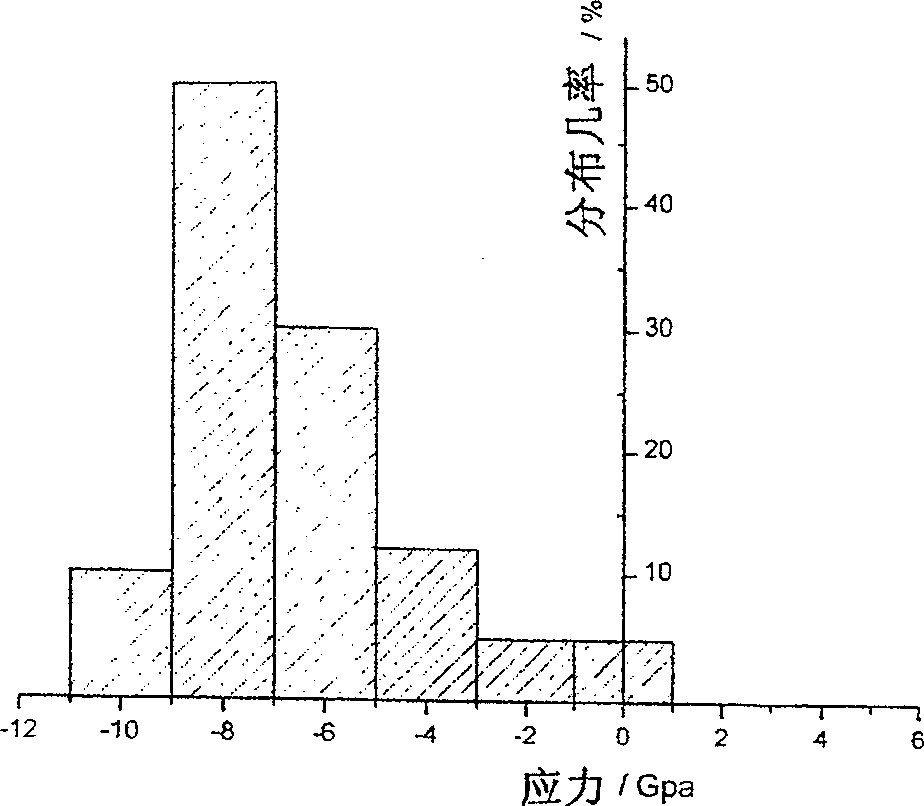
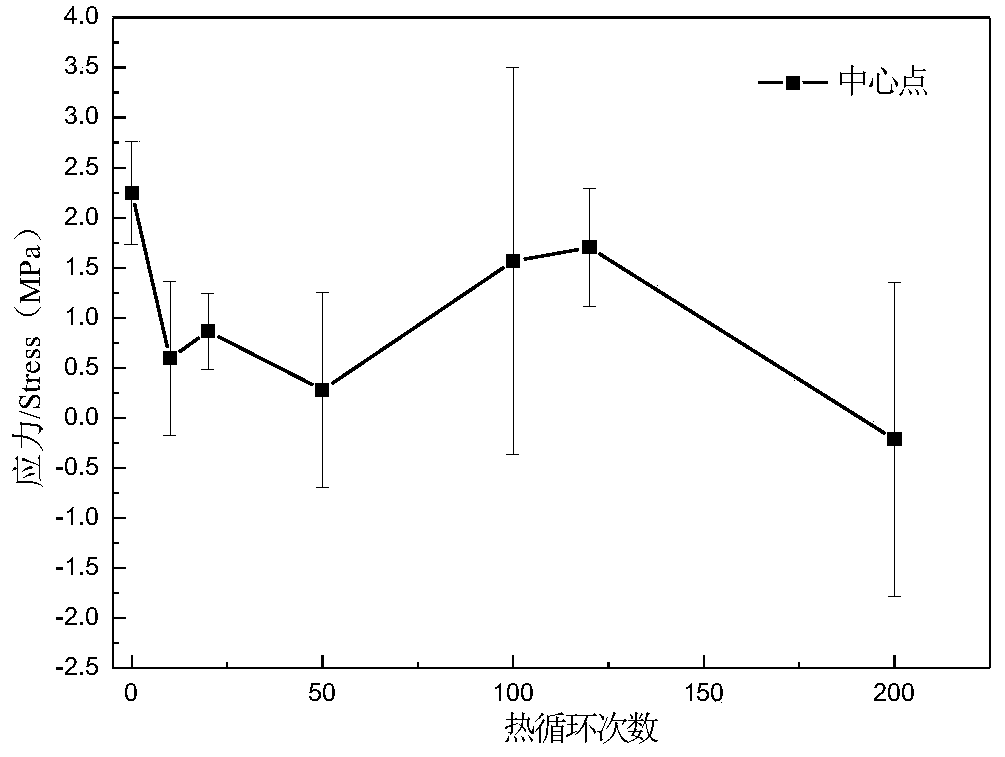
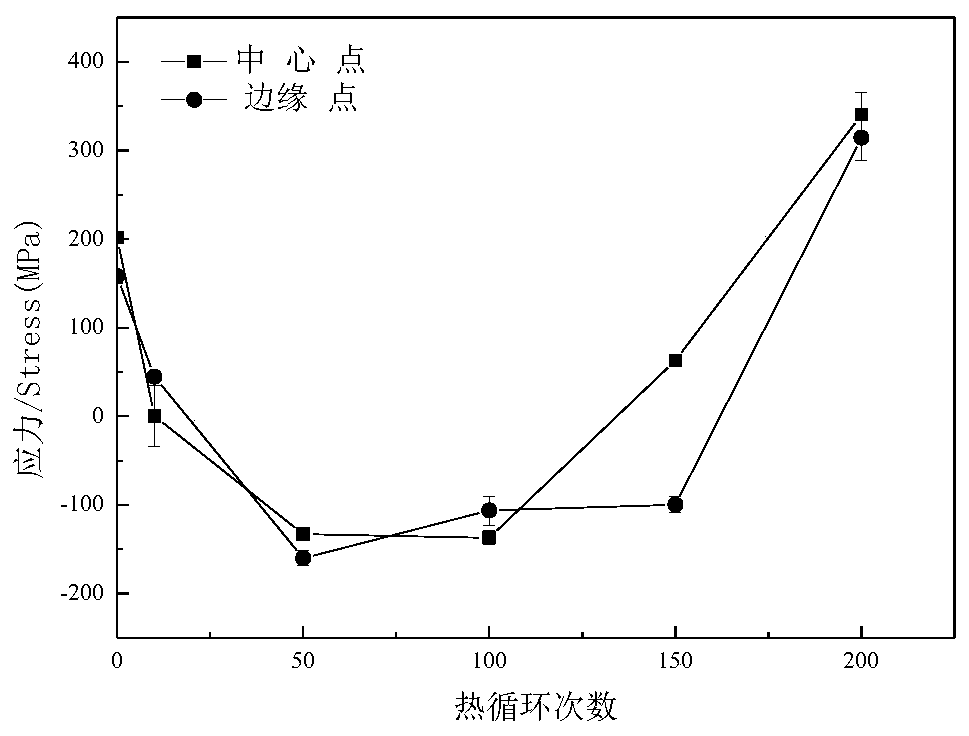
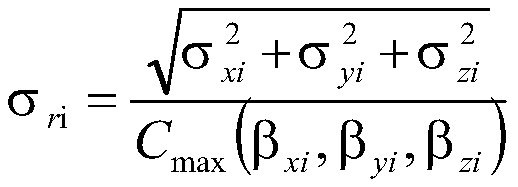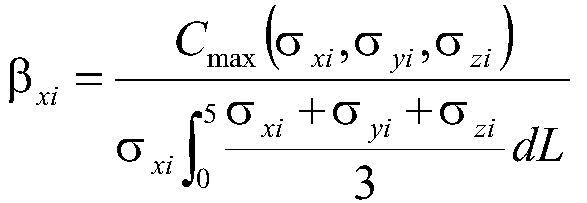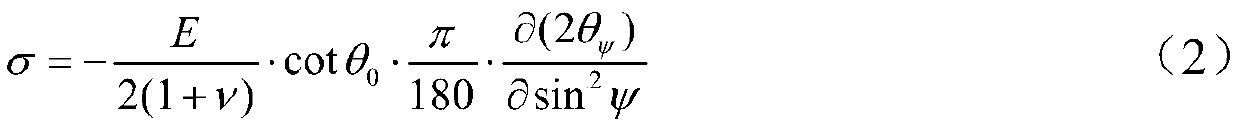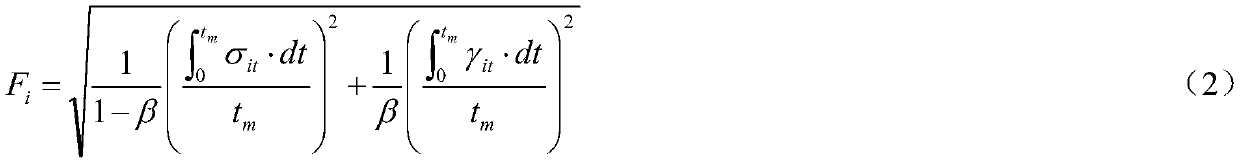Patents
Literature
36 results about "Macroscopic stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
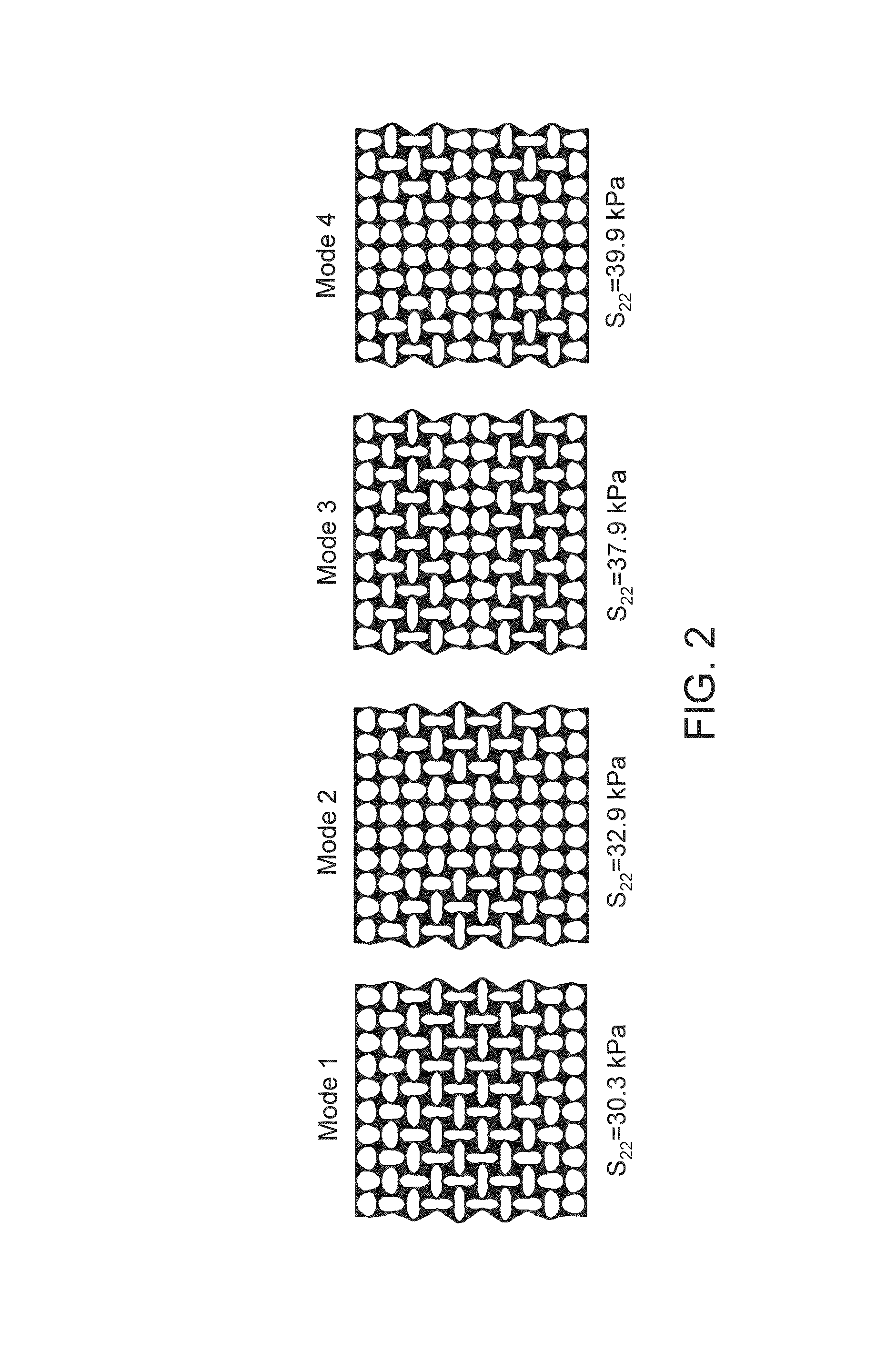
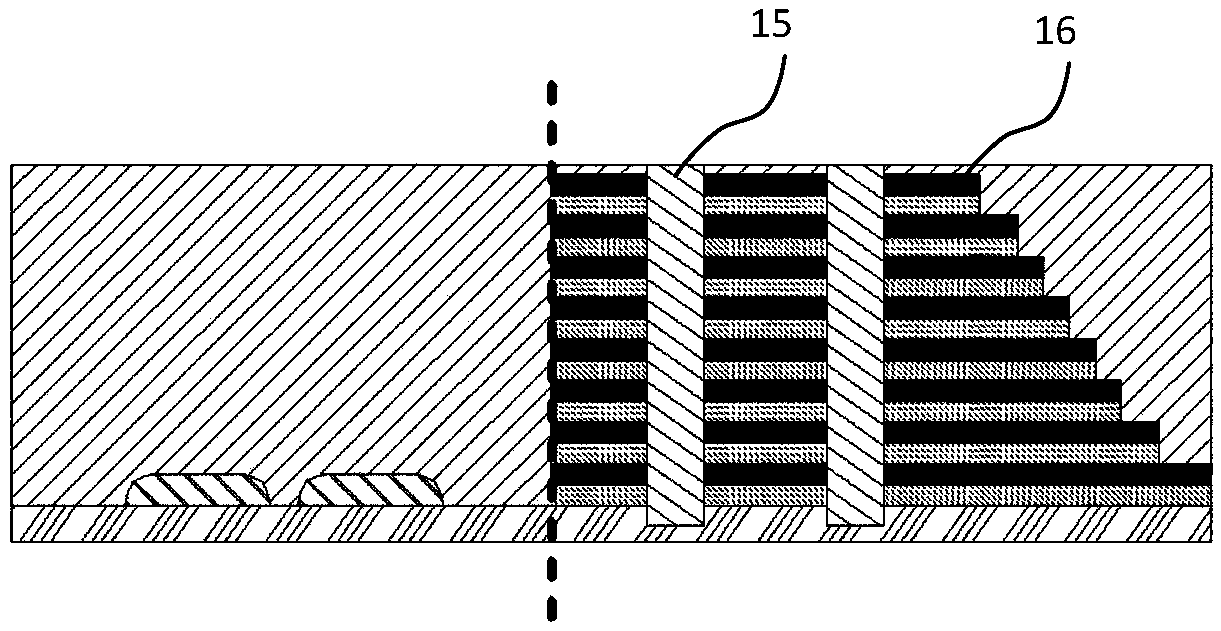
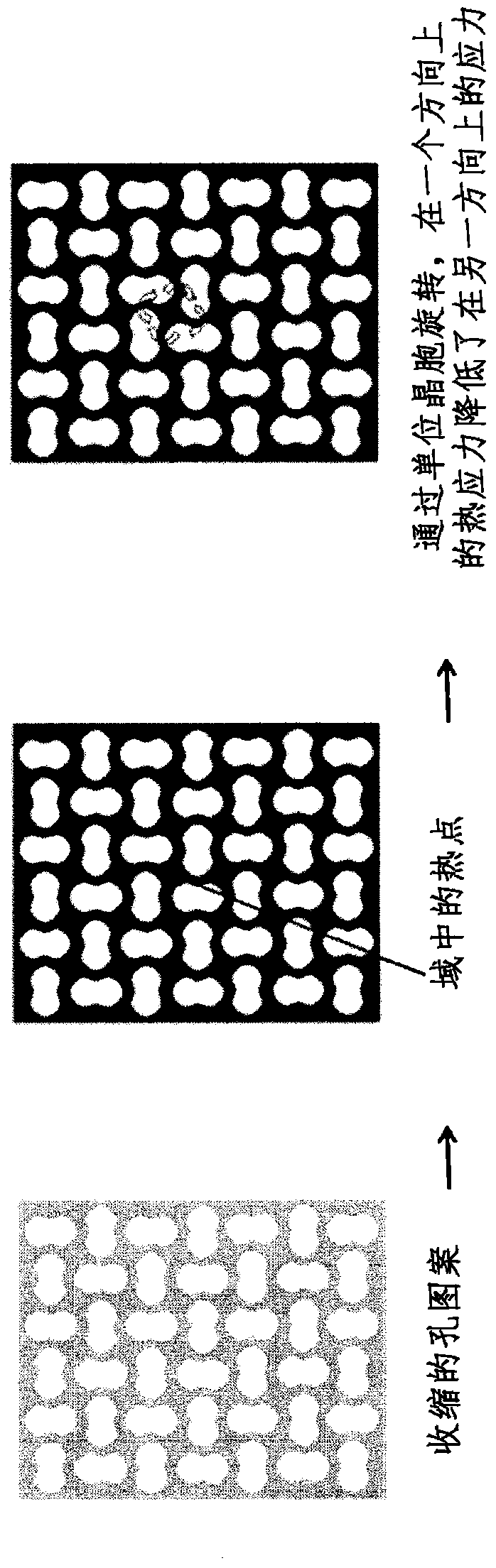
Pattern production and recovery by transformation
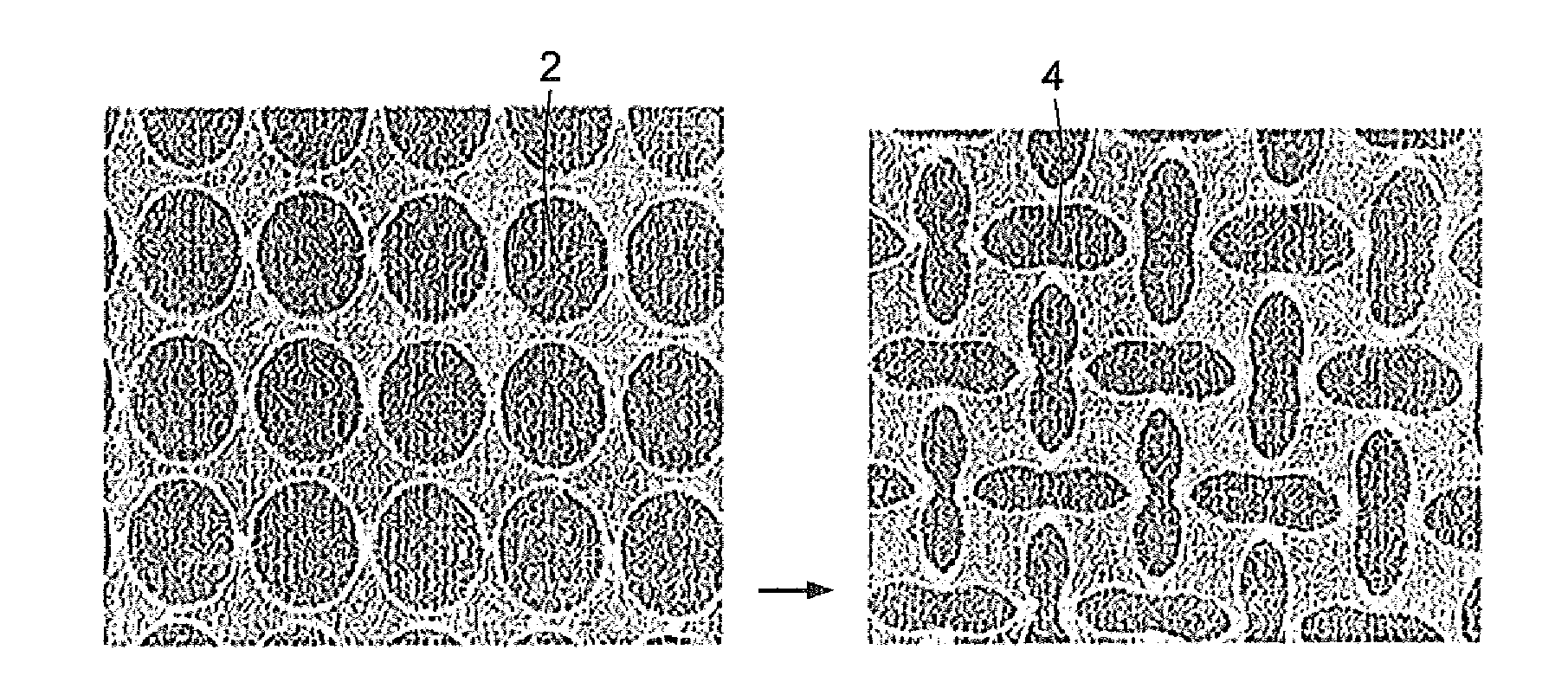
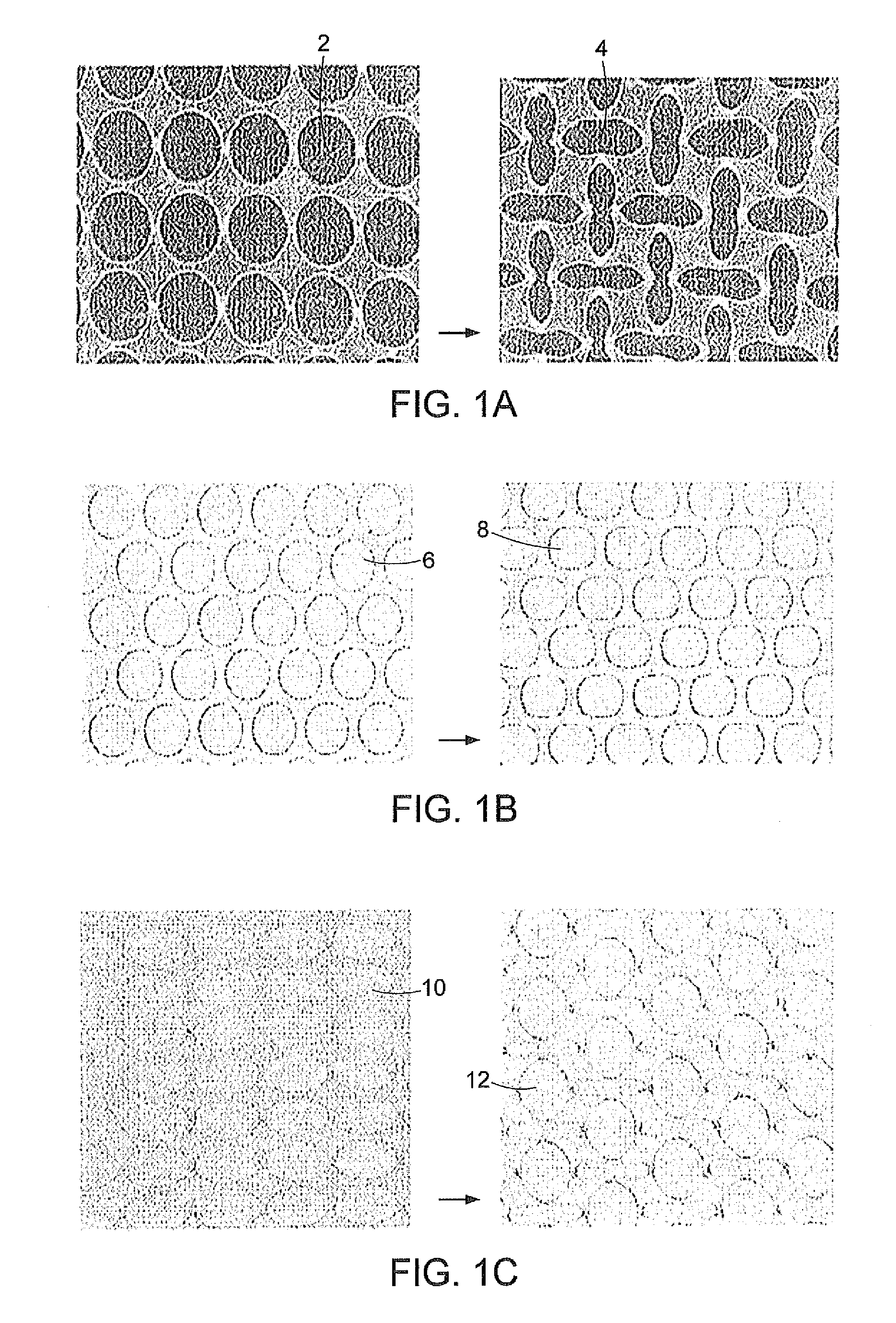
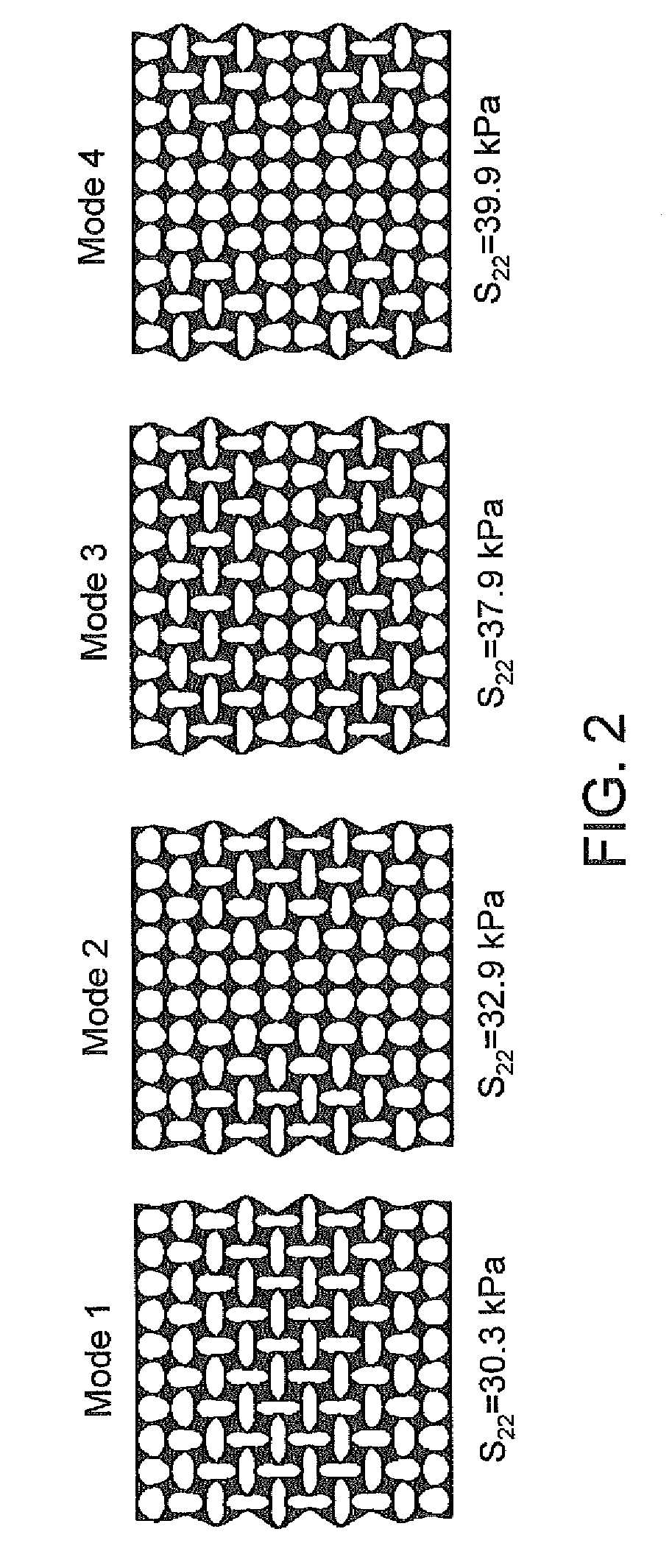
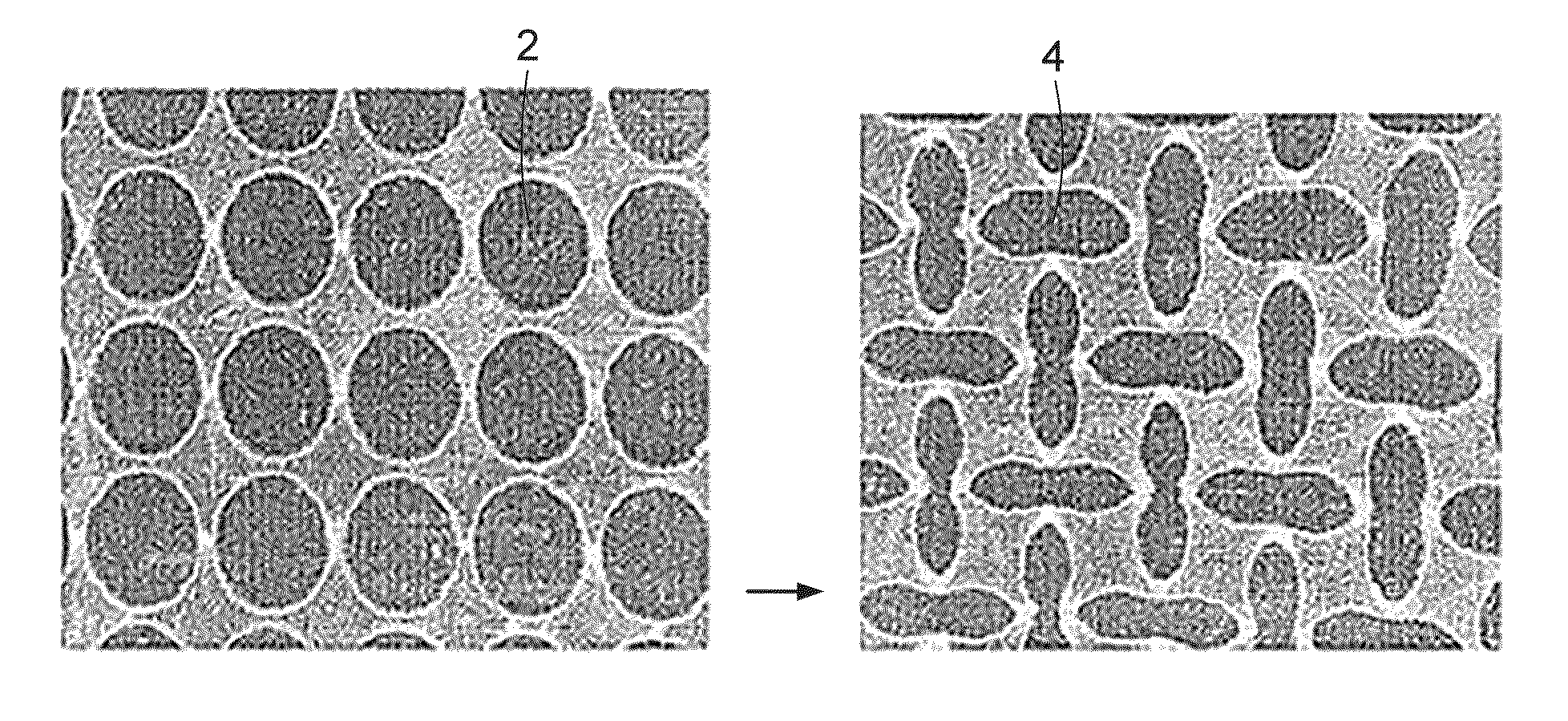
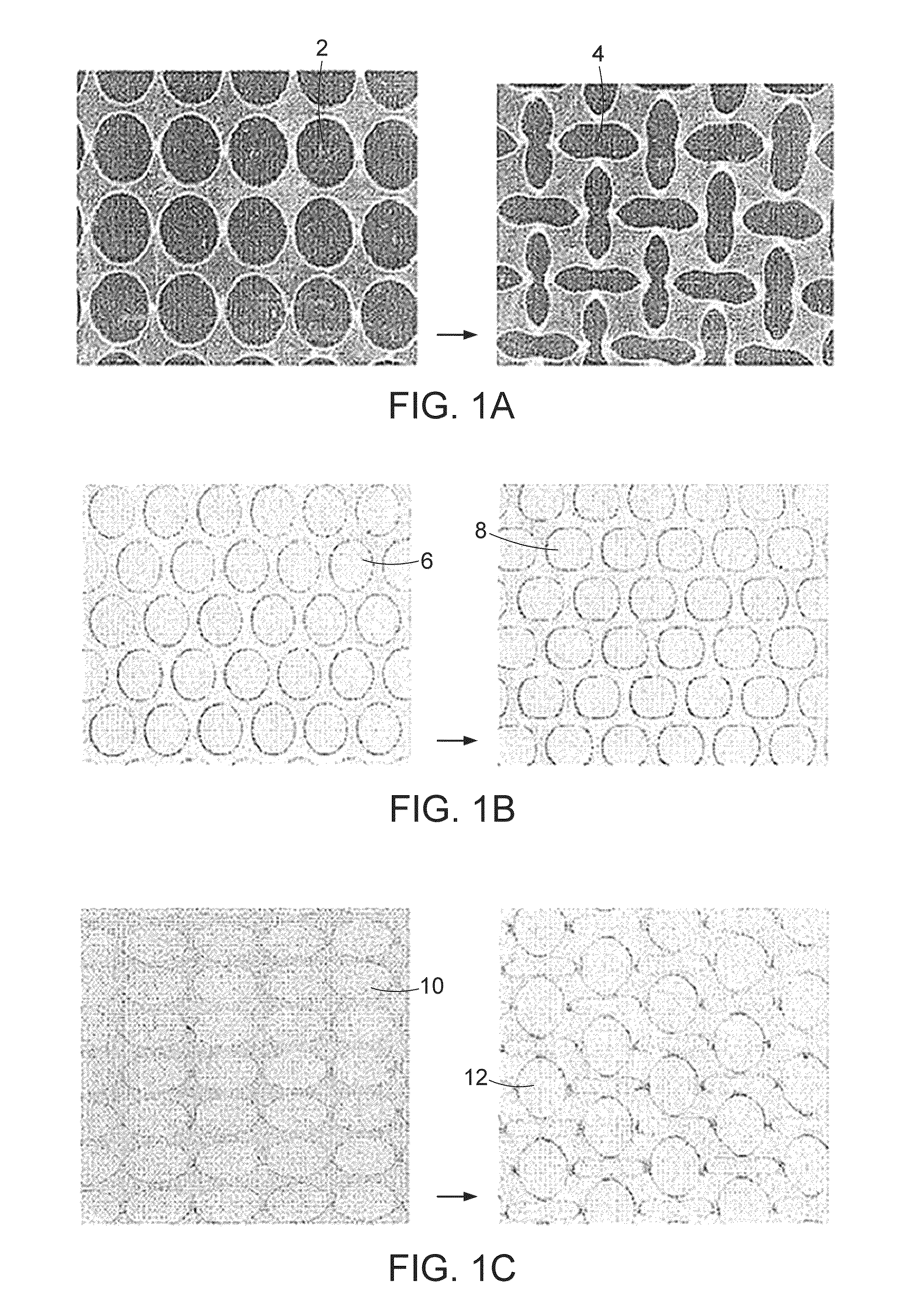
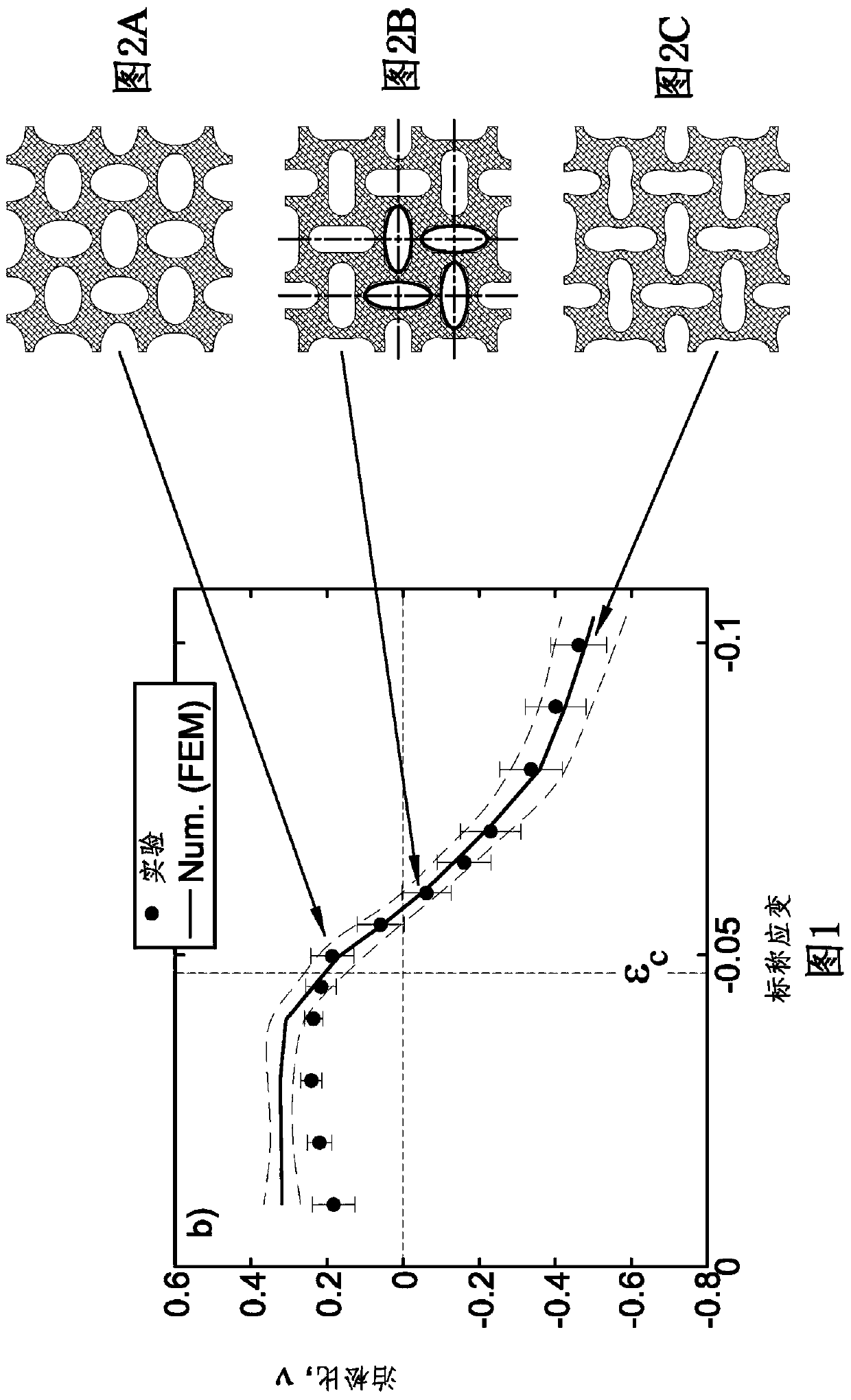
A transformative periodic structure includes a plurality of elastomeric or elasto-plastic periodic solids that experiences a transformation in the structural configuration upon application of a critical macroscopic stress or strain. The transformation alters the geometric pattern changing the spacing and the shape of the features within the transformative periodic structure. For the case of elastomeric periodic structures upon removal of the critical macroscopic stress or strain, the transformative periodic solids are recovered to their original form. For the case of elasto-plastic periodic structures upon removal of the critical macroscopic stress or strain, the new pattern is retained. Polymeric periodic solids can be recovered to their original form by heating or plasticizing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
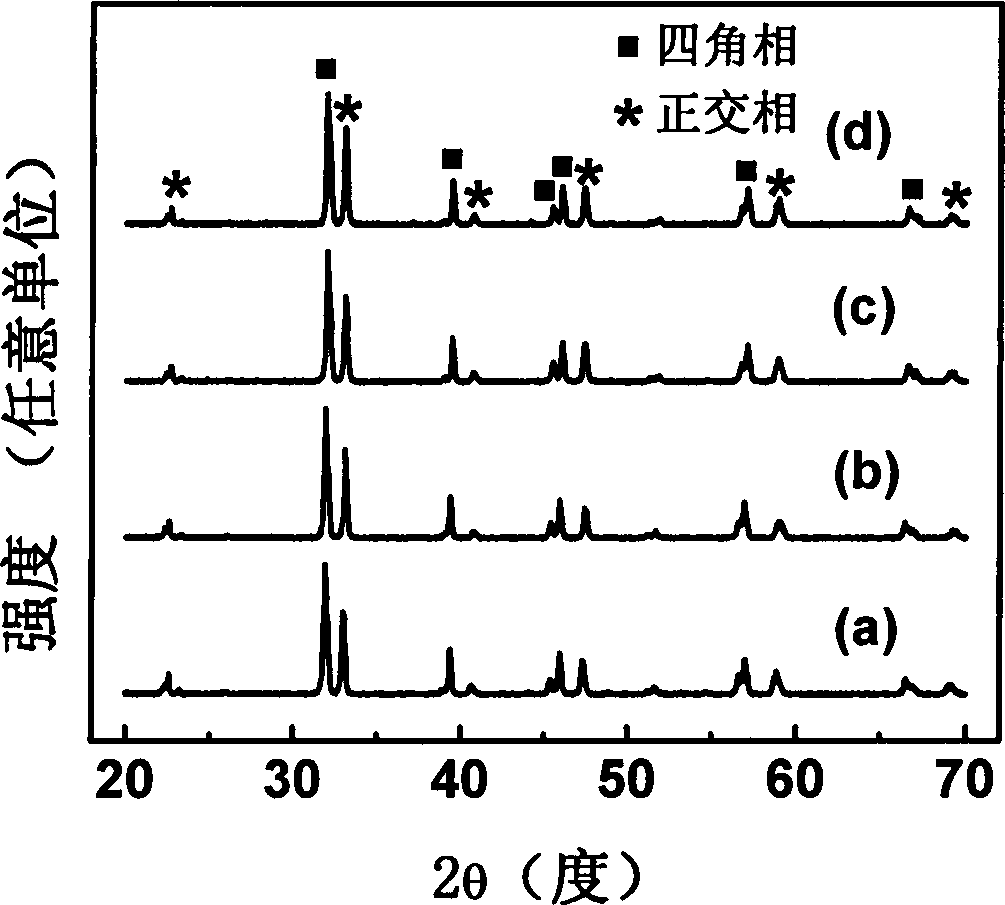
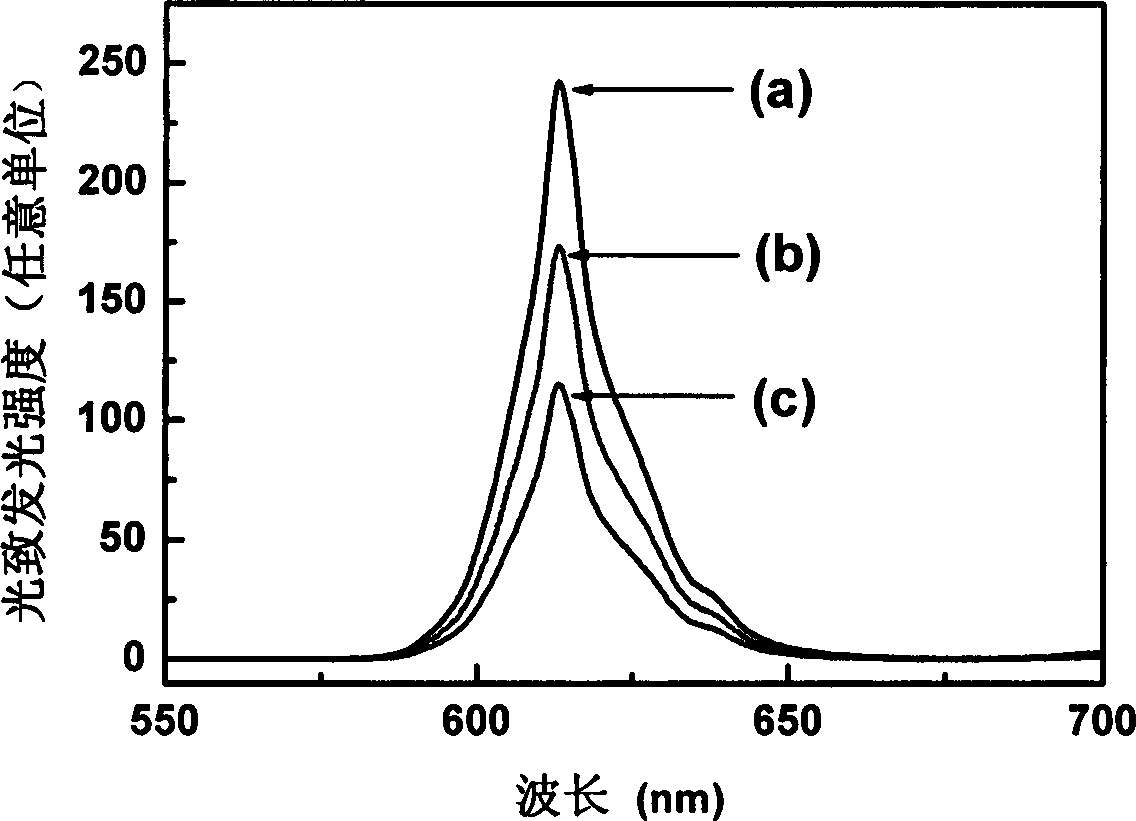
Red high-brightness elastic stress luminescent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103468258ANo generationNo pollution in the processForce measurement by measuring optical property variationLuminescent compositionsDisplay deviceStress sensor
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Preparation method and structure of three-dimensional memory
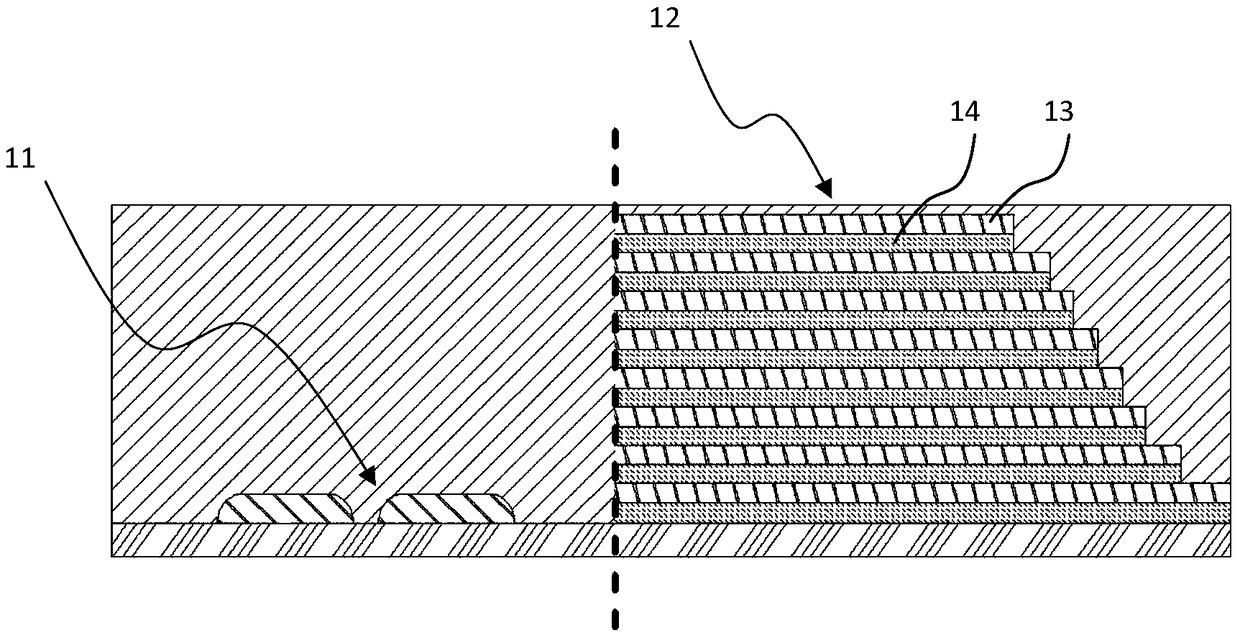
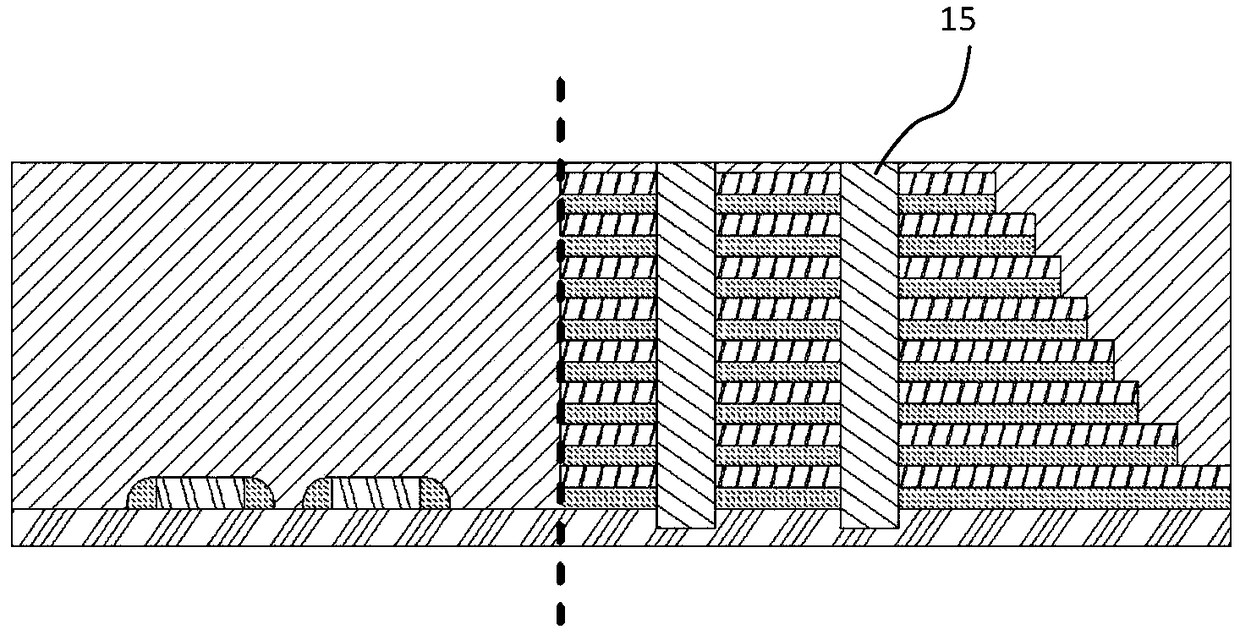
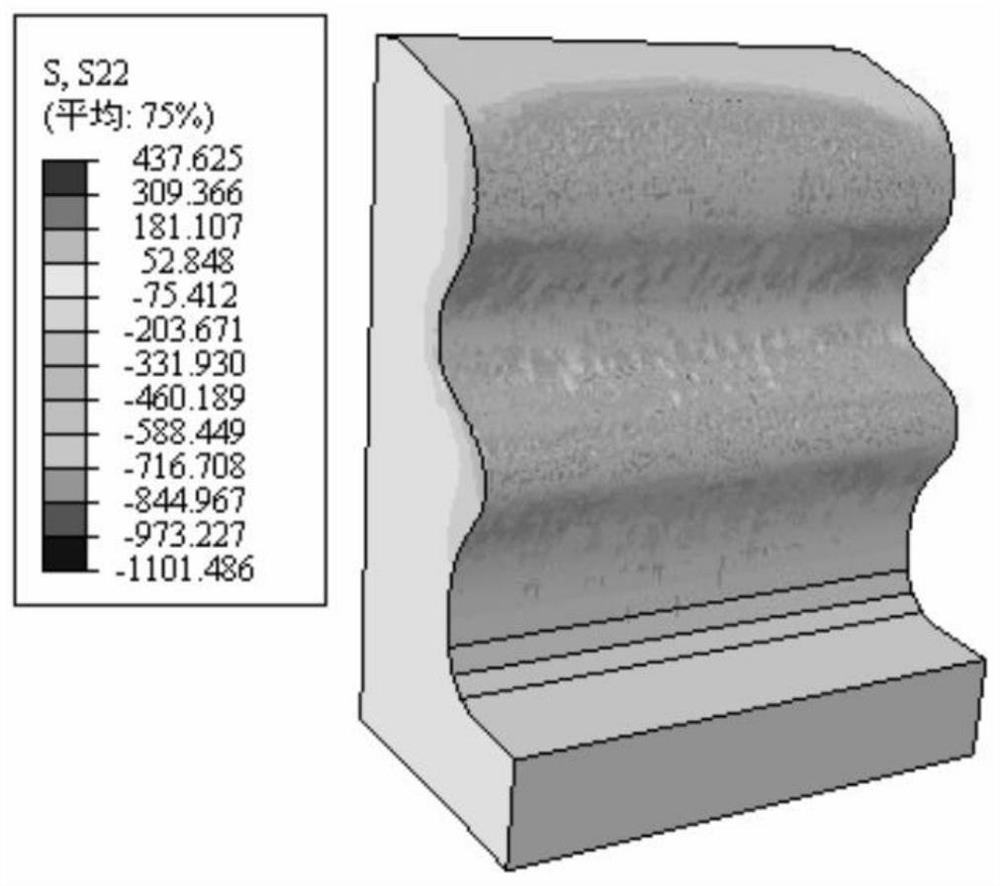
InactiveCN107706182ANo contact failureImprove macro stress distributionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact failureSilicon oxide
The invention provides a preparation method and a structure of a three-dimensional memory. According to the preparation method and the structure, a contact hole technology of a peripheral circuit region is advanced to be prior to a metal gate technology of an array memory region, so that etching of a contact hole to release of silicon oxide film stress of the peripheral circuit region is realized,distribution of macroscopic stress of a wafer is improved, and bending is effectively reduced. In addition, the contact hole technology of the peripheral circuit region is arranged prior to the metalgate technology of the array memory region, so that nonuniformity of local stress of the metal gate technology of the array memory region cannot cause contact failure of a peripheral circuit. The preparation method and the structure are realized by the following technical schemes.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Dynamic progressive failure analysis method for composite material multi-scale model
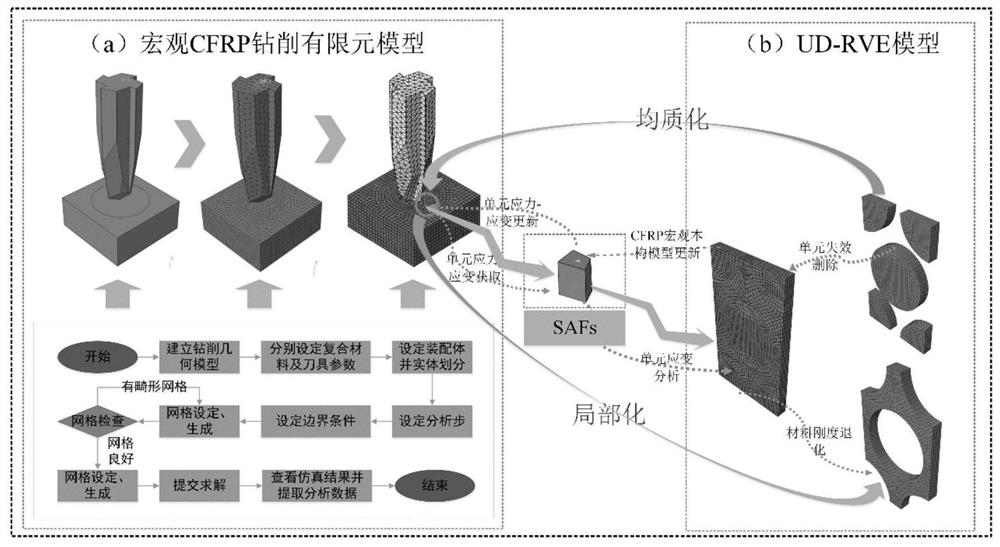
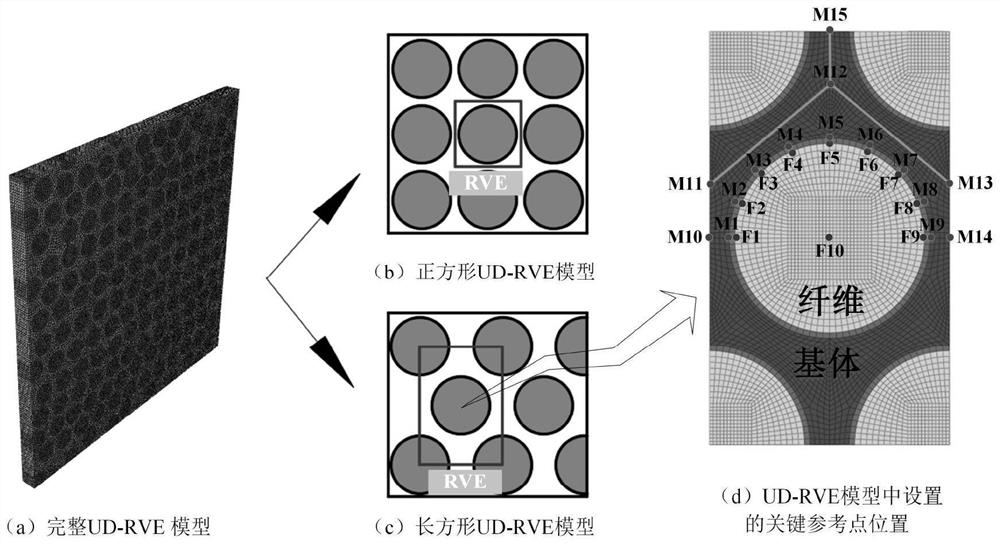
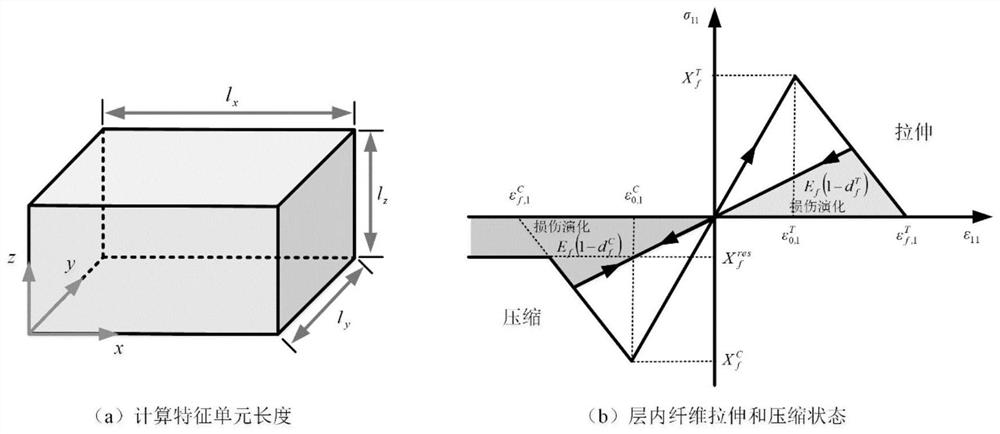
The mechanical response and progressive damage behaviors of the composite material laminated plate structure generated under the dynamic working condition are studied. Firstly, different mechanical behaviors of fibers and a matrix in a microscopic state are considered, and a three-dimensional multi-scale dynamic progressive damage evolution law model based on a microscopic failure theory is provided. Based on micro-component degradation elastic parameters in a typical representative volume unit model, a novel fiber and resin matrix damage evolution rule model and a failure unit auxiliary deletion criterion are provided; and secondly, a relationship model of macroscopic stress and representative volume unit microcosmic stress in the composite material model is built by adopting a stress amplification coefficient, and thus simulating in-layer and interlayer damage behaviors of the composite material under the cutting action of the dagger drill in combination with a bilinear cohesive force unit model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
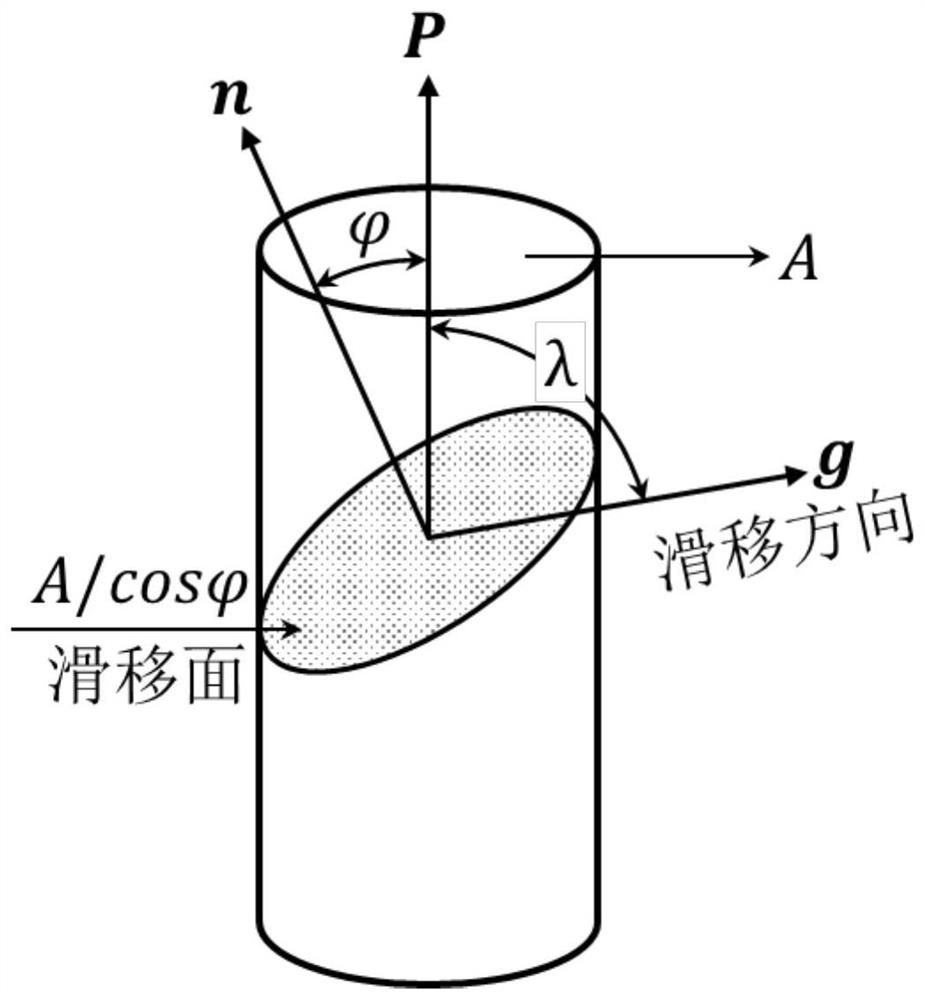
TKD (transmission Kikuchi diffraction)-based determining method for stress state of single grain of polycrystalline material
InactiveCN109142402AMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionCrystalline materialsStressed state
