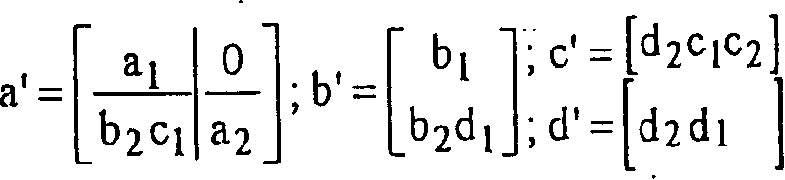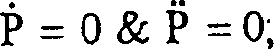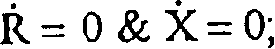Method and apparatus for turn coordination gain as function of flap position
A technology of flap and wing electronics, applied in the field of new system of turn coordination gain of aircraft yaw damper, which can solve the problem that the gain adjuster cannot optimally provide turn coordination, diverging or converging turns, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Figure 2 shows a simplified state-of-the-art yaw damper 201 which is used to generate a yaw damping command, YDCMD, to control the deflection of the rudder during a turn. This YDCMD signal is typically provided to one or more yaw damping servos that drive the rudder of the aircraft. This particular yaw damper 201 has been used on Boeing 747-400 aircraft. The yaw damper 201 uses data input from an inertial reference unit on the aircraft to calculate a rudder command (YDCMD) corresponding to the actual aircraft conditions at the time. The yaw damping servo then converts the electrical signal from the yaw damper 201 to control turbulent flow to the actuator pistons that drive the aircraft's rudders.
[0018] The inputs to the yaw damper 201 include: N y , represents the lateral acceleration of the aircraft; R, represents the yaw rate of the aircraft; Φ, represents the roll angle of the aircraft; P, represents the roll rate of the aircraft. The above parameters are provi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com