Coding and decoding method for integrity check and error correction of DNA sequence
A DNA sequence and integrity verification technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as the limitation of error correction ability, destroy the purity of the original sequence, and difficult error correction ability, etc., and achieve the effect of flexible length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] In order to facilitate those of ordinary skill in the art to understand and implement the present invention, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the implementation examples described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit this invention.
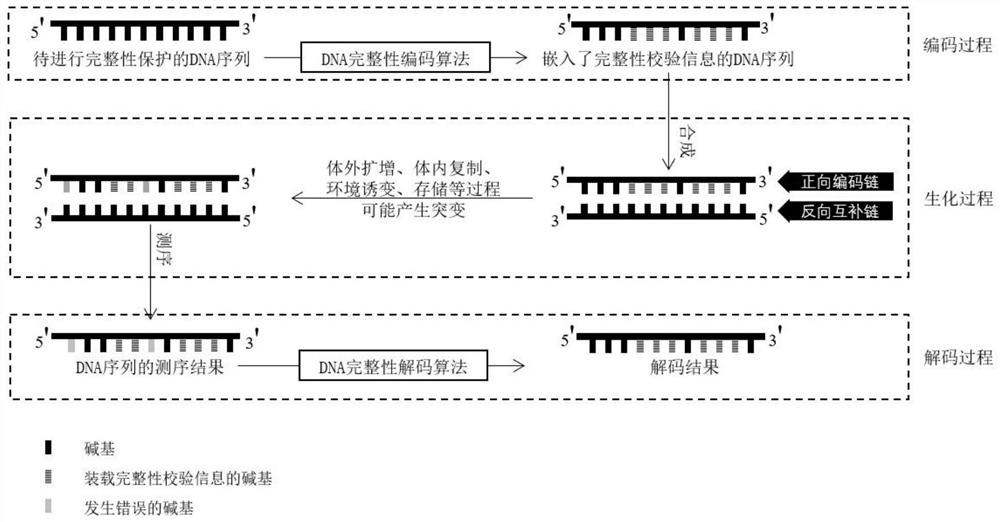
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the encoding and decoding method of DNA sequence integrity checking and error correction of the present invention comprises the following steps:
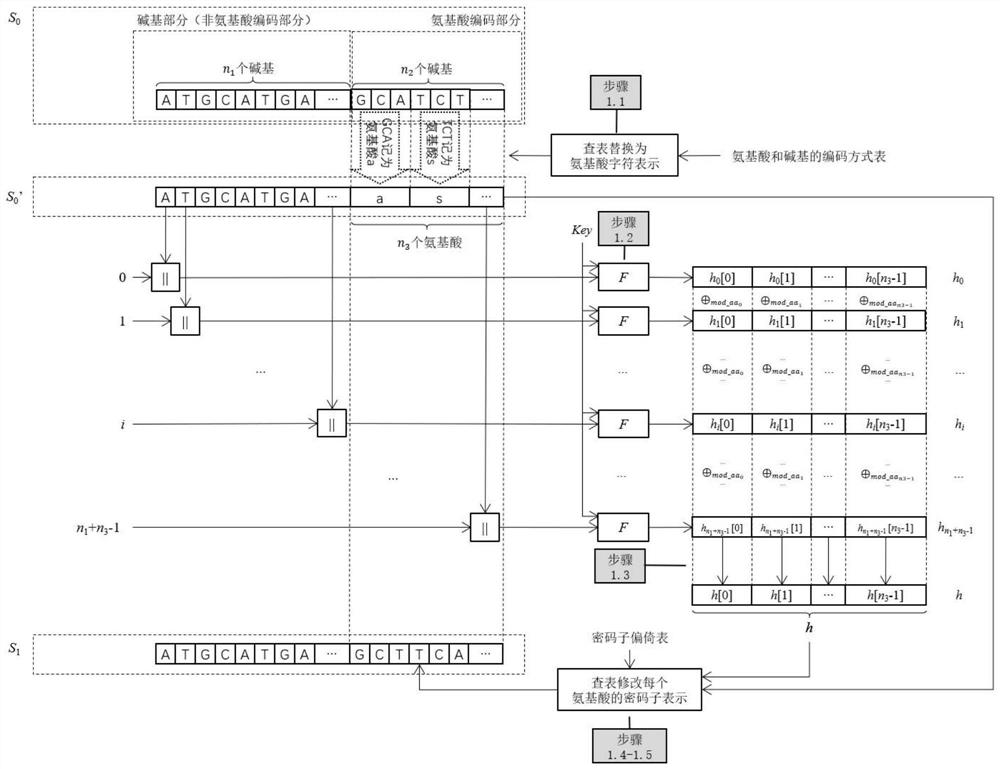
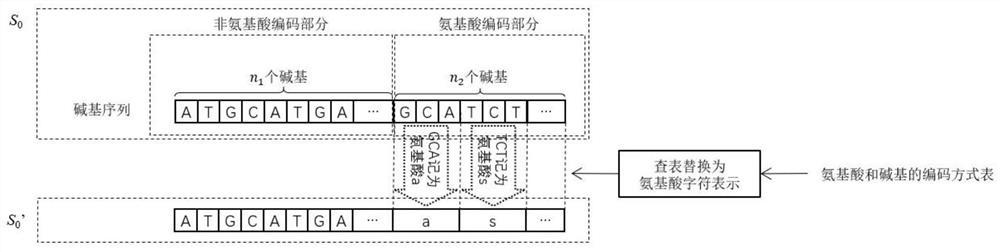
[0032] Step 1: Encoding (embedding of integrity information). The DNA coder uses the DNA integrity coding algorithm, uses the key shared by the coder and the decoder and the codon bias table Table_CodonBias, the DNA sequence S to be integrity protected 0 Perform calculations and output the DNA sequence S embedded with integrity check information 1 ,See figure 2 .
[0033] The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com