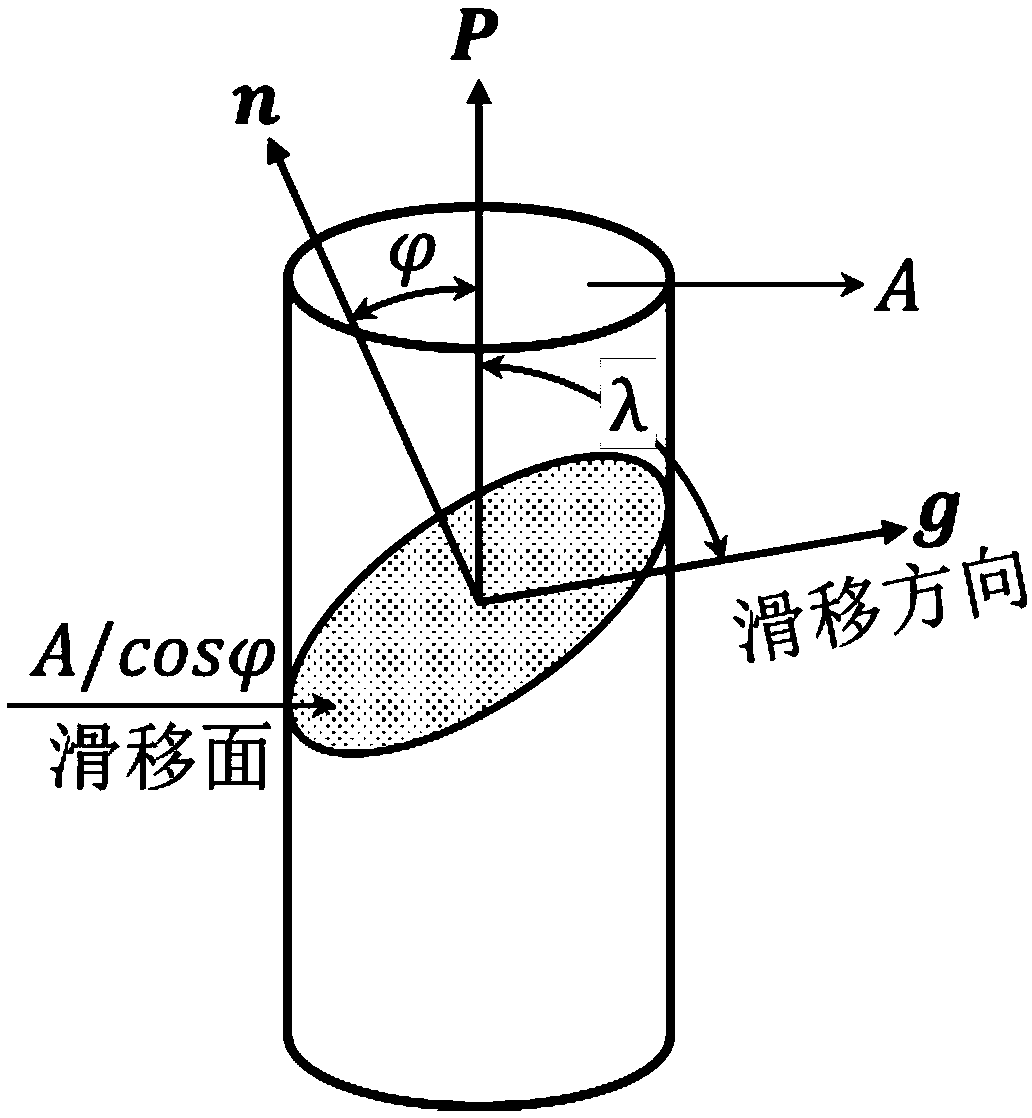
The invention aims to provide a TKD (transmission Kikuchi diffraction)-based determining method for stress state of a single grain of a polycrystalline material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: the to-be-studied single grain is determined firstly, whether dislocation density of the grain and several surrounding grains has order-of-magnitude difference is determined,if the density has order-of-magnitude difference, further analysis can be performed, and a slip system open in the grains is determined; then specific orientation distribution of the grains is obtained by adopting the TKD analysis technology; the slip system is input into a Schmid factor calculation part of an HKL Channel 5 system, the macroscopic stress direction is adjusted simultaneously, an obtained Schmid factor value is enabled to be consistent with a predicted result, then the macroscopic force is the stress direction of the grains and is also the stress direction of the single grain. The method is applicable to any crystalline material, the specific stress state of the single grain in the material in a deformation process can be calculated well, and one definite and effective method is provided for studying the microscopic deformation mechanism of the polycrystalline material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Testing method for microscopic deformation of material
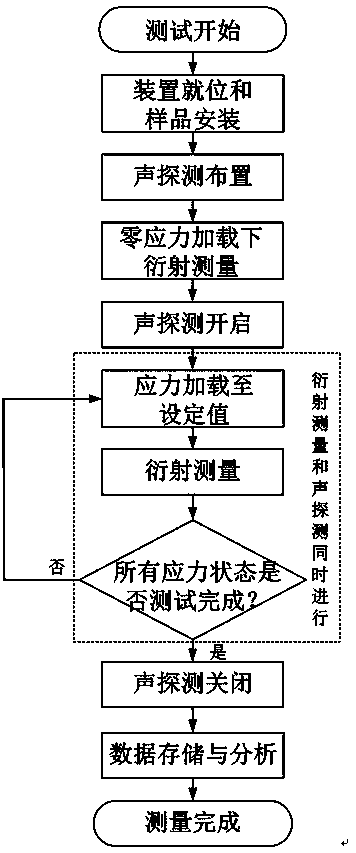
ActiveCN106644704ASolve the problem of relatively single measurement functionRealize in-situ non-destructive measurementUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansDislocationMacroscopic stress
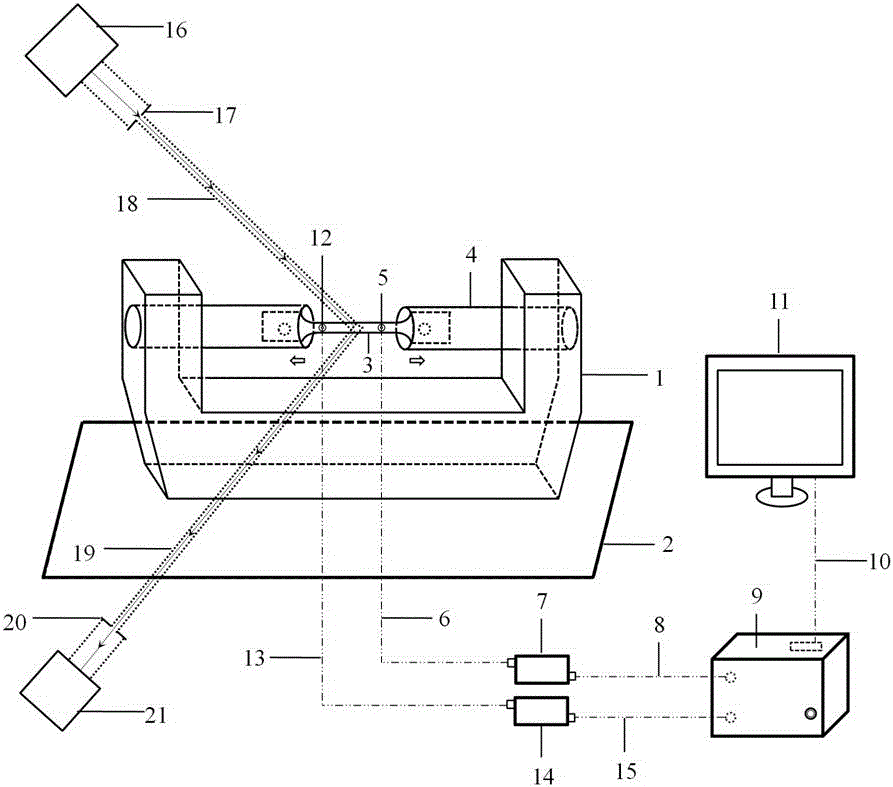
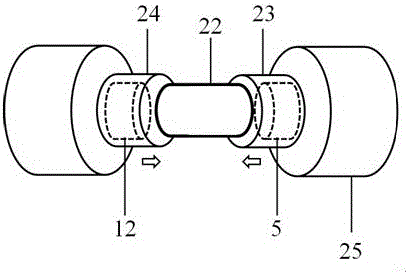
The invention provides a testing method for microscopic deformation of a material. The method employs a combination of symmetric diffraction experiments and dual-channel acoustic detection to test information about evolution of a microstructure in a sample in the whole stress loading process and realizes direct in-situ nondestructive measurement of inner static and dynamic microscopic deformation information of a block material. According to the method, a corresponding measurement crystal face is selected according to the crystal structure of the sample; and in a geometric layout that a radiation source and a detector are symmetrically arranged at two sides of a stress loading device, static microscopic deformation information including interplanar spacing, oriented direction and the like in different stress loading phases are measured by using diffraction experiments, and dynamic microscopic deformation like twin crystal nucleation and dislocation movement in the process of stress loading are continuously measured by using a dual-channel acoustic probe. The testing method for the microscopic deformation of the material is applicable to monitoring and analysis of inner microscopic mechanism and process of metal alloy materials in the process of macroscopic stress loading and to testing of characteristic deformation information like fracture failure of non-metal alloy materials.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Pattern production and recovery by transformation
A transformative periodic structure includes a plurality of elastomeric or elasto-plastic periodic solids that experiences a transformation in the structural configuration upon application of a critical macroscopic stress or strain. The transformation alters the geometric pattern changing the spacing and the shape of the features within the transformative periodic structure. For the case of elastomeric periodic structures upon removal of the critical macroscopic stress or strain, the transformative periodic solids are recovered to their original form. For the case of elasto-plastic periodic structures upon removal of the critical macroscopic stress or strain, the new pattern is retained. Polymeric periodic solids can be recovered to their original form by heating or plasticizing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
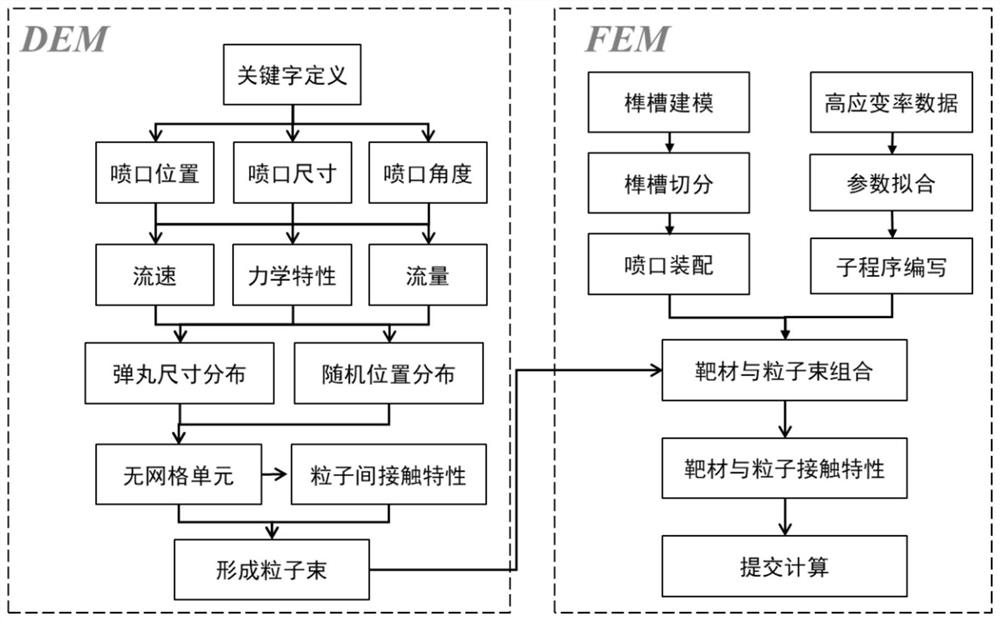
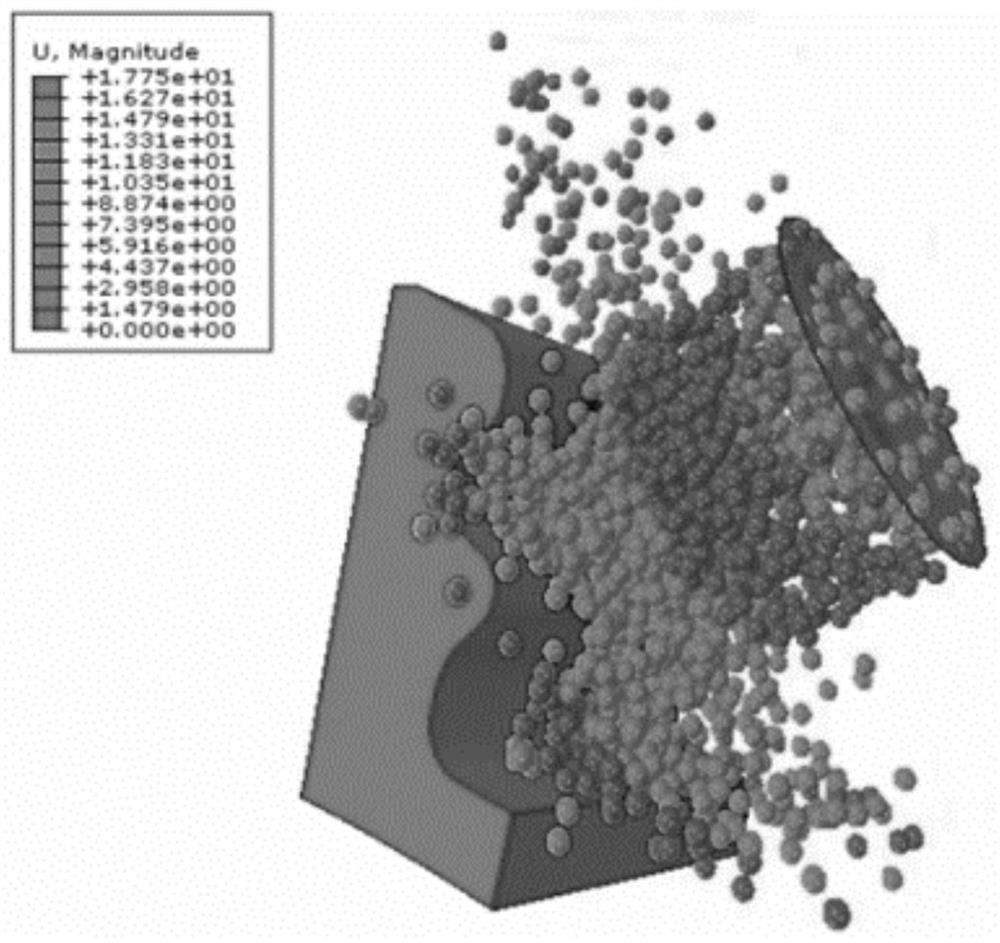
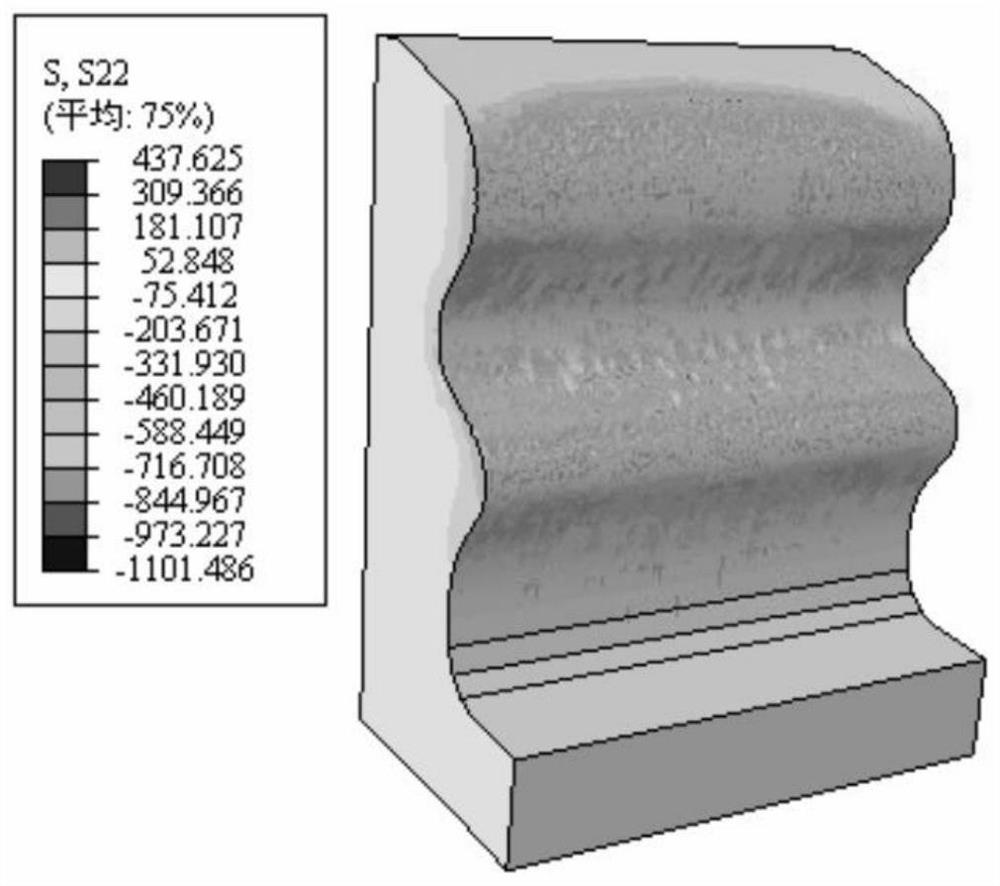
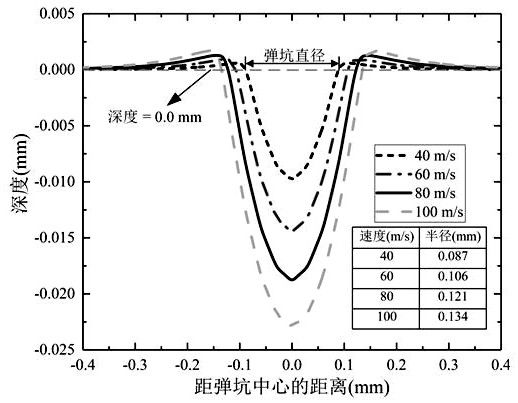
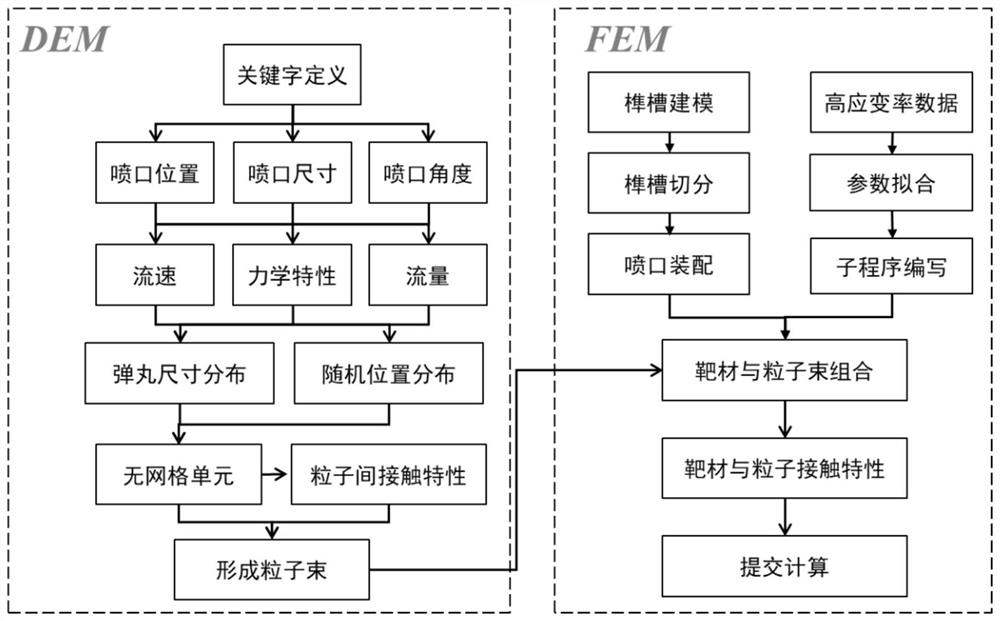
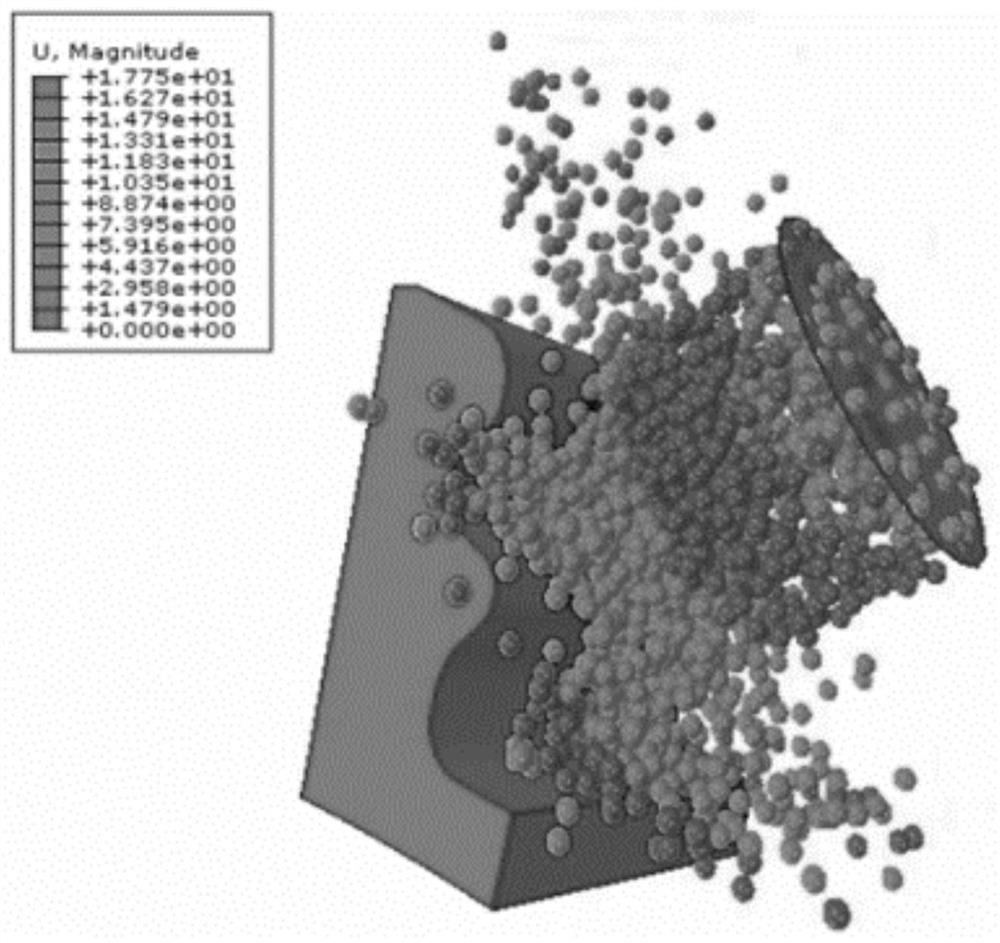
Turbine mortise shot blasting discrete element-finite element coupling multi-scale simulation method
ActiveCN111797554ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleModelSim
