Time constraint type parallel machine energy-saving scheduling method based on collaborative algorithm
A type of parallel machine, time-constrained technology, applied in the energy industry, control/regulation systems, comprehensive factory control, etc., can solve problems such as the difficulty of maintaining the solution performance and complexity of a single meta-heuristic algorithm, and achieve benefits for sustainable development, The effect of reducing energy consumption and good search performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
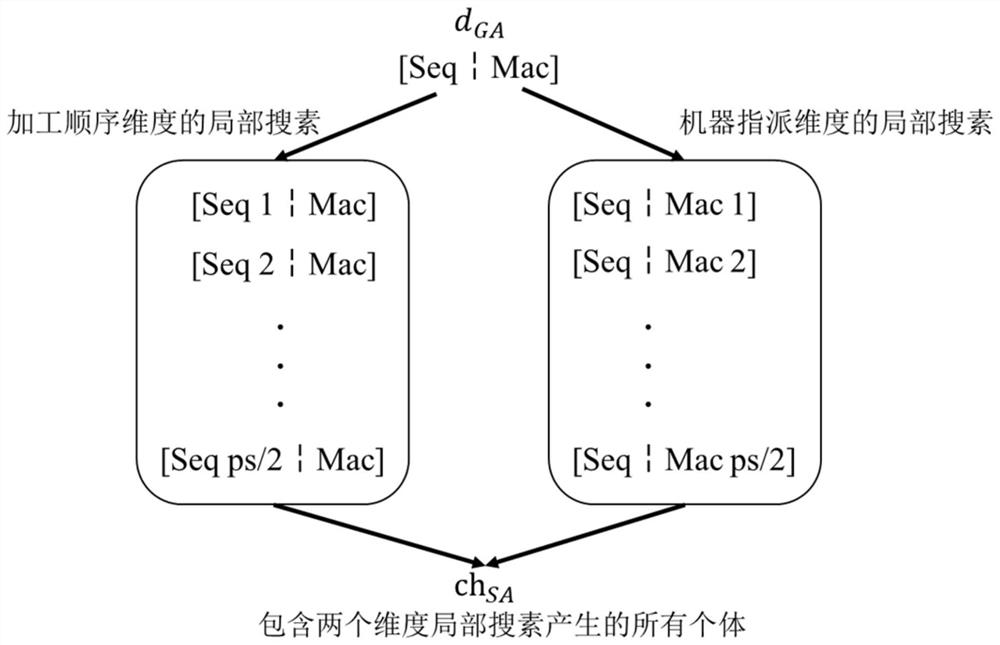
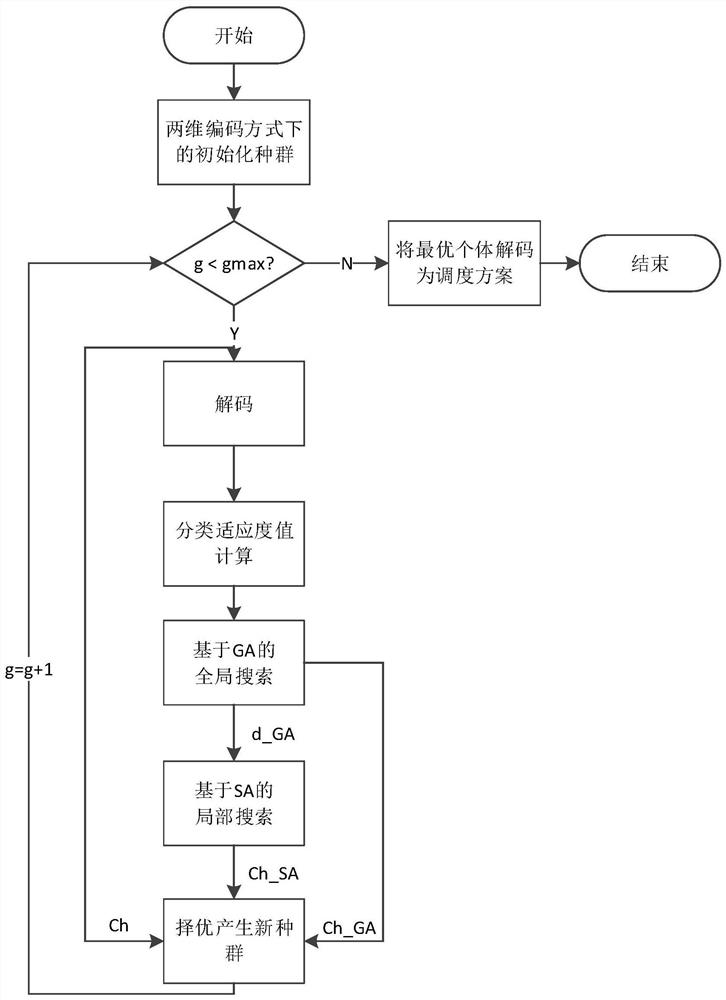
[0058] The present invention designs a parallel machine energy-saving scheduling method considering time constraints, which is specifically implemented according to the following steps:
[0059] Step 1: For the energy-saving scheduling problem of parallel machines considering time constraints, formally describe in mathematical symbols, and specify the performance indicators considered:
[0060] (101) Define basic production parameters: N is the number of workpieces, M is the number of machines, pp ij Machining power when machining workpiece i for machine j, w ij is the processing time of workpiece i on machine j, ip j is the idle power of machine j waiting for a job, rt i is the arrival time of workpiece i.
