Structure and control method of bionic robot intelligent power arm with multiple sensors
A bionic robot and multi-sensor technology, applied in the structural field of the intelligent power arm of the bionic robot, can solve the problems of limited torque, limited practicality, and limited structural space, so as to automatically adjust the grasping force, improve the driving efficiency, and eliminate mutual effect of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046]A structure of a bionic robot intelligent power arm with multiple sensors, including several knuckles and several finger roots, and also includes a power group and a pulling group, one end of the pulling group is fixedly connected to the power group, and the pulling group The other end of the knuckle is fixedly connected with the base of the finger.
[0047] In this embodiment, 20 motors and 20 flexible ropes are set.
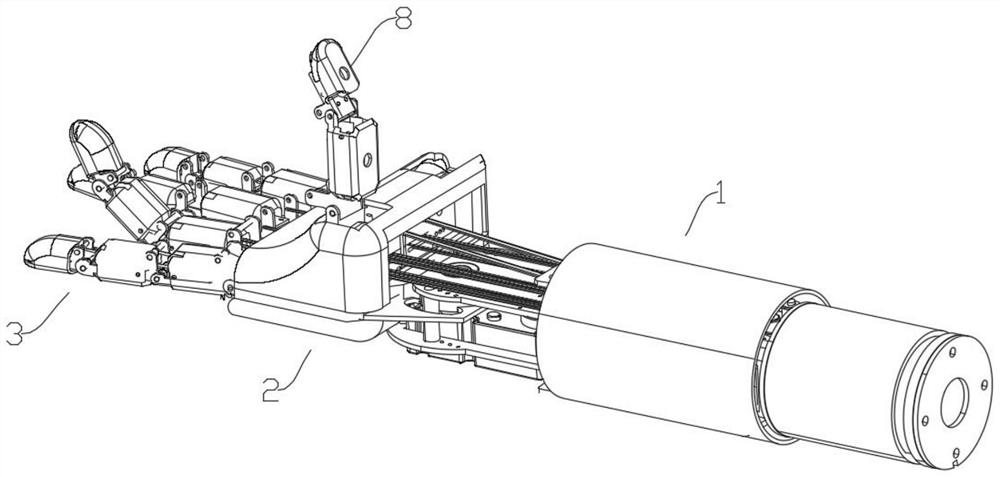
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown, the structure of a bionic robot intelligent power arm with multiple sensors includes a forearm 1, a palm 2, 4 fingers 3 and a thumb 8. This kind of robotic hand is set up like a human hand and can serve humans.
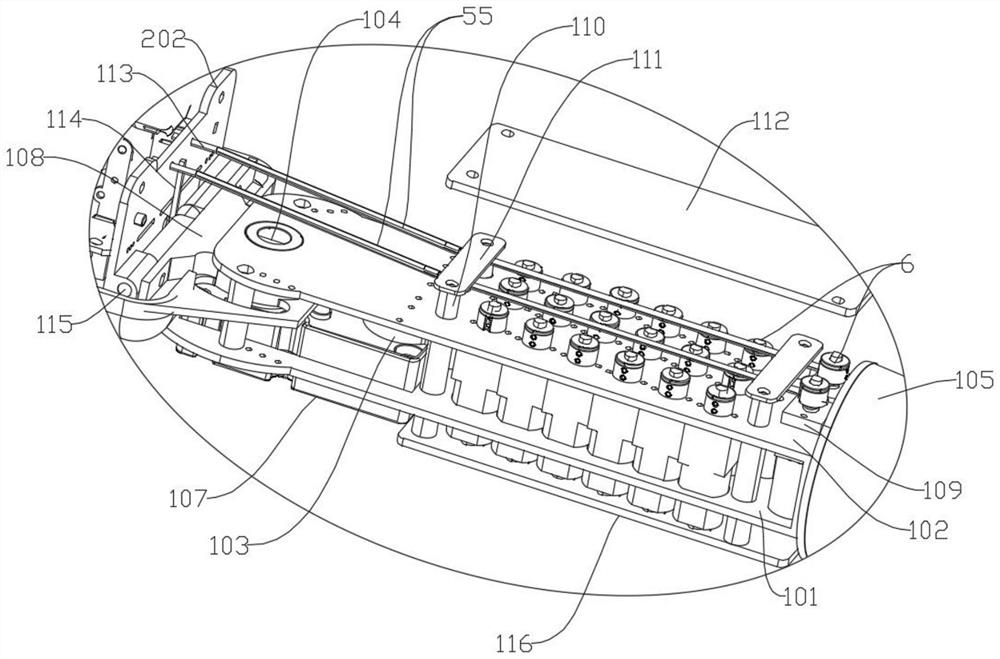
[0049] Such as figure 2 As shown, the palm 2 and the forearm 1 form the wrist left and right movement and wrist bending movement in the two directions of the cross, wherein the wrist left and right movement is formed by the rotation of the arm shaft 104, and the wrist bending movement is formed by the support ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Such as Figure 13 and Figure 14 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is: the difference from embodiment 1 is that embodiment 1 uses 20 motors, of which 4 motors are used to control the root of 4 fingers, and the 4 motors correspond to The flexible rope is worn on the palm; in the present embodiment, at least 17 motors are used, specifically 18 motors, of which 1 motor is used to control the root of 4 fingers, and the flexible rope corresponding to the 1 motor ( Figure 14 The back flexible rope (56) in the middle is worn on the back of the hand.