The invention relates to a turbine mortise shot blasting discrete element-finite element coupling multi-scale simulation method which comprises the following steps: (1) cutting a mortise structure tobe researched according to the symmetry of the mortise structure, and endowing a constitutive model with a high strain rate; (2) setting the relative positions of a nozzle and the mortise according tothe actual process condition, defining the size and angle of the nozzle, and completing the modeling of the mortise and the nozzle; (3) acquiring dislocation evolution model parameters based on the stress-strain data under the high strain rate, establishing a dislocation evolution model of the mortise material, and associating the grain size, the dislocation density and the macroscopic stress-strain; (4) defining a particle generator * Particle by using a DEM module, setting bullet parameters, combining the mortise with the nozzle, and setting contact characteristics between pellets and the mortise; and (5) carrying out numerical simulation, and obtaining surface integrity parameters after mortise structure strengthening.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High-energy shot blasting surface hardness numerical simulation method
ActiveCN112100885ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleEngineering
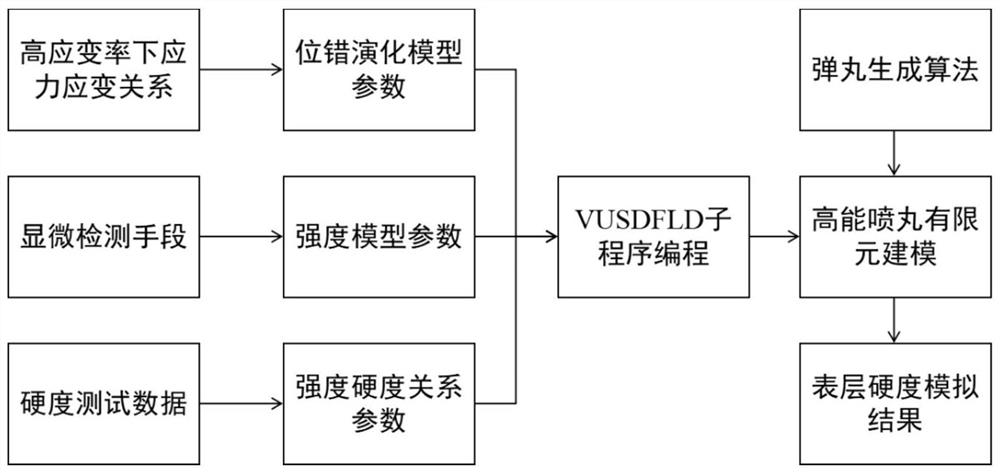
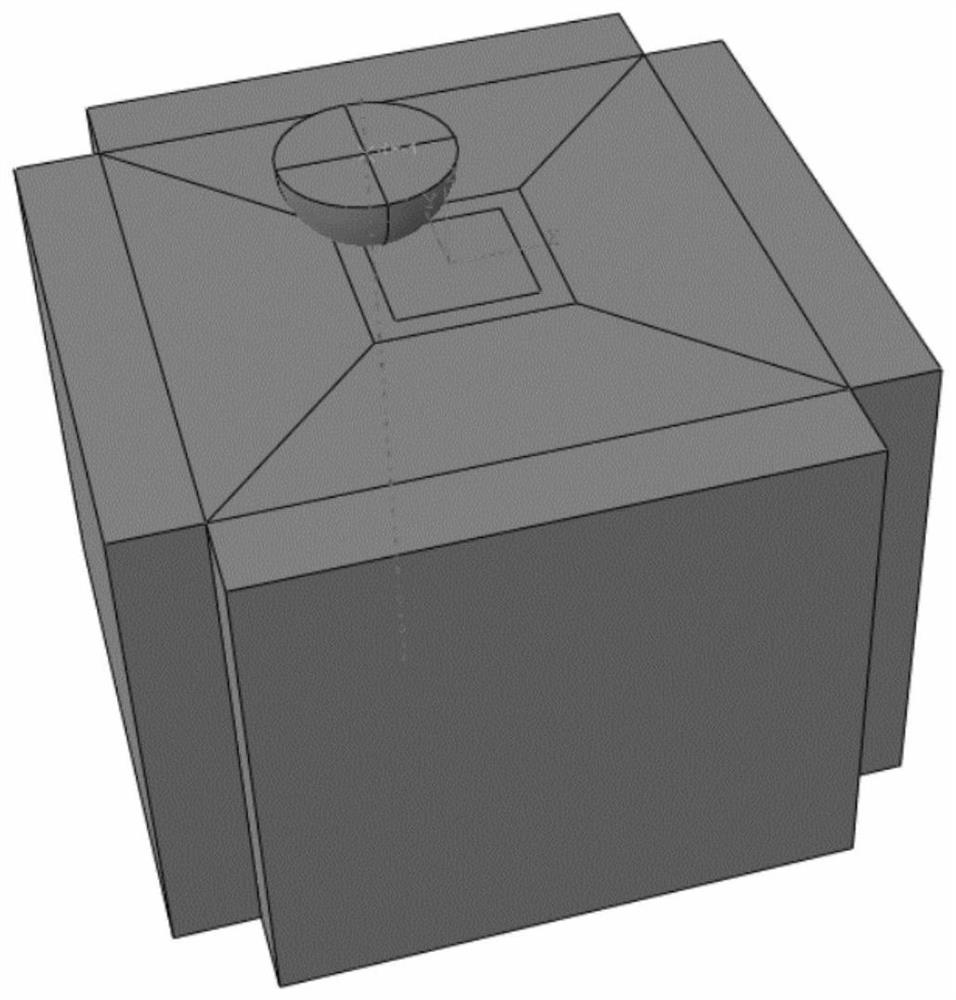
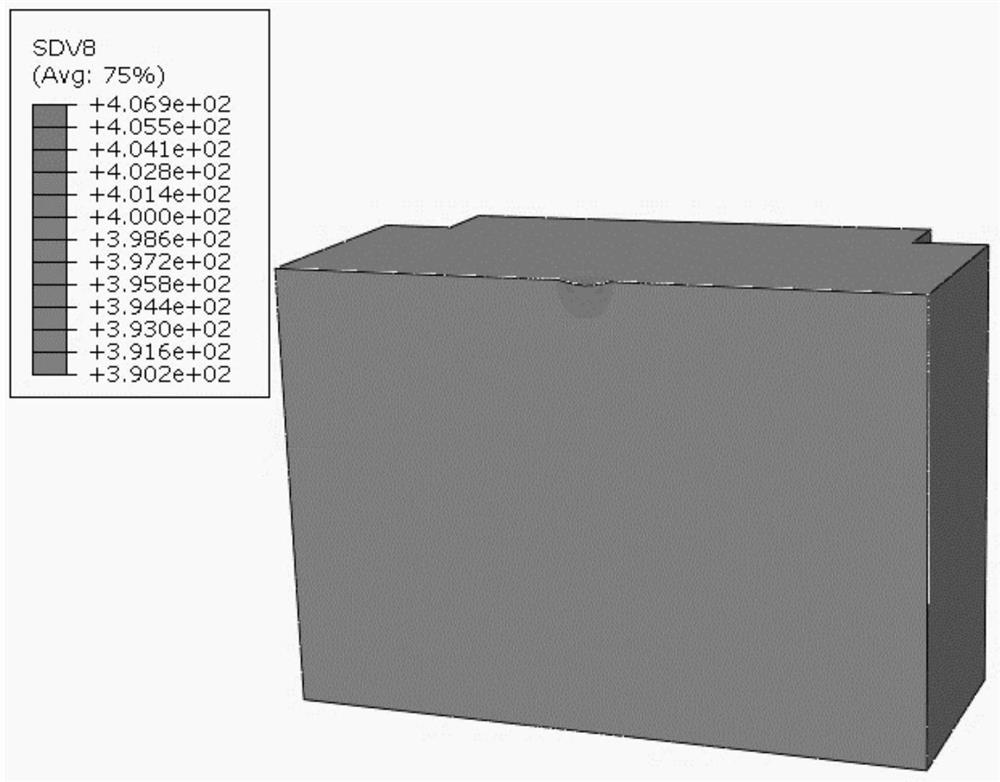
The invention relates to a high-energy shot blasting surface hardness numerical simulation method which comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring dislocation evolution model parameters based on stress-strain data under a high strain rate, establishing a dislocation evolution model of a to-be-studied material, and associating grain size, dislocation density and macroscopic stress-strain; (2) acquiring strength model parameters, establishing a strength model of the to-be-researched material, and associating the strength with the grain size; (3) acquiring parameters in the strength and hardness relationship based on the test data, establishing the strength and hardness relationship of the to-be-researched material, and associating the surface hardness with the strength; (4) conducting programming by using a VUSDFLD subprogram of ABAQUS finite element software, and establishing a relationship between the surface hardness and macroscopic parameters based on the relationship among the dislocation evolution model, the strength model and the strength and hardness to complete programming; and (5) conducting shot peening strengthening numerical simulation based on ABAQUS software, and obtaining surface hardness distribution after strengthening.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Laser additive manufacturing method for La2O3/(Cu, Ni) functionally graded composites
ActiveCN109097620AShort preparation cycleHigh hardnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyOxide ceramicsRare earth
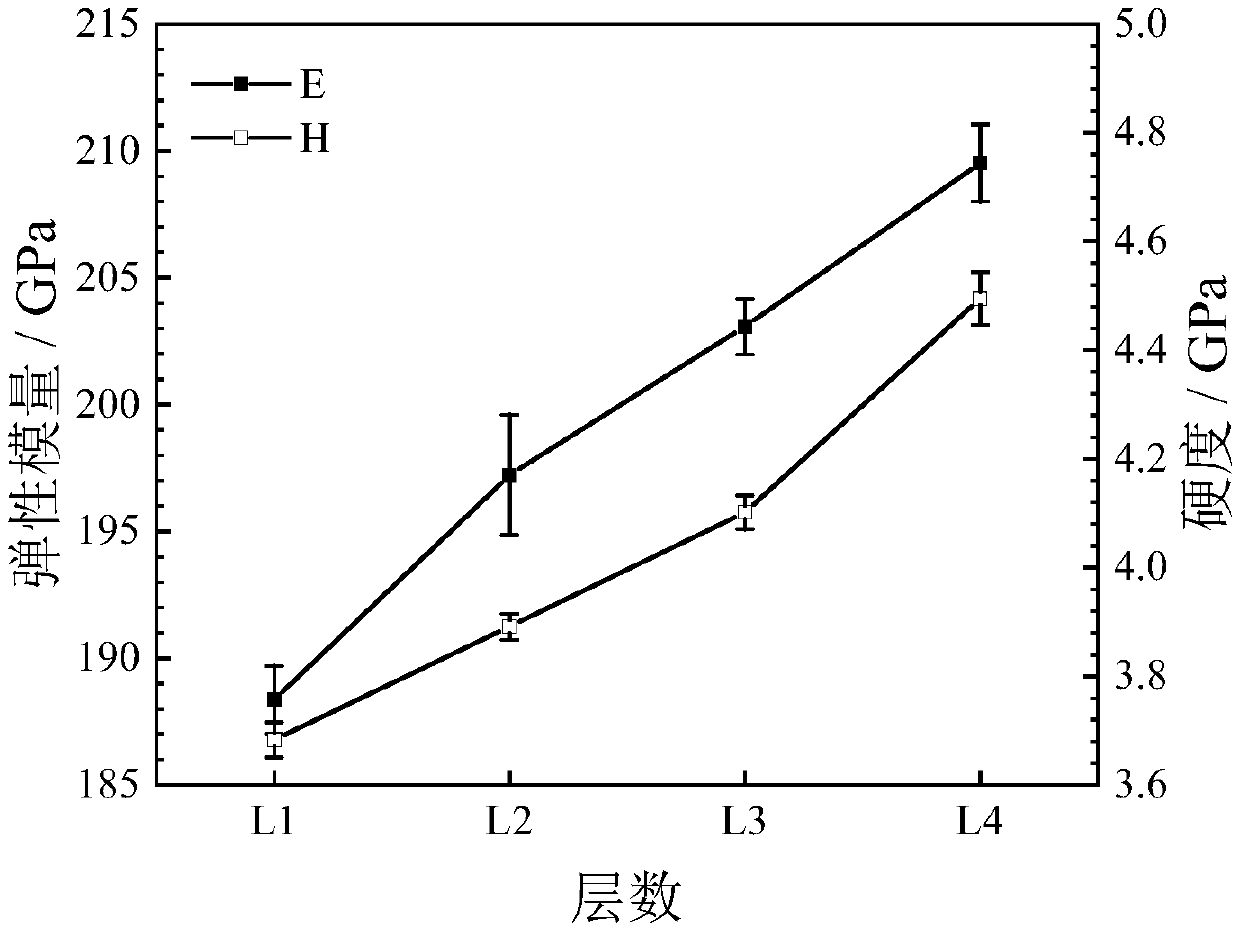
The invention discloses a laser additive manufacturing method for La2O3 / (Cu,Ni) functionally graded composites. The laser additive manufacturing method comprises the following steps that raw materialpowder is prepared, specifically, La2O3 powder of rare earth metal oxide ceramics and Ni-based self-melting alloy powder are proportioned by a certain mass percentage, and the balance is Cu powder; pretreatment of a Cu substrate is performed; the preheating of the Cu substrate is performed; and the La2O3 / (Cu,Ni) gradient functional composites are manufactured by a laser additive. According to thelaser additive manufacturing method for the La2O3 / (Cu,Ni) functionally graded composites, La2O3 can improve the strength of materials, the organization is improved, a Ni-base self-melting alloy can improve the wettability of a melt, bonding strength of La2O3 and a metal matrix is improved, the obtained La2O3 / (Cu,Ni) functionally gradient composites have smooth macroscopic stress transition in a gradient layer, microscopic stress decreases gradually from bottom layer to top layer, and hardness and elastic modulus show the characteristics of gradient transition.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Heterostructure simulation method based on ABAQUS
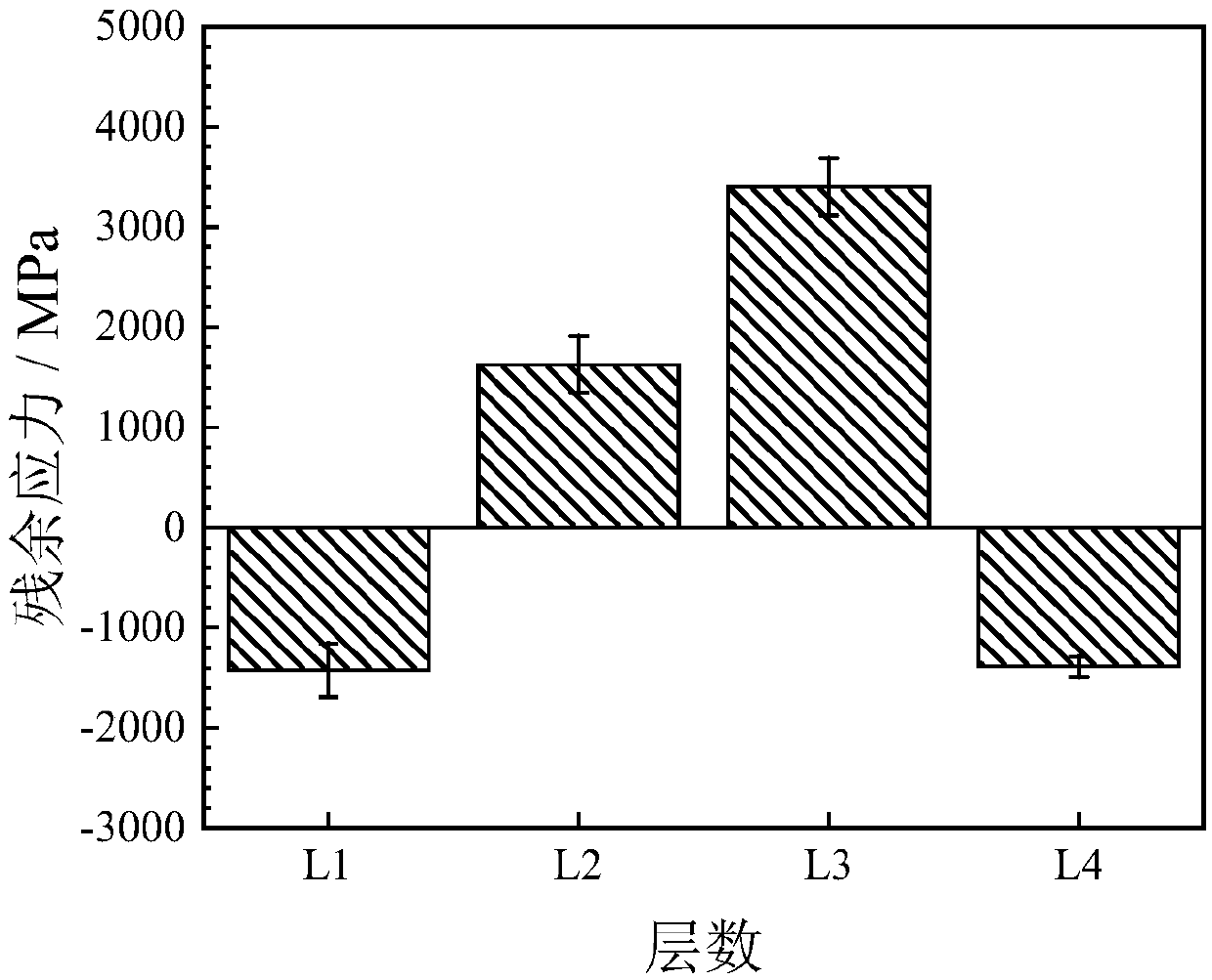
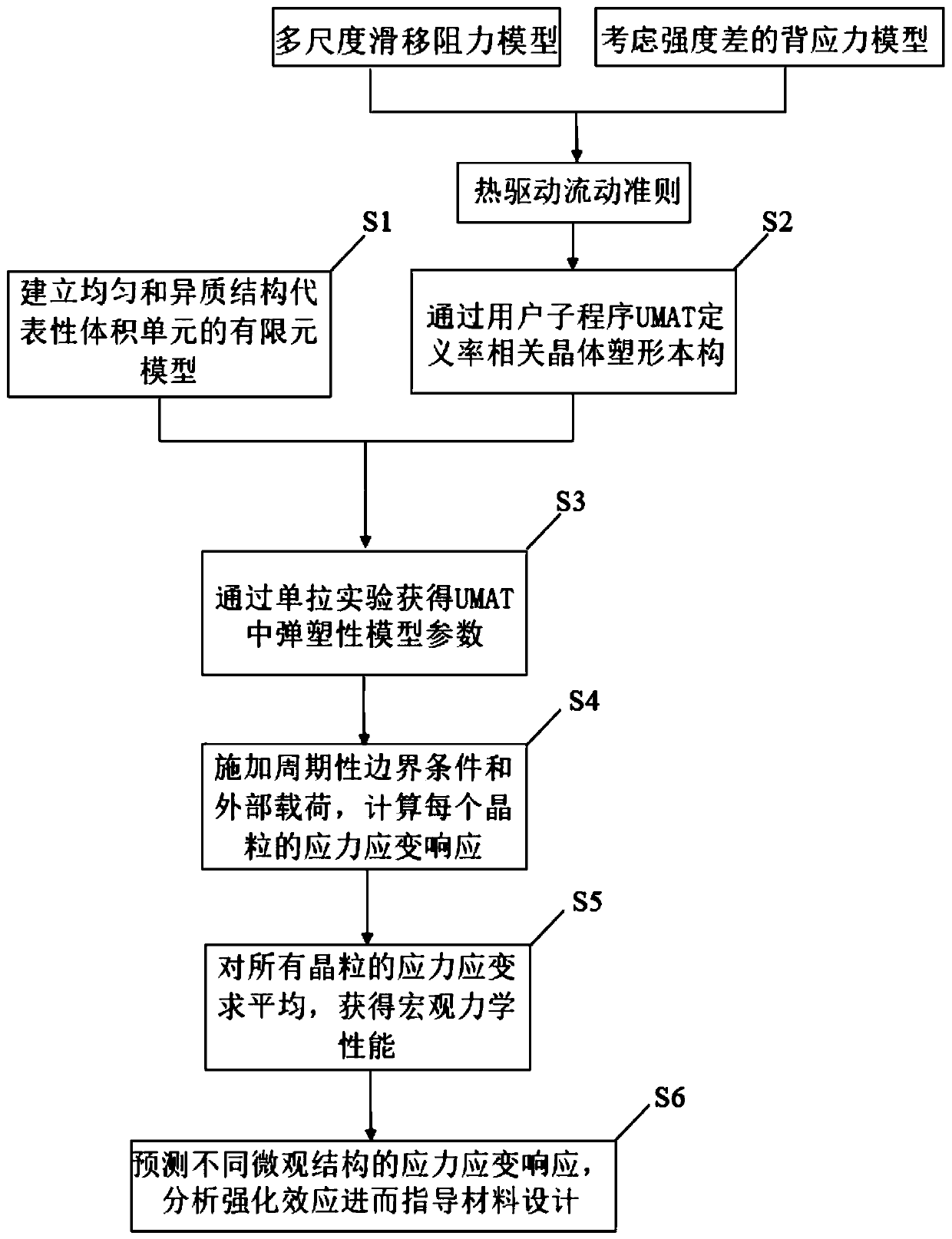
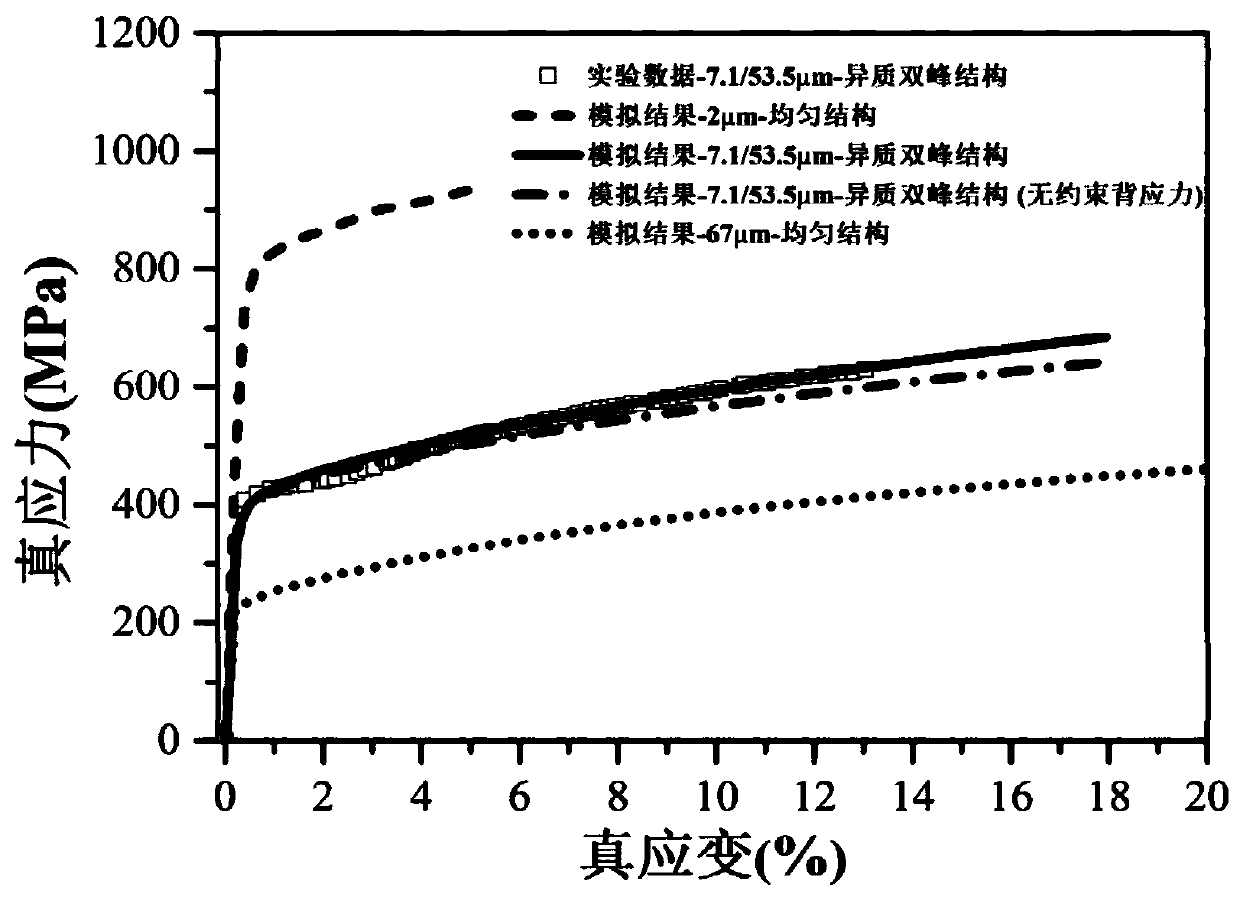
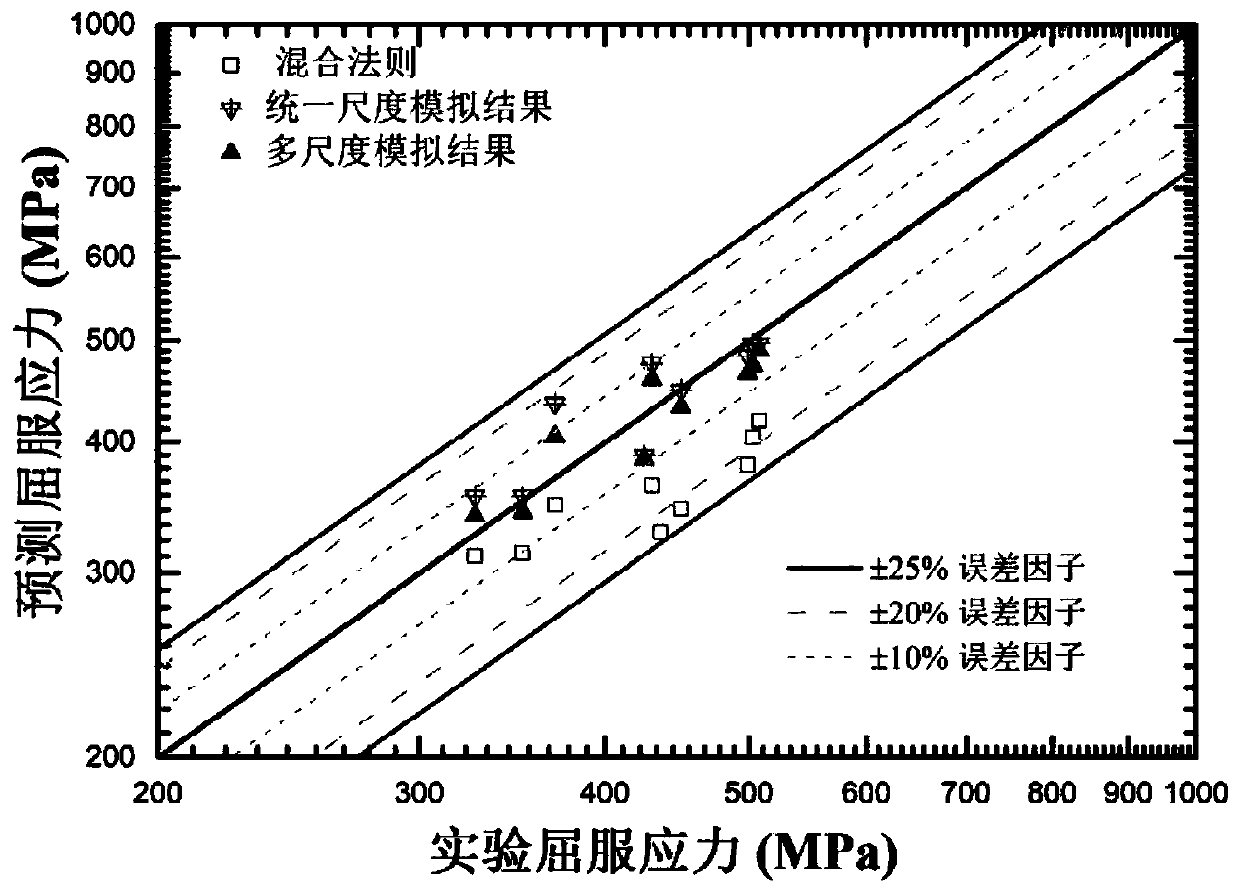
ActiveCN110765688ASolve the problem of back stress strengtheningIntuitiveDesign optimisation/simulationHeterojunctionMacroscopic scale
