A Low-Illumination Image Enhancement Method Based on Local Contrast Stretching
A local contrast and image enhancement technology, which is applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that the image details, texture and clarity of the enhanced image cannot be guaranteed, and the quality of the enhanced image is poor, so as to achieve enhanced brightness contrast and improved The effect of image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
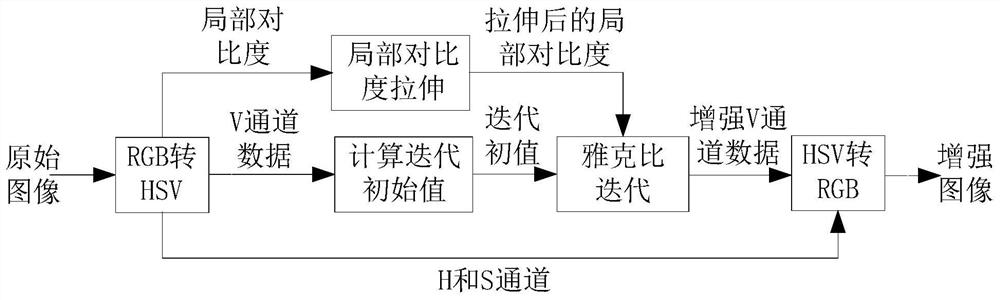
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 This embodiment will be described. A low-illuminance image enhancement method based on local contrast stretching described in this embodiment, the method is specifically implemented through the following steps:
[0020] Step 1, collect the original RGB image, convert the collected original RGB image into an HSV image, and obtain the V channel data, H channel data and S channel data of the HSV image;
[0021] Step 2, performing local contrast stretching on the local contrast of the V channel data of the HSV image to obtain the stretched local contrast;
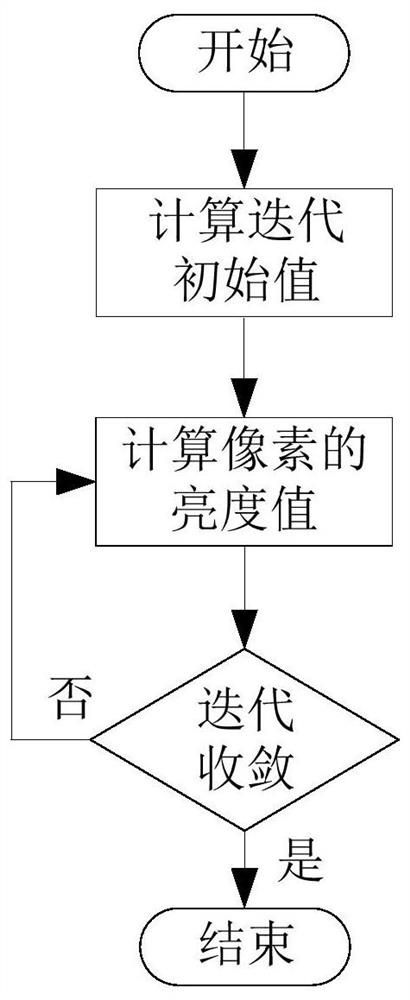
[0022] Step 3, performing grayscale mapping on the V channel data of the HSV image to obtain an initial iteration value;
[0023] Step 4, use the stretched local contrast and iterative initial value to calculate the enhanced V channel data, convert the HSV image formed by the H channel data, the S channel data and the enhanced V channel data into an RGB image, and obta...
specific Embodiment approach 2
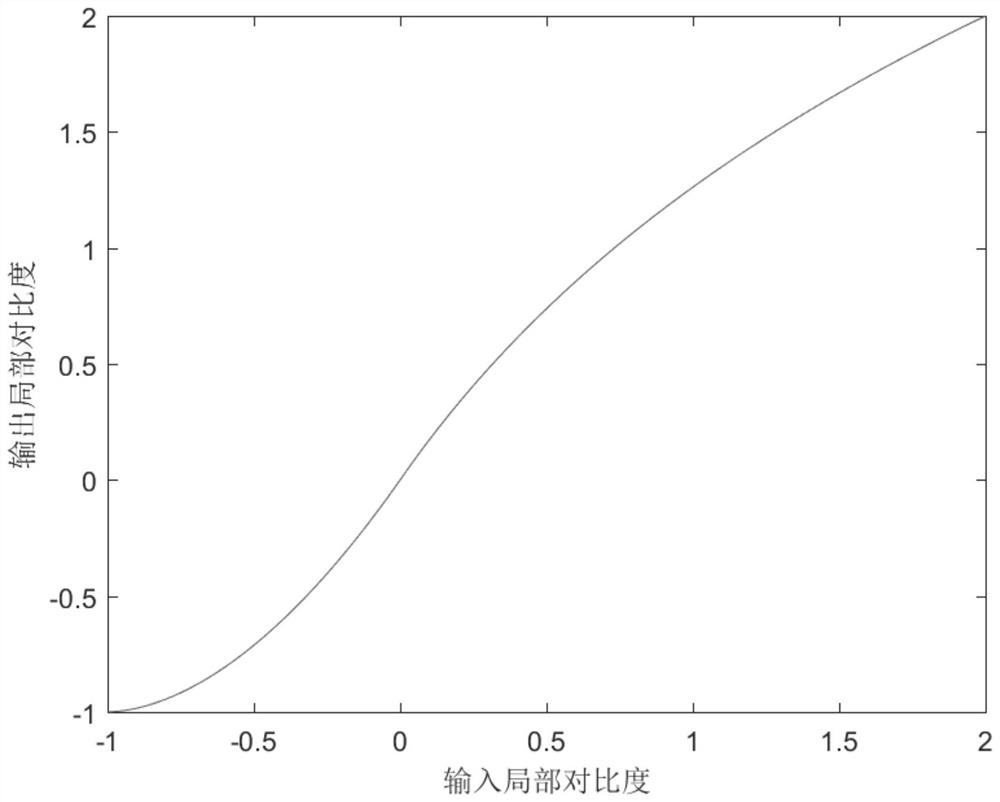
[0024] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 This embodiment will be described. The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment one is: the specific process of the second step is:
[0025] The form of the local contrast stretching function is shown in formula (1):
[0026]
[0027] in: Represents the stretched local contrast of the V channel pixel (x, y), C x,y Indicates the local contrast of the pixel point (x, y) in the V channel data obtained in step 1; A(0.45), B(0.45), A(1) and B(1) are intermediate functions.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is: the expressions of the intermediate functions A (0.45), B (0.45), A (1) and B (1) are respectively:
[0029] A(0.45)=max[(C x,y +1) 0.45 ] (2)
[0030] B(0.45)=min[(C x,y +1) 0.45 ] (3)
[0031] A(1)=max(C x,y +1) (4)
[0032] B(1)=min(C x,y +1) (5)
[0033] Among them: max means to take the maximum value, and min means to take the minimum value.
[0034] In this embodiment, in the process of obtaining the maximum and minimum values, it is necessary to traverse the local contrast of each pixel in order to obtain (C x,y +1) 0.45 The maximum and minimum values of (C x,y +1) maximum and minimum values.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com