A Current Sampling Circuit Based on Bridge Circuit
A current sampling and bridge circuit technology, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of being unable to distinguish the positive induced current circuit of the transformer, so as to protect the safety of the circuit and avoid the induced current , to ensure the effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
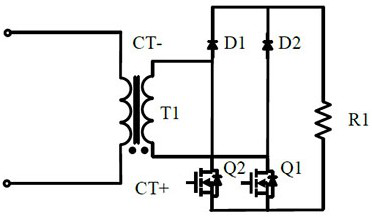
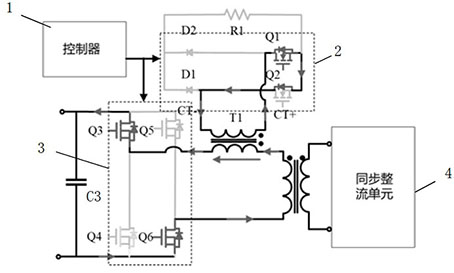
[0028] Embodiment 1: A current sampling circuit based on a bridge circuit, including a rectifier circuit 2, the rectifier circuit includes a first rectifier bridge arm formed by connecting a first switching tube Q1 and a second diode D2 in series, and a second switching tube Q2 The second rectification bridge arm is formed by connecting in series with the first diode D1, wherein the first rectification bridge arm and the second rectification bridge arm are connected in parallel, and the common node of the first switching tube and the second diode forms the first rectification bridge The midpoint of the arm, the common node of the second switch tube and the first diode forms the midpoint of the second rectifier bridge arm; the detection resistor unit (such as figure 1 The detection resistor R1 in the middle) is connected in parallel with the first rectifier bridge arm and the second rectifier bridge arm; the current transformer T1 includes a primary winding and a secondary windi...
Embodiment 2
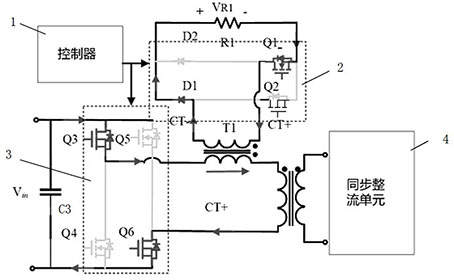
[0033] Embodiment 2, a current sampling circuit based on a bridge circuit. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the primary winding of the current transformer T1 and the secondary winding of the current transformer T1 have different names. Connection, all the other structures are the same as in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, when the controller controls the conduction of the MOS transistor Q3 and the MOS transistor Q6, it also controls the synchronous conduction of the MOS transistor Q2 (that is, the MOS transistor Q3, the MOS transistor Q6 and the Q2 receive the same control signal). When the secondary side synchronous rectification is turned on, the primary side circuit will flow an induced current (such as Figure 6 As shown by the middle arrow, it can also be called negative current), at this time, the primary current of the current transformer T1 flows in from the terminal with the same name, and the secondary current of the current transform...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3. In this embodiment, the end with the same name of the primary winding of the current transformer T1 is connected to the primary winding of the transformer, and the primary winding of the current transformer T1 is connected to the primary winding of the transformer and the second bridge arm of the full bridge circuit. Between the midpoints, the current transformer T1 is connected to the terminal with the same name, and the other circuit connection structures are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com