The invention provides a heterostructure simulation method based on ABAQUS. The heterostructure simulation method comprises the following steps: establishing a 2D representative volume unit of a uniform structure and a heterostructure; correcting the sliding resistance model and the back stress model and writing the sliding resistance model and the back stress model into a user subprogram UMAT soas to define an elastic-plastic constitutive equation of the crystal; determining material parameters in the UMAT by utilizing the stretching curves of the three different structures; applying a periodic boundary condition and an external load, and calculating a stress-strain response of each crystal grain by utilizing ABAQUS; averaging stress and strain of all crystal grains; changing parameterssuch as microstructure and grain orientation of the model, predicting and analyzing corresponding macroscopic stress-strain response, strengthening effect and microcosmic deformation cloud atlas, andcomparing to obtain the optimal microstructure. According to the heterostructure simulation method, the grain size effect and extra back stress strengthening of the heterostructure are considered, theheterostructure can be simulated, and the heterostructure simulation method has the advantages of being visual, high in applicability and high in accuracy.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Box type structure heavy deformation prediction method based on macroscopic stress and residual stress extension
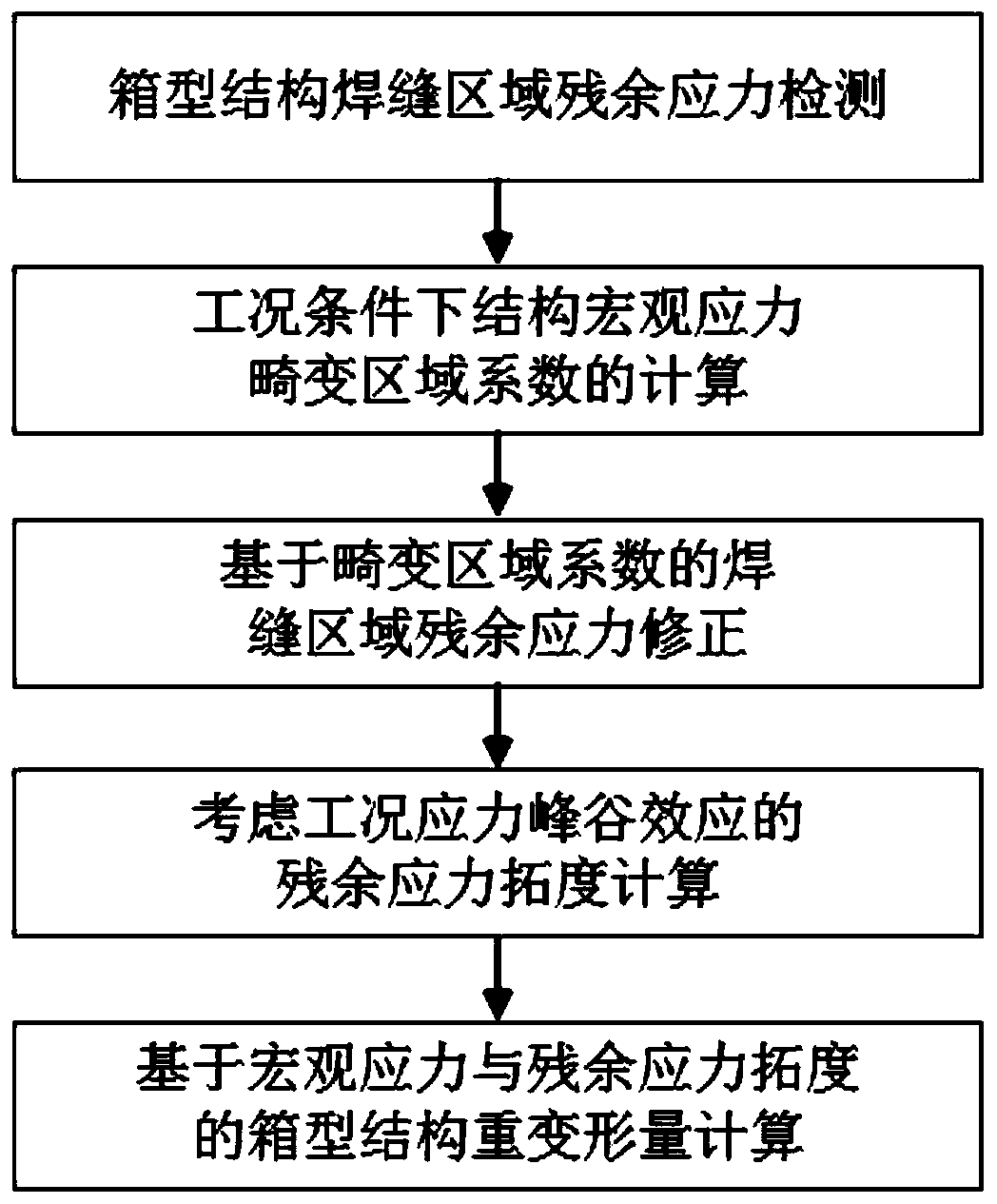
InactiveCN111339699ARealize detectionOvercome limitationsGeometric CADForce measurementMacroscopic scaleCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a box-type structure heavy deformation prediction method based on macroscopic stress and residual stress extension. The method comprises the following steps: S1, detecting residual stress of a weld joint area of a box-type structure; s2, calculating a macroscopic stress distortion region coefficient of the structure under a working condition; s3, correcting the residual stress of the weld joint area based on the distortion area coefficient; s4, calculating the residual stress topology considering the peak-valley effect of the working condition stress; and S5, calculating the heavy deformation of the box-type structure based on the extension of the macroscopic stress and the residual stress. The method is high in detection precision, and has important practical significance for realizing real-time evaluation of the heavy deformation distribution of the box-type structure.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
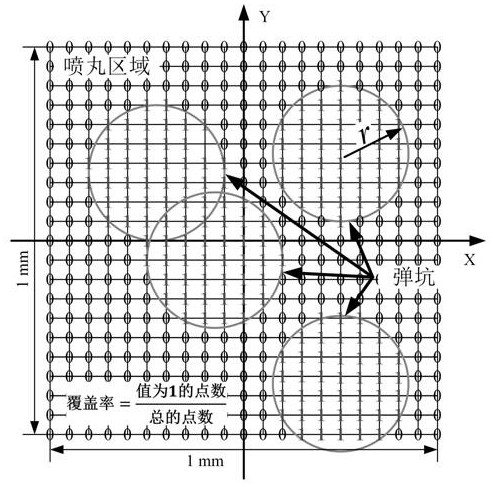
Prediction method for microstructure evolution of shot peening strengthening material
PendingCN111814373AImprove the effect of strengthening treatmentDeepen understandingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a prediction method for microstructure evolution of a shot peening strengthening material. The prediction method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a three-dimensional shot peening model by using an ABAQUS platform; 2, embedding a constitutive equation based on dislocation density evolution into the shot peening strengthening three-dimensional model; 3, measuring the radius of the crater; 4, calculating the number of shots required in a unit area when the shot blasting coverage rate reaches a set value; 5, establishing a shot peening strengthening three-dimensional model with multiple randomly distributed shots; and 6, analyzing the process that the projectile flow impacts the target body by using an ABAQUS / Express solver, and calculating to obtain the dislocation cell size and the dislocation density distribution. The method has the technical effects that under the condition of considering the relationship between the macroscopic stress-strain fieldand the microstructure of the material, the evolution data of the microstructure of the material by different shot peening strengthening parameters is obtained, the understanding of shot peening process parameters is deepened, the shot peening process parameters are optimized, and the shot peening strengthening treatment effect is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
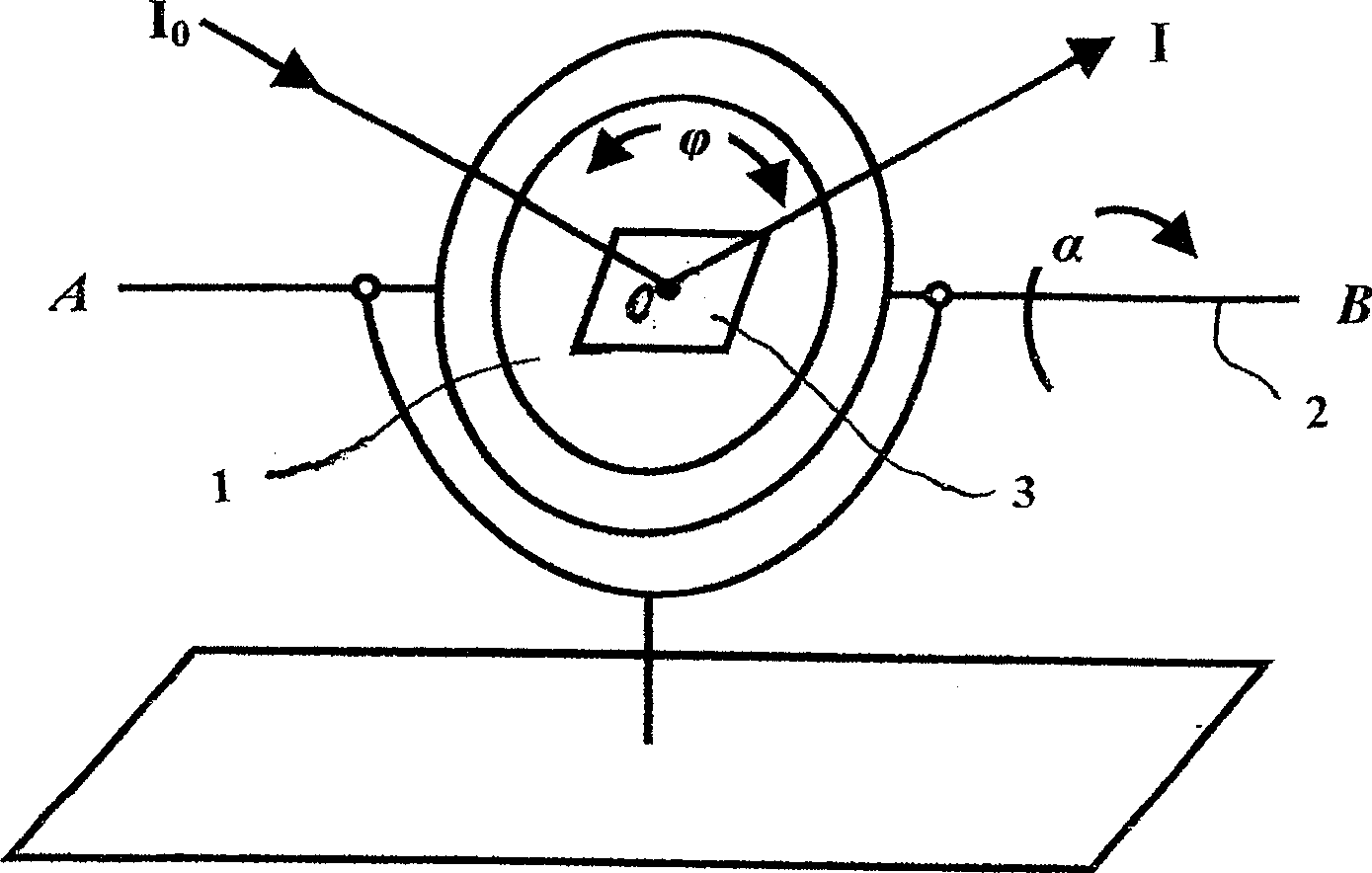
X ray diffraction instrument and method for detecting macro stress in micro area
InactiveCN100504349CChoose intuitivelyChoose accuratelyForce measurementUsing mechanical meansX-rayCrystal plane
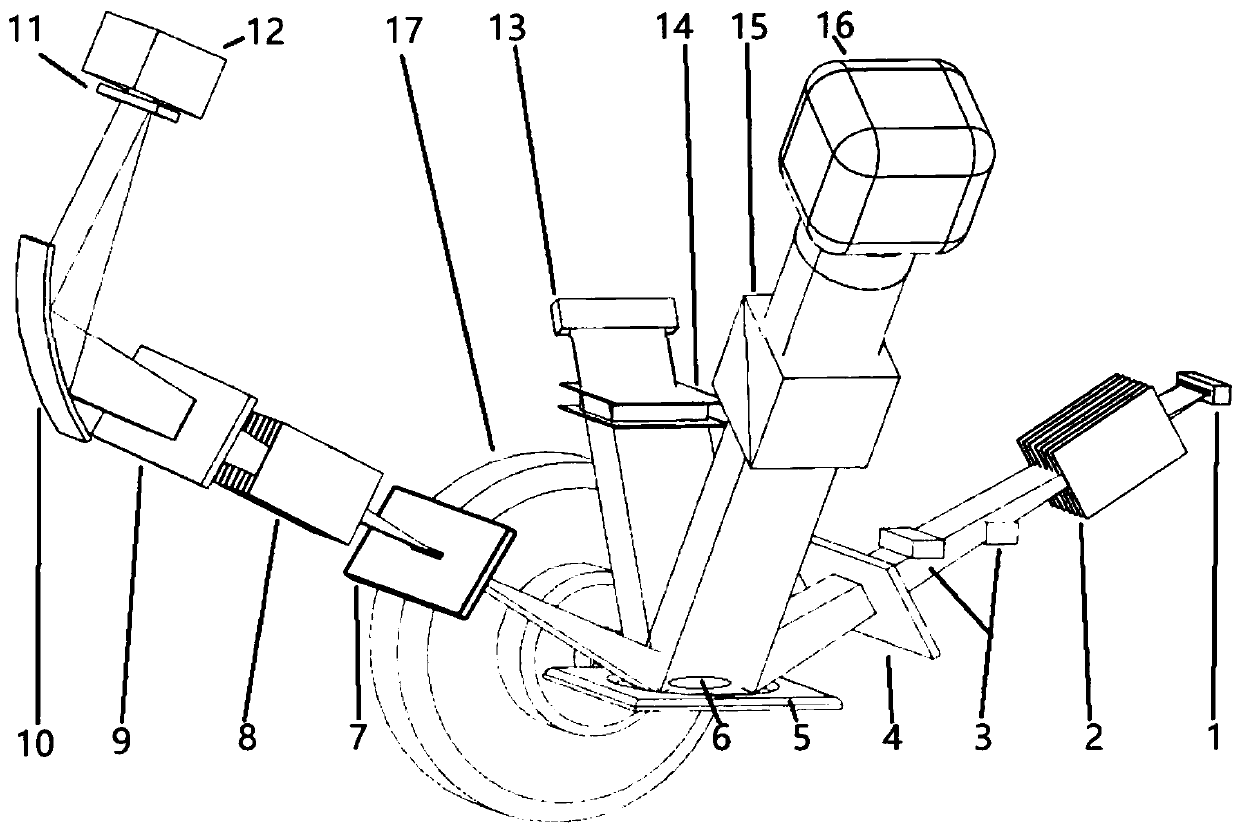
The X-ray diffraction device and method for detecting macroscopic stress in a micro region of the invention belong to the testing field. The setup, consisting of an x-ray diffractometer, is equipped with a rotating detection stage. Detection steps: adjust the surface of the tested sample on the rotating detection platform to be perpendicular to the diffraction circle platform of the X-ray diffractometer, and set the roll rotation axis on the intersection line between the diffraction circle plane and the sample surface; select the stress detection point O under the microscope; Angle Φ sets the stress detection direction; determine the roll angle α; re-observe the stress detection point O under the microscope, adjust the detection point O to coincide with the center of the diffraction circle; measure the selected diffraction crystal plane; Several 2θα data; calculate the macroscopic stress value in the direction perpendicular to the roll axis AB in the small area of point O. The invention can detect the macroscopic stress in any specified direction in any specified tiny area of the sample, and detect the stress change gradient and stress distribution inhomogeneity.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Nondestructive testing method for residual stress in thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN109764995AReal-time monitoring of service statusApparatus for force/torque/work measurementX-rayMeasurement precision
