Method of immune modulation by modulating ABCF1
A technology for immune response and autoimmune diseases, applied in the field of immune regulation, which can solve problems such as lack of transmembrane domains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Example 1: A novel ubiquitin E2-conjugating enzyme, ABCF1, reverse-regulates TLR4 endocytosis and cytokine storm during sepsis
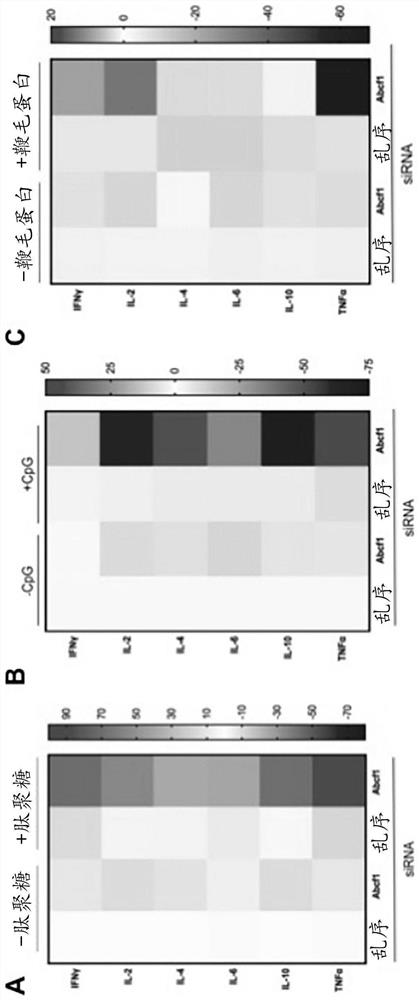
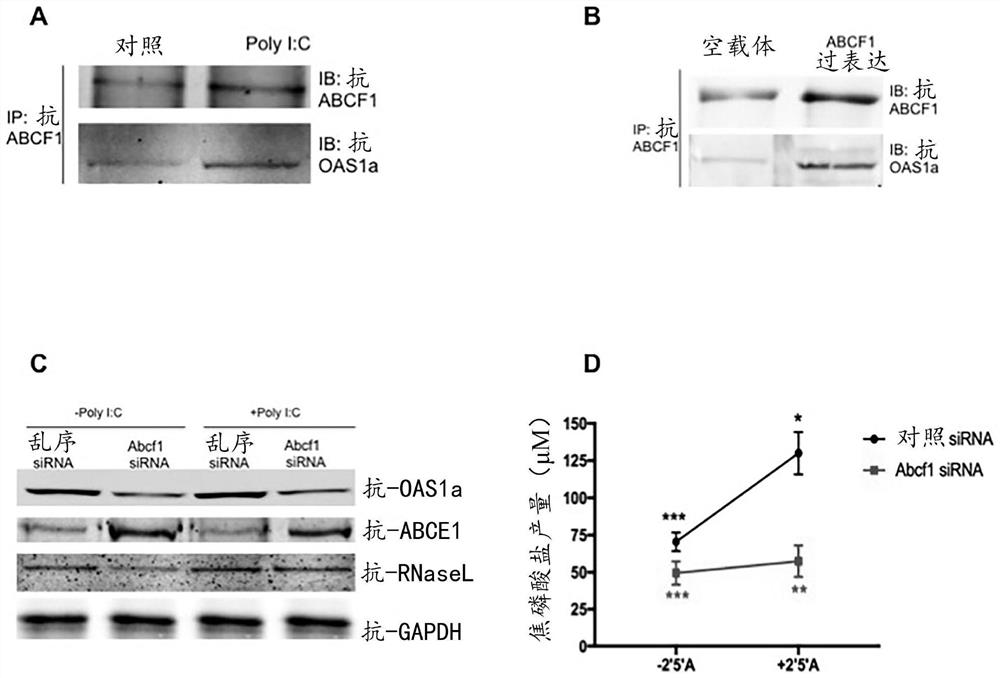
[0072] ABCF1 counter-regulates inflammation through TLR2 and TLR9. It binds to OAS1, regulates dsRNA viral cleavage and controls viral infection. After LPS stimulation, ABCF1 regulates ITAM phosphorylation in FcyR II A and regulates E. coli phagocytosis in BMDM.
[0073] Materials and methods
[0074]Mice and cells: Bone marrow cells were isolated from the femur and tibia of C57BL / 6 mice and matured into macrophages as described (Trouplin et al., 2016). Abcf1+ / - mice (Het) were prepared as previously described (Wilcox et al., 2017), and C57BL / 6J (Jackson Laboratories; 000664) mice were used as wild-type (WT) controls for in vivo experiments.
