Functional electrical stimulation system and method for regulating and controlling joint torque and rigidity
A technology of functional electrical stimulation and joint torque, applied in electrotherapy, artificial respiration, physical therapy, etc., can solve problems such as inability to control joint stiffness and insufficient stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
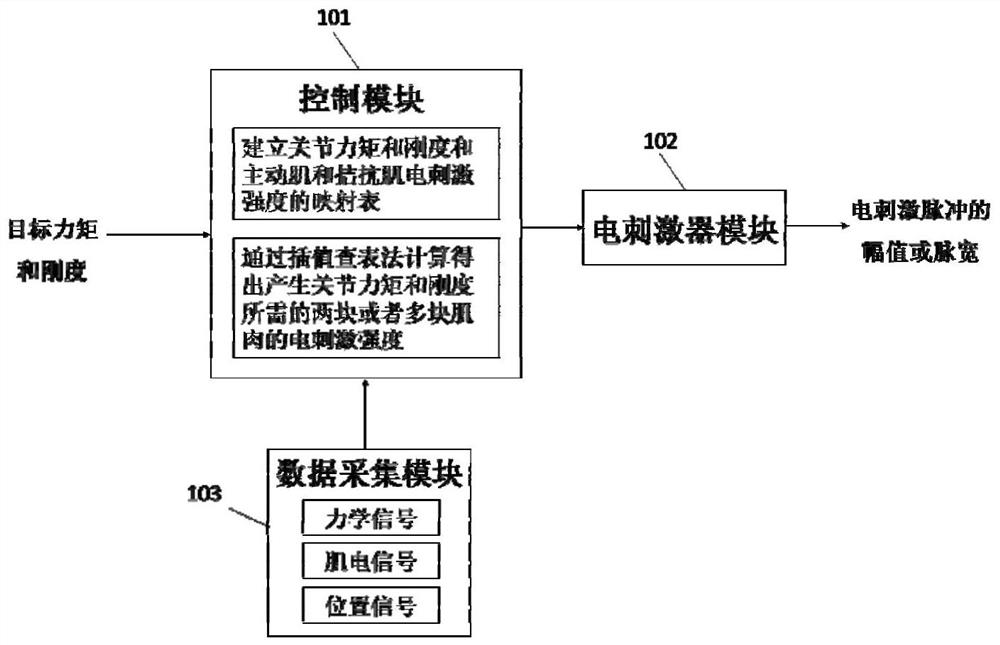
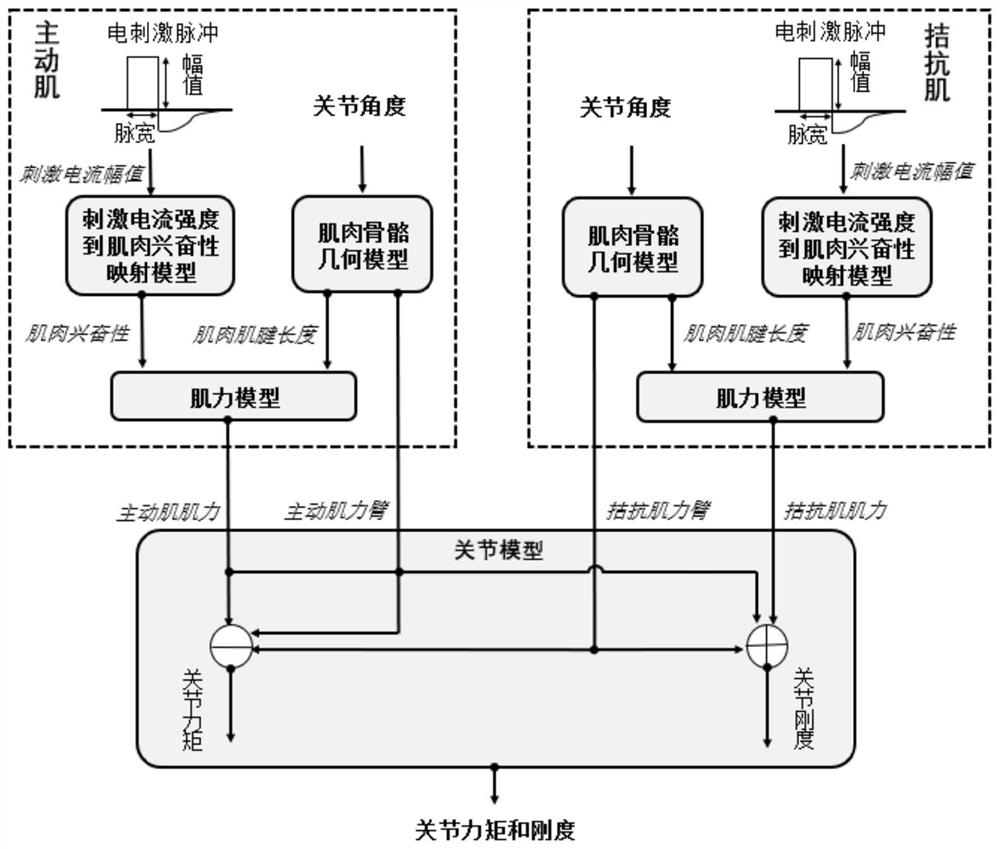
[0093] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a functional electrical stimulation system for regulating joint torque and stiffness, which can generate desired torque and stiffness by electrically stimulating a pair of agonist muscles and antagonist muscles. The following is a specific experiment to verify the feasibility of the functional electrical stimulation system for regulating joint torque and stiffness provided by the embodiment of the present invention, specifically: including a control module, an electrical stimulator module, and a data acquisition module; wherein:
[0094]The control module is used to send strength signals to the electric stimulator module in real time, including a prediction model of joint torque and stiffness, used to generate a mapping table of joint torque and stiffness and agonist muscle and antagonistic muscle electrical stimulation intensity, and Including an interpolation lookup table algorithm to find the electrical stimulati...