The invention discloses a nondestructive testing method for residual stress at different depths in a thermal barrier coating, and the method is used for carrying out nondestructive detection on the residual stress at different depths in the thermal barrier coating of an aero-engine by adopting an X-ray diffraction instrument. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, placing and fixinga thermal barrier coating test piece on a sample table, enabling a normal direction of a sample to be consistent with a normal direction of an incident ray, setting the scanning range, adjusting the power of a ceramic X-ray tube, the frequency of the X-ray, the reproducibility of an angular instrument, the controllable minimum step, the maximum counting rate of a PIXcel3D super-energy detector, the sample table direction correction and other factors, emitting the X-ray with the specific frequency, and determining the residual stress at different depths in the thermal barrier coating on the basis of a relation between the displacement of an X-ray diffraction peak and the macroscopic stress. According to the nondestructive testing method for the residual stress in the thermal barrier coatinghas high measurement precision and efficiency and good reproducibility, and is widely applied to nondestructive detection of the residual stress of the thermal barrier coating of the aero-engine.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
A tkd Determination Method for Single Grain Stress State of Polycrystalline Material
InactiveCN109142402BMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMacroscopic scaleCrystalline materials
The invention aims to provide a TKD (transmission Kikuchi diffraction)-based determining method for stress state of a single grain of a polycrystalline material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: the to-be-studied single grain is determined firstly, whether dislocation density of the grain and several surrounding grains has order-of-magnitude difference is determined,if the density has order-of-magnitude difference, further analysis can be performed, and a slip system open in the grains is determined; then specific orientation distribution of the grains is obtained by adopting the TKD analysis technology; the slip system is input into a Schmid factor calculation part of an HKL Channel 5 system, the macroscopic stress direction is adjusted simultaneously, an obtained Schmid factor value is enabled to be consistent with a predicted result, then the macroscopic force is the stress direction of the grains and is also the stress direction of the single grain. The method is applicable to any crystalline material, the specific stress state of the single grain in the material in a deformation process can be calculated well, and one definite and effective method is provided for studying the microscopic deformation mechanism of the polycrystalline material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
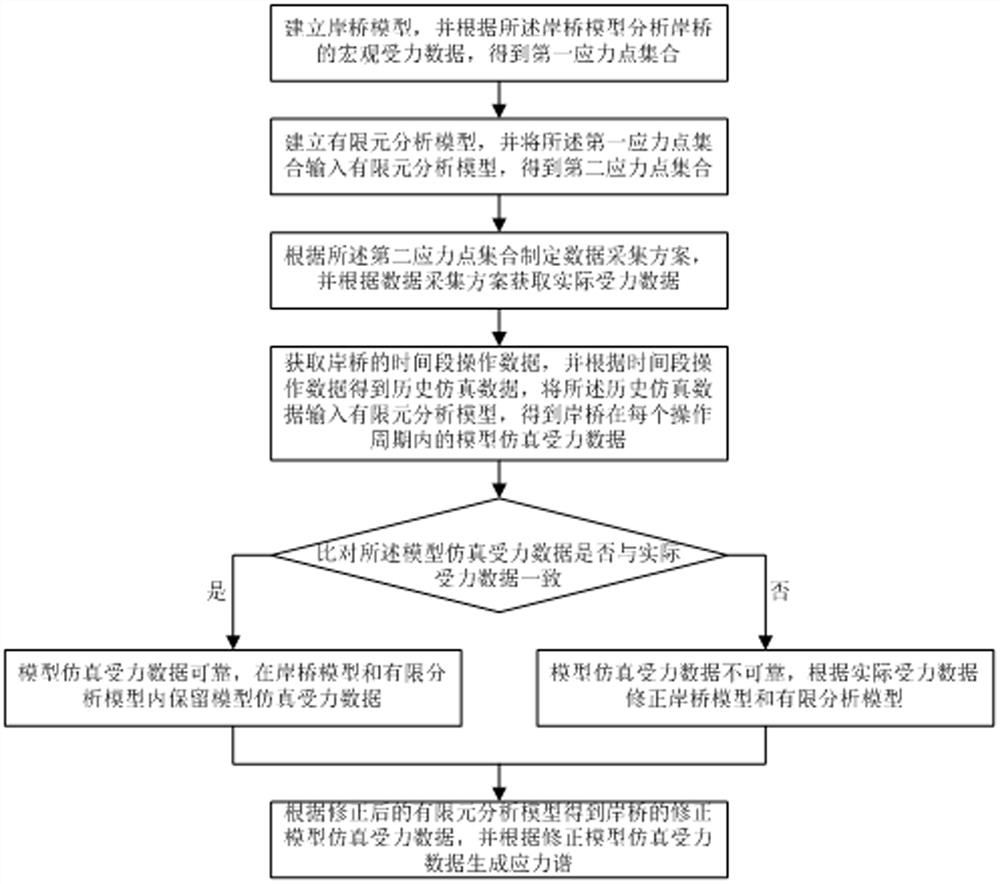
Fatigue monitoring method and life prediction method of quay crane structure
ActiveCN114282423AImprove accuracySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationAnalytic modelElement analysis
The invention relates to a fatigue monitoring method and a life prediction method of a quay crane structure in the technical field of equipment performance monitoring, and the method comprises the following steps: building a quay crane model, and analyzing the macroscopic stress data of a quay crane to obtain a first stress point set; establishing a finite element analysis model, and inputting the first stress point set into the finite element analysis model to obtain a second stress point set; formulating a data acquisition scheme, and obtaining actual stress data; obtaining time period operation data of the quay crane to obtain historical simulation data, and inputting the historical simulation data into the finite element analysis model to obtain model simulation stress data; verifying the reliability of the simulation stress data of the model according to the actual stress data, and correcting the quay crane model and the finite element analysis model; according to the corrected finite element analysis model, corrected model simulation stress data of the quay crane is obtained, a stress spectrum is generated, the method has the advantage of being high in accuracy, and the bottleneck that fatigue monitoring obtained through a traditional fatigue monitoring method is not accurate is broken through.
