Method for radionuclide identification by utilizing Compton scattering case statistics
A Compton scattering and radionuclide technology, applied in the field of radionuclide identification using Compton scattering case statistics, can solve the problem of asynchrony between radionuclide imaging and radionuclide identification, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
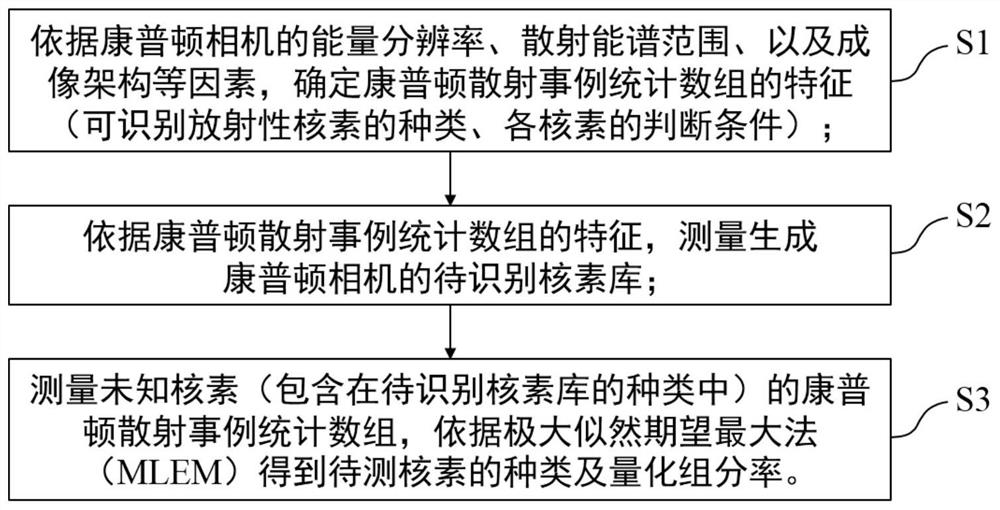
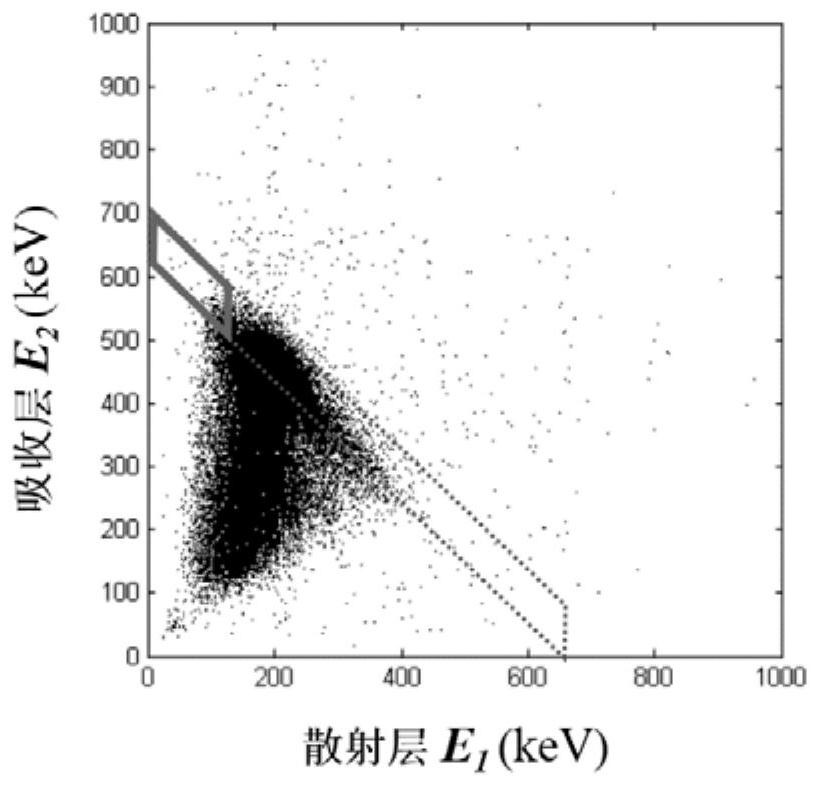
[0030] The invention proposes a method for identifying radionuclides by using statistics of Compton scattering events to realize quantitative identification of unknown radionuclides by a Compton camera. This method first utilizes the statistical array characteristics of the Compton scattering events determined by the Compton camera to measure and generate the nuclide library to be identified by the Compton camera; Statistical array of Su-Compton scattering events, according to the maximum likelihood expectation maximization method to obtain the species of the nuclide to be measured and the quantitative component ratio.
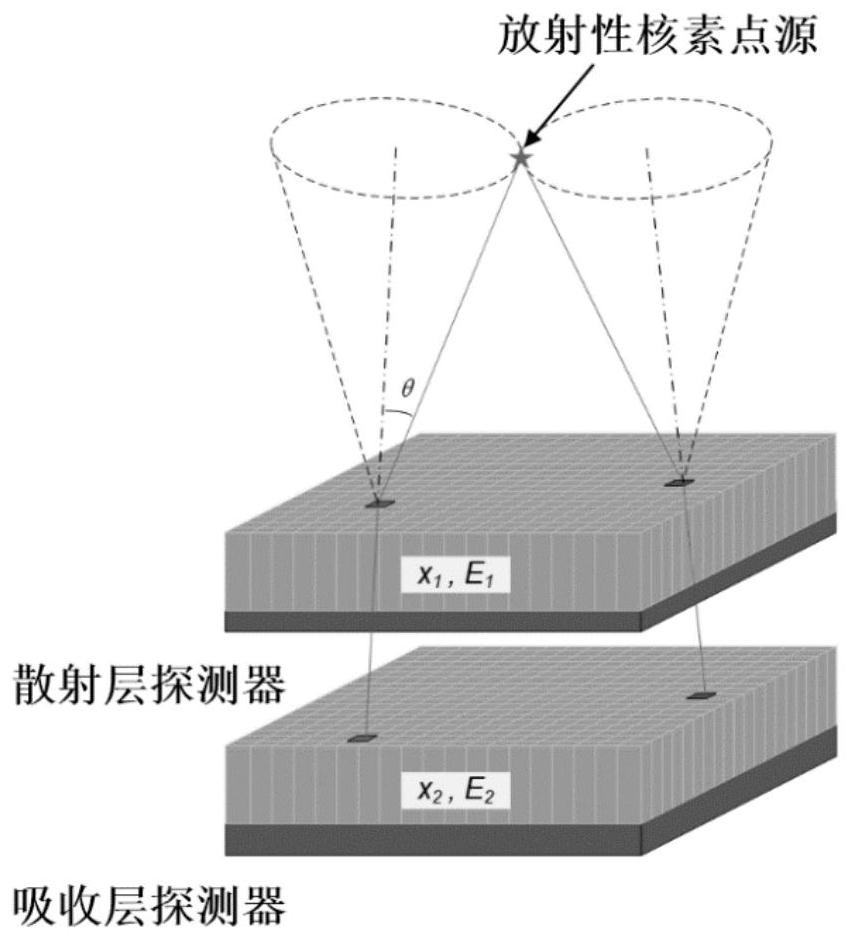
[0031] In this embodiment, a Compton camera with a double-layer detector structure is taken as an example, and the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0032] Step S1: According to the energy resolution of the Compton camera, the range of the scattering energy spectrum, and the imaging structure, et...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com