A disease-resistant locus qsrv6.1, molecular markers and applications of black-streaked dwarf disease in southern rice
A technique for black-streaked dwarfism and molecular markers, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
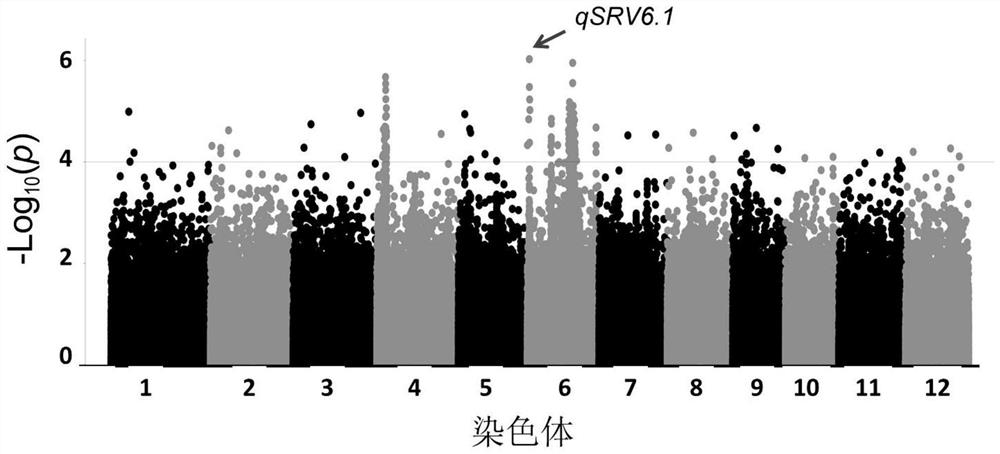
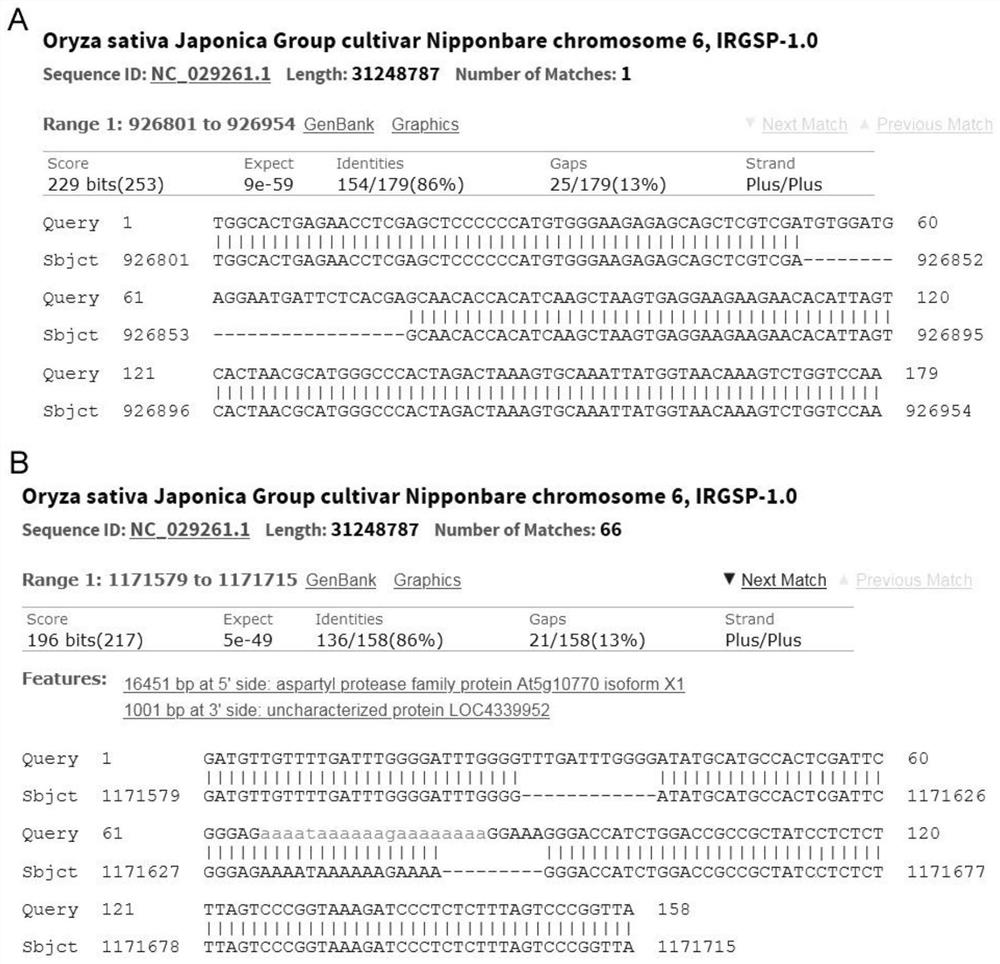
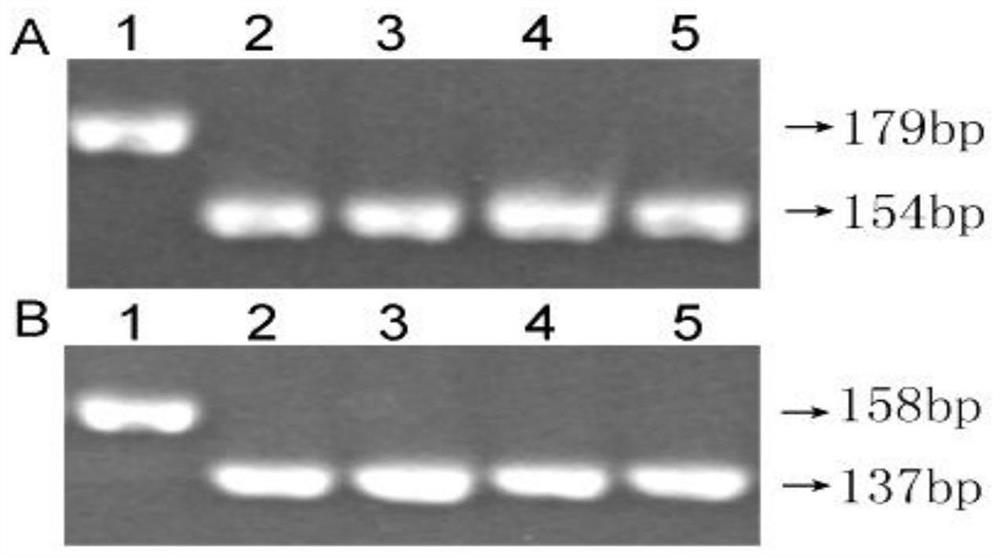
[0026] 1. Mining of resistance loci to southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease (SRBSDV)
[0027] The identification of SRBSDV resistance adopts the field natural induction identification method. 500 rice resources were planted in the SRBSDV disease nursery in Xiangli Town, Xing'an County, Guangxi. No pesticides were sprayed during the seedling field stage, and seedlings were transplanted per plant. Each variety was planted in 4 rows*10 plants with a row spacing of 16cm*18cm. The disease-resistant variety was W44, and the control susceptible variety was TN1. All varieties were set 3 repetitions, 3 repetitions were randomly arranged in 6 fields according to the numbering order of the tested varieties, and 5 TN1 plants were planted in protection rows and induced rows around the fields, with a plant spacing of 10cm, and only one insecticide was sprayed during the entire growth period (insecticide Single) Control rice leaf roller. About 30 days after transplanting, the phenoty...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com