[0061] (102) Define scheduling index: energy consumption E, including E p is the processing energy consumption, E i is the idle energy consumption; satisfying the maximum completion time C max Less than the requirements of the limit value D.
[0062] (103) Define s...
Embodiment 1
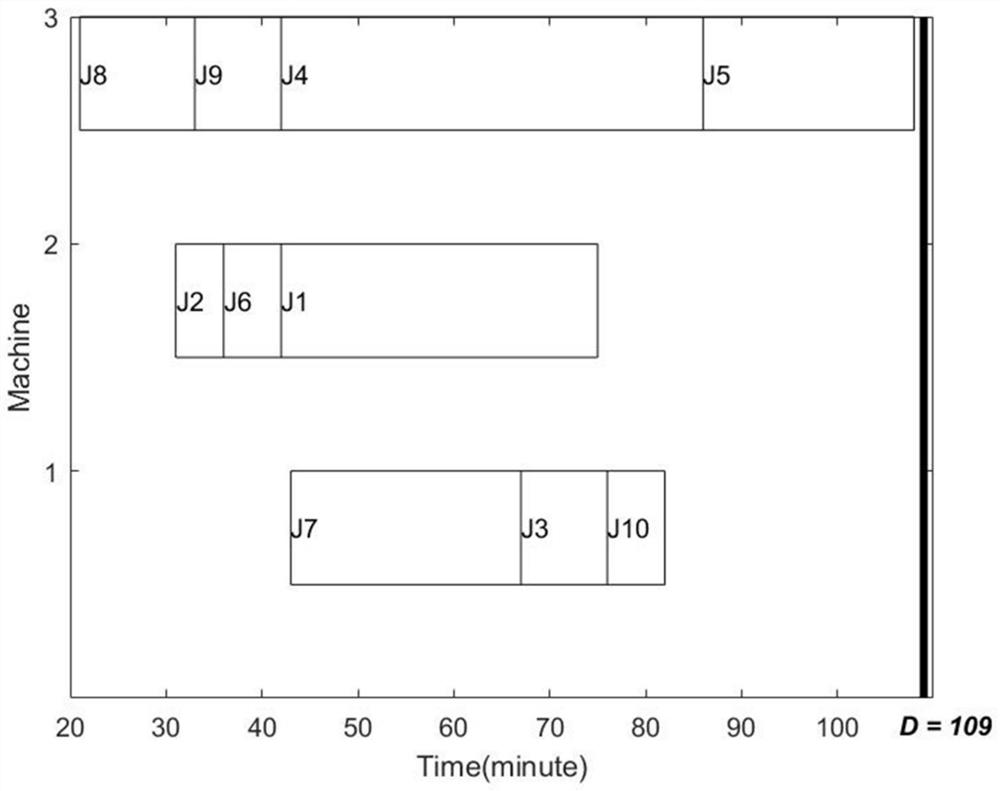
[0102] Example 1: Scheduling instance of 10*3 scale
[0103] A rubber molding workshop has 3 parallel molding machines and 10 workpieces to be processed. The idle power ip of each machine, the arrival time rt of each workpiece, the processing power pp and the processing time w of each machine when processing each workpiece are shown in Table 1-Table 3 respectively.
[0104] Table 1 The idle power of each machine (the unit of ip is kw)
[0105] MachineMachine idle power ip M1 4 M2 4 M3 6
[0106] Table 2 The arrival time of each workpiece (the unit of rt is min)
[0107] Workpiece Job Arrival time rt J1 42 J2 31 J3 20 J4 36 J5 32 J6 24 J7 43 J8 21 J9 30 J10 22
[0108] Table 3 Processing power (the unit of pp is kw) and processing time (the unit of w is min) of processing each workpiece by each machine
[0109]
[0110] The limit value D that requires the maximum completion t...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Comparison of algorithm performance: CA vs.GA vs. PSO
[0125] By comparing the solution results of different algorithms, the advantages of the collaborative algorithm (CA) designed in the present invention in solving the energy-saving scheduling problem of parallel machines considering time constraints are verified. The selected comparison algorithms are commonly used algorithms in the field of parallel machine scheduling: Genetic Algorithm (GA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). Among them, considering the particularity of the problem in the present invention, the classification fitness value calculation method is used in GA and PSO to solve the problem.
[0126] The cases used to verify the performance of the algorithm have four different scales. The three algorithms are used to solve the cases of each scale 10 times, and the average energy consumption target value of each case is recorded for each algorithm. The results are shown in Table 6 below (all...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com