An information storage device for embedded system
An embedded system and information storage technology, applied in memory systems, special data processing applications, memory architecture access/allocation, etc., can solve problems such as no longer writing, affecting correctness or accuracy, and damage to the writing area, to achieve The effect of reducing storage efficiency and avoiding frequent writing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
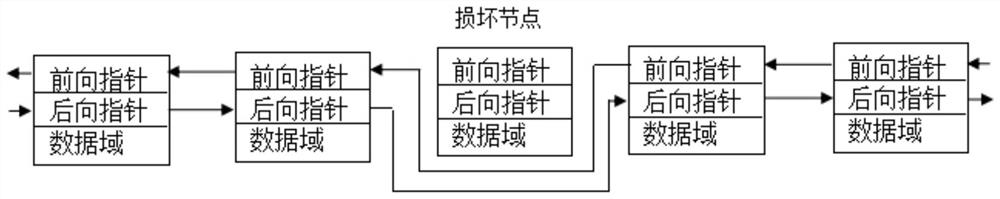
[0025] An information storage device for an embedded system, the storage device is composed of a memory, the memory includes a storage linked list and a free linked list, the storage linked list and the free linked list are composed of linearly arranged nodes, and in the nodes of the storage linked list and the free linked list, the forward pointer and The backward pointers correspond to each other, and the nodes are composed of a forward pointer, a backward pointer and a data field. The steps of the storage device power-down storage method are as follows:
[0026] S1: When the memory is powered on and initialized for the first time, two blank doubly linked lists are created in the memory, namely the storage linked list and the free linked list;
[0027] S2: When storing data, the storage linked list compares the data with the stored data to detect whether the data has been stored. If the stored data lacks a node that duplicates the data to be stored, a linked list is extracted...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The steps to check the data based on S3 are as follows:
[0032] After the data is updated to the data field of the storage location, the data is read, and the consistency of the written and read data is checked. If the written data is consistent with the read data, the detection node moves to the next storage node;
[0033] If the written data and read data are inconsistent, the physical space corresponding to the storage node is damaged, the node is deleted from the storage linked list, and a new node is picked from the free linked list. If it is damaged due to power failure, the damaged node is detected by the method of reading and detection, and when writing and reading data, the damaged node is skipped, so as to avoid frequent writing and reading of data on the damaged node, resulting in space write Into corruption and the system does not work properly.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The steps to perform write check on data based on S4 are as follows:
[0036] After extracting a new node from the free linked list, before writing to the new node, check whether the data to be written is equal to the last written data, if the written data is the same as the last written data, cancel the write into the process;
[0037] If the written data is different from the last written data, it will be written. Before writing the data, the stored data will be compared with the last written data, and the data will be written only when the data to be written is different from the original data. Write, avoid frequent writing and reduce the storage efficiency of the memory.
[0038] Working principle: When the memory is powered on and initialized for the first time, two blank doubly linked lists are created in the memory, namely the storage linked list and the free linked list. When storing data, the storage linked list compares the data with the stored data to detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com