Luneberg lens reflector and passive radar reflection ball comprising same
A Lumberg lens, passive radar technology, applied in instruments, radio wave measurement systems, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of reflection area influence, reflection area instability due to environmental influence, and radar false target construction reflection area, etc. Solve the effect of inconvenient processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
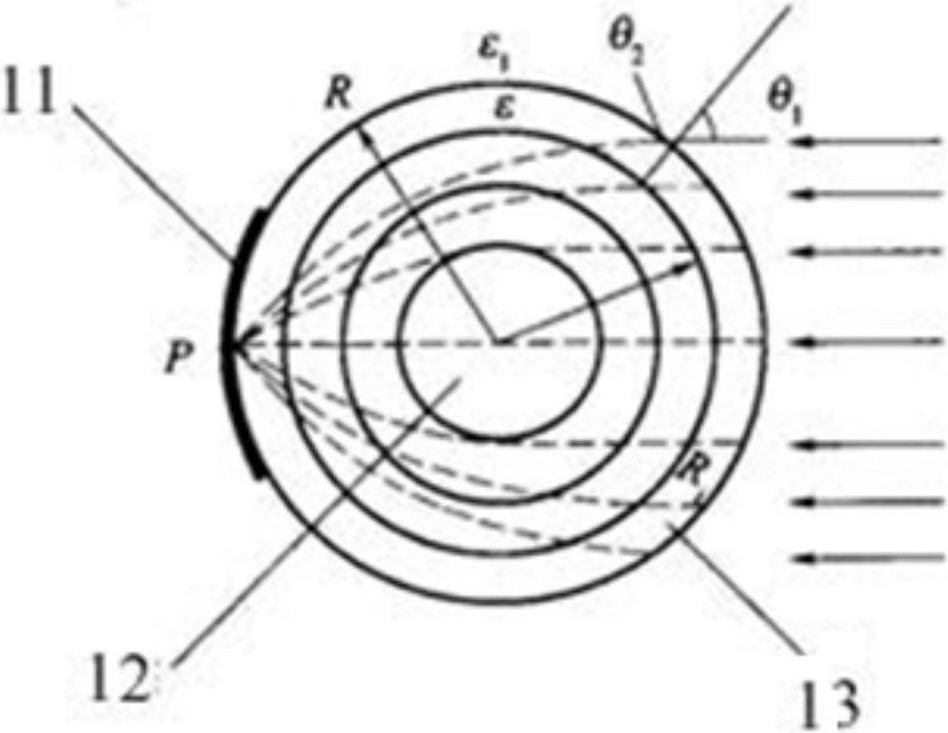
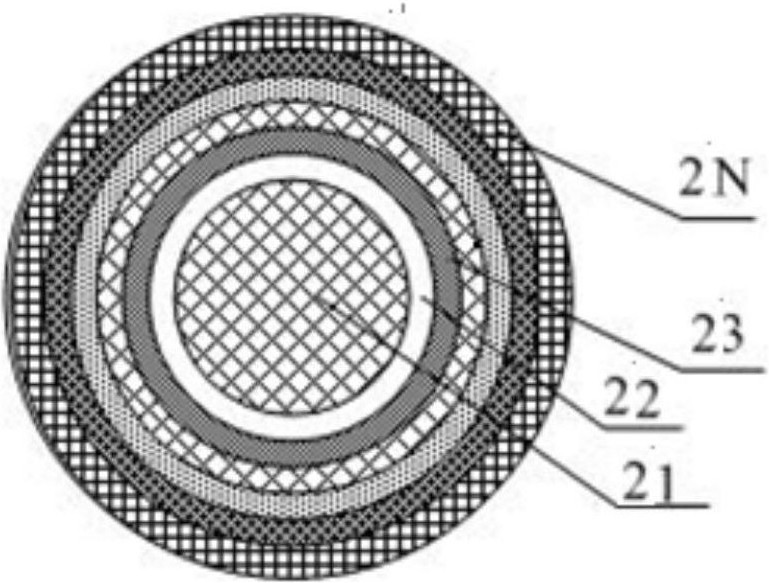
[0043] refer to figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , the Lunberg lens reflector includes a spherical core, the first dielectric spherical layer surrounds the outside of the spherical core, the second dielectric spherical layer surrounds the outside of the first dielectric spherical layer, and so on, the dielectric spherical layer N is surrounded by the outermost layer. The dielectric constants of different dielectric spherical layers are different, and gradually decrease from the center of the sphere to the outside. It is preferable that the dielectric constant of the outermost layer is the same as that of air. Different dielectric layers have different thicknesses.
[0044] The bottom of the Lunberg lens reflector is provided with a circular arc surface reflection area for converging electromagnetic waves for reflection, preferably the arc surface is a metal reflection area.
[0045] figure 2 is a top view schematic diagram of the medium layer structure of the maximum di...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A molding method of a Lunberg lens reflector, comprising the following steps:
[0048] s01, perform parameter design according to the reflective area of the Lunberg lens reflector body, the parameter design is to first determine the radius of the sphere and the thickness of the dielectric sphere layer, the dielectric sphere layer contains a plurality of dielectric layers with different dielectric constants, and then determine the medium The number of layers and the corresponding thickness of the dielectric layer gradually expand from the dielectric layer close to the center of the sphere to the outermost dielectric layer, thereby dividing the Lunberg lens reflector body into multiple circles;
[0049] s02, the designed circle is formed by 3D printing, and the next layer is printed after one layer is printed;
[0050] s03, use the medium to print the metal reflective surface in the arc area;
[0051] s04, splicing the dielectric sphere and the metal reflective surface...
Embodiment 3
[0055] refer to Figure 4 , a passive radar reflector, comprising a shell 1, a Lunberg lens reflector 2, a handle 3, and a chassis 4, wherein the shell 1 is hollow, the Lunberg lens reflector 2 is arranged inside the shell 1, and the chassis 4 is fixed Connected to the bottom of the housing 1, a handle 3 is arranged symmetrically in the middle of the outer wall of the housing 1, for connecting the radar reflecting spheres in series.
[0056] Preferably, the housing 1 is a rigid spherical shape, and the mass of the Lunberg lens reflector 2 is greater than that of the housing 1 , so that the chassis 4 , the housing 1 and the Lunberg lens reflector 2 form a tumbler structure.
[0057] In other embodiments, the handle 3 can also be arranged on the chassis 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com