Rotary tool for double-sided friction stir welding, double-sided friction stir welding device, and double-sided friction stir welding method
A rotary tool and friction stir technology, applied in the field of rotary tools for double-sided friction stir welding, can solve problems such as undocumented, inability to obtain joints, and no consideration of metal plate joining, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
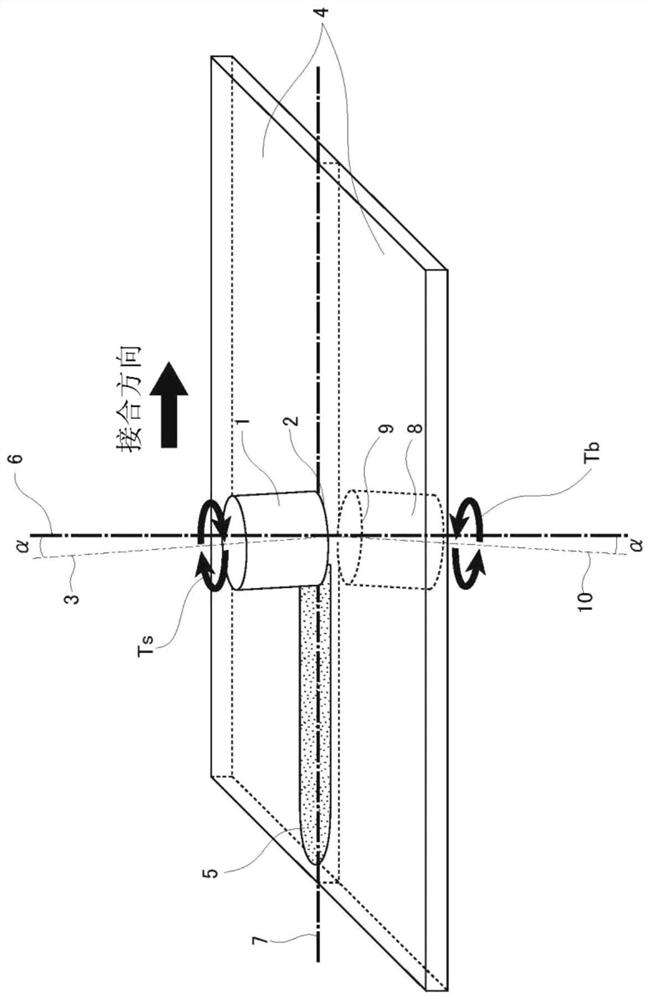
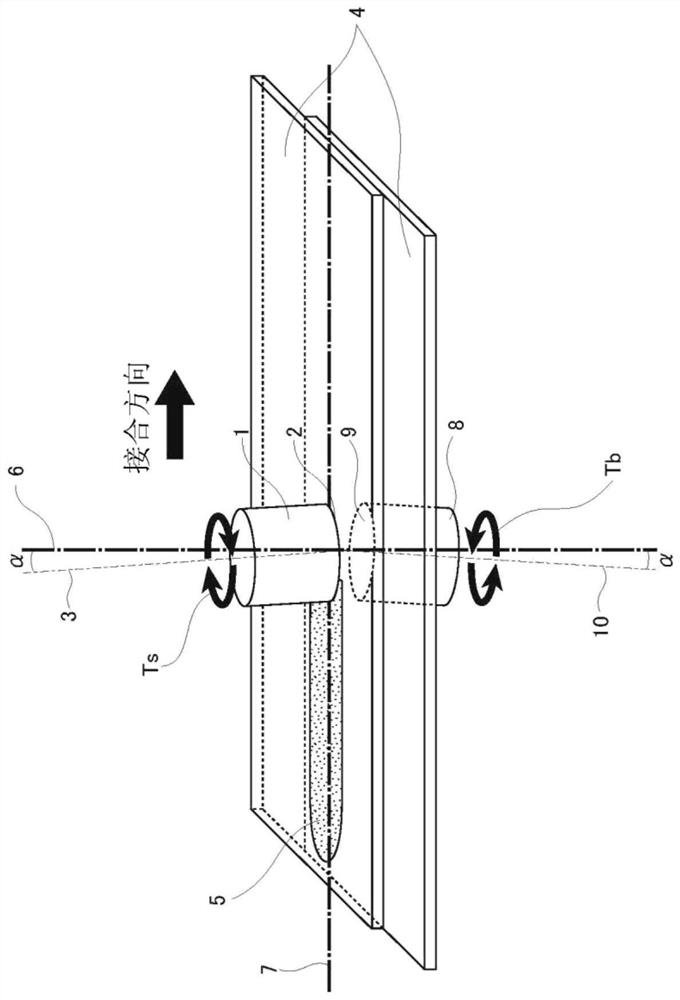
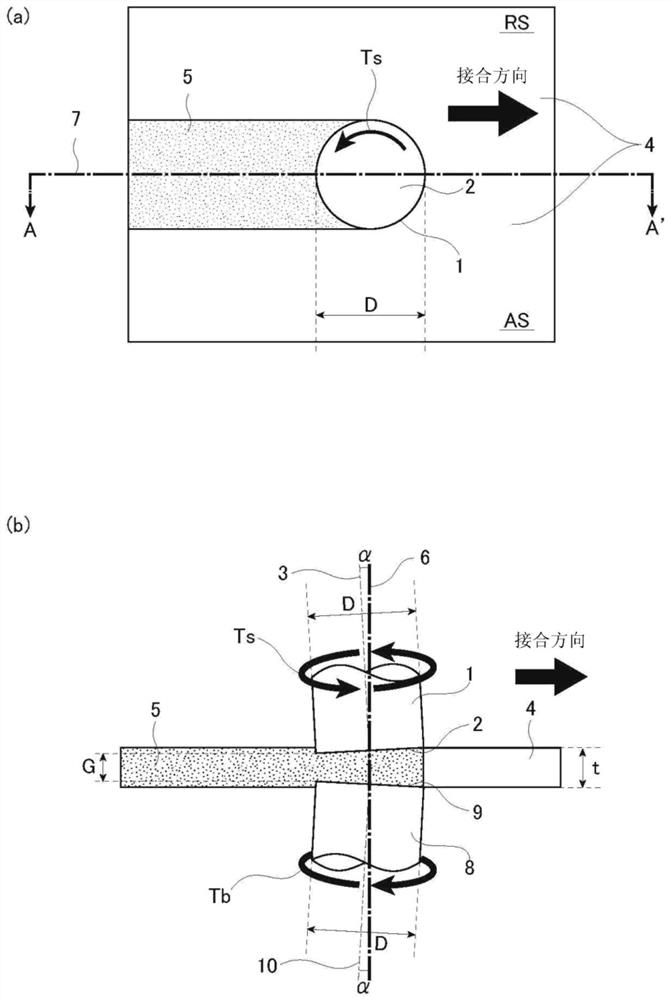
[0089] like Figure 5 (a) and Figure 5 As shown in (b), the rotary tools 1 and 8 of the present invention according to the first embodiment are constituted only by the end portion 11 whose round end is formed into a planar shape 11a. In the planar tip portion 11 , the tip surface that contacts the metal plate is constituted by one plane perpendicular to the rotation axes of the rotary tools 1 , 8 . Unlike conventional rotary tools, this end face does not have a probe protruding toward the metal plate. In addition, if Figure 5 As shown in (b), the rotary tools 1 and 8 can be provided with one or more spiral (helical) steps 12 in the direction opposite to the above-mentioned rotation direction at the tip portion 11 . In addition, the above-described step portion 12 b or groove portion 12 c is provided on the step portion 12 .
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0091] like Image 6 (a) and Image 6 As shown in (b), the rotary tools 1 and 8 according to the second embodiment are composed only of the tip portion 11 having a rounded tip and a convex curved surface 11b, and the tip of the rotary tool protrudes. The conventional rotary tool has a probe that protrudes toward the metal