Owner:HANGZHOU TITAN NEW ENERGY TECH
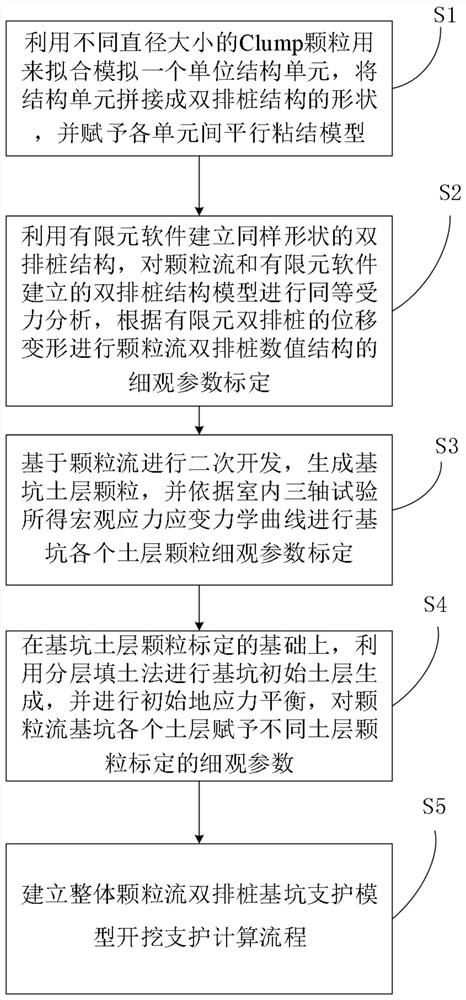
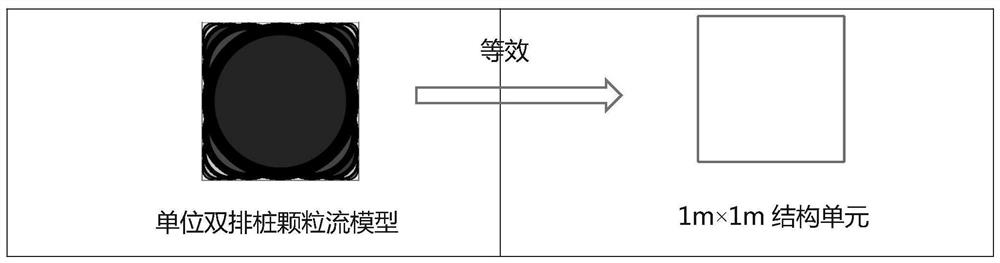
Double-row pile foundation pit supporting particle flow numerical simulation method
ActiveCN113627061AEffective analog restorationMeet engineering needsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationParticle flowTriaxial shear test
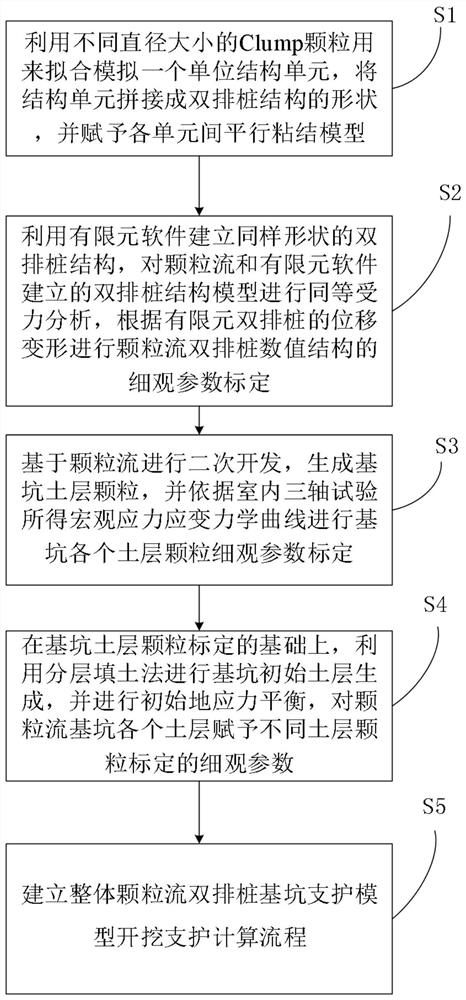
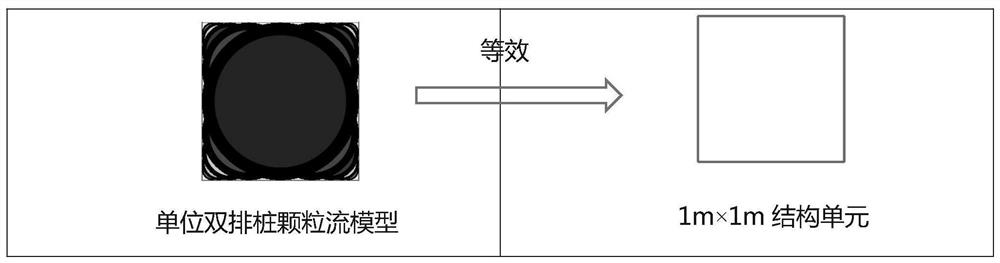
The invention relates to the technical field of numerical simulation, and discloses a double-row pile foundation pit support particle flow numerical simulation method, which comprises the following steps of fitting and simulating a unit structure unit by using Clump particles with different diameters, and splicing the structure unit into the shape of a double-row pile structure; establishing a double-row pile structure with the same shape through finite element software, conducting equivalent stress analysis on a double-row pile structure model, and conducting mesoscopic parameter calibration of a particle flow double-row pile numerical value structure according to displacement deformation of finite element double-row piles; generating foundation pit soil layer particles based on the particle flow, and carrying out mesoscopic parameter calibration of each soil layer particle of the foundation pit according to a macroscopic stress-strain mechanical curve obtained by an indoor triaxial test; generating an initial soil layer of the foundation pit by using a layered filling method, and endowing each soil layer of the particle flow foundation pit with meso-parameters calibrated by different soil layer particles; and establishing an excavation support calculation process of the integral particle flow double-row pile foundation pit support model. According to the invention, numerical simulation of double-row pile support is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGSHE GRP
A test method for microscopic deformation of materials
ActiveCN106644704BRealize in-situ non-destructive measurementSolve the problem of relatively single measurement functionUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansDislocationMacroscopic stress
The invention provides a testing method for microscopic deformation of a material. The method employs a combination of symmetric diffraction experiments and dual-channel acoustic detection to test information about evolution of a microstructure in a sample in the whole stress loading process and realizes direct in-situ nondestructive measurement of inner static and dynamic microscopic deformation information of a block material. According to the method, a corresponding measurement crystal face is selected according to the crystal structure of the sample; and in a geometric layout that a radiation source and a detector are symmetrically arranged at two sides of a stress loading device, static microscopic deformation information including interplanar spacing, oriented direction and the like in different stress loading phases are measured by using diffraction experiments, and dynamic microscopic deformation like twin crystal nucleation and dislocation movement in the process of stress loading are continuously measured by using a dual-channel acoustic probe. The testing method for the microscopic deformation of the material is applicable to monitoring and analysis of inner microscopic mechanism and process of metal alloy materials in the process of macroscopic stress loading and to testing of characteristic deformation information like fracture failure of non-metal alloy materials.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Non-oriented electrical steel sheet and method for producing same
ActiveUS11408041B2Reduce residual stressReducing an average Taylor factorInorganic material magnetismFurnace typesElectrical steelMechanical engineering
A non-oriented electrical steel sheet according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes 2.0 to 4.0% of Si, 0.05 to 1.5% of Al, 0.05 to 2.5% of Mn, equal to or less than 0.005% of C (excluding 0%), equal to or less than 0.005% of N (excluding 0%), 0.001 to 0.1% of Sn, 0.001 to 0.1% of Sb, 0.001 to 0.1% of P, 0.001 to 0.01% of As, 0.0005 to 0.01% of Se, 0.0005 to 0.01% of Pb, 0.0005 to 0.01% of Bi, a remainder of Fe, and inevitable impurities, as wt %, wherein a Taylor factor (M) of each crystal grain included in a steel sheet is expressed in Formula 1, and an average Taylor factor value of the steel sheet is equal to or less than 2.75:M=στCRSS[Formula1](here, σ is a macro stress, and τCRSS is a critical resolved shear stress).
