Dynamic Young's Laser Interference Fringe Calibration System and Detector Pixel Geometric Position Deviation Calibration Method
A technology of interference fringes and lasers, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices and instruments, can solve the problems of unsuitable engineering applications, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and clear principles, broad prospects, and large data calculation and processing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
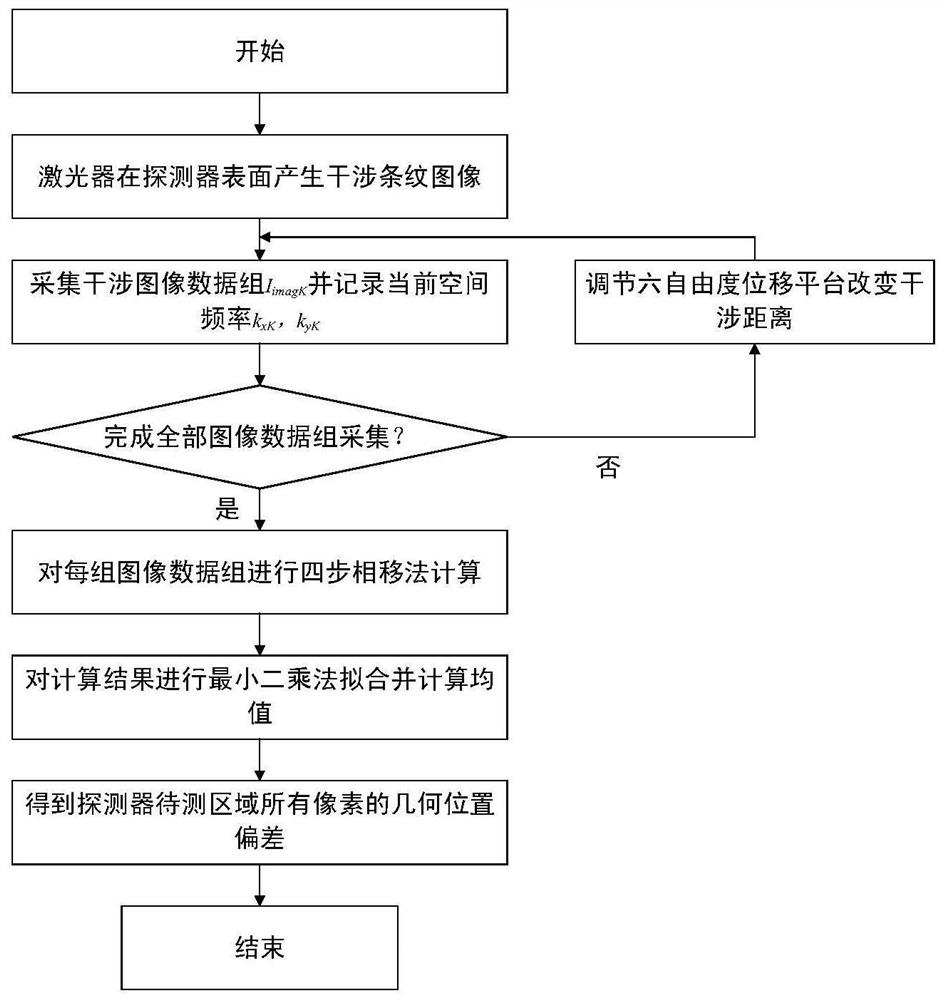
[0054] The following is attached figure 1 The present invention is described in detail with specific examples.
[0055] Step 1: Build a dynamic Young's laser interference fringe calibration system
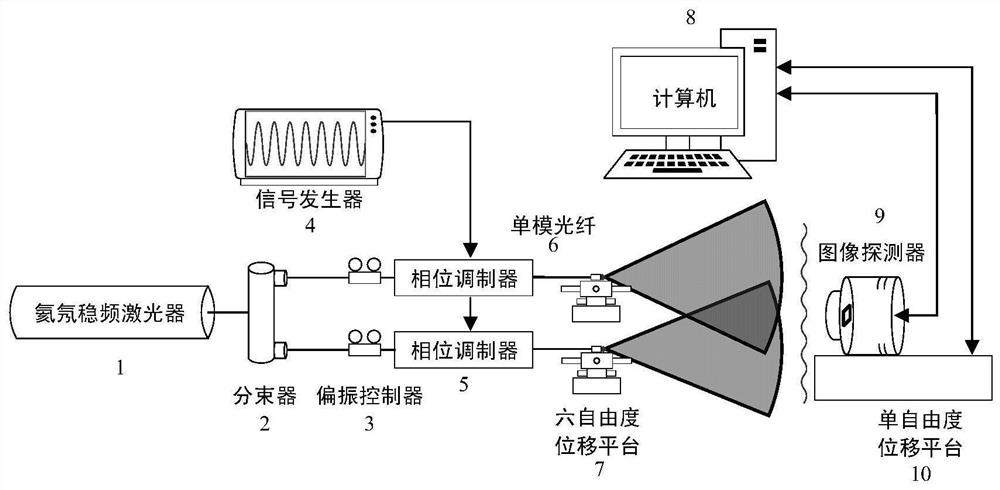
[0056] The composition diagram of the calibration system is attached figure 2 As shown, it consists of a helium-neon laser 1, a fiber beam splitter 2, a polarization controller 3, a signal generator 4, a phase modulator 5, a single-mode optical fiber 6, a six-degree-of-freedom displacement platform 7, a computer 8, an image detector 9 and The single-degree-of-freedom displacement platform 10 is composed. Monochromatic, frequency-stabilized helium-neon lasers produce laser light with a wavelength of 632.8nm. After passing through the laser beam splitter, they are divided into two coherent beams with the same frequency and phase; the interference quality is improved by the polarization controller, and then enter two niobium beams respectively. In the lithium-ion phase modulator, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com