plate, and the shoulder and the probe are in a discontinuous shape, while the convex curved end portion 11 has a continuous shape without the probe and forms an approximately same slope. In other words, in the convex curved terminal portion 1, the terminal surface in contact with the metal plate is constituted by a curved surface (paraboloid, ellipsoid, or spherical surface) protruding toward the center direction, and includes rotation in the vertical direction relative to the metal plate. In the cross-sectional shape of the axis, it is a curve with substantially the same radius of curvature. In addition, if Image 6 As shown in (b), the rotary tools 1 an...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0096] like Figure 7 (a) and Figure 7 As shown in (b), the rotary tools 1 and 8 according to the third embodiment are constituted only by the tip portion 11 having a rounded tip and a concave curved surface 11c, and the tip of the rotary tool is recessed. The conventional rotary tool has a probe that protrudes toward the metal plate, and has a discontinuous shape at the shoulder and the probe, while the concave curved end portion 11 has a continuous shape without the probe, and has approximately the same shape. inclined surface. In other words, in the concave curved end portion 1, the end surface in contact with the metal plate is composed of a curved surface (paraboloid, ellipsoid, or spherical surface) that is concave toward the center direction, and includes the rotation axis in the vertical direction relative to the metal plate. In the cross-sectional shape, it is a curve with approximately the same radius of curvature. Additionally, if Figure 7 As shown in (b), the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com