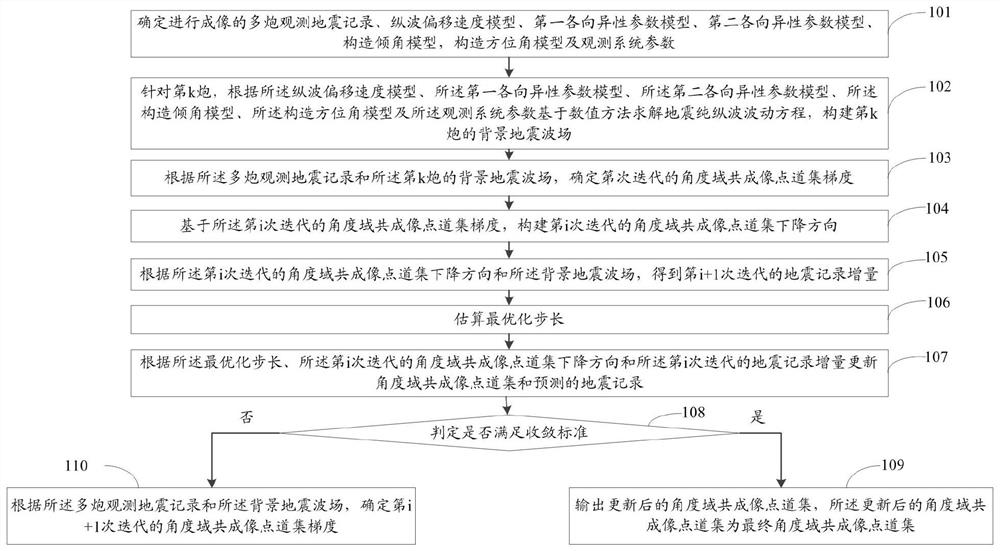
A method and system for extracting common imaging point gathers in angle domain of seismic data
A technology for common imaging point gathers and seismic data, which is applied in the field of seismic data angle domain common imaging point gather extraction, can solve the problems of unbalanced amplitude, limited acquisition aperture, and low resolution of angle domain common imaging point gathers, etc. To achieve the effect of improved accuracy, high signal-to-noise ratio and high resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
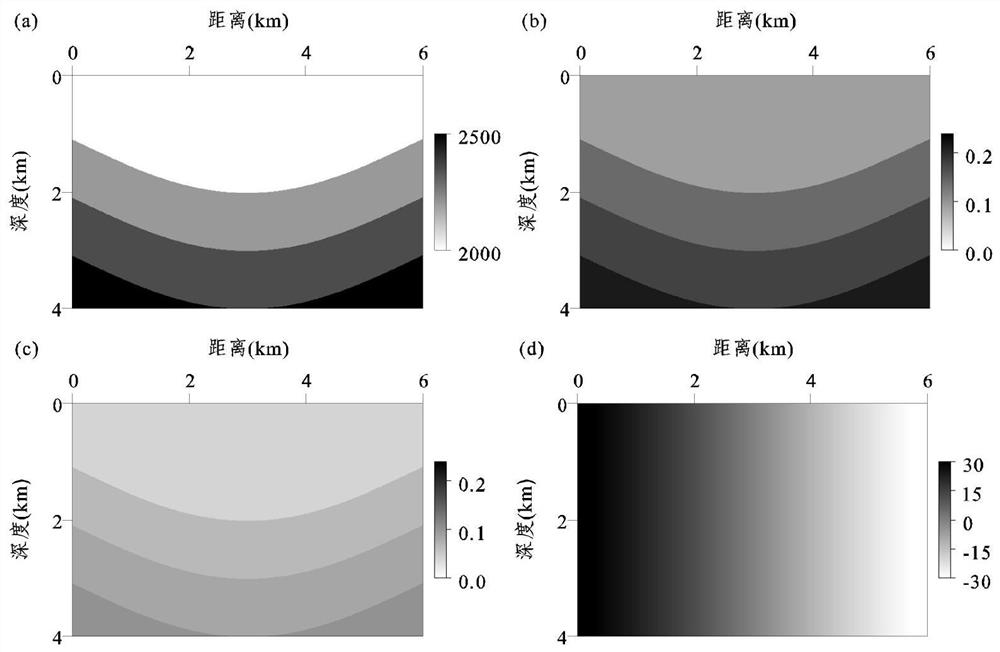
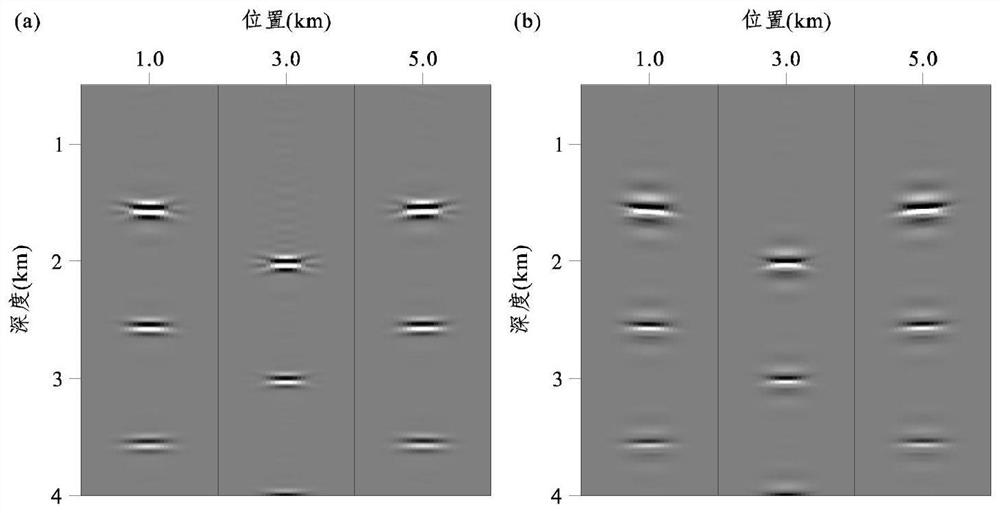
[0133] figure 2 is a two-dimensional layered medium model, (a) P-wave migration velocity model v p , (b) the first anisotropic parameter model ε, (c) the second anisotropic parameter model δ, (d) the structural dip angle model θ. The model has a depth of 4km and a lateral width of 6km. The spatial grid size used for offset is 10m, a total of 41 shots, the initial shot point is located at the left end of the model, the shot point is placed on the surface, the shot interval is 150m, each shot can receive up to 641 channels, the minimum offset distance is 0km, and the maximum offset distance 3.2km, track spacing 10m, recording time length 4.0s, time step 1ms, the main frequency of 15Hz is used as the source time function of the Lake wavelet. image 3 yes figure 2 The local offset domain common imaging point gather of the shown 2D layered medium model: where, image 3 (a) is the common imaging point gather in the local offset domain obtained by the traditional method, imag...
example 2
[0135] Figure 6 is the anisotropic Marmousi-2 model provided by the present invention, (a) P-wave migration velocity model v p , (b) the first anisotropic parameter model ε, (c) the second anisotropic parameter model δ, (d) the structural dip angle model θ. This model is one of the international standard models to verify the effects of various imaging methods. The model has a depth of 5.4km and a lateral width of 27.2km. The spatial grid size used for the offset is 10m, with a total of 109 shots. The initial shot point is located at 2.8km from the model, and the shot point is placed on the surface. The offset distance is 0m, the maximum offset distance is 2500m, the track spacing is 10m, the recording time length is 5.5s, and the time step is 1ms. The Reich wavelet with a main frequency of 30Hz is used as the source time function. Figure 7 yes Figure 6 The seismic record section of the anisotropic Marmousi-2 model shown: where, Figure 7 (a) the observation log of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com