Alternating pole permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor for wide area operation
A technology for assisting synchronous and reluctance motors, which is applied to synchronous motors, motors, and magnetic circuits with stationary armatures and rotating magnets. problem, to achieve the effects of strong short-circuit current suppression ability, weak magnetic field speed expansion ability, and low no-load back electromotive force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
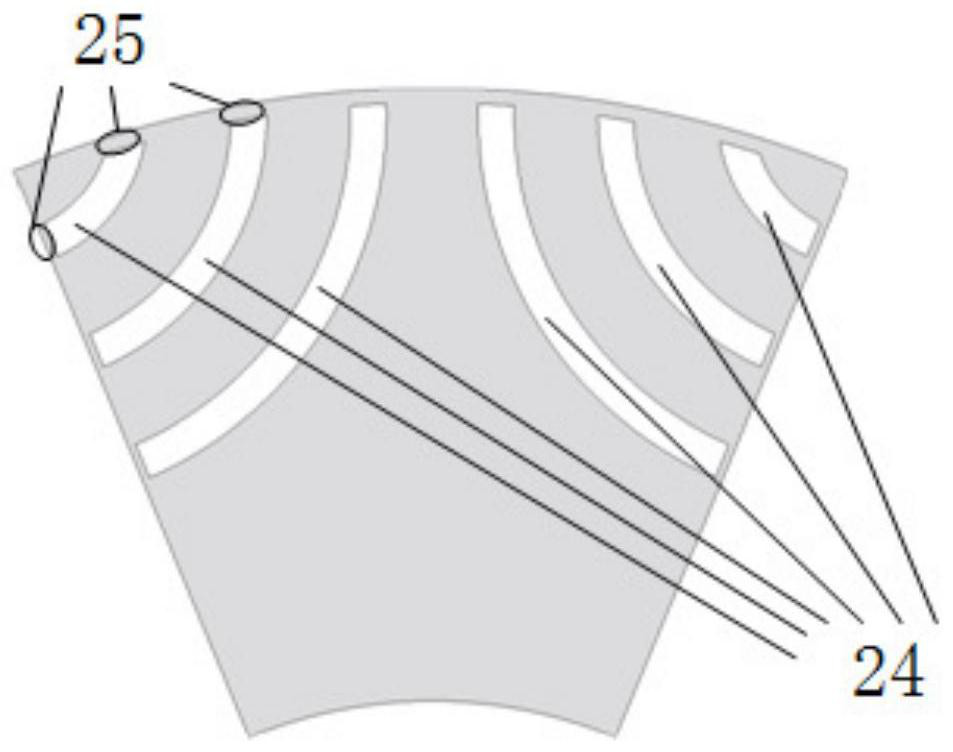
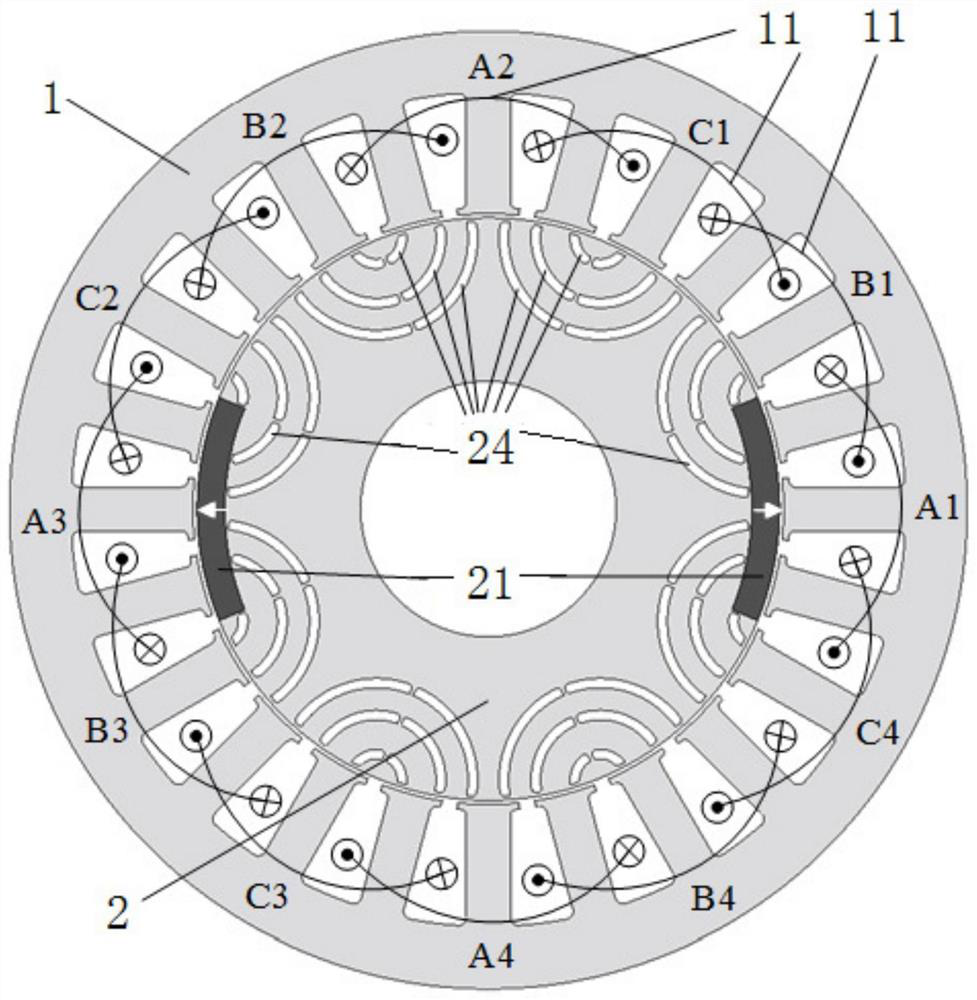
[0055] With three-phase m=3, Ns=24, p=4, p r = 3,p m =1 as an example; figure 2 shown)
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, an alternating pole permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor operating in a wide area includes a stator and an alternating pole synchronous reluctance rotor arranged coaxially from the outside to the inside.
