Method for judging weak surrounding rock tunnel primary support cavity
A technology for primary support and weak surrounding rock, which is applied to the analysis of solids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, and measuring devices. It can solve problems such as low efficiency and cumbersome methods, and achieve convenience. The effect of discovering and increasing the horizontal detection range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A method for identifying primary support voids in weak surrounding rock tunnels, comprising:
[0067] For directly accessible areas:
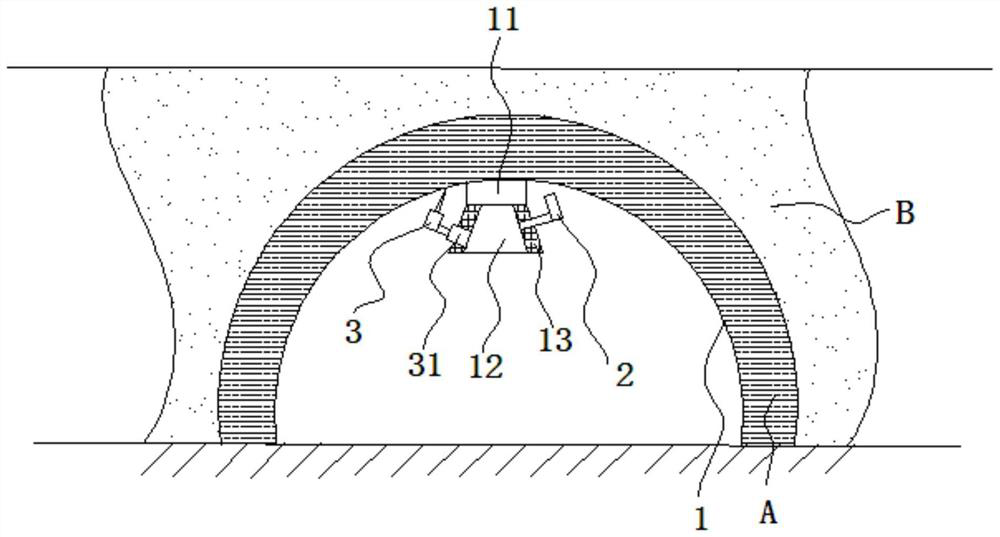
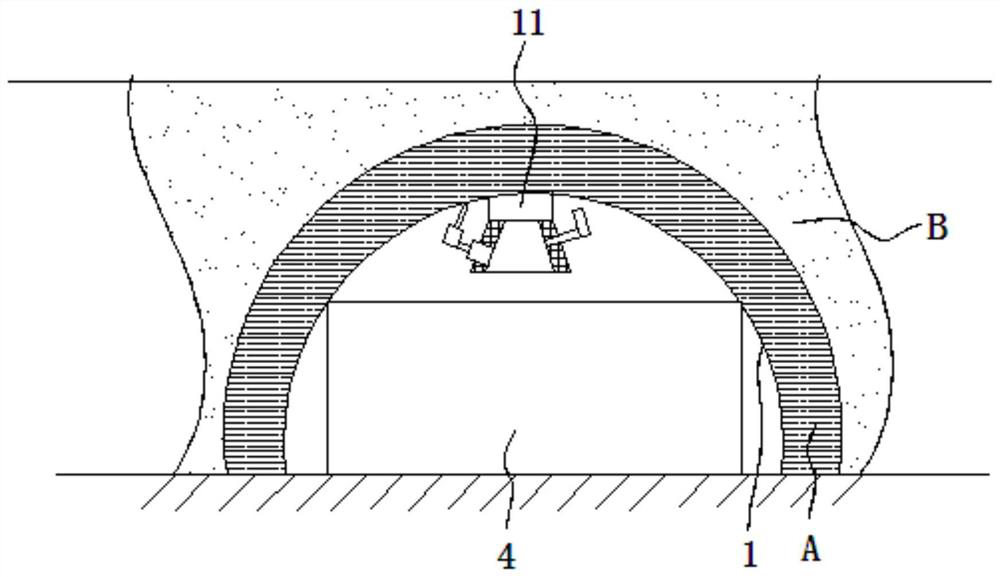
[0068] The area that is more than 25 cm away from the steel arch is the area where the initial support can directly contact. The area that can be directly contacted is tested by tapping from one end to the other end along the arch direction of the initial support. Drilling treatment. If there is a fall of virtual ballast at the drilling position, it is judged that the position of the cavity is inside the primary support; There are no holes.
