High-speed train brake disc material with stable friction coefficient and preparation method thereof
A high-speed train, friction coefficient technology, applied in the direction of brake discs, brake types, brake components, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient friction stability, high low temperature brittleness tendency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
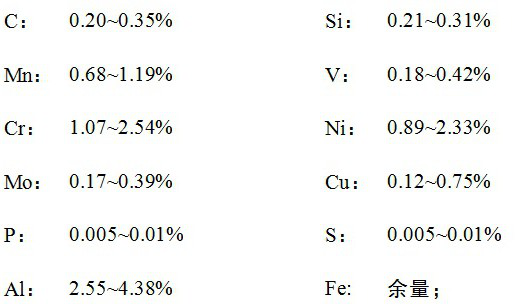
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, a high-speed train brake disc material with a stable friction coefficient, in terms of mass percentage, its raw materials and proportioning are as follows:
[0036]
[0037] A preparation method of a high-speed train brake disc material with a stable coefficient of friction, comprising the following steps:
[0038] S1. Proportion the brake disc elements according to the above composition requirements, and add them into the electric furnace to heat to 1580°C to fully melt them to obtain molten steel;
[0039] S2. Adding a nucleating agent to fully molten molten steel, followed by casting into an ingot;
[0040] S3. Forging is carried out by multi-directional die forging to obtain a forging billet;
[0041] S4. The obtained forged billet is subjected to three-stage performance heat treatment of normalizing-quenching-tempering, that is, the obtained high-stable train brake disc material.
[0042] The high-speed train brake disc material wit...
Embodiment 2
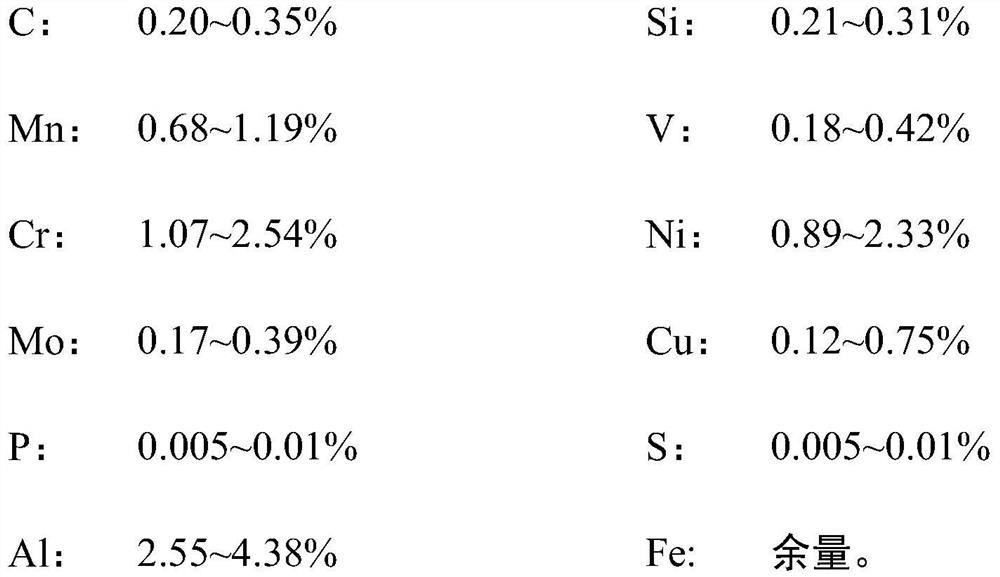
[0053] A high-speed train brake disc material with a stable coefficient of friction, in terms of mass percentage, its raw materials and proportions are as follows:
[0054]
[0055] A preparation method of a high-speed train brake disc material with a stable coefficient of friction, comprising the following steps:
[0056] S1. Proportion the elements of the brake disc according to the above composition requirements, and add it into the electric furnace to heat it to 1690°C to fully melt it to obtain molten steel;
[0057] S2. Adding a nucleating agent to fully molten molten steel, followed by casting into an ingot;
[0058] S3. Forging is carried out by multi-directional die forging to obtain a forging billet;
[0059] S4. The obtained forged billet is subjected to three-stage performance heat treatment of normalizing-quenching-tempering, that is, the obtained high-stable train brake disc material.
[0060] The high-speed train brake disc material with a stable friction c...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is only:
[0072] A high-speed train brake disc material with a stable friction coefficient, its raw materials and proportions are as follows: C: 0.25%; Si: 0.25%; Mn: 0.83%; V: 0.30%; Cr: 1.68% ; Ni: 1.96%; Mo: 0.25%; Cu: 0.50%; P: 0.008%; S: 0.006%; Al: 3.50%;
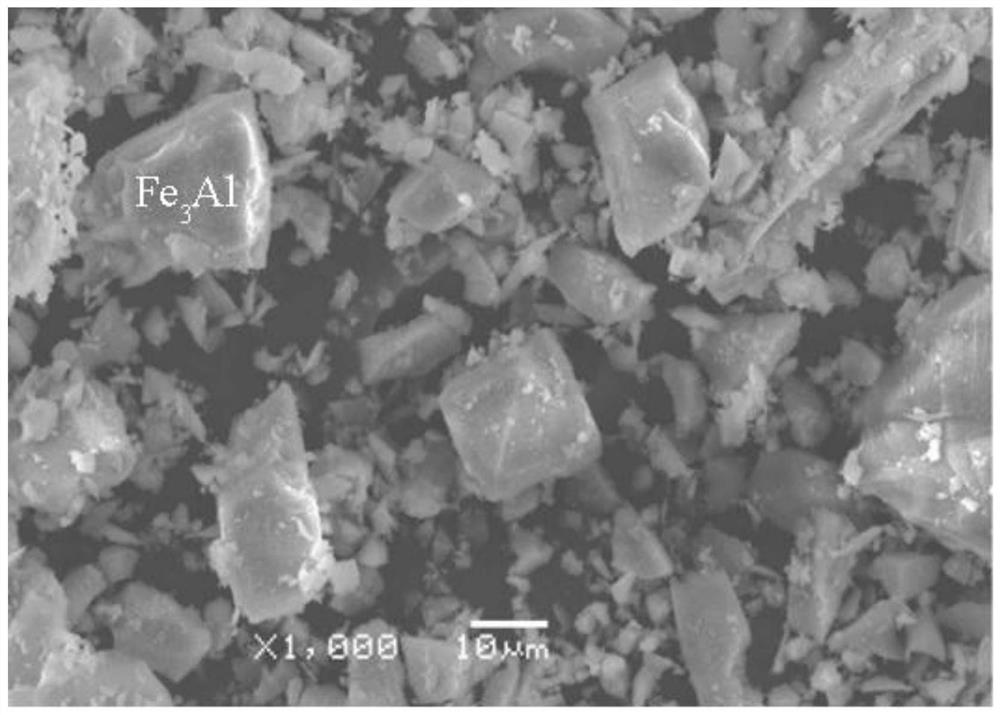
[0073] A preparation method of a high-speed train brake disc material with a stable coefficient of friction, the Fe 3 The particle size range of the Al ultrafine phase is 5-15 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com