Anti-hvem antibodies and use thereof
An antibody and reagent technology, applied in the field of immunotherapy, which can solve problems such as side effects, suboptimal patient response rate, adverse reactions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0176] Example 1: Identification of HVEM as an immune blocking target
[0177]A high-throughput genome-wide primary siRNA screen consisting of approximately 8,300 genes was run on 2 patient-derived melanoma cell systems. Killing was assessed using an LDH-based cytotoxicity assay 96 hours after siRNA transfection by overnight co-culture with TILs. Successful knockdown of positive controls was assessed by FACS. Using the same design as the primary screen—in which positive hits were defined based on their Z-score and percent killing enhancement—a confirmatory screen consisting of 360 genes was validated on eight melanoma cell systems, Correction was made for the effect of siRNA on proliferation. Finally, a validation screen consisting of 54 genes was performed on 5 melanoma cell systems. HVEM was found to have strong positive hits as a potential immunotherapy target.
Embodiment 2
[0178] Example 2: Selection of scFv for HVEM
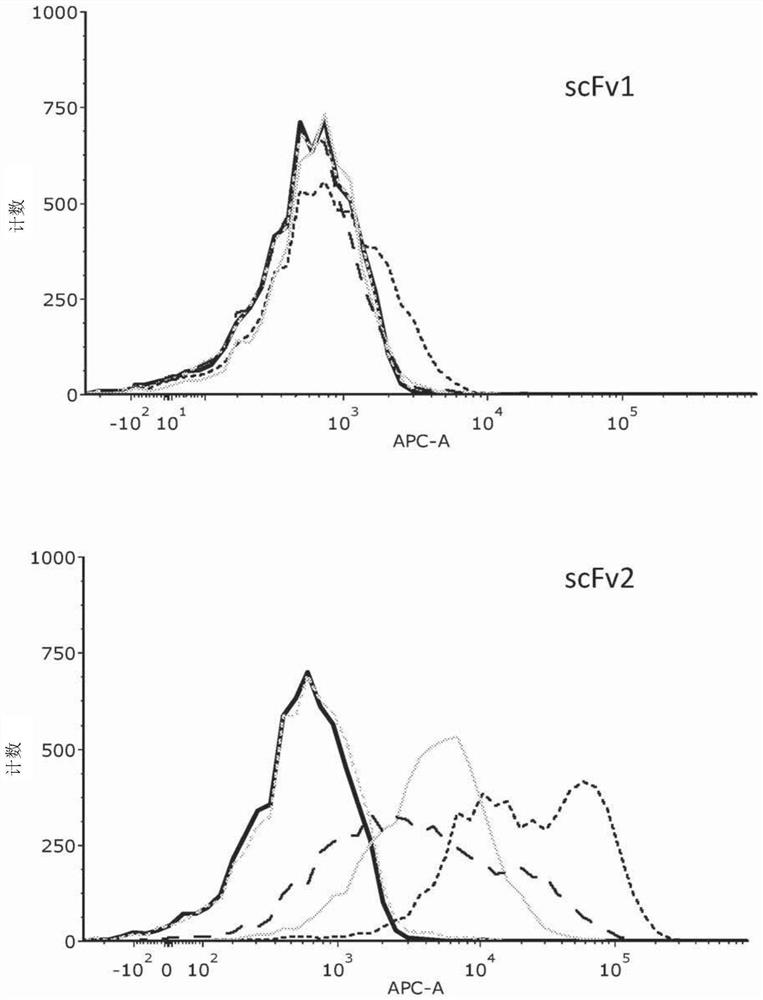
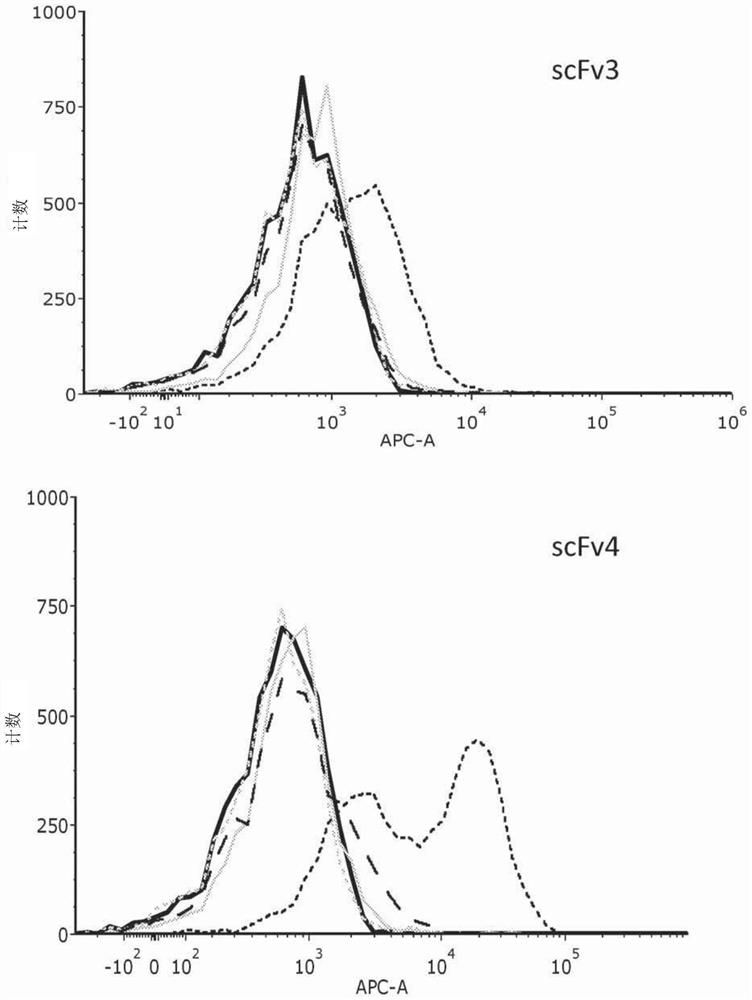
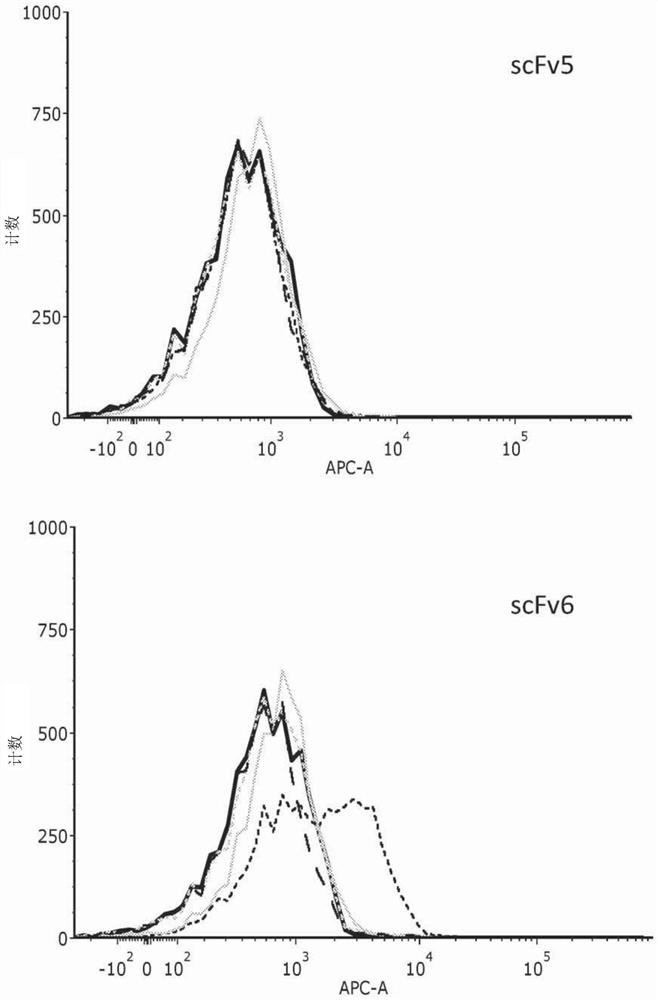
[0179] Having established HVEM as a potential target for therapeutic immune blockade in cancer therapy, single-chain antibody fragments (scFv) that can bind to HVEM were isolated and assayed. scFvs were isolated as described above (Materials and Methods). Six selected scFvs were screened for binding to recombinant human, mouse and cynomolgus HVEM (see Table 1). Five of the six showed strong binding to human recombinant HVEM (hrHVEM) expressed in CHO-K1 cells as measured by cellular ELISA. CHO-K1-null cells were used as a negative control. Two of these five showed very strong binding to mouse recombinant HVEM (mrHVEM), while the other three showed much weaker binding. One of the five also showed strong binding to monkey (cynomolgus) HVEM, while three of the others showed much weaker binding. FACS analysis was used to confirm these results. The scFv contained a HIS tag and an anti-HIS second APC-conjugated antibody was used to ...
Embodiment 3
[0183] Example 3: Anti-HVEM IgG Antibodies
[0184] Although the single chain antibody scFv2 was effective at blocking the HVEM-BTLA interaction, a fully IgG monoclonal antibody (mAb) was designed from the scFv2 light and heavy chains, specifically the CDRs. The scFv2 was sequenced and the light and heavy chains were cloned into an IgG4 backbone (excluding the S228P mutation). The complete sequence of this mAb heavy chain is present in SEQ ID NO:9 and the light chain is present in SEQ ID NO:10. The presence of intact IgG antibodies was confirmed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting ( image 3 ).
[0185] Next, the binding of the new mAbs to recombinant HVEM from humans, mice and monkeys was assessed as before. Binding to hrHVEM was assessed by ELISA as before. The new mAbs strongly bind hrHVEM ( Figure 4A ). Binding was also assessed by FACS as before. CHO-K1 empty, CHO-K1 hrHVEM, CHO-K1 mrHVEM, and CHO-K1 crHVEM cells were incubated with 20 μg / ml antibody or hIgG4 isotype...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com