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method of making a timepiece spring from monocrystalline material and timepiece spring obtained by this method
PendingUS20220326657A1High mechanical strengthPolycrystalline material growthAcoustic indicationWaferingEngineering
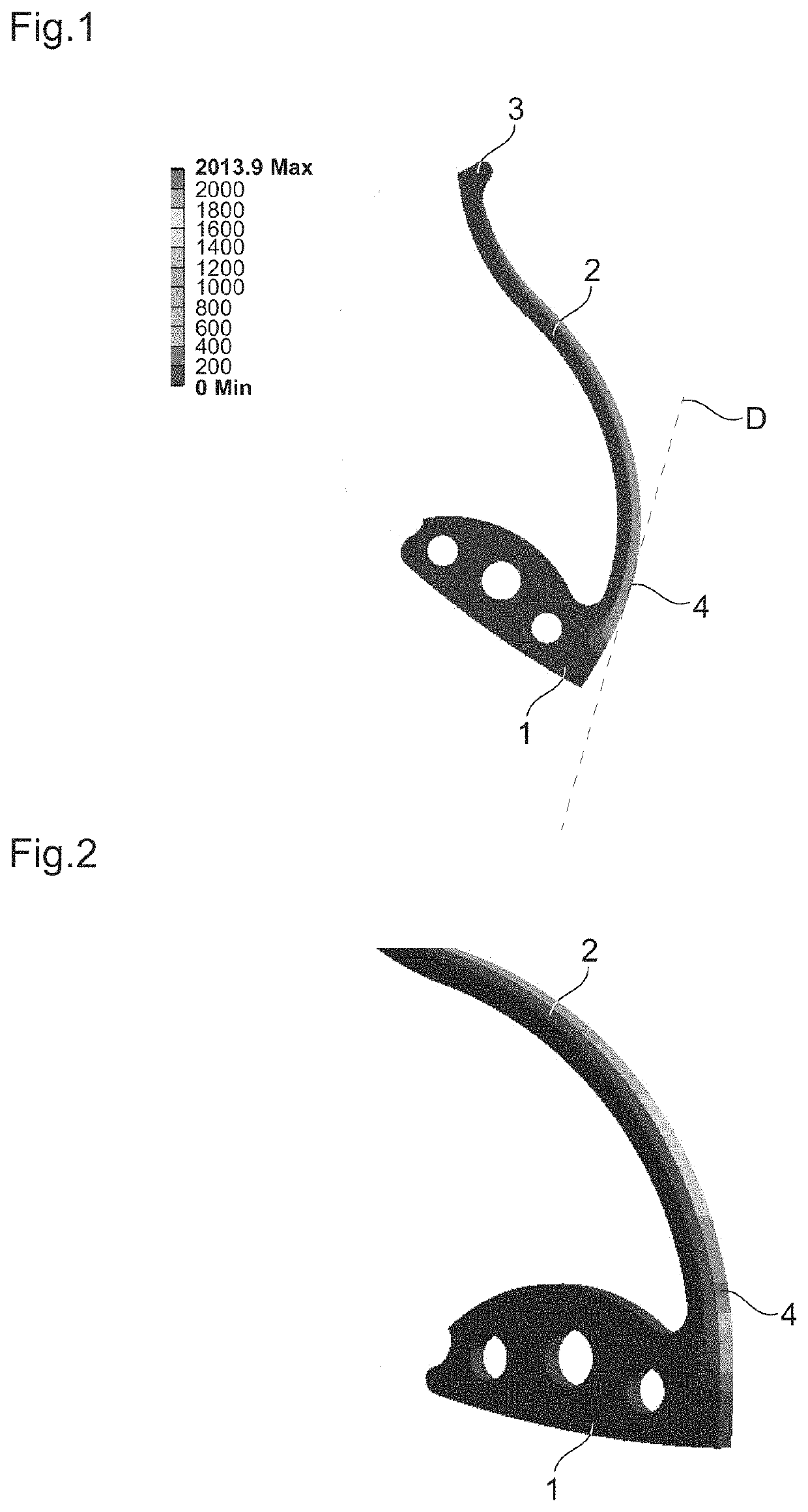
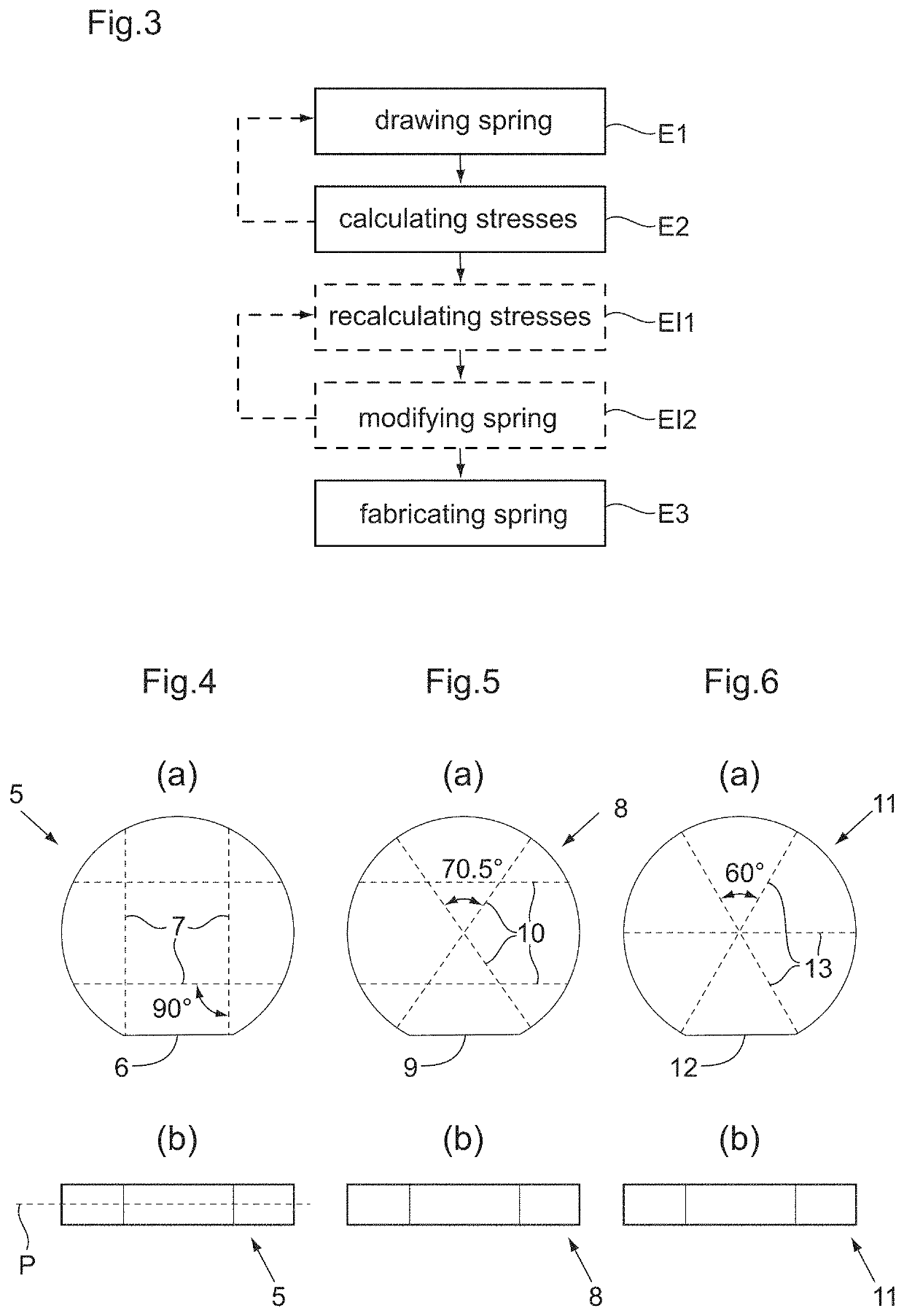
Disclosed is a method of making a timepiece spring from monocrystalline material including the following steps: drawing the spring; identifying one or more zones of weakness of the spring in which or in at least one of which the spring will break in the event of excessive deformation; manufacturing the spring from a wafer of monocrystalline material extending in a determined plane, while orienting the spring in the wafer such that the direction of the macroscopic stresses in the or each zone of weakness when the spring is deformed is substantially parallel to a plane of cleavage of the material intersecting the determined plane. Also disclosed is a timepiece spring obtained by such a method.
Owner:PATEK PHILIPPE SA
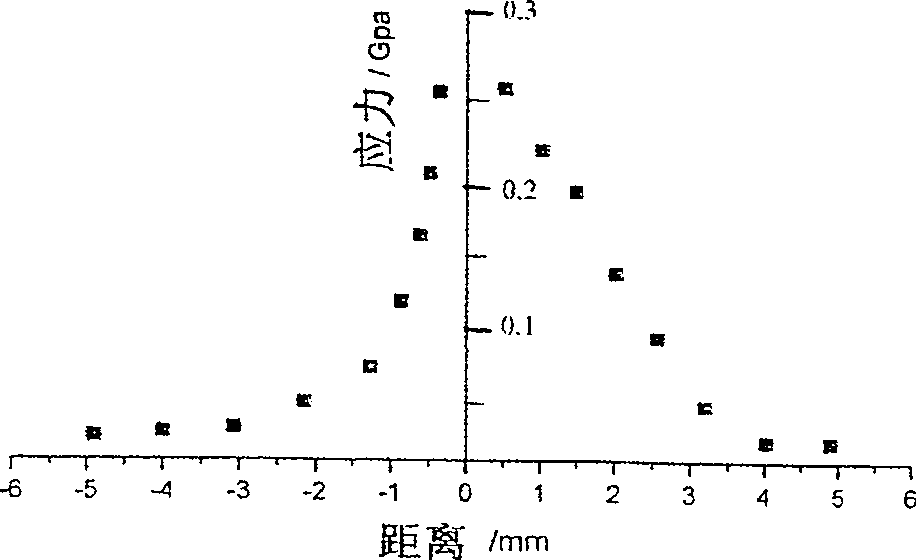
Cross-scale thin film stress test system and test method
PendingCN111380633AEasy to operateSave time and costForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMacroscopic scaleThin membrane
The invention designs a cross-scale thin film stress test system and test method. Firstly, a sample film is placed on a sample plate, helium-neon laser passes through reflected light of an uneven film, an optical signal is converted into an amplified electric signal after the helium-neon laser is received and processed by an array line CCD, the warping degree is calculated by a computer, the macroscopic stress of the film is obtained after formula derivation, and an area needing to be further measured is determined; then the local microscopic stress is continuously measured by utilizing the X-ray diffraction principle under the condition that the sample is not moved. X-rays are reflected by crystal faces to obtain a plurality of beams of diffracted rays, inter-crystal-face deformation is obtained through X-ray diffraction conditions, and stress borne by the microcrystal is obtained through calculation. By means of the technical method, time and materials for monitoring the macroscopicwarping condition and the microcosmic grain arrangement state of the thin film material can be greatly saved, and the stress state of the thin film material can be detected according to the measurement result. The invention has the advantages of simplicity and quickness in operation, time cost saving and wide application range.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A preparation method and structure of a three-dimensional memory
ActiveCN107482015BNo contact failureImprove macro stress distributionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEtchingHemt circuits
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
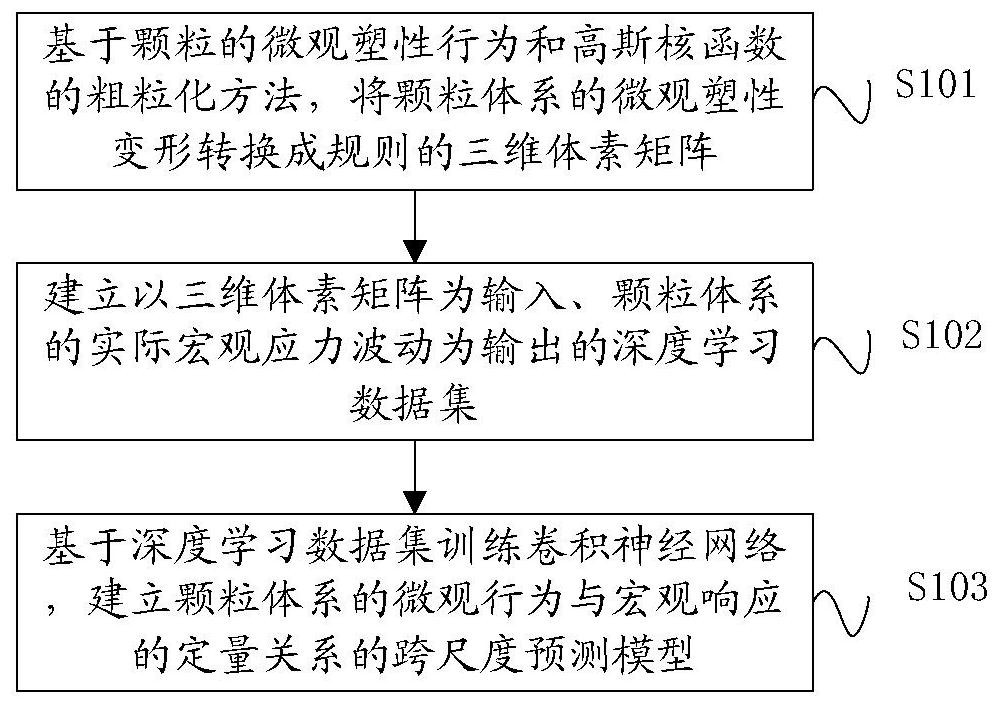
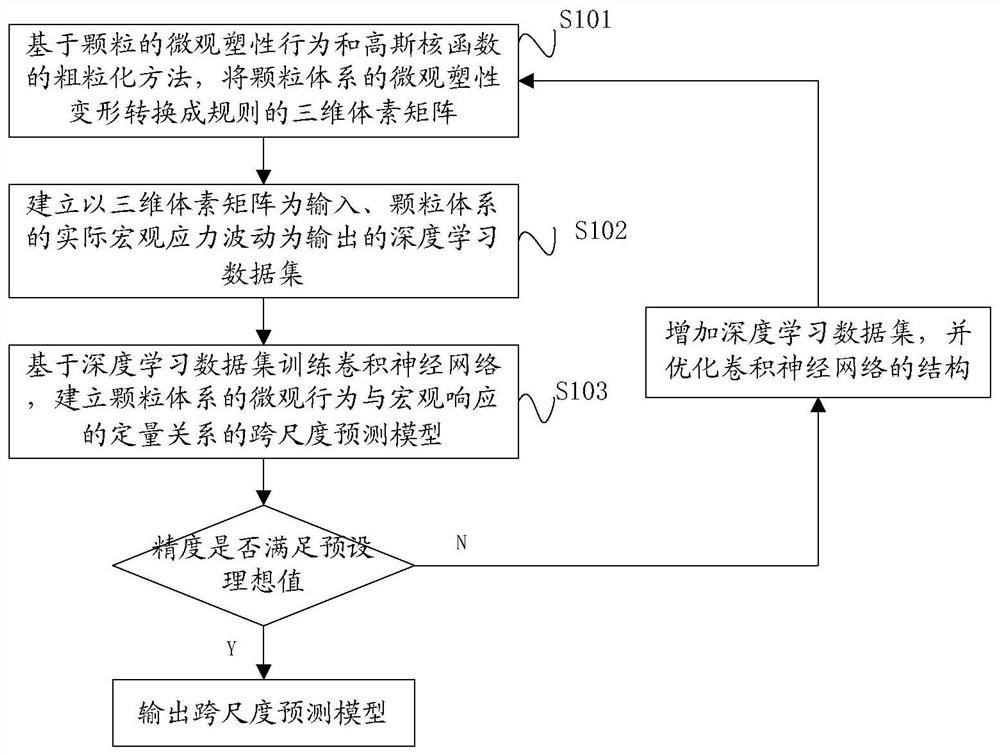
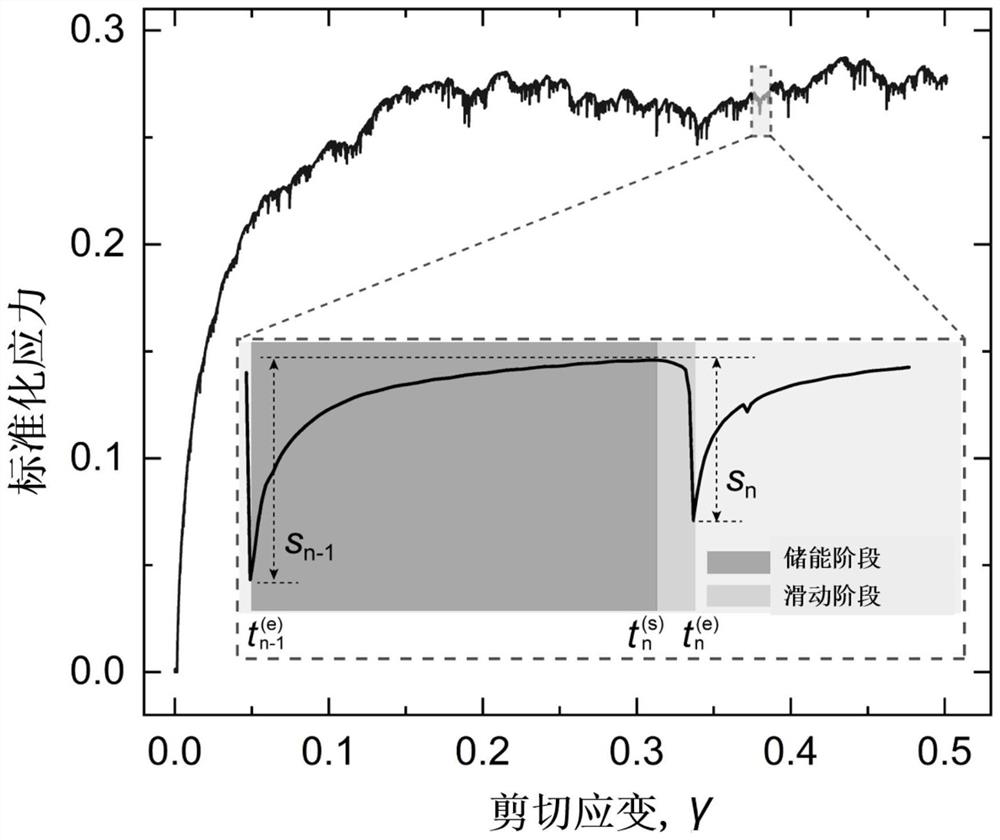
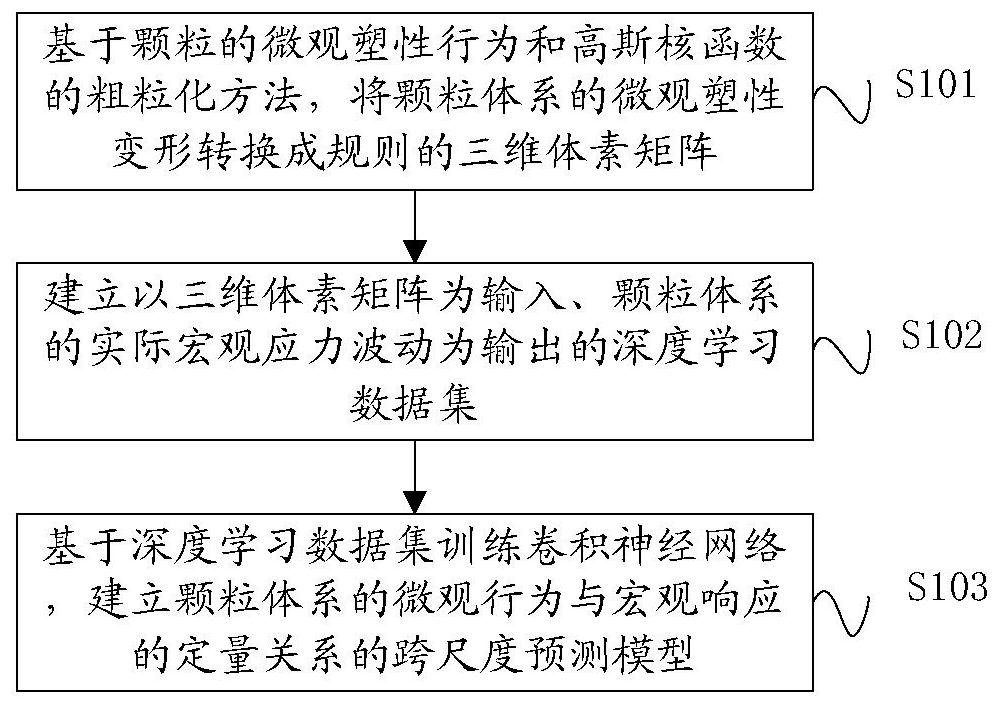
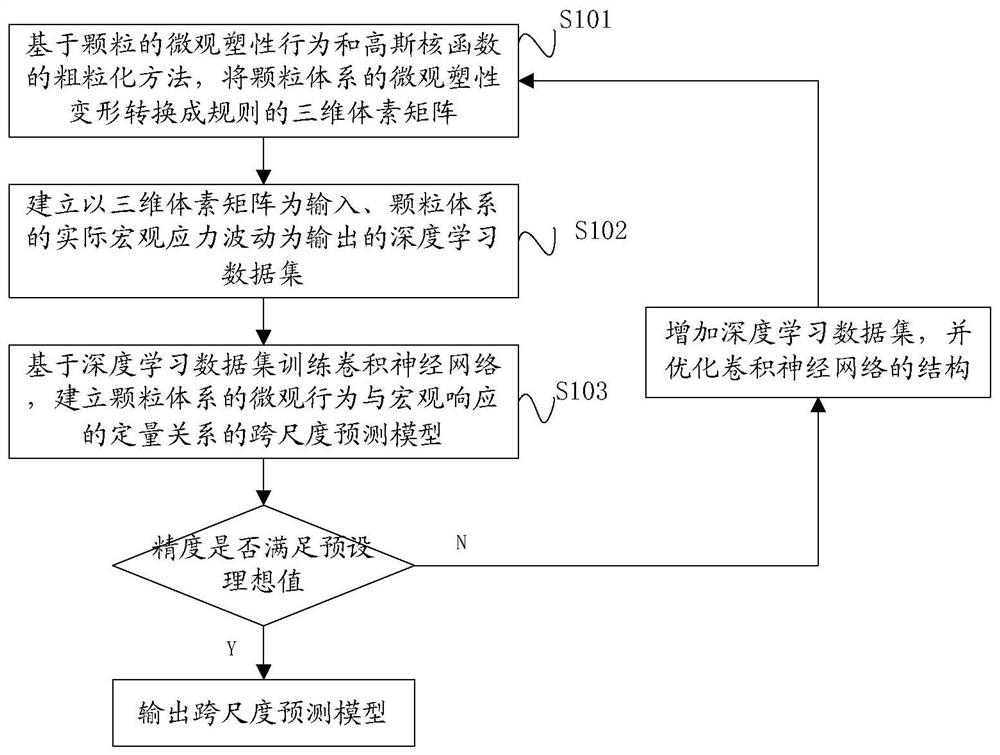
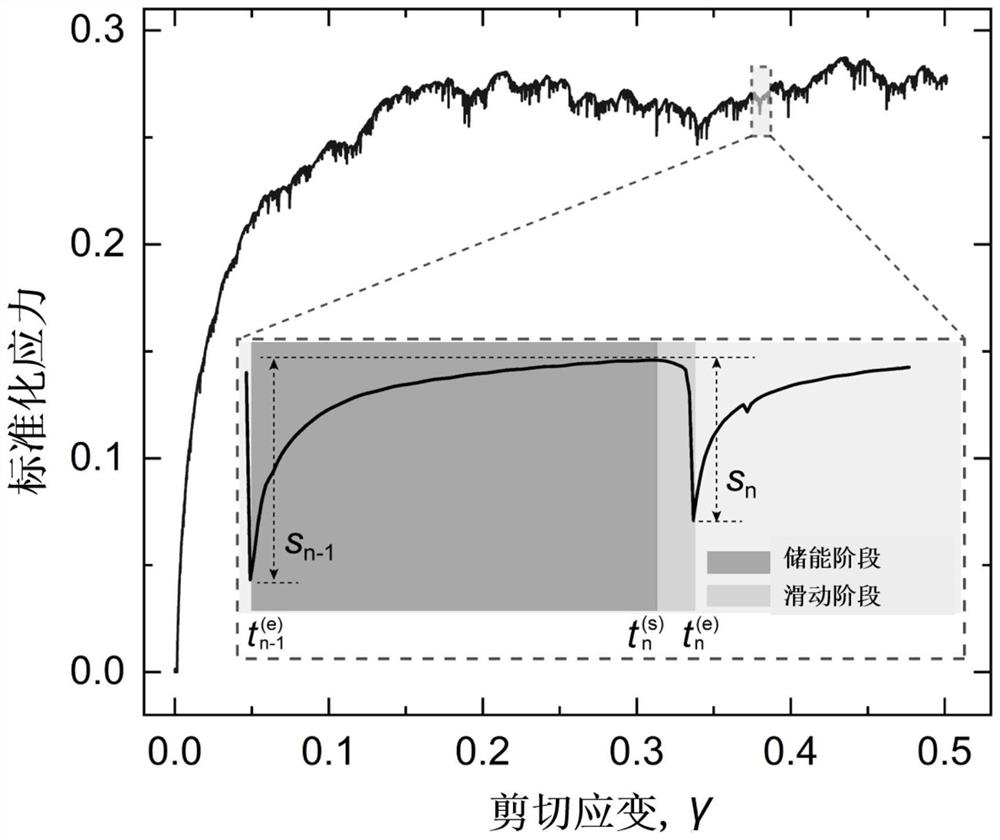
A Prediction Method of Macroscopic Stress Fluctuation in Granular System Based on Convolutional Neural Network
ActiveCN113361184BBuild quantitative relationshipsNew and effective wayDesign optimisation/simulationMicrocosmVoxel
The invention relates to a method for predicting macroscopic stress fluctuations of a granular system based on a convolutional neural network, which comprises the following steps: converting the microscopic plastic deformation of the granular system into regular The three-dimensional voxel matrix; establish the deep learning data set with the three-dimensional voxel matrix as the input and the actual macroscopic stress fluctuation of the granular system as the output; train the convolutional neural network based on the deep learning data set, and establish the microcosmic stress fluctuation of the granular system A cross-scale predictive model of the quantitative relationship between behavior and macroscopic responses. The present invention relates to a method for predicting macroscopic stress fluctuations of granular systems based on convolutional neural networks, which can establish the quantitative relationship of granular systems from microscopic plastic behavior to macroscopic mechanical responses, and is useful for macroscopic stress fluctuation prediction and macro-micro cross-scale research of granular materials. Provides a new and effective way.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A Numerical Simulation Method of Particle Flow for Double-row Pile Foundation Pit Support
ActiveCN113627061BEffective analog restorationMeet engineering needsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMacroscopic scaleEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of numerical simulation, and discloses a numerical simulation method for supporting particle flow in a double-row pile foundation pit, comprising: using Clump particles of different diameters to fit and simulate a unit structural unit, Splicing into the shape of a double-row pile structure; use finite element software to establish a double-row pile structure of the same shape, perform equal stress analysis on the double-row pile structure model, and calculate the particle flow double-row pile value according to the displacement and deformation of the finite element double-row pile. The meso-parameter calibration of the structure; the soil layer particles of the foundation pit are generated based on the particle flow, and the micro-parameters of each soil layer of the foundation pit are calibrated according to the macroscopic stress-strain mechanics curve obtained by the indoor triaxial test; the layered filling method is used to carry out the foundation pit The initial soil layer is generated, and each soil layer of the particle flow foundation pit is given the meso-parameters calibrated by different soil layers; the overall particle flow double-row pile foundation pit support model is established. The invention realizes the numerical simulation of double row pile support.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGSHE GRP
A Discrete Element-Finite Element Coupling Multiscale Simulation Method for Turbine Tenon and Groove Shot Peening
ActiveCN111797554BDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleData acquisition
