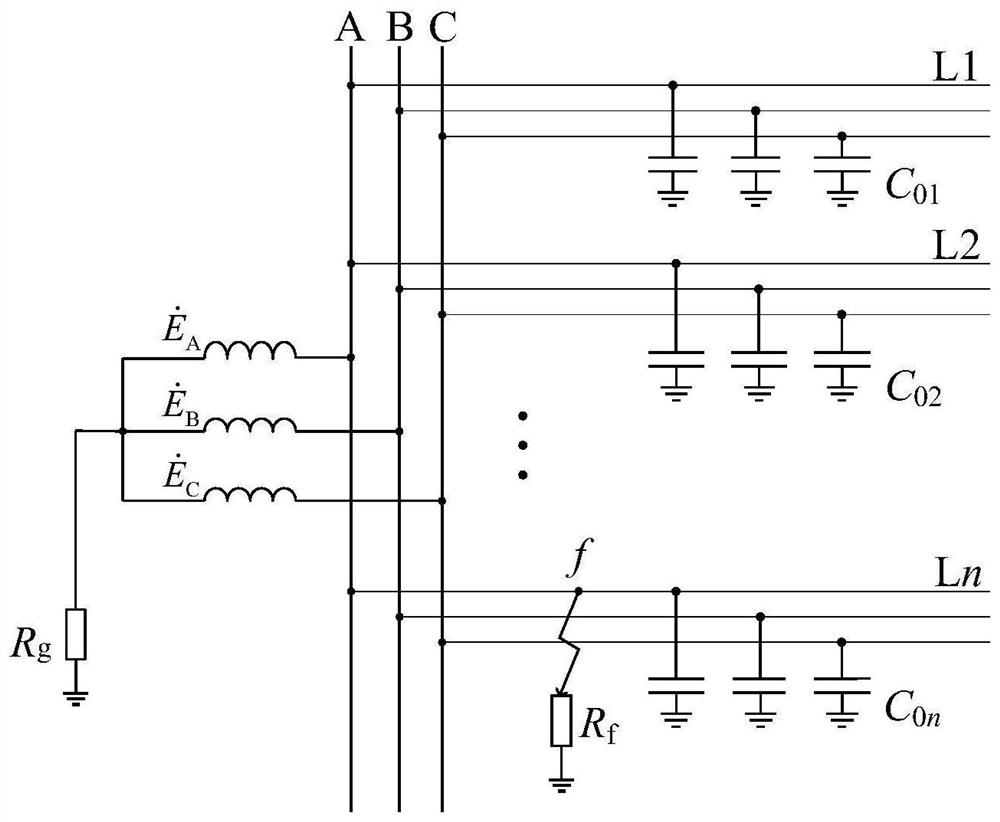
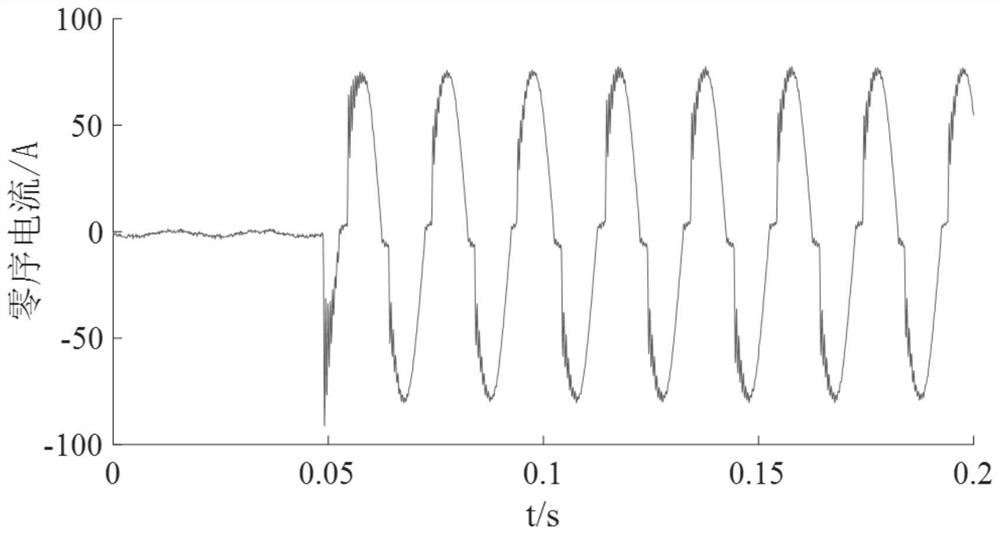
Thermal stability principle-based intermittent grounding protection method for small-resistance grounding system
A low-resistance grounding and grounding protection technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of exceeding the limit of fault times, difficult to fully adapt to complex and changeable, complex fault handling problems, etc., and achieve strong anti-noise interference ability. , The protection threshold value is set objectively, and the effect of improving the reliability of power supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
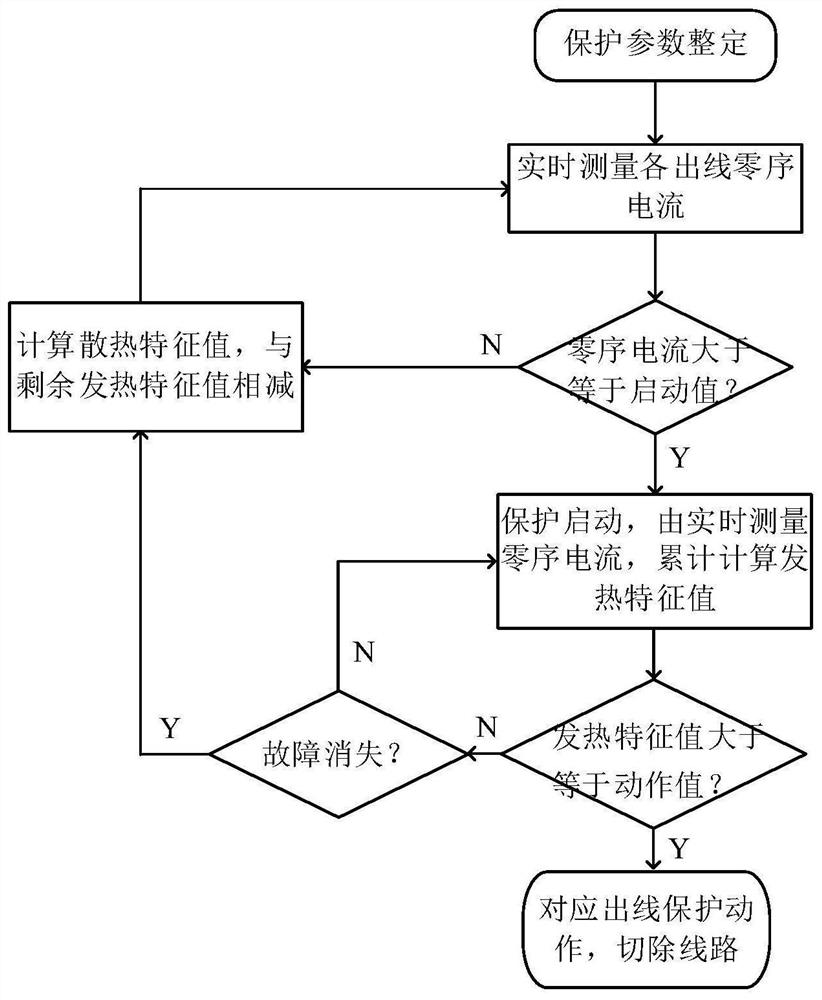
[0031] An intermittent grounding protection method for small resistance grounding systems based on the principle of thermal stability, the processing flow is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0032] Step 1: Read the zero-sequence current parameters at the outlets of each line in real time. If the zero-sequence current of a certain line is greater than the protection start threshold, the protection method of the corresponding line is activated. Go to step 2. If the line zero-sequence current is less than or equal to the protection start threshold , the protection method is not started, and the heat dissipation characteristic value of each line is calculated correspondingly based on the remaining heat characteristic value of each line, and subtracted from the heat characteristic value until the heat characteristic value is zero, and then p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com