Electrified railway double-current system traction power supply system and control method thereof
A technology for traction power supply systems and electrified railways, applied to electrical components, power lines, and individual AC networks with different frequencies, etc., can solve problems such as the complexity of transportation networks, achieve the effects of improving utilization effects, reducing construction area and costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
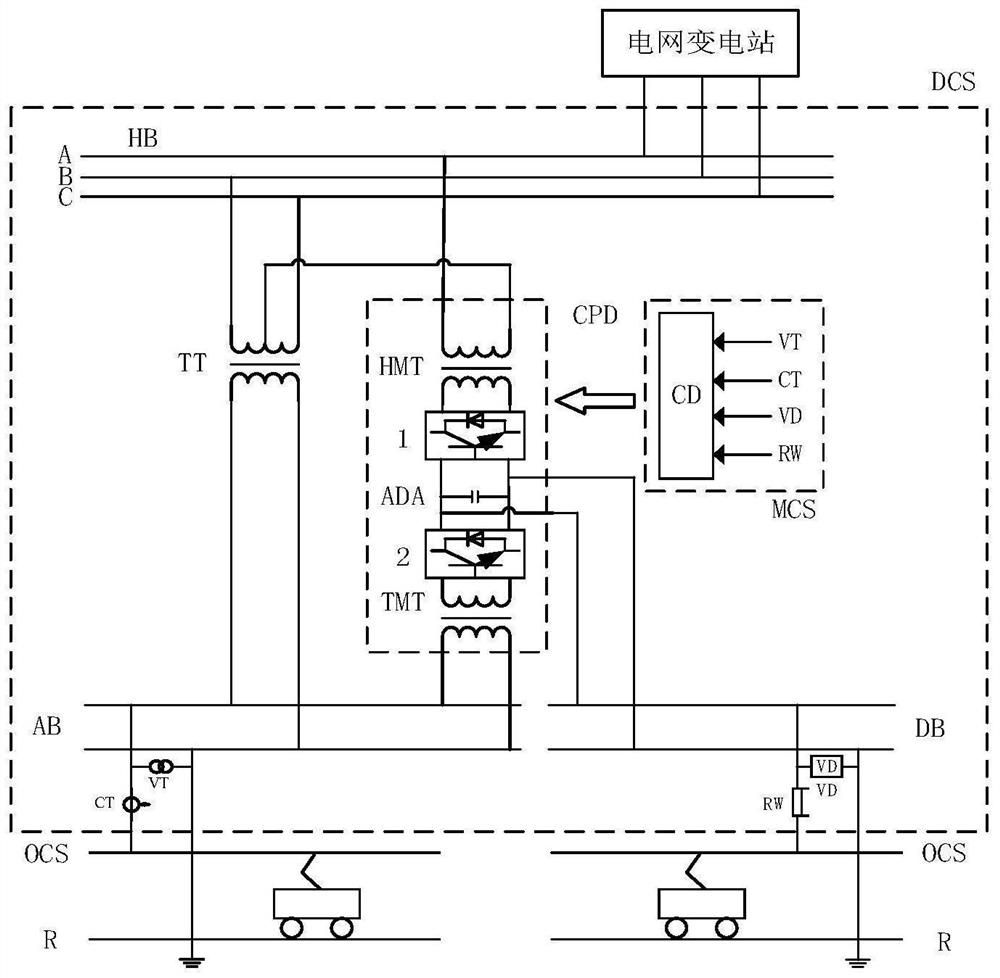
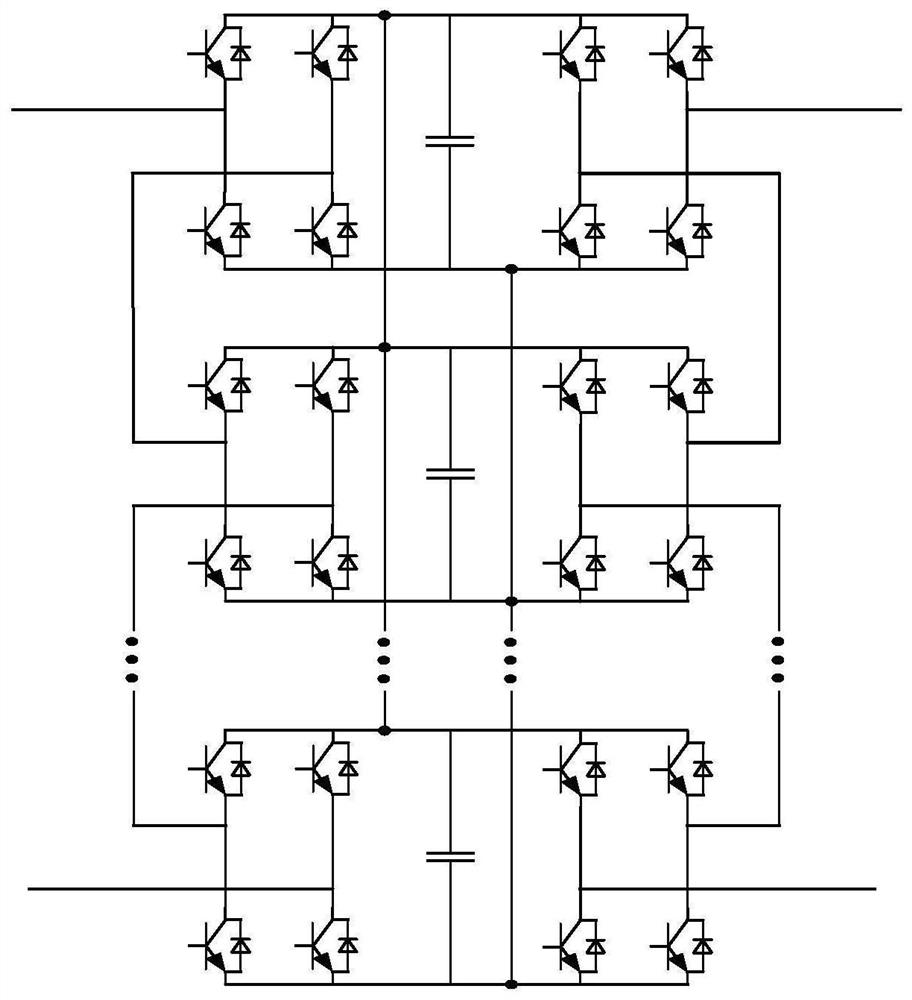
[0029] like figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a dual-current traction power supply system for electrified railways. Two terminals of the primary side of the traction transformer TT are connected to any two phases of the three-phase high-voltage bus HB, and the secondary side is connected to the AC On the bus AB; the same-phase compensation device CPD includes a high-voltage matching transformer HMT, an AC-DC converter ADA, and a traction matching transformer TMT; the primary side of the high-voltage matching transformer HMT is connected to the three-phase high-voltage bus HB, so that the secondary winding of the traction transformer TT and The voltage phase difference of the secondary winding of the high-voltage matching transformer HMT is 90°, the traction matching transformer TMT is connected with the AC bus AB, the DC side of the AC-DC-AC converter ADA is parallel connected with the DC bus DB; one end of the AC bus AB is connected in series ...