The invention relates to a discrete element-finite element coupling multi-scale simulation method for turbine tenon-groove shot peening. The steps are as follows: (1) cutting the to-be-researched tenon-groove structure according to the symmetry of the tenon-groove structure, and endowing it with a high strain rate constitutive model ; (2) Set the relative position of the nozzle and the groove according to the actual process, define the size of the nozzle and the angle of the nozzle, and complete the modeling of the groove and the nozzle; (3) Obtain the parameters of the dislocation evolution model based on the stress-strain data under high strain rate, Establish the dislocation evolution model of the tenon and groove material, and correlate the grain size, dislocation density and macroscopic stress and strain; (4) use the DEM module to define the particle generator *Particle, set the projectile parameters, combine the tenon and groove with the nozzle, and set the projectile (5) Carry out numerical simulation to obtain the surface integrity parameters after strengthening of the tenon and groove structure.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Particle system macroscopic stress fluctuation prediction method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN113361184ABuild quantitative relationshipsNew and effective wayDesign optimisation/simulationVoxelData set
The invention relates to a particle system macroscopic stress fluctuation prediction method based on a convolutional neural network, and the method comprises the following steps: converting the microcosmic plastic deformation of a particle system into a regular three-dimensional voxel matrix based on the microcosmic plastic behavior of particles and a coarse graining method of a Gaussian kernel function; establishing a deep learning data set which takes the three-dimensional voxel matrix as input and takes actual macroscopic stress fluctuation of the particle system as output; and training a convolutional neural network based on the deep learning data set, and establishing a cross-scale prediction model of the quantitative relationship between the microscopic behavior and the macroscopic response of the particle system. According to the particle system macroscopic stress fluctuation prediction method based on the convolutional neural network, the quantitative relation of the particle system from the particle microcosmic plastic behavior to the macroscopic mechanical response can be established, and a brand-new and effective way is provided for macroscopic stress fluctuation prediction and macroscopic and microcosmic cross-scale research of particulate matter.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
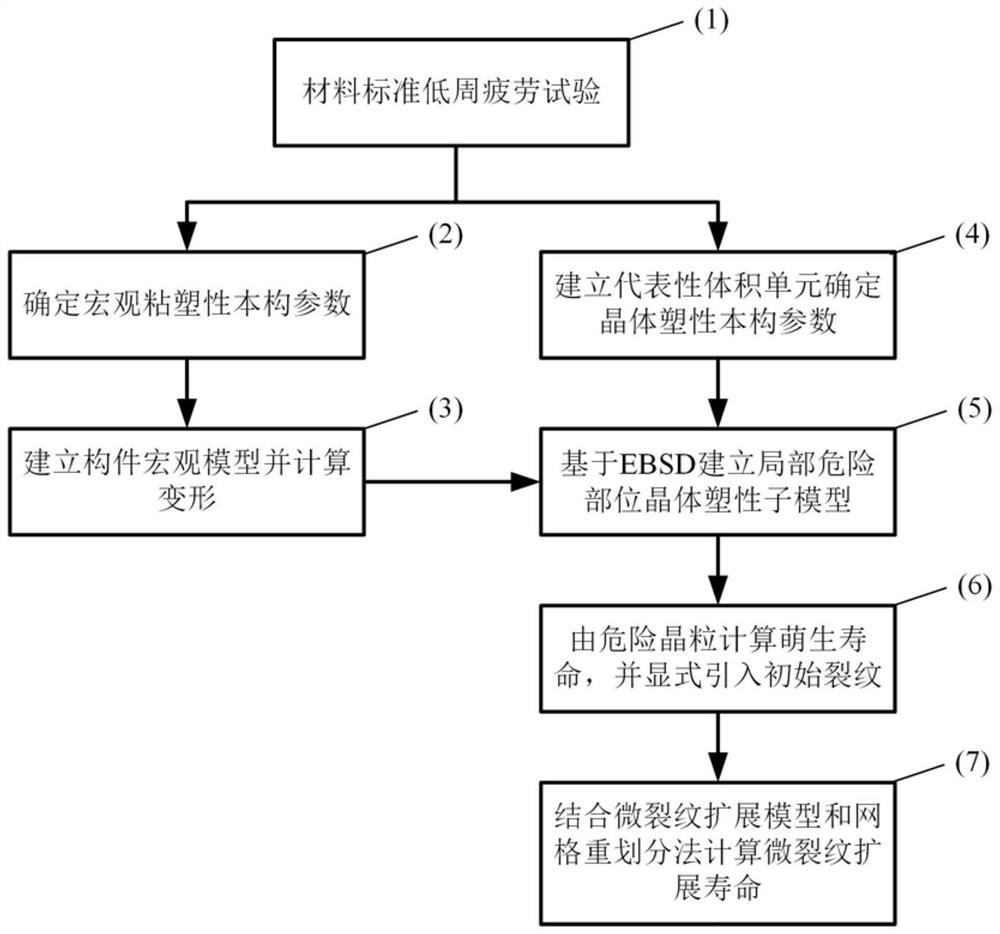
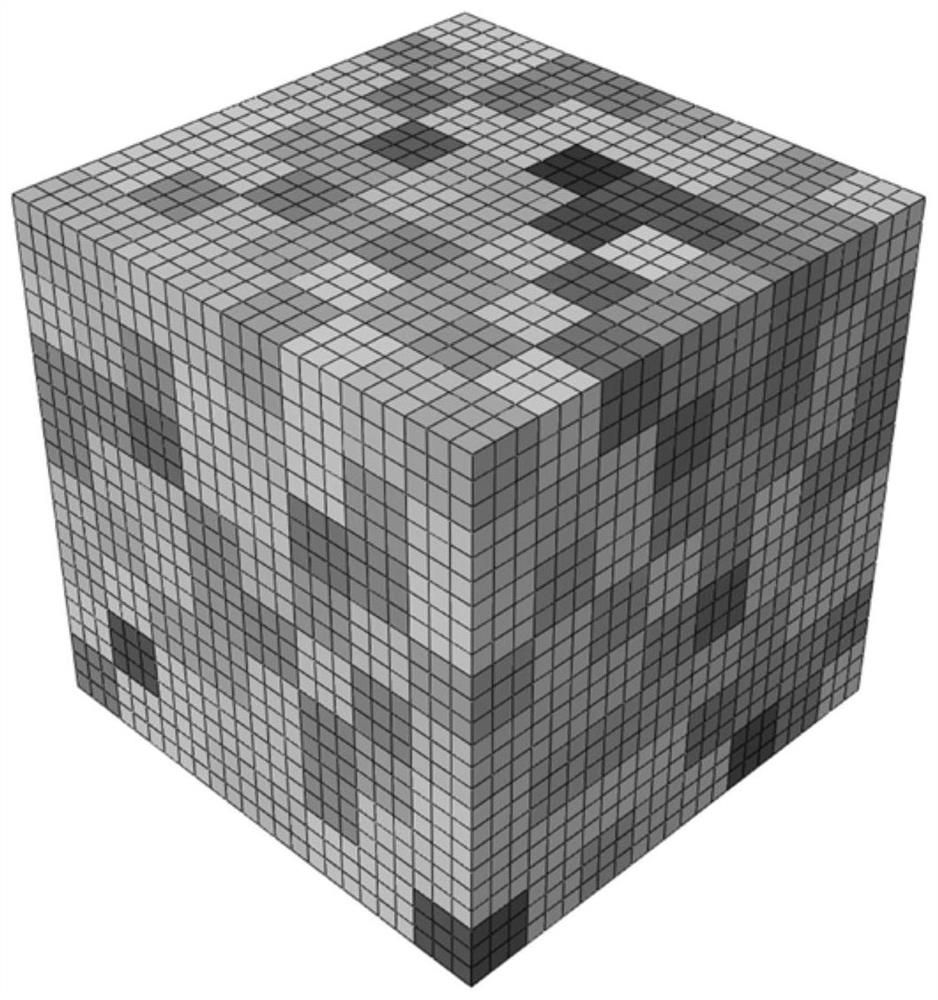
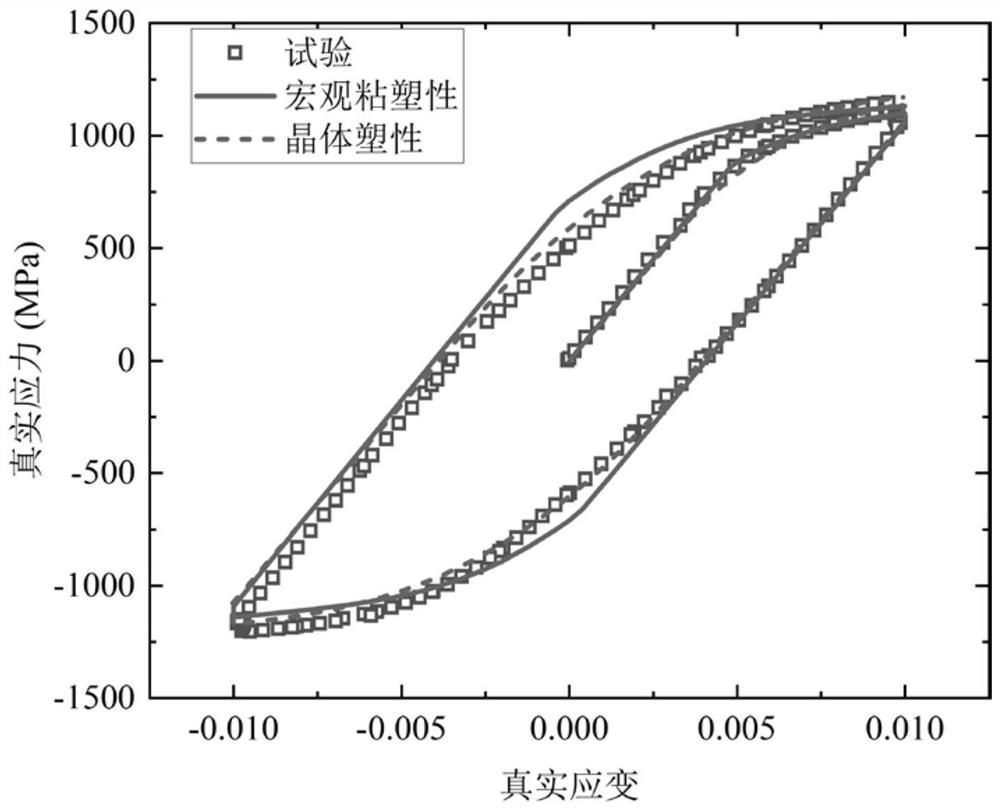
Fatigue microcrack propagation prediction method based on EBSD characterization and crystal plasticity
PendingCN114662356ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelFatigue loading
The invention discloses a fatigue microcrack propagation prediction method based on EBSD characterization and crystal plasticity. The fatigue microcrack propagation prediction method comprises the following steps: acquiring a stress-strain hysteresis loop; compiling a macroscopic viscoplastic constitutive model, and determining parameters of the macroscopic viscoplastic constitutive model; establishing a finite element model of the macroscopic component, endowing the finite element model with viscoplastic constitutive material parameters, carrying out fatigue loading to obtain a macroscopic stress field and a displacement field of the component, and preliminarily determining a dangerous part of the component; compiling a crystal plastic constitutive model, and determining parameters of the model; establishing a local mesoscopic model; dangerous crystal grains are determined; initial cracks are introduced, and the initiation life is determined through a crack initiation model; the accumulated strain energy dissipation density distribution of the cracked crystal grains and the adjacent crystal grains is judged at the tip of the crack, the end point of the initial crack serves as the starting point, and a new crystal penetrating crack continues to be introduced into the slippage system with the maximum accumulated strain energy dissipation density; and determining the microcrack propagation life. The method can consider the influence of the microstructure features of local grains on the crack propagation behavior.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
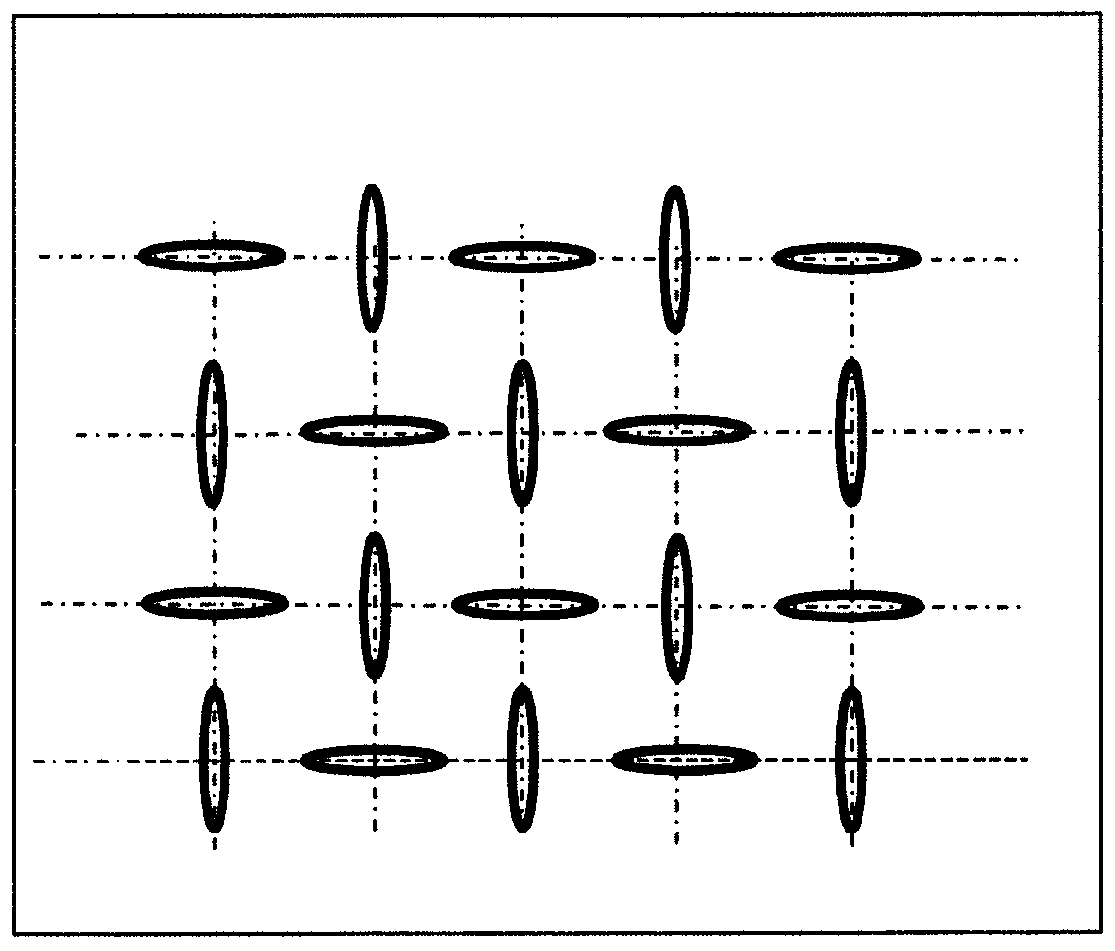
Pore structure with repeating pattern of elongated pores
Disclosed herein are porous structures, systems and devices having porous structures, and methods of making porous structures. Pore structures are disclosed with a repeating pattern of elongated pores designed to provide negative Poisson's ratio behavior under macroscopic stress and strain loading. The pattern may comprise horizontal and vertical oval holes arranged in horizontal and vertical lines spaced at equal distances in both dimensions. The center of each hole is located at the intersection of the two lines. Vertical elliptical holes and horizontal elliptical holes alternate on horizontal and vertical lines, so that any vertical hole is surrounded by a horizontal hole along the line (and vice versa), and the next vertical hole is found to lie on both diagonals superior. Due to the arrangement of the pores, they can also function as cooling and / or damping holes, as well as stress reducing features.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
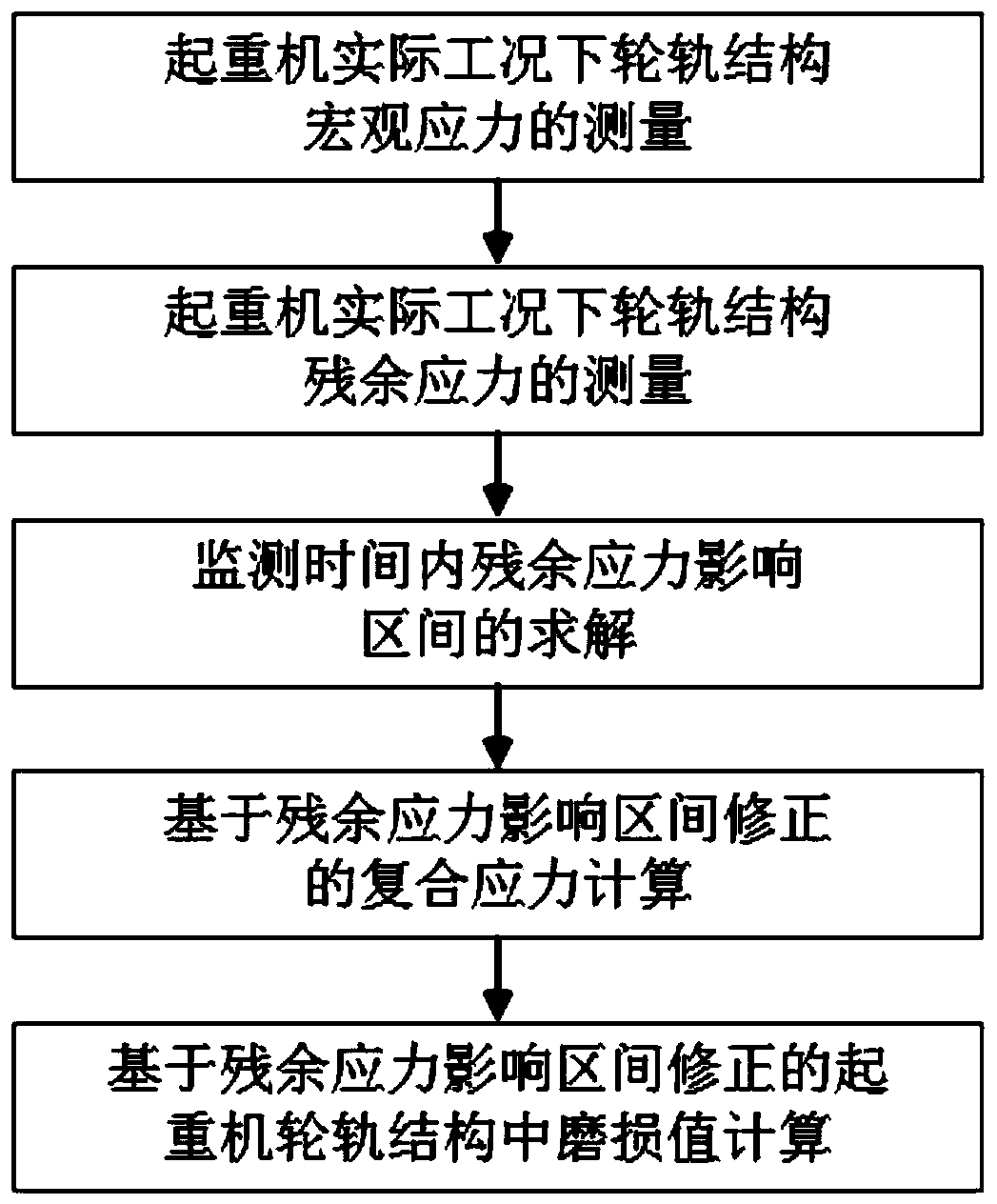
Crane wheel rail wear monitoring method based on residual stress influence interval correction
ActiveCN111241741ADegree of wearImprove securityDesign optimisation/simulationProcess efficiency improvementControl engineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a crane wheel rail wear monitoring method based on residual stress influence interval correction. The method comprises the following steps: S1, measuring macroscopic stress ofa wheel rail structure of a crane under actual working conditions; s2, measuring the residual stress of the wheel rail structure of the crane under the actual working condition; s3, solving a residualstress influence interval in the monitoring time; s4, calculating composite stress based on residual stress influence interval correction; and S5, calculating a wear value in the crane wheel rail structure based on residual stress influence interval correction. The method is high in detection precision, and has important practical significance in real-time monitoring of crane wheel rail wear.
Owner:南京市特种设备安全监督检验研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com