Underdetermined blind source separation method and device based on structured sparse subspace clustering
An underdetermined blind source separation, subspace technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, pattern recognition in signals, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of weak robustness, insufficient accuracy, and narrow application range. Achieve a wide range of applications, improve the accuracy of signal recovery, and reduce the amount of computation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
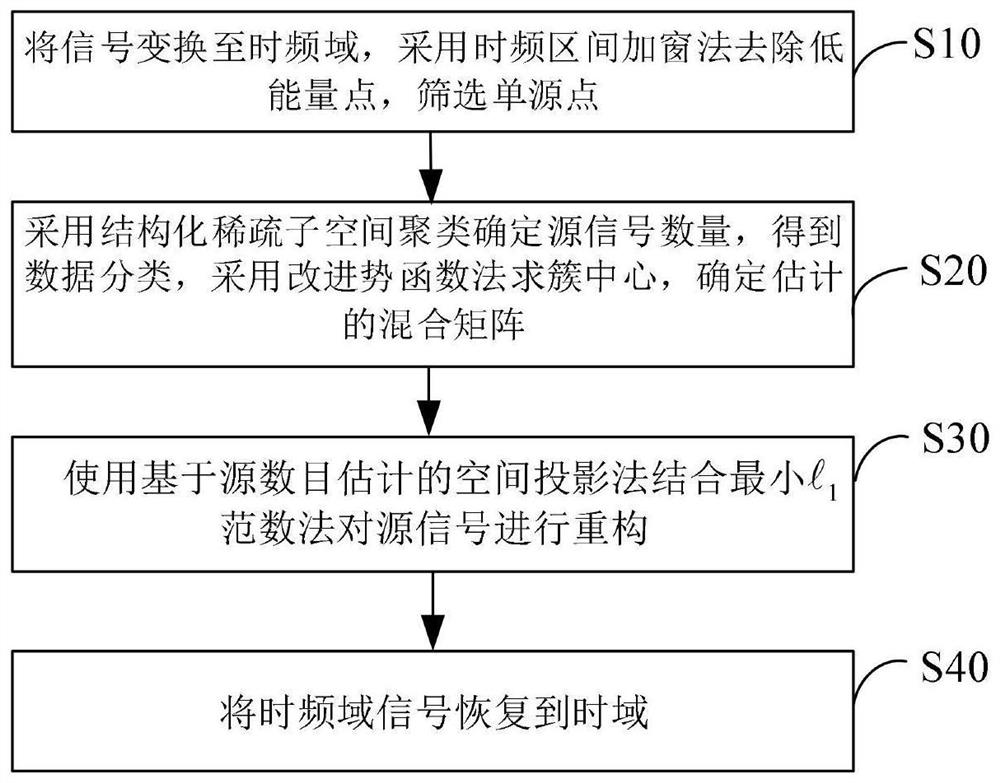
[0086] Embodiment one, such as figure 1 As shown, it is a flowchart of an underdetermined blind source separation method based on structured sparse subspace clustering, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0087] Transform the source signal to the time-frequency domain, use the time-frequency interval windowing method to remove low-energy points, and screen out single source points;
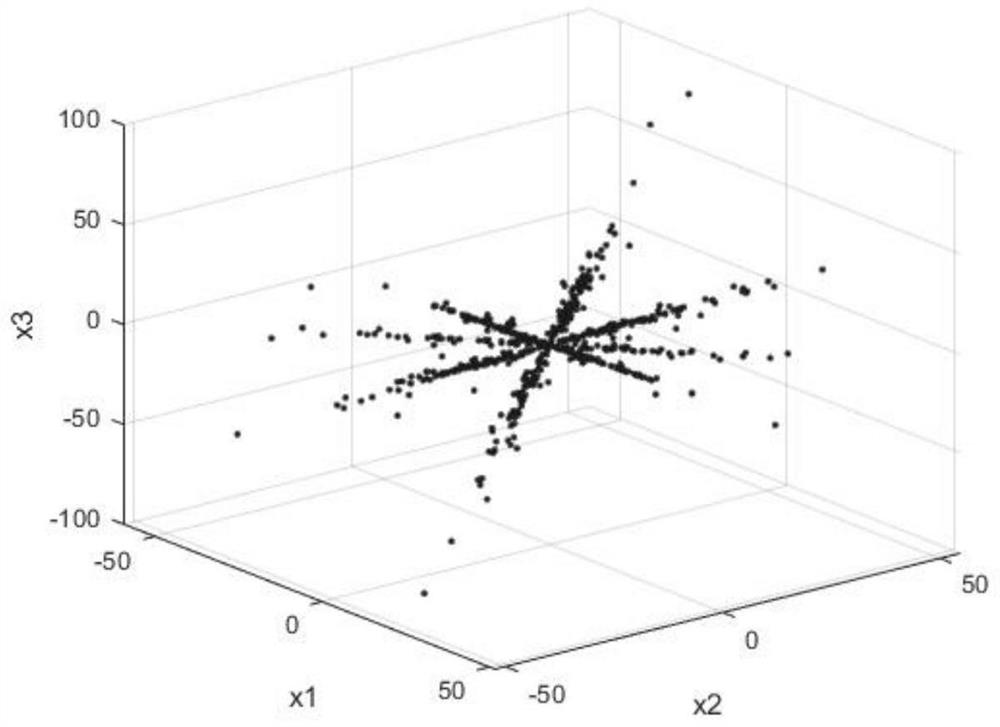
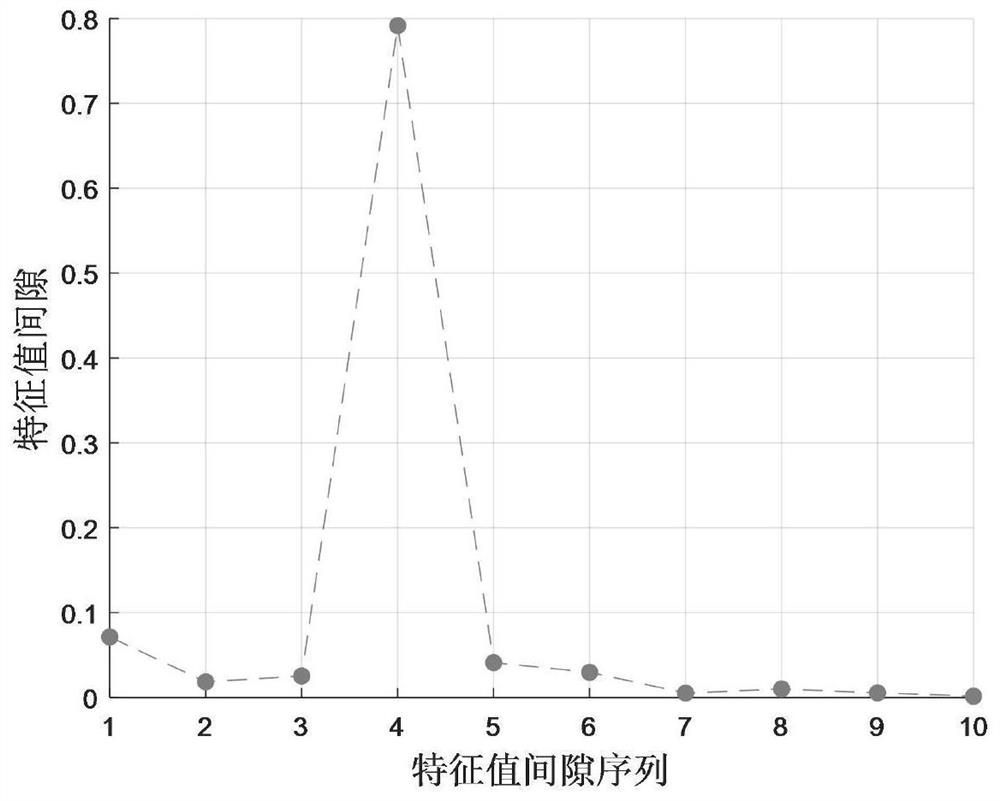
[0088] Using structured sparse subspace clustering to explore the subspace distributed in the single source point, determine the number of signal sources and each cluster to which the single source point belongs, use the improved potential function method to find the cluster center, and estimate the mixing matrix based on the cluster center;
[0089] Based on the mixing matrix, using the spatial projection method based on the estimation of the number of sources combined with the minimum The norm method reconstructs the source signal;
[0090] The reconstructed source signal in th...
Embodiment 2
[0143] In the second embodiment, the speech signal is selected as the source signal, and a specific underdetermined blind source separation method based on structured sparse subspace clustering is described.
[0144] Step 1, select the speech signal, the blind source separation model for underdetermined instantaneous mixing in the time domain can be expressed as:
[0145]
[0146] Among them, s(t)=[s 1 (t), s 2 (t),...,s n (t)] T Indicates n source signals, x(t)=[x 1 (t), x 2 (t),...,x m (t)] T Indicates m-way observation signals. A=[a 1 , a 2 ,...,a n ]∈R M×n (m<n) means an unknown mixing matrix. Due to the poor sparsity of the signal in the time domain, the time domain signal x(t) is transformed into the sparse time-frequency domain by short-time Fourier transform to obtain X(t, f). When the sparsity is guaranteed, if only one source plays a dominant role in a certain time-frequency interval, and the values of other source signals are 0 or close to 0, the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com