Dominant indegenous plant functional group based three-dimensional plant collocation pattern of trees, shrubs and herbs
A technology of trees, shrubs, grasses and plants is applied in the field of three-dimensional plant matching patterns of trees, shrubs and grasses, and can solve problems such as discounts on ecological protection achievements, ecological disasters, and green deserts.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0036] Example 1: Plant collocation pattern in plain and hilly areas
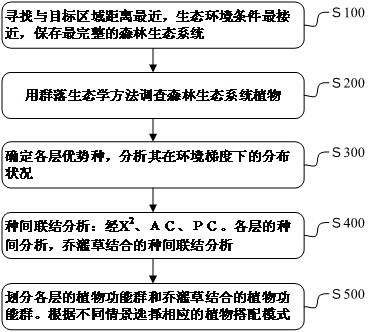
[0037] (1) Within the scope of the Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve, low-altitude areas (700m-1200m), look for areas with relatively little human interference, relatively intact forest ecosystems, and relatively flat terrain.
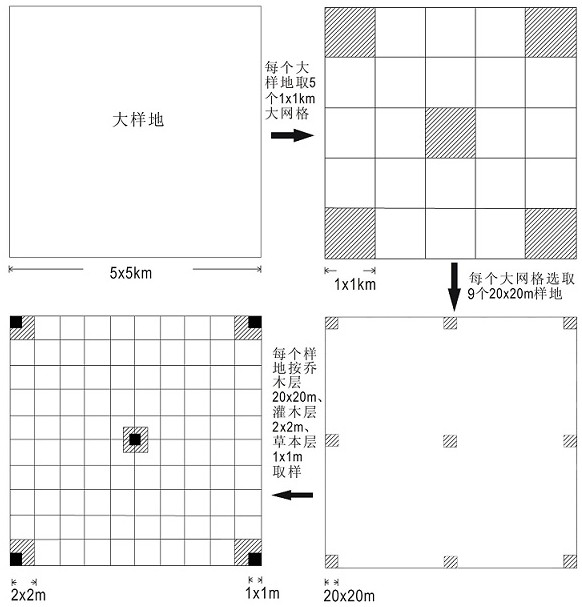
[0038] (2) Conduct community ecology surveys in the region: Set up sample plots and quadrats in different areas of the forest ecosystem, and conduct plant surveys in the quadrats. The survey indicators include: coverage of the arbor layer, species, number of individuals, tree Height, branch height, crown height, crown width, base diameter, DBH, etc.; shrub layer coverage, species, number of individuals, tree height, crown width, base diameter; herb layer coverage, species, number of individuals, height , crown width, base diameter (cluster diameter), and also investigate the age structure of the community and the degree of human influence.
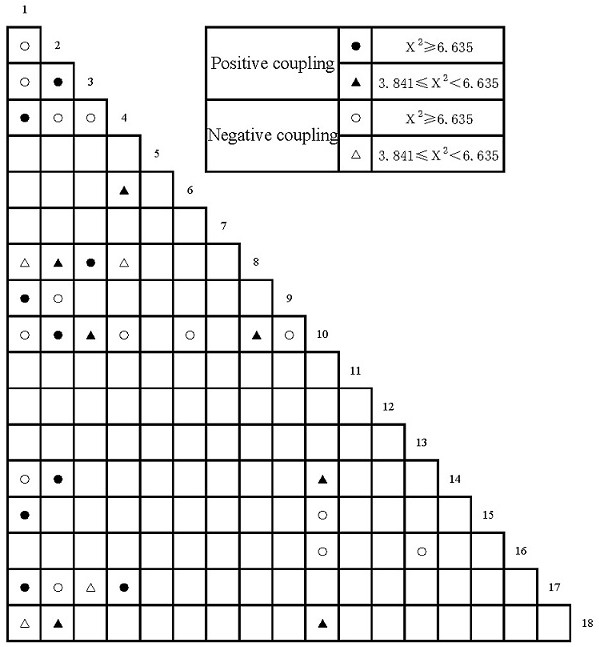
[0039] (3) Select the dominant species accor...
example 2
[0044] Example 2: Plant collocation pattern in low-altitude mountainous areas
[0045] (1) Within the scope of the Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve, in the middle and low altitude areas (1100m-1400m), look for areas with relatively little human interference and relatively complete preservation of forest ecosystems.
[0046] (2) Conduct community ecology surveys in the region: Set up sample plots and quadrats in different areas of the forest ecosystem, and conduct plant surveys in the quadrats. The survey indicators include: coverage of the arbor layer, species, number of individuals, tree Height, branch height, crown height, crown width, base diameter, DBH, etc.; shrub layer coverage, species, number of individuals, tree height, crown width, base diameter; herb layer coverage, species, number of individuals, height , crown width, base diameter (cluster diameter), and also investigate the age structure of the community and the degree of human influence.
[0047] (3) Select the do...
example 3
[0052] Example 3: Plant collocation pattern in middle and high altitude mountainous areas
[0053] (1) Within the scope of the Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve, in the middle and high altitude areas (1400m-1800m), look for areas with relatively small human disturbance and relatively complete preservation of forest ecosystems.
[0054] (2) Conduct community ecology surveys in the region: Set up sample plots and quadrats in different areas of the forest ecosystem, and conduct plant surveys in the quadrats. The survey indicators include: coverage of the arbor layer, species, number of individuals, tree Height, branch height, crown height, crown width, base diameter, DBH, etc.; shrub layer coverage, species, number of individuals, tree height, crown width, base diameter; herb layer coverage, species, number of individuals, height , crown width, base diameter (cluster diameter), and also investigate the age structure of the community and the degree of human influence.
[0055] (3) Se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com