Dynamic progressive failure analysis method for composite material multi-scale model
A composite material, failure analysis technology, applied in CAD numerical modeling, constraint-based CAD, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as observation and understanding of mechanical, machining deformation, material failure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
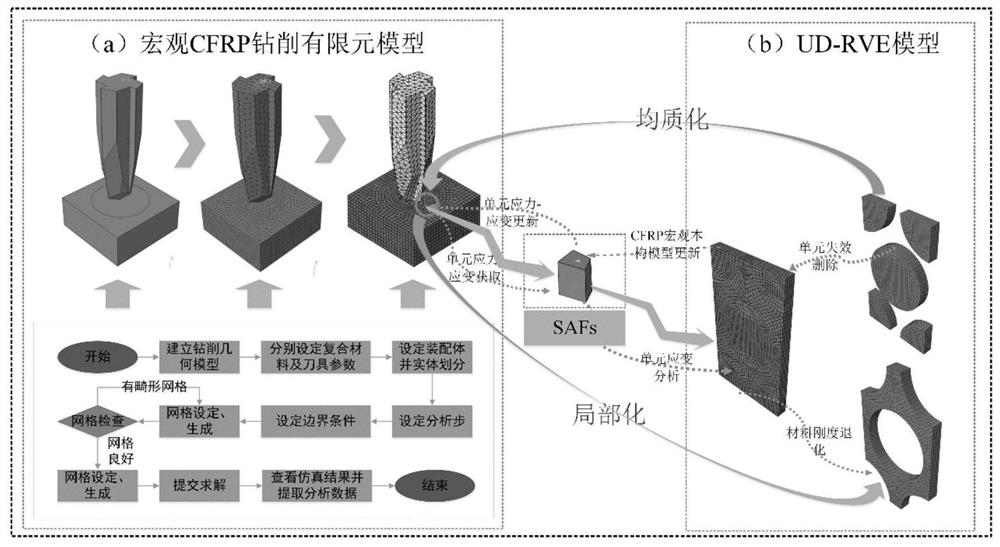
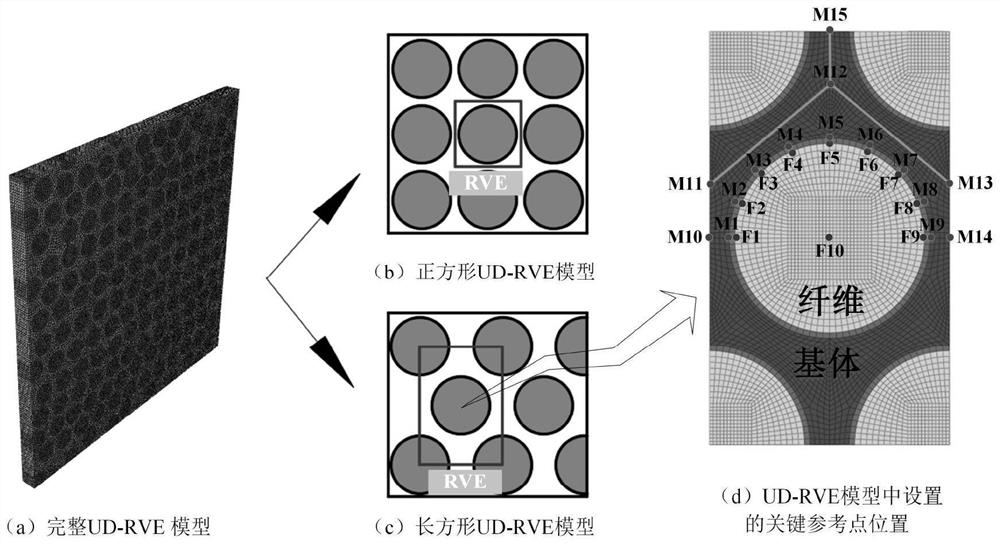
[0026] The macroscopic stress of the composite laminate structure and the microscopic stress of each component structure are bridged by the stress amplification factor, and the stress amplification factor can be obtained by the finite element analysis result of the representative volume element containing the fiber and the matrix. After the stress amplification factor is obtained, the macro-micro conversion equation is used to realize the conversion of macro-stress to micro-stress. The expression of the macro-micro conversion equation is shown in equations (1), (2), (3):
[0027]
[0028]
[0029]
[0030] In formulas (1)~(3): σ i Indicates the stress at n points of the fiber or matrix, where n is the stress analysis point, i=1~6; Represents the macroscopic stress component of the composite laminate, j = 1~6; It is expressed as the stress amplification factor under the action of the mechanical load at n points, p=1-6, k=1-6.
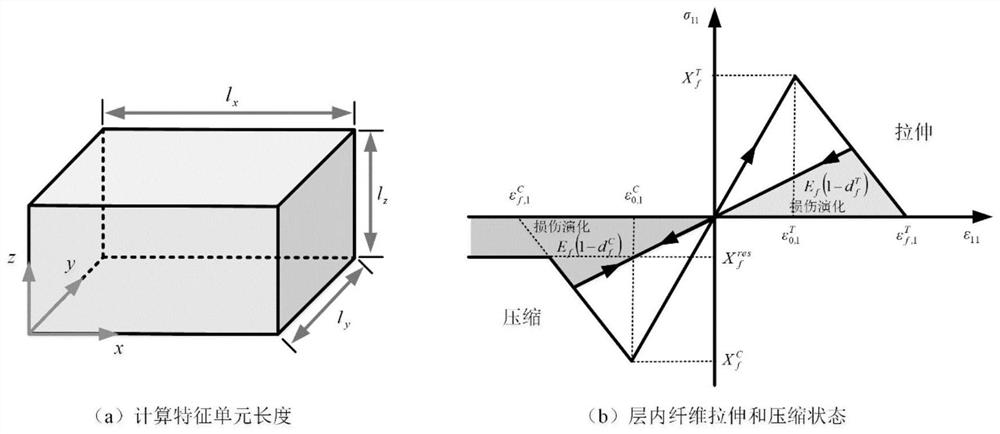
[0031] Based on the failure theory of micromechanics, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com