High temperature superconductor cable
A superconductor and cable technology, applied in the field of high-temperature superconductor cables, can solve problems such as damaged tape
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
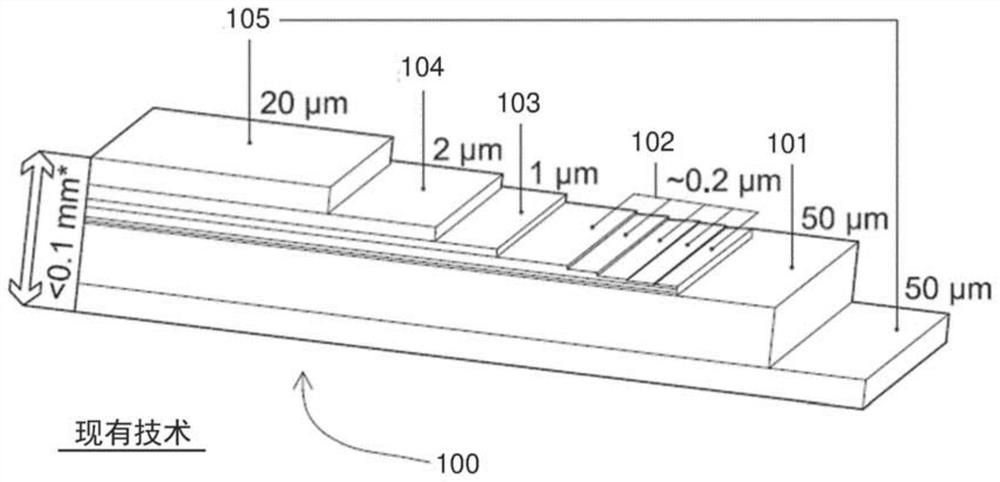
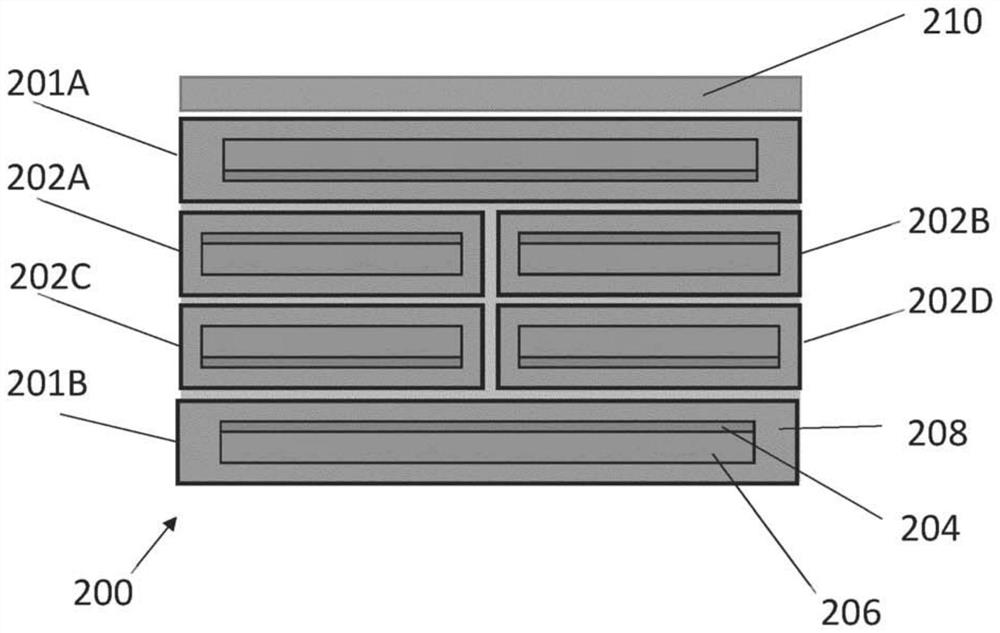
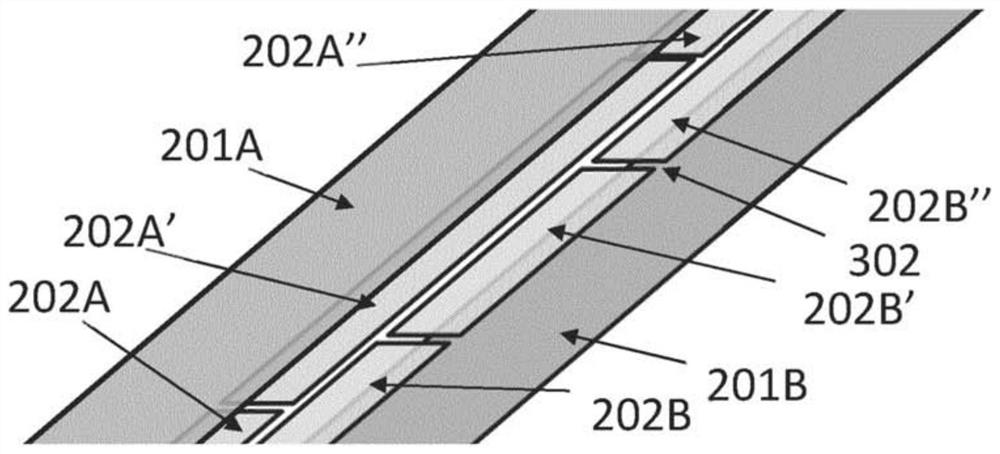
[0046] The present invention relates to an HTS cable comprising stacked HTS ribbons that allows the current distribution across the cable width and between ribbons to be adjusted to produce a more uniform current density. This allows the creation of an HTS magnet in which the current density is more uniformly distributed between the strips and / or in which the HTS magnet is more uniform across each turn. These properties greatly contribute to the design of HTS magnets, as the "real" properties of the magnets, such as the uniformity of the magnetic field, will be more similar to what HTS magnet designers thought.
[0047] The current distribution across the width of the cable can also be adjusted so that it is intentionally non-uniform, with the aim of making the magnetic field angle to the ab plane of the ReBCO layer in each strip as close to zero as possible. This maximizes the critical current of the cable. As described below, the voltage developed across the HTS cable also ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| critical temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| critical temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com