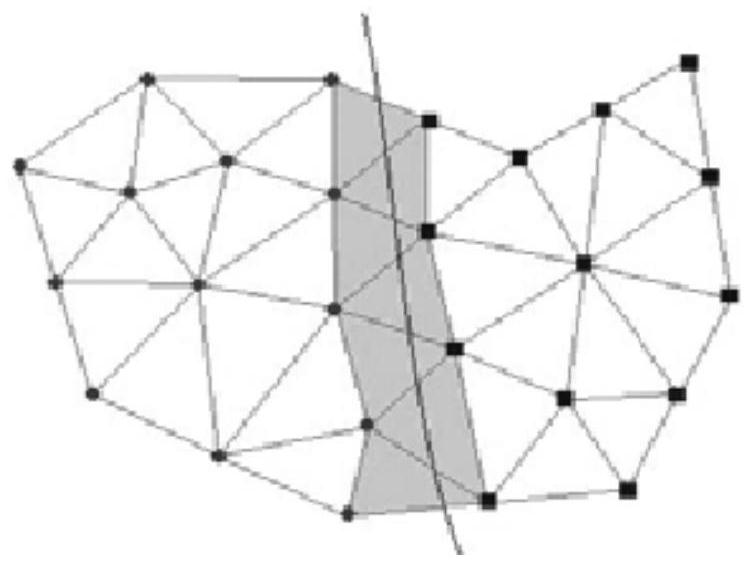
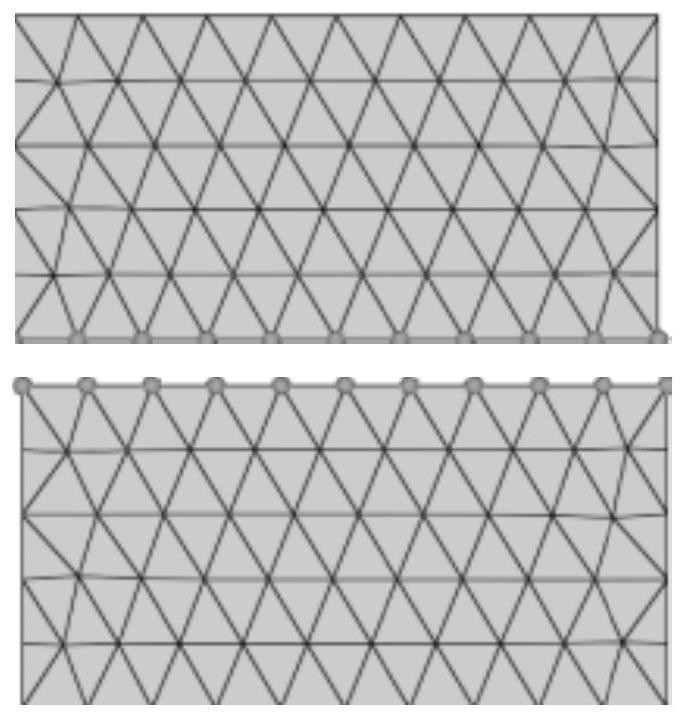
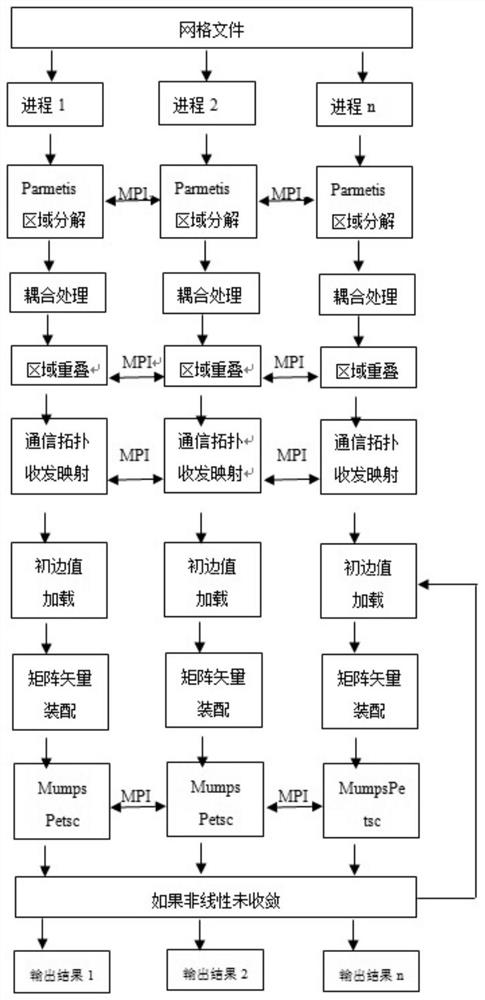
Finite element parallel computing method based on node overlapping type region decomposition without Schwarz alternation
A technology of area decomposition and parallel computing, applied in complex mathematical operations, design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc. Alternate iterative convergence problem and overlapping region selection problem, flexible and efficient solution methods, and the effect of improving program performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the solutions of the present invention, the following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only It is an embodiment of a part of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
[0049] It should be noted that the terms "first" and "second" in the description and claims of the present invention and the above drawings are used to distinguish similar objects, but not necessarily used to describe a specific sequence or sequence. It is to be understood that the data so used are interchangeable under appropriate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com