[0069] For areas not directly accessible:
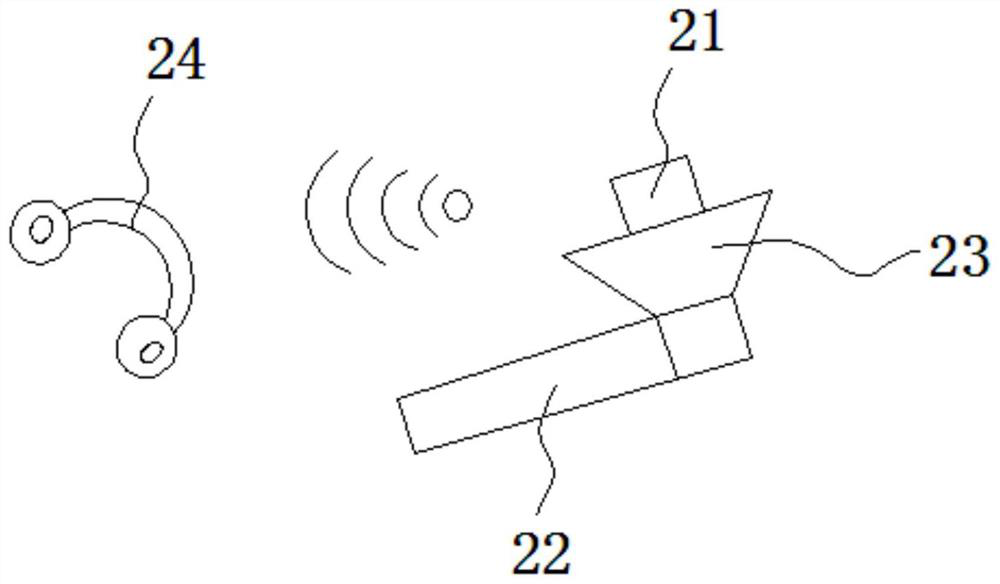
[0070] Step 1. The area less than 25 cm away from the steel arch is the area where the initial support cannot be directly contacted. For the area that cannot be directly contacted, set a drilling point every less than 100 cm along the arch direction of the initial support. When encountering the connection of the steel arch frame, an additional drilling...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Replace step 1 of Example 1 for areas that cannot be directly contacted with: the area that is less than 25 cm away from the steel arch is the area that cannot be directly contacted by the initial support, and the area that cannot be directly contacted is along the arch direction of the initial support Set a drilling point at a position less than 100 cm, and set a drilling point at the connection of the steel arch frame, and drill all the drilling points. The drilling angle is 60° and the depth is 30°. cm.
[0074] The rest of the parameters are exactly the same as in Embodiment 1, and the operation method and identification method are also completely the same.
Embodiment 3
[0076] Replace step 1 of Example 1 for areas that cannot be directly contacted with: the area that is less than 25 cm away from the steel arch is the area that cannot be directly contacted by the initial support, and the area that cannot be directly contacted is along the arch direction of the initial support Set a drilling point at a position less than 100 cm, and set one more drilling point at the joint of the steel arch frame, and perform drilling processing on all drilling points. The drilling angle is 45° and the depth is 25°. cm.
[0077] The rest of the parameters are exactly the same as in Embodiment 1, and the operation method and identification method are also completely the same.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com