Embodiment 2
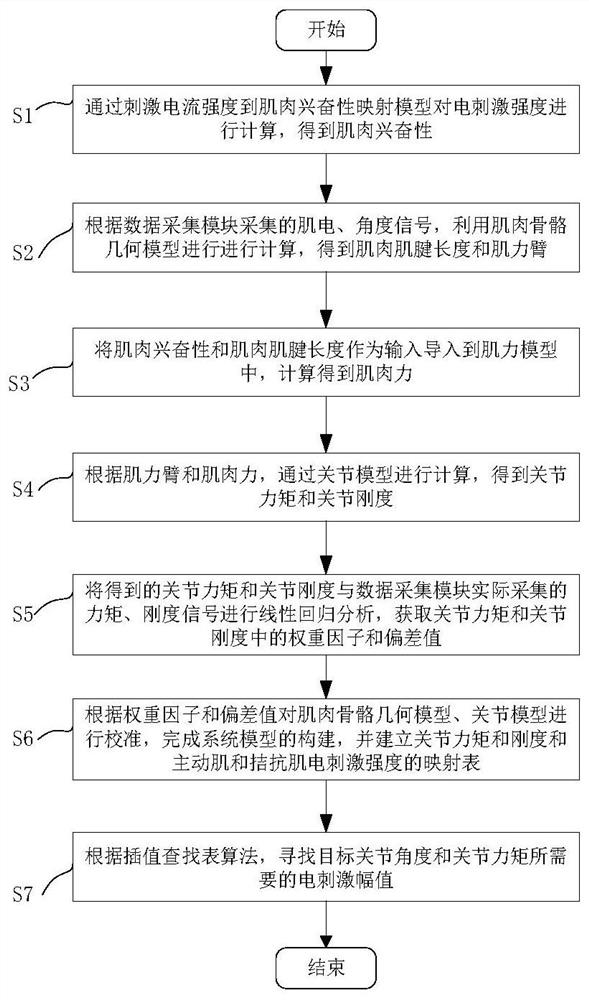
[0108] More specifically, on the basis of Example 1, such as image 3 As shown, a functional electrical stimulation method for regulating joint torque and stiffness is provided, comprising the following steps:
[0109] S1: Calculate the electrical stimulation intensity through the stimulation current intensity-to-muscle excitability mapping model to obtain muscle excitability;
[0110] S2: According to the myoelectricity and angle signals collected by the data acquisition module, the musculoskeletal geometric model is used for calculation to obtain the muscle tendon length and muscle moment arm;
[0111] S3: Import the muscle excitability and muscle tendon length into the muscle strength model as input, and calculate the muscle force;
[0112] S4: According to the muscle arm and muscle force, calculate through the joint model to obtain the joint torque and joint stiffness;
[0113] S5: Perform linear regression analysis on the obtained joint torque and joint stiffness and th...
Embodiment 3
[0168] More specifically, a muscle of a subject varies in electrical stimulation intensity as Figure 5 Under the stimulation signal of the triangle wave of the "input signal", it can cause the joint to produce such as Figure 5 The joint moments and stiffnesses of the "Output Moments and Stiffnesses". For the case of electrical stimulation of tibialis anterior muscle and gastrocnemius at the same time, the relationship between electrical stimulation intensity and joint torque is as follows: Image 6 As shown, the relationship between electrical stimulation intensity and joint stiffness is as follows Figure 7 shown.
[0169] Calibrate the stiffness and moment prediction model through the muscle maximum voluntary contraction test experiment, and obtain the personalized parameter l st and F mt . In the maximum voluntary contraction force test, the torque, angle and EMG signals of the joints are collected and processed by filtering; the preprocessed angle and EMG signals ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com