Inhaled statins as bronchodilators to improve lung function in respiratory diseases
A technology of statins and inhalers, which is used in the field of inhaling statins as bronchodilators to improve lung function in respiratory diseases, and can solve problems such as lung function decline and airway stenosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0184] Example 1: Relaxation of ASM Contractility
[0185] The following experiments demonstrate that statins induce relaxation of the ASM in resting, non-stimulated cells.
[0186] Contractile Force Screening : Human ASM cells in 96-well plates in custom NuSil TM Grow to confluence on 8100 Elastic Substrate (Avantor, Inc., Radnor, PA) (R. Rokhzan et al., LabInvest (2019) Vol. 99 No. 1: No. 138 -145 pages). Fluorescent beads (approximately 400 nm in diameter) were embedded in the substrate surface so that traction forces could be calculated based on the displacement of these beads. To measure traction force, an inverted epifluorescence microscope (DMI6000B, Leica Inc., Germany) equipped with a heated chamber (37°C), a monochrome camera (Leica DFC365 FX) and a motorized stage was used. Aerial images of substrate-embedded fluorescent beads were recorded at 10X magnification. Based on the displacement of the bead relative to the cell-free model (resolution about 15 μm), ...
Embodiment 2
[0197] Example 2: histamine-induced contraction
[0198] These experiments were performed to determine the ability of statins to reduce ASM contraction induced by exposure to histamine.
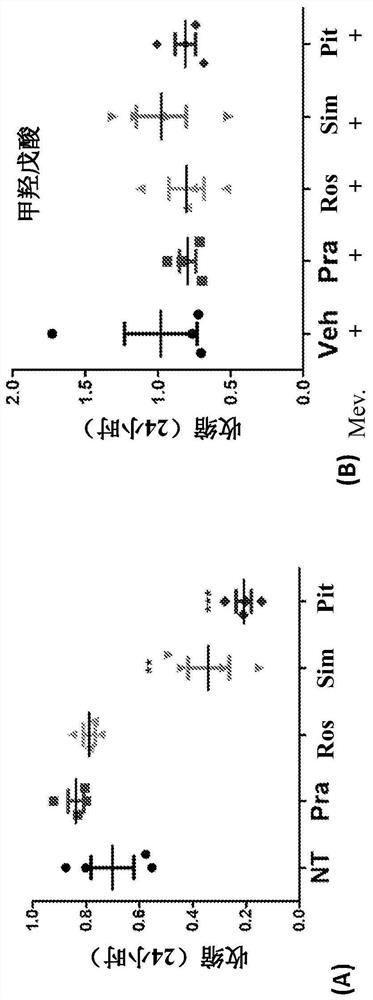
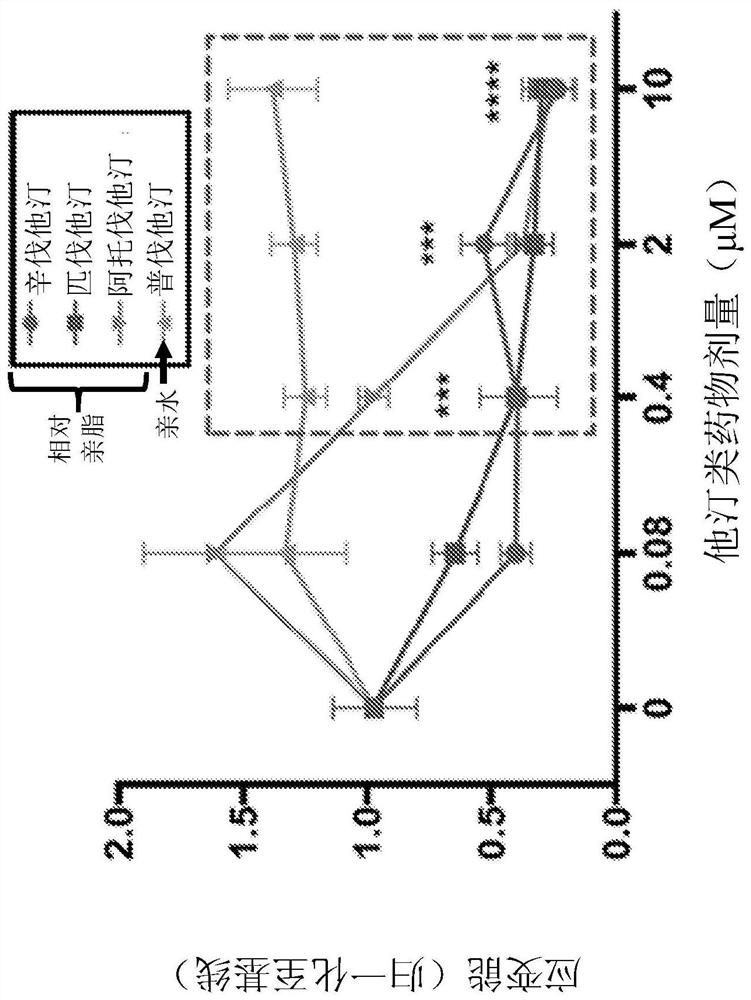
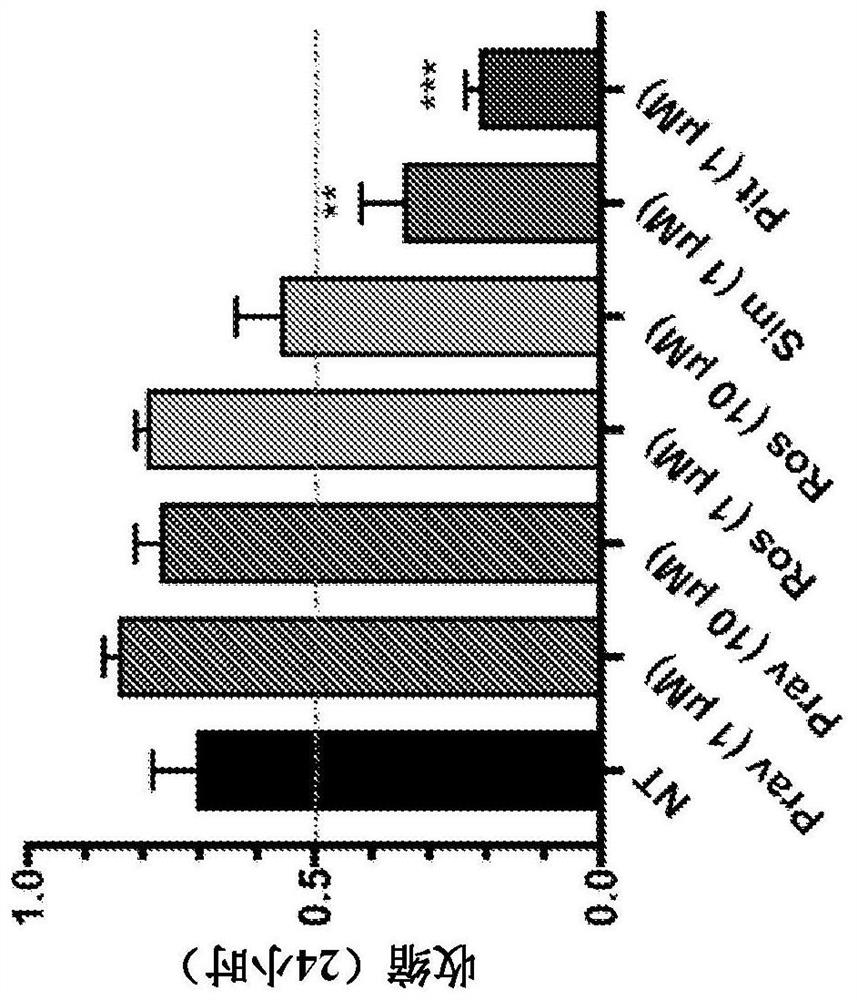
