Heat-shrinkable polyester-based film
A technology of heat shrinkage and polyester, applied to flexible coverings, identification devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of uneven thickness, low heat resistance, loss of film heat shrinkability, etc., and achieve small thickness unevenness , High heat shrinkage effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
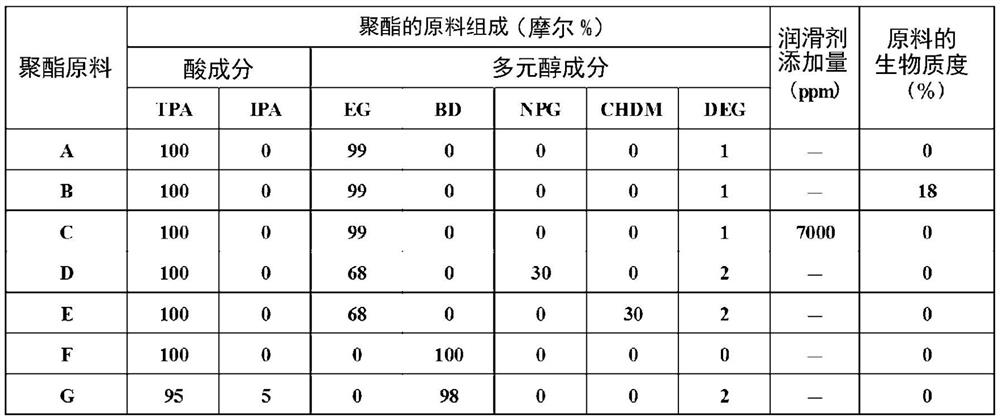
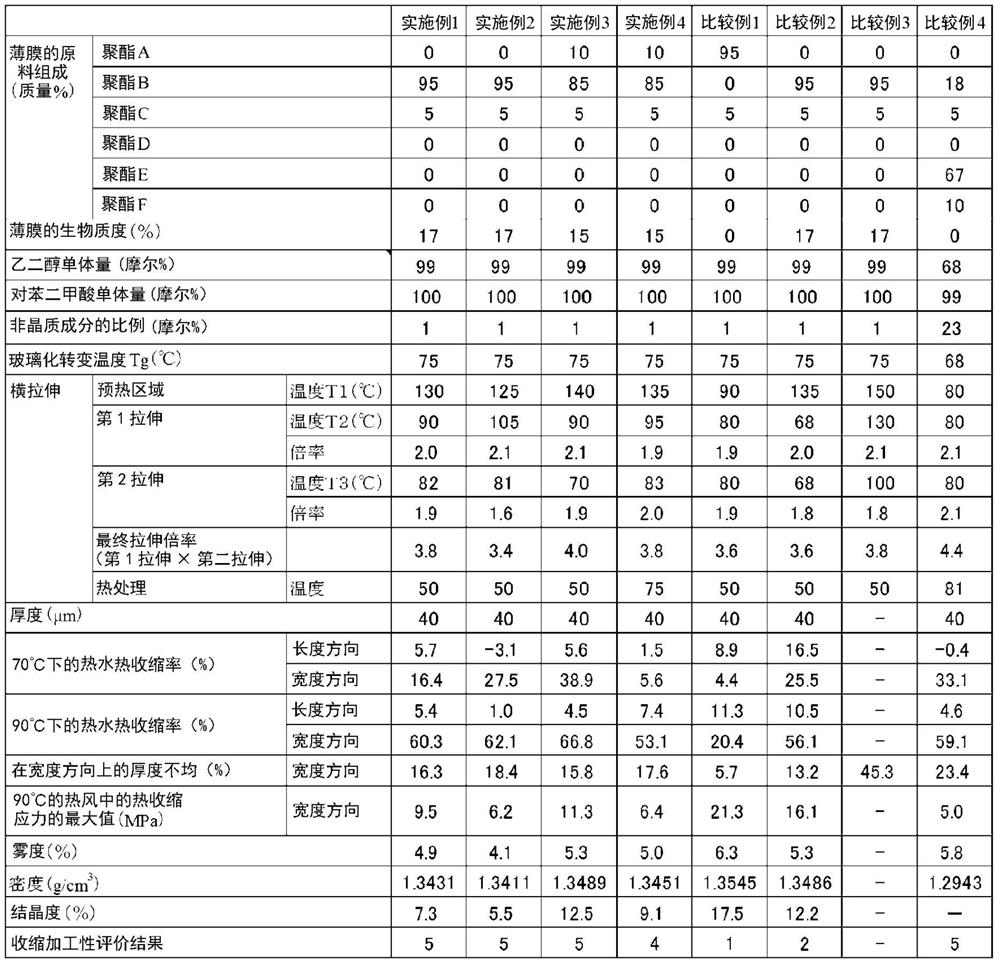
[0149] Mix polyester B and polyester C at a mass ratio of 95:5 and put them into the extruder. The mixed resin was melted at 280° C., extruded from a T die, wound on a rotating metal roll whose surface temperature was cooled to 30° C., and quenched to obtain an unstretched film with a thickness of about 150 μm. The Tg of the unstretched film was 75°C.