[0075] Transfection: All gene knockdown in cells with liposomes TM RNAiMAX transfection reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific; 13778075) was accomplished by RNAi interference according to the manufactur...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: ABCF1 controls endocytosis of TLR4 through its E2-binding activity
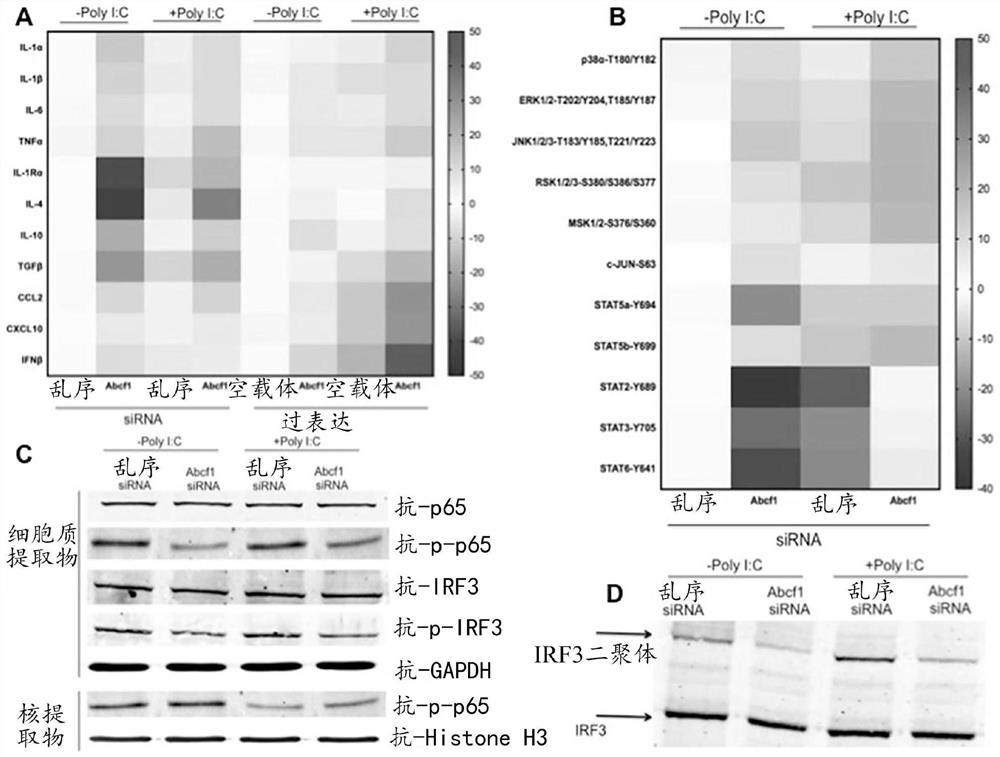
[0112] Here, ABCF1 is described as an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, a novel activity among ABC transporters involved in regulating and controlling key elements of cytokine secretion through ubiquitination, modulating TLR4 endocytosis and controlling sepsis-mediated Leading ET period.
[0113] result
[0114] ABCF1 switches macrophage polarization to the M2b phenotype: To investigate whether ABCF1 regulates the switch in macrophage polarization, LPS-stimulated Abcf1 siRNA-treated and overexpressed BMDMs were analyzed for M1 and M2 specificity by flow cytometry Levels of cell surface markers. The levels of M1-specific markers such as CD86 and MHC-II were highest in Abcf1 siRNA-treated cells, followed by ABCF1-overexpressed cells ( Figure 8 A). On the other hand, the levels of M2a-specific CD206 in Abcf1 siRNA-treated and ABCF1-overexpressed cells were the same or slightly lower than th...
Embodiment 3
[0142] Example 3: ABCF1 regulates the transition from SIRS to ET phase during sepsis:
[0143] Sepsis is a biphasic disease characterized by an initial hyperinflammatory phase, also known as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), followed by an immunocompromised phase, termed endotoxin tolerance (ET). The SIRS phase showed massive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL1β, TNFα, IL-6, and downregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, IL-4, IL-1Rα, while the ET phase showed the complete opposite. In SIRS, intense inflammatory insults often lead to impaired contractility, reduced cardiac index and ejection fraction, leading to circulatory collapse. Persistent circulatory failure leads to disruption of the microcirculation and vasculature, leading to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), a major determinant of sepsis mortality. Transition to the ET phase suppresses the overall inflammatory response, and death during this phase may be due...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com