs
[0146] The annotation results are consistent, but the start and stop sites are missing in the examples, and three letters are used for amino acids.
[0147] Functional area notes: both exonic; results consistent.
[0148] Variation type annotations:
[0149] Comparative example: frameshift deletion
[0150] Example: del_frameshift_stoploss
[0151] In the example, the stoploss information is successfully annotated.
[0152] Gene information:
[0153] Comparative example: Symbol: FOXD4L5
[0154] Example: Symbol: FOXD4L5, EntrezID: 653427
[0155] In the comparative example, ANNOVAR has no EntrezID information.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com