[0090] The second reset member 10 in this embodiment adopts a spring; a spring is fixed between two adjacent connecting seats 301, and the root of the index finger and the root of the little finger are all provided with small holes 58 on the side of the back of the hand, and one of the motors 67 is installed on the inside of the palm board 201 ( Figure 15 shown), the back flexible rope 56 pas...
Embodiment 3
[0094] On the basis of Embodiment 2, the difference with Embodiment 2 is that the two direct motors used to control the thumb in Embodiment 2 are fixed on the forearm, while the two motors in this embodiment It is fixed on the back of the hand, which can not only reduce the load on the forearm, but also shorten the length of the forearm, and at the same time increase the strength of the thumb movement.
[0095] Such as Figure 13 , Figure 14 As shown, shown in the figure is an illustration on the basis of Embodiment 2.
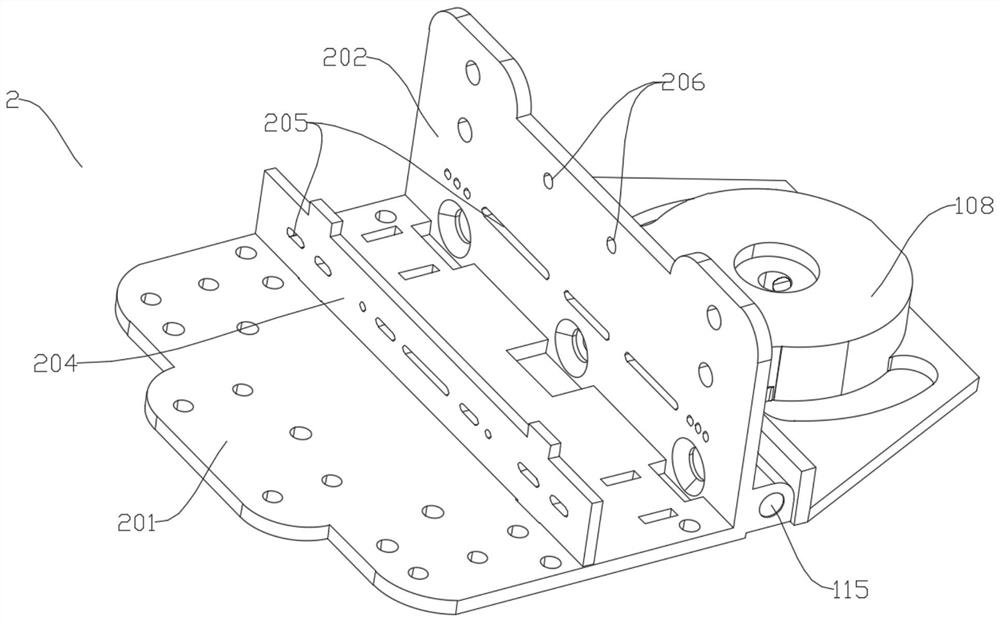
[0096] As shown in the figure, 2 motors 61 are fixed on the back of the hand, and the corresponding flexible rope passes through 2 dispersing holes 205 at the base of the thumb ( Figure 11 shown), then go around the pulley 809 and be connected to the corresponding first power shaft ( Figure 9 shown in ).
[0097] In this embodiment, the two motors that control the thumb are transferred from the arm to the back of the hand, reducing the weight of the arm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com