Embodiment 2
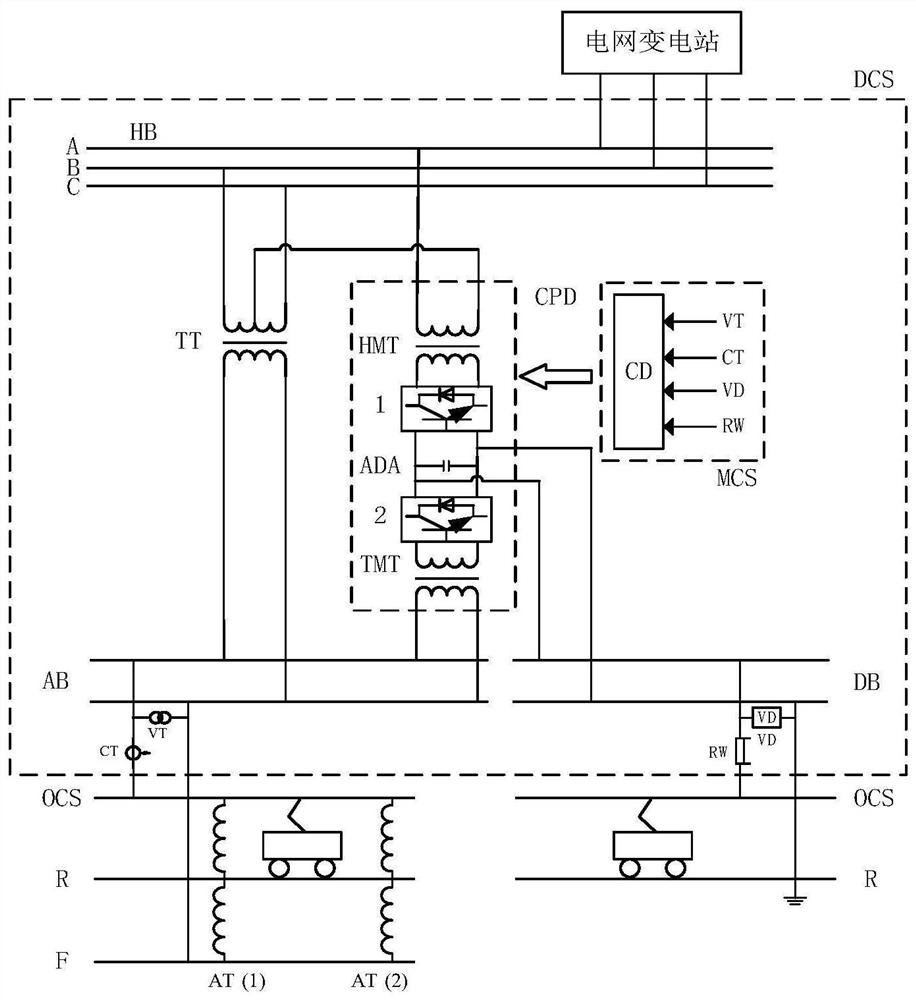
[0032] like Figure 4 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a dual-current traction power supply system for electrified railways. The primary side of the traction transformer TT is connected to any two phases of the three-phase high-voltage bus HB, and the primary side of the high-voltage matching transformer HMT is connected to the three-phase high-voltage bus HB is connected so that the voltage phase difference between the secondary winding of the traction transformer TT and the secondary winding of the high-voltage matching transformer HMT is 90°; TT constitutes a balanced connection, in which the secondary winding of the traction transformer TT and the secondary winding of the high-voltage matching transformer HMT form a 90° voltage phase difference.
Embodiment 3
[0034] like Figure 5 As shown, the present invention provides a schematic flow chart of a method for controlling electric railway dual-stream traction power supply, and the specific steps are:
[0035] (1) Set the compensation target as the negative-sequence allowable amount S of the three-phase high-voltage bus HB ε ;
[0036] (2) Calculate the measured voltage and current values through the controller CD of the comprehensive compensation measurement and control system MCS, and calculate the AC load power S L1 and DC load power S L2 , to obtain the maximum AC negative sequence power generated by the AC load power and DC load power passing through any channel of the traction transformer or high-voltage matching transformer and DC maximum negative sequence power And judge its relationship with the three-phase high-voltage bus negative-sequence allowable S ε relationship; if or and At this time, there is no need to compensate the negative sequence; if and At ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com