Flexible control method and device for dynamically reconstructing battery module
A battery module and dynamic reconfiguration technology, which is applied to battery circuit devices, circuit devices, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to solve the consistency of module units, and achieve the effect of ensuring performance consistency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
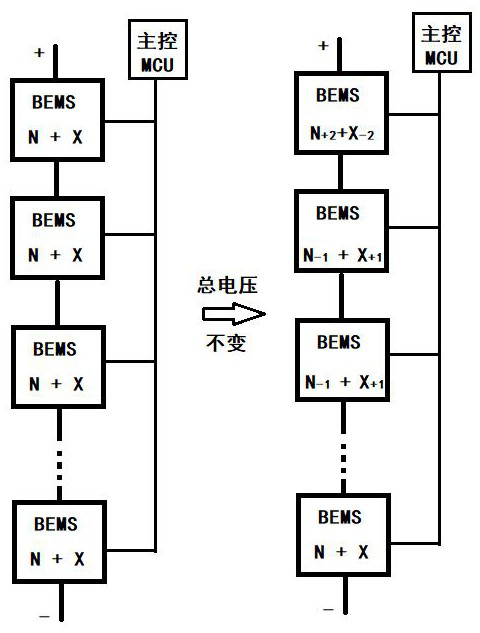
[0035] Implementation Mode 1, see figure 1 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment is a flexible charging / discharging control method for dynamically reconfigured battery modules. The battery module is a series battery module composed of n module units connected in series. The i-th module The unit is composed of Ni+Xi battery units connected in series, i=1, 2, 3,...n, and the charging / discharging control method includes:
[0036] During the charging / discharging process, Nx and Xx in each series module unit are dynamically iteratively adjusted, and each iteration adopts the method of synchronous equivalent reverse redundant quantity to adjust the module unit with the highest terminal voltage and the lowest terminal voltage module unit;
[0037] Iterations continue until all modules are filled / emptied.
[0038]The difference between the flexible charging / discharging control method described in this embodiment and the prior art is that in the charging / discharging process, the ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further limitation of the flexible charging / discharging control method for a dynamically reconfigured battery module described in Embodiment 1. The said each iteration adopts a synchronous equivalent reverse redundant quantity The process of adjusting the module unit with the highest terminal voltage and the module unit with the lowest terminal voltage is as follows:
[0050] Ni=Ni-j of the modular unit with the highest terminal voltage, and Xi=Xi+j at the same time;
[0051] Ni=Ni+j of the modular unit with the lowest terminal voltage, and Xi=Xi-j at the same time;
[0052] j=1 or 2.
[0053] During the charge and discharge process, according to the set time period, according to the virtual voltage value of the series module monomer, the Nx and Xx of the two series module monomers with the highest and lowest voltage values are dynamically adjusted, and the adjustment configuration adopts Synchronous equivalent reverse redundant qu...
Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Embodiment 3. This embodiment is a further limitation of the flexible charge / discharge control method for a dynamically reconfigurable battery module described in Embodiment 1 or 2. In this embodiment, when the first charge / discharge ends, a step is added :
[0061] At the end of each charge / discharge, for the first w group of module units with the highest virtual voltage value Ni=Ni+1, and corresponding Xi=Xi-1, this parameter will be used as the next Startup parameters for the charge / discharge process.
[0062] In this embodiment, at the end of charging / discharging, the parameters of the first w group of module units with the highest virtual voltage among the module units are adjusted, and the adjusted parameters are used as the starting parameters for the next charging / discharging, so that the next The initial state of one charge and discharge is more suitable for the state of the battery module itself, which improves the charging efficiency of the next charge and a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com