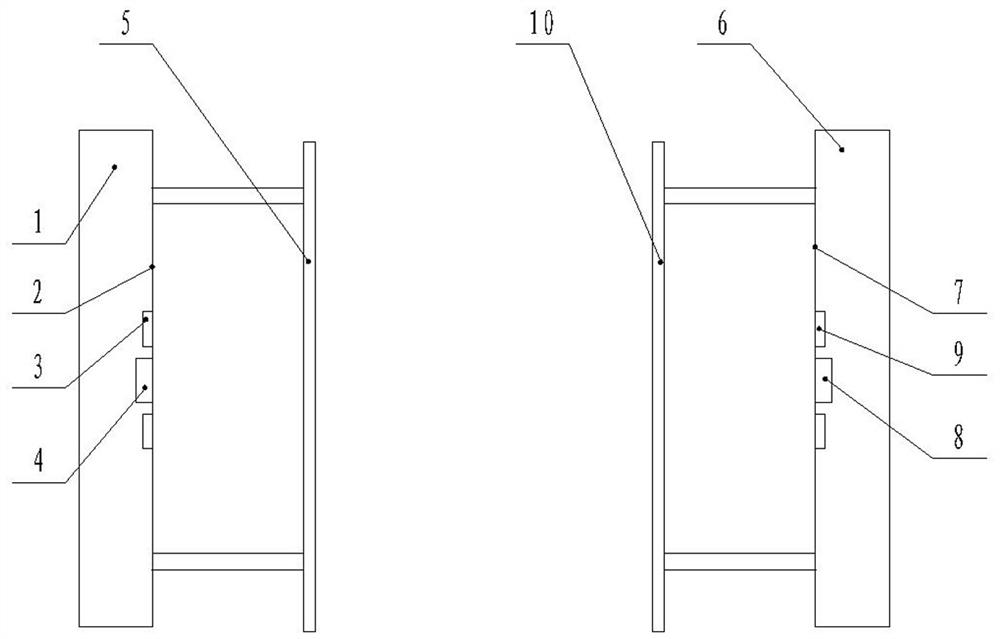
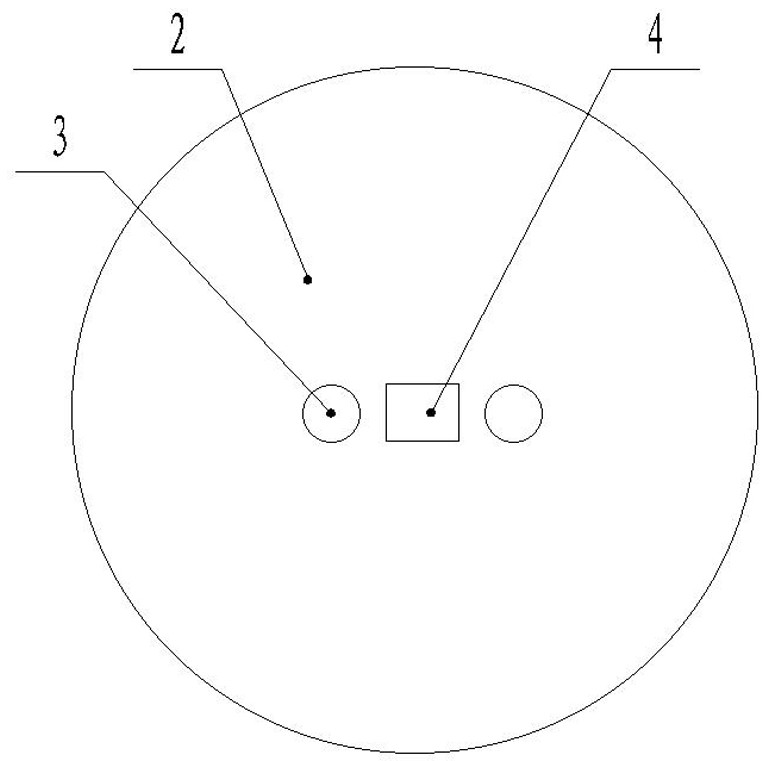
