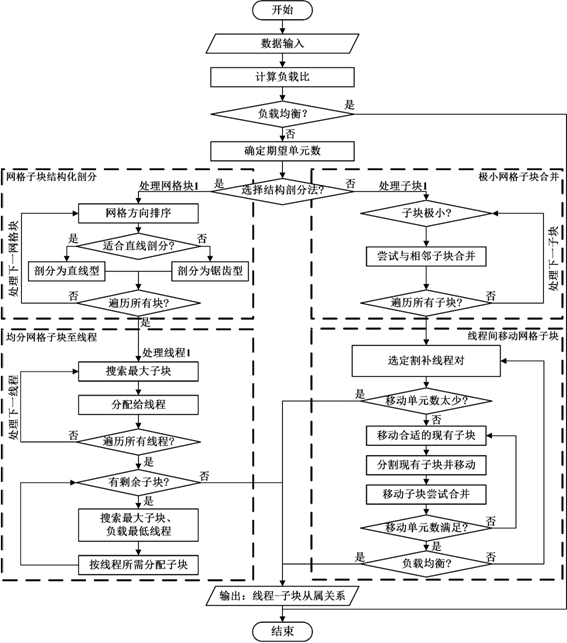
A Load Balancing Method of Dynamic Computing Domain in Parallel Simulation of Aircraft Aerodynamic Characteristics
A technology of load balancing and aerodynamic characteristics, applied in computing, computer parts, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as discount of acceleration effect, reduce adverse effects, reduce the number of grid blocks, and ensure flexibility and adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
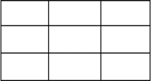
[0141] The flow around a supersonic two-dimensional wedge with Mach number 2.5 is simulated with 4 threads. Fig. 3 has shown the effect of the load balancing technology of dynamic computing domain in the parallel simulation of the present invention in supersonic two-dimensional system wedge problem simulation; Among the figure η represents the ratio of the grid volume of convective dynamic domain and preset computing domain, N max Represents the total number of iterations required for solution convergence. During the entire solution process, the convective dynamic domain first increases from the far field of the wall surface, and then shrinks from upstream to downstream, and continues to change. From the grid division in the figure, it can be seen that the technology of the present invention firstly divides the grid into 4×1 linear division, as shown in Figure 3(a); then it develops into a zigzag division, as shown in Figure 3(b) and 3(c) Shown; in the change to hierarchica...
Embodiment 2
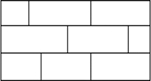
[0143] Simulate the supersonic flat plate laminar flow problem of Mach number 3.5 with 12 threads, Fig. 5 has shown the effect of the load balancing technology of dynamic computing domain in the parallel simulation of the present invention in the supersonic flat plate laminar flow problem simulation; Among the figure, η v Represents the ratio of the mesh volume of the viscous dynamic domain to the preset computational domain. The convective and viscous dynamic domains first increase from the wall to the far field, and then shrink from the far field to the wall. As can be seen from the grid division in the figure, the technology of the present invention firstly divides the grid into 12×1 linear division, such as Figure 5(a) and 5(b) shown; then developed into a zigzag split, such as Figure 5(c) , 5(d) and 5(e); the final reply is a 6×2 linear subdivision, as shown in Figure 5(f). It can be seen from the change curve of the number of grid sub-blocks and load ratio shown in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com