Single-rotor disc applied to disc type motor
A disk motor and single rotor technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems affecting the compactness of the rotor disk structure, large cage margin, difficult production and processing, etc., and achieve the requirement of reducing positioning accuracy , Improving the compactness of the structure and good consistency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
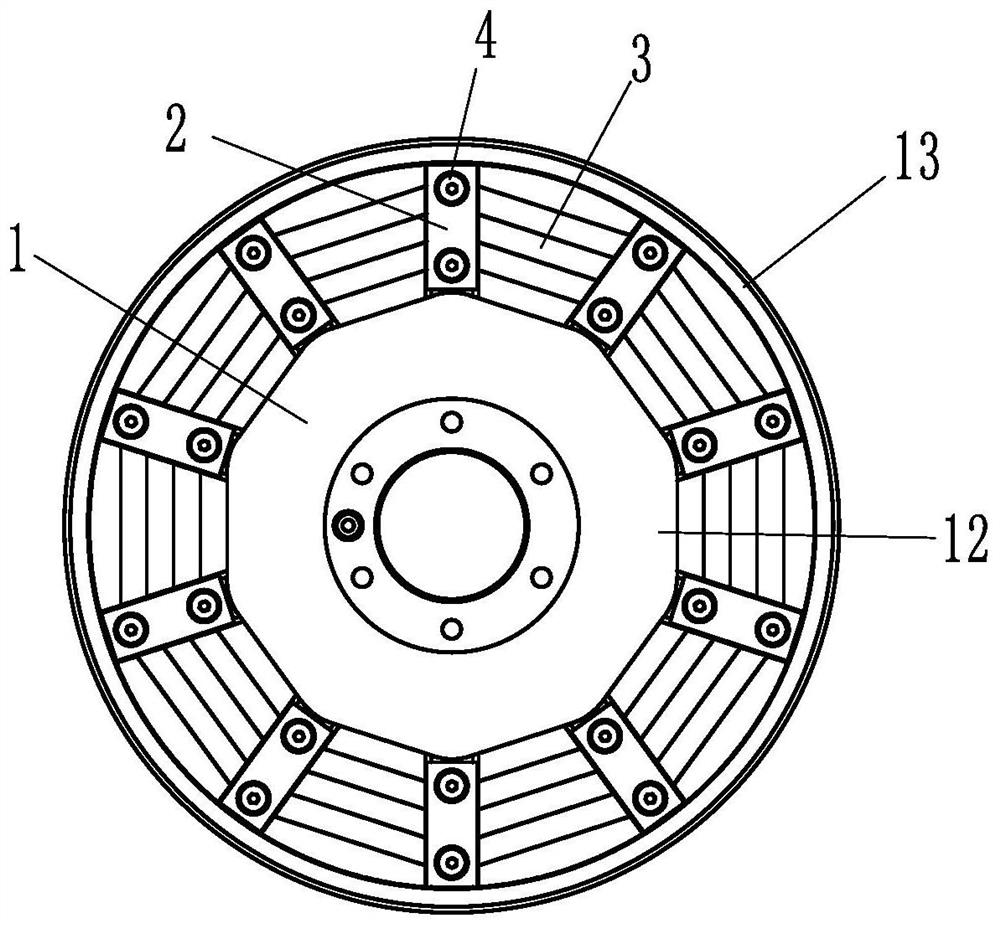
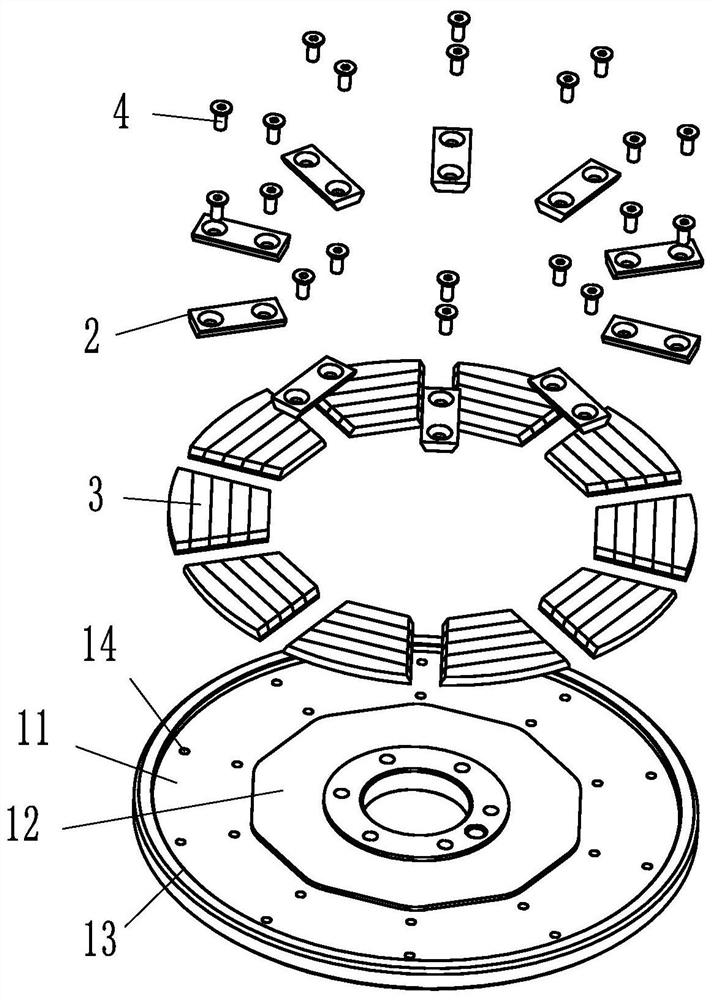
[0027] like Figures 1 to 4 As shown, it is a single-rotor disk applied to a disk motor, including a mounting disk 1, an annular mounting groove 11 is provided inside the mounting disk 1, and an upwardly protruding annular flange is provided on the inner and outer edges of the mounting groove 11 The shape of the inner ring 12 of the installation groove 11 is a regular polygon, and the shape of the outer ring 13 of the installation groove 11 is a circle. The mounting groove 11 can be directly formed by milling a cylinder. The mounting plate 1 is provided with ten sets of mounting holes 14 distributed in a circular array, the mounting holes 14 are located in the mounting groove 11 and the array axis of the ten sets of mounting holes 14 is the axis of the mounting plate 1 . Each set of mounting holes 14 is provided with aligned magnetic steel pressure blocks 2 , and a single set of mounting holes 14 includes two threaded holes, and the two threaded holes are located in the radia...
Embodiment 2