[0199]Cells were pretreated with pitavastatin and simvastatin acid at doses of 0 μM, 0.08 μM, 0.4 μM, 2 μM, 10 μM or 50 μM for 24 hours and then stimulated with histamine (10 μM). pitavastatin ( Figure 4A ) and simvastatin ( Figure 4B ) significantly reduced histamine-induced ASM contractions in both complete and serum-free media ( Figure 4C ). In complete medium, 0.08 μM pitavastatin was sufficient to inhibit histamine-mediated contraction of ASM ( Figure 4A ). However, to achieve similar protection, a 5× molar excess of simvastatin (SA) ( Figure 4B ). In serum-free medium, 0.4 μM pitavastatin and 10 μM simvastatin provided a similar degree of protection against histamine-induced contractions.
[0200] The time-dependent effects of SA and pitavastatin suggest that the ASM rela...
Embodiment 3
[0204] Example 3: deep breathing relaxation
[0205] This experiment shows that pitavastatin enhances the ASM relaxation effect of simulated deep breathing compared to the beta2-agonist isoproterenol.
[0206] Normal ASMs were treated with pitavastatin (1 μM, 24 hours, n=7), isoproterenol (10 μM, 30 minutes, n=6) or vehicle (n=7) and detected by CFS as described above. Figure 12 A shows that pretreatment with pitavastatin significantly inhibited basal ASM contraction compared to untreated controls. Shrinkage values normalized to untreated controls are shown. Figure 12 B shows that ASM cells rapidly and significantly abolished their contractions in response to a subsequent single stretch-no-stretch maneuver simulating deep breathing (10% amplitude, 4 sec duration). The contractile force is gradually recovered within 180 seconds. While force ablation was similar in all three groups, subsequent force recovery was significantly inhibited by pitavastatin treatment (*p<0.05...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com