Compositions and methods for detecting Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
A technology for detecting viruses and samples, which is applied in the field of in vitro diagnostics and can solve problems such as the complexity of actual virus diversity and characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0098] The following examples and figures are provided to aid in the understanding of the present invention, the true scope of which is set forth in the appended claims. It should be understood that modifications may be made in the procedures set forth without departing from the spirit of the invention.
[0099] The test is fully automated sample preparation (nucleic acid extraction and purification) followed by PCR amplification and detection. The system used is 6800 / 8800System, which consists of sample supply module, transfer module, processing module and analysis module. Automated data management by 6800 / 8800System execution.
[0100] The master mix contains detection probes specific for EBV and control nucleic acids. The specific EBV and control detection probes are each labeled with one of two unique fluorochromes that serve as reporters. Each probe also has a second dye that acts as a quencher. Reporter dyes are measured at defined wavelengths, allowing detection...
example 1
[0102] Example 1: Design of primers and probes for detection of EBV by real-time PCR
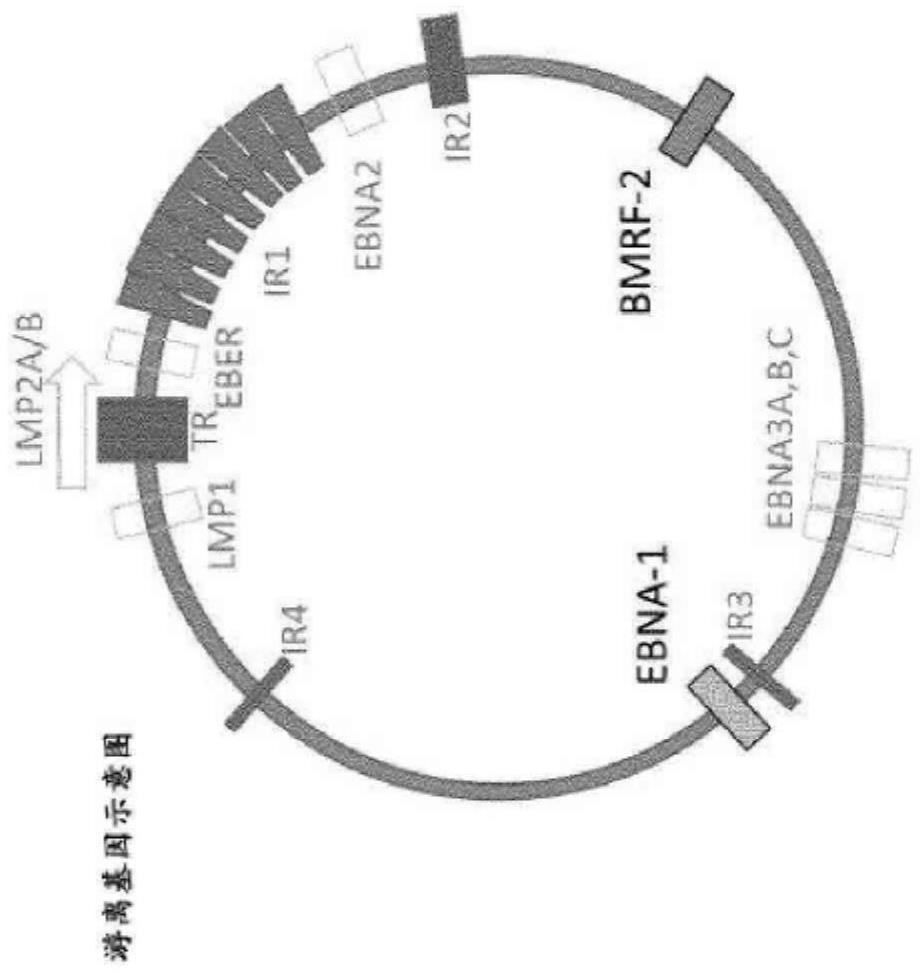
[0103] The EBV nucleic acid test was designed with two targets in mind. The two targets chosen were BMRF2 and EBNA1 and are shown in Figure 1. These candidates can be used individually or dually together in dual target assays. If used as a dual target assay, two sets of primers and probes (each detecting EBNA1 or BMRF2) were employed. As shown in Table 1 above, the primers for the BMRF2 target have the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 1 and 3, and the probe for the BMRF2 target has the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2. In addition, as shown in Table 1 above, the primers for the EBNA1 target have the nucleic acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 4 and 6, and the probe for the EBNA1 target has the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 5. The amplicon generated by the primers targeting BMRF2 is a 96 base pair long amplicon, and as figure 2 shown (and where primers and probes overlap the am...
example 2
[0104] Example 2: EBV Primers and Probes to Detect BMRF2 and EBNA-1 of EBV in a Real-Time PCR Assay
[0105] The EBV nucleic acid assay was tested using primers / probes for detection of BMRF2 (SEQ ID NO: 1-3) and EBNA1 (SEQ ID NO: 4-6). A complete procedure for the EBV assay was run. Four types of EBV-containing samples were used: (1) EBV-infected Raji cell extracts spiked into EBV-negative plasma; (2) extracted EBV DNA (extracted from the B95-8 cell line from AdvancedBiotechnologies (Cat. No. 17-926-500)); (3) Qnostics EBVAnalytic Panel (EBV1604009C); and (4) 1 of EBV st WHO International Standard. The reagents used include 6800 / 8800 Universal PCR Master Mix, with Features and conditions for use with the 6800 / 8800, and the use of Amplification and detection techniques. The final concentration of oligonucleotides in the master mix was 0.3 μM for primers and 0.1 μM for probes. adopted The 6800 / 8800PCR Profile is shown in Table 2 below:
[0106]
[0107] Table 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com