[0029] like Figure 5 As shown, the difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the pressing surface 21 is a bent stepped surface. Therefore, the mating surface 31 is a stepped surface mated with the pressing surface 21 . After the steel briquetting block and the magnetic steel 3 are mated, the matching accuracy of the end faces is low. Even if there is a processing error, the magnetic steel 3 will not move in the magnetic steel briquetting block 2, which is more convenient for assembly and has high stability.
Embodiment 3
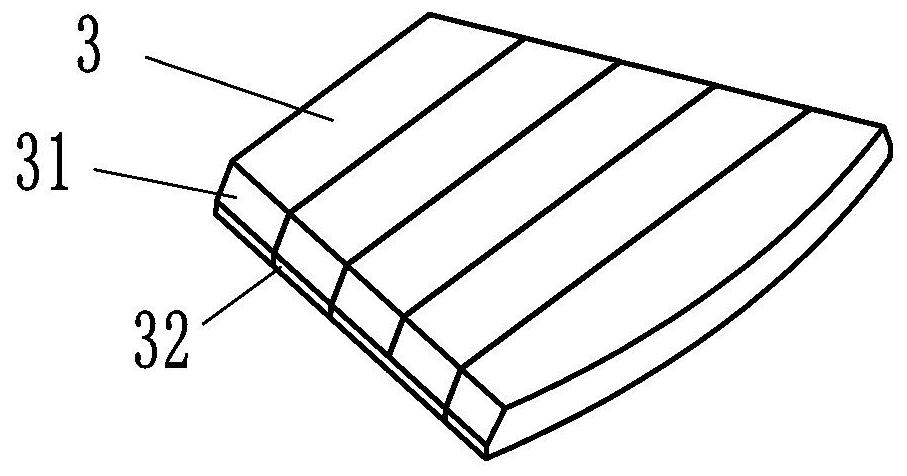
[0031] like Figure 6 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 lies in that four protruding rack pieces 22 are arranged in the pressing surface 21 . The rack plate 22 is a strip-shaped sheet structure, and the four rack plates 22 are equal and arranged in parallel, and the rack plates 22 are parallel to the bottom side of the magnetic steel pressing block 2; the adjacent rack plates 22 are on the pressing surface 21 The distance above is equal to the width of the rack plate 22. The rack piece 22 forms an outwardly convex elastic structure, which can be made of softer material than the magnetic steel. When there is a gap between the magnetic steel briquetting block 2 and the magnetic steel 3 due to processing errors, the rack piece 22 is bent to fill the pressure. The gap between the tight surface and the matching surface can assist the compression of the magnetic steel briquetting block 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com