Polarimetric SAR image terrain classification method based on self-supervised representation learning
A technology for classification and characterization of ground objects, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of poor robustness, low classification accuracy of classifiers, and a large number of other problems, and achieve the effects of enhancing robustness, improving classification accuracy, and reducing demand.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
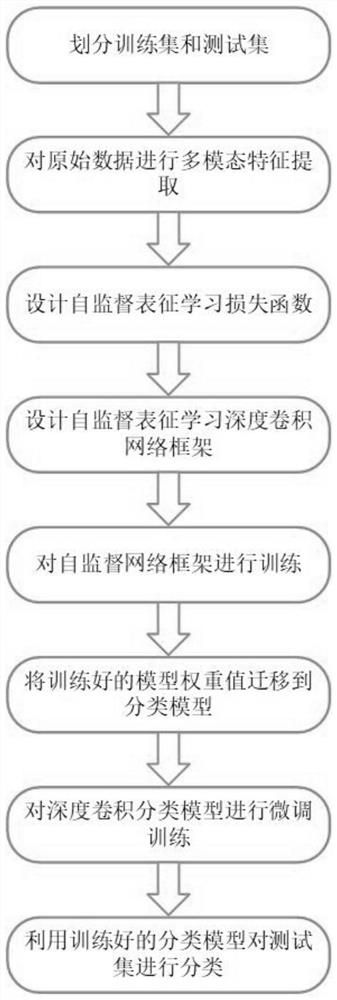
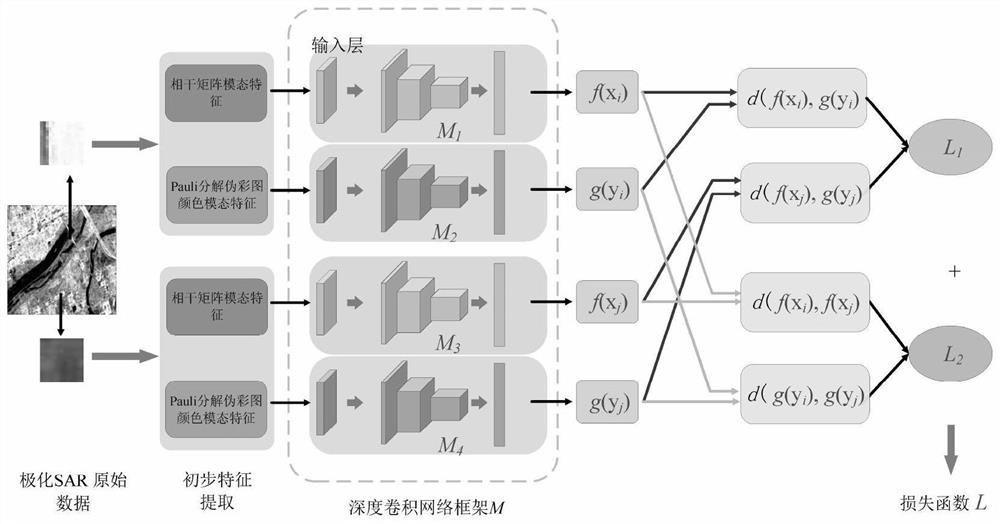
[0032] The implementation scheme of this example is: select two modal feature representations of polarimetric SAR data, and use the designed loss function and deep convolutional network framework to perform self-supervised representation learning features without using label information Extract the training, and then initialize the deep convolutional network classifier with the learned parameters, then fine-tune the classifier with the labeled training samples, and finally classify the test samples.
[0033] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0034] Step 1, divide the training set and test set.
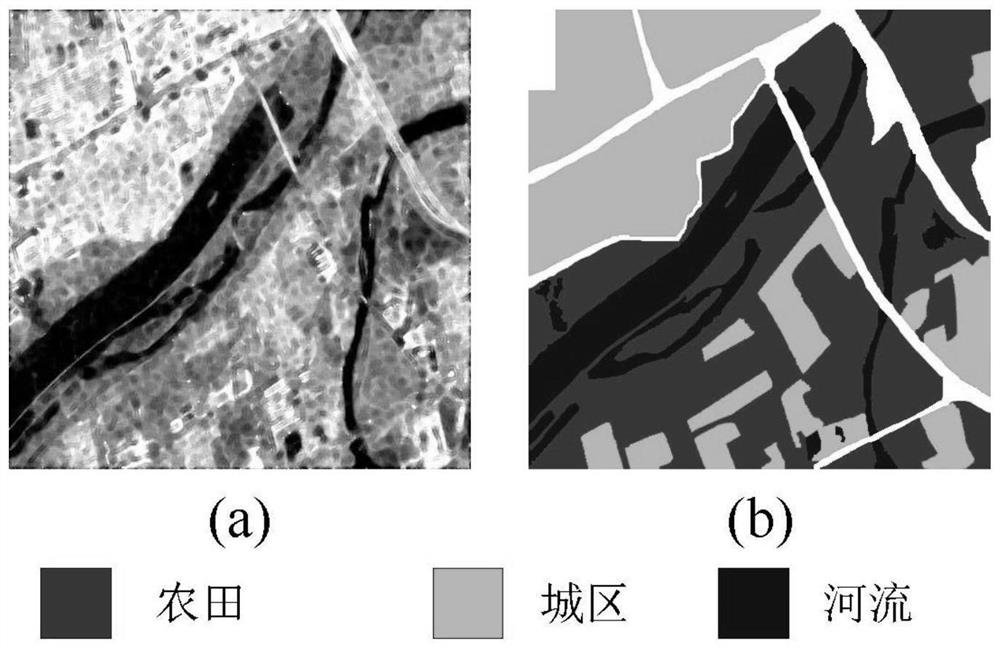
[0035] Obtain polarimetric SAR image data from different satellites, select an image sub-block from the image data as a data set S, and randomly select 5% of the unlabeled pixel data from the data set as the training set S for self-supervised representation learning 1 , randomly select 1% of the pixel data with label information as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com