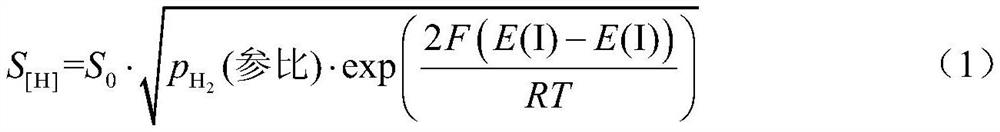A device and method for nondestructively measuring hydrogen content in solid steel
A hydrogen content, solid technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of slow measurement speed, small hydrogen diffusion coefficient, uneven distribution of hydrogen, etc., to achieve accurate testing, simple testing steps, and testing speed fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
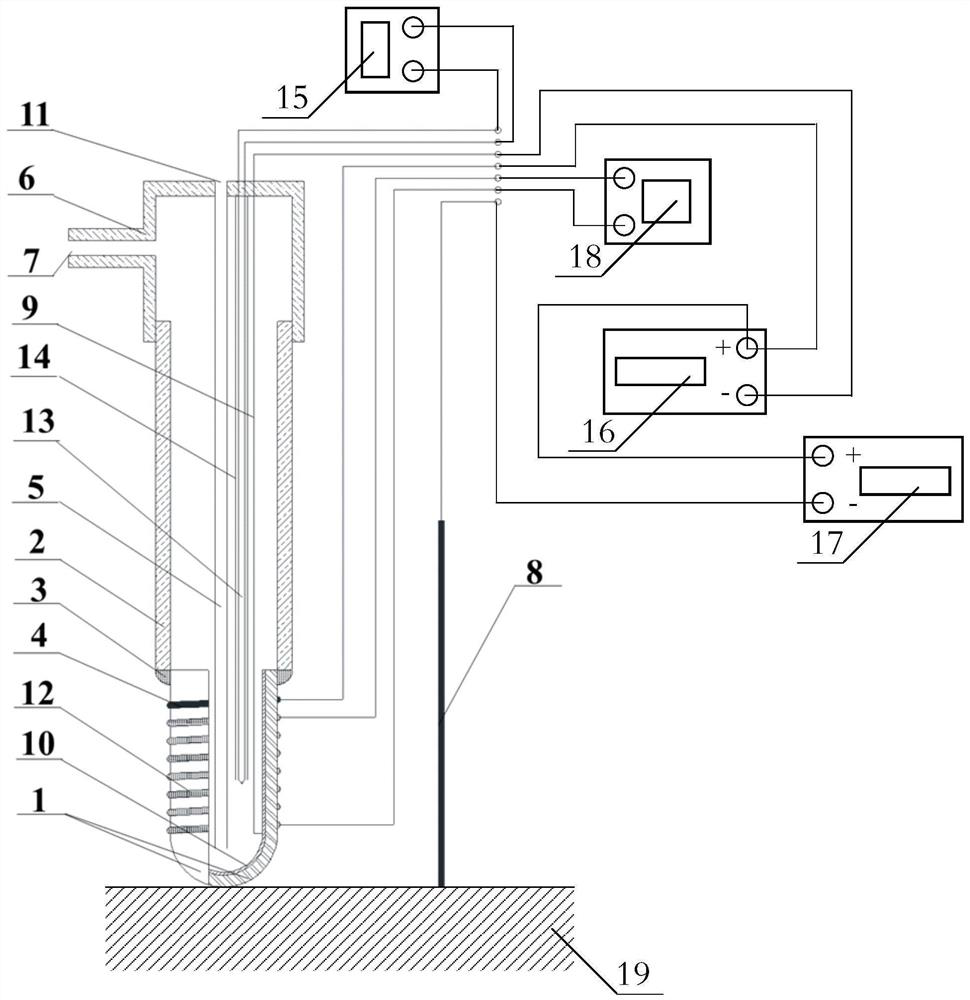
[0077] The structure of the device for non-destructive measurement of hydrogen content in solid steel is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes a high-temperature proton conductor 1, a support tube 2 and a sealing cover 6;
[0078] The high-temperature proton conductor 1 is barrel-shaped, the outer wall is coated with a porous electrode 4 and the auxiliary thermal electrode 12, and the inner wall is coated with a reference electrode 10; the top of the high-temperature proton conductor 1 and the bottom end of the support tube 2 are sealed and bonded by a high-temperature adhesive 3 fixed together;
[0079] The support pipe 2 is cylindrical, and the top end is sealed and fixed with the sealing cover 6; the sealing cover 6 is an inverted barrel shape, and the side wall is provided with an air outlet pipe 7, the air inlet pipe 5 passes through the top plate of the sealing cover 6, and the bottom of the air inlet pipe 5 The end is located inside the high temperature proton cond...
Embodiment 2
[0099] The structure of the device for non-destructively measuring the hydrogen content in solid steel is the same as in Example 1;
[0100] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0101] (1) The reference gas is N 2 -H 2 Standard gas; solid steel material to be tested is 304 austenitic steel;
[0102] (2) The target temperature is 1000±0.5°C (1273±0.5K);
[0103] (3) The measured voltage between the inner wall and the outer wall of the high-temperature proton conductor 1 is -0.1136V, and the voltage between the inner wall of the high-temperature proton conductor 1 and the solid steel 19 to be measured is -0.0872V measured by the second voltmeter 17;
[0104] S at 1000°C 0 =5.79ml / 100g;
[0105] Measured hydrogen content S [H] = 2.33ml / 100g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com