[0057] Alternatively, the alternating pole synchronous reluctance rotor can also be coaxially sleeved on the outer periphery of the stator, that is, the outer rotor.
[0058] The stator includes a stator core 1 and an armature winding 11 wound in a stator slot of the stator core.
[0059] The number of stator slots above is preferably Ns=24, and the armature winding preferably includes A, B, and C three-phase windings, wherein phase A can be formed by connecting A1, A2, A3, and A4 coils in series, or by A1-A2, A3-A4 respectively Connect in series and then in parallel; B phase and C phase and so on.
[0060] The number of pole pa...
example 2
[0072] Example 2: Permanent magnet pole offset in Example 1
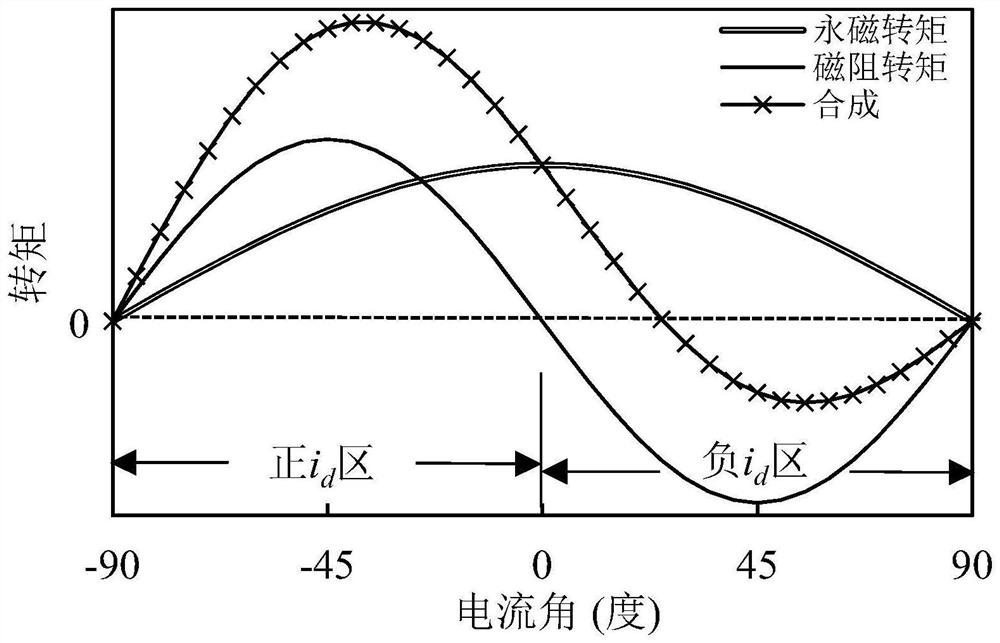
[0073] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the permanent magnet torque reaches the maximum value when the current angle is 0 degrees, while the reluctance torque obtains the maximum value when the current angle is -45 degrees; and; low torque synthesis rate. Therefore, on the basis of Embodiment 1, this Embodiment 2 shifts the permanent magnet poles by a certain angle, specifically as Figure 4 shown.
[0074] The offset angle of the permanent magnet pole relative to the reluctance pole is preferably less than or equal to 1 / 4 pole pitch, preferably 1 / 8 of the pole pitch in this embodiment, so that the current angle at which the permanent magnet torque obtains the maximum torque approaches the reluctance rotation The torque obtains the current angle of the maximum torque (abbreviation: moment angle approximation), thereby increasing the synthesis rate of the permanent magnet torque and the reluctance torque, an...
example 3
[0076] Example 3: p=4, p r = 2, p m = 2
[0077] Such as Figure 6 As shown, there are two connected permanent magnet poles, and there are also two connected reluctance poles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com