[0150] The obtained unstretched film was introduced into a transverse stretching machine (tenter), and preheated at 130° C. for 5 seconds. The preheated film was continuously introduced into the first half of the lateral stretching region, and laterally stretched at 90° C. to 2.0 times. Next, in the second half region of the lateral stretching, it was laterally stretched at 82° C. to 1.9 times. The final transverse stretch ratio was 3.8 times. Finally, after heat treatment at 50° C. for 3 seconds in the heat treatment zone, cool, cut and remove both edges, and wind it into a roll with a width of 500 mm to continuously produc...
Embodiment 2~4
[0152] In said Example 1, the film of Examples 2-4 was manufactured similarly to Example 1 except having changed the conditions of transverse stretching and polyester raw material as shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 5
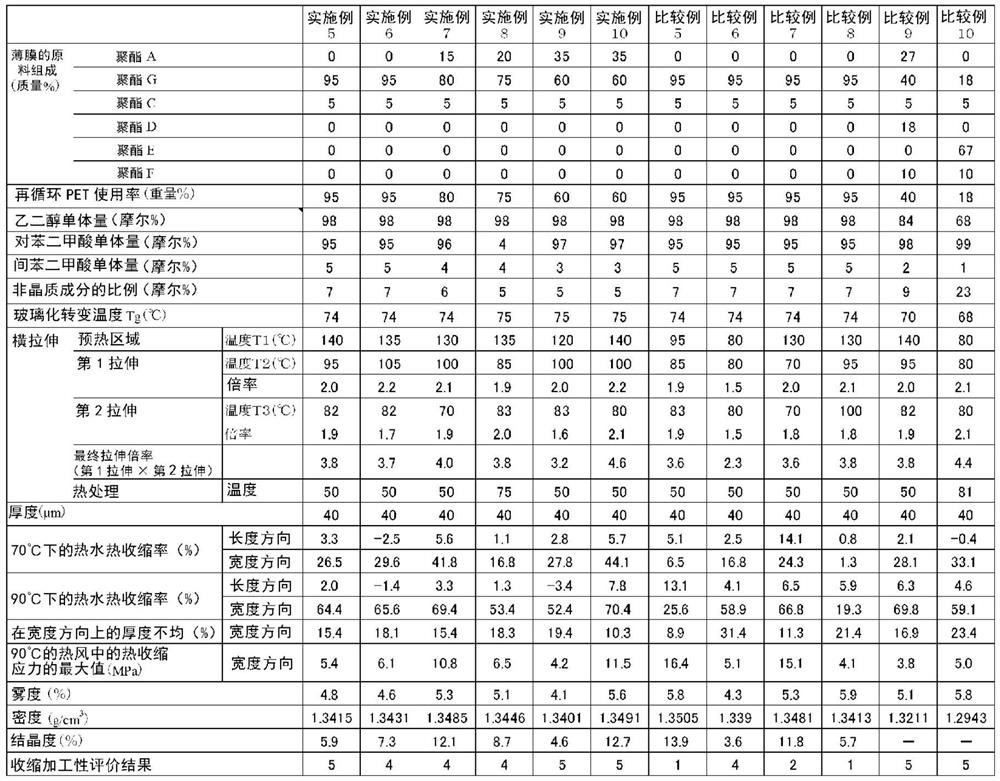
[0168] Mix polyester G and polyester C at a mass ratio of 95:5 and put them into the extruder. The mixed resin was melted at 280° C., extruded from a T die, wound on a rotating metal roll whose surface temperature was cooled to 30° C., and quenched to obtain an unstretched film with a thickness of about 150 μm. The Tg of the unstretched film was 74°C.
[0169] The obtained unstretched film was introduced into a transverse stretching machine (tenter), and preheated at 140° C. for 5 seconds. The preheated film was continuously introduced into the first half of the lateral stretching region, and laterally stretched at 95° C. to 2.0 times. Next, in the second half region of the lateral stretching, it was laterally stretched at 82° C. to 1.9 times. The final transverse stretch ratio was 3.8 times. Finally, heat treatment at 50° C. for 3 seconds in the heat treatment zone, cooling, cutting and removing both edges, and winding into a roll with a width of 500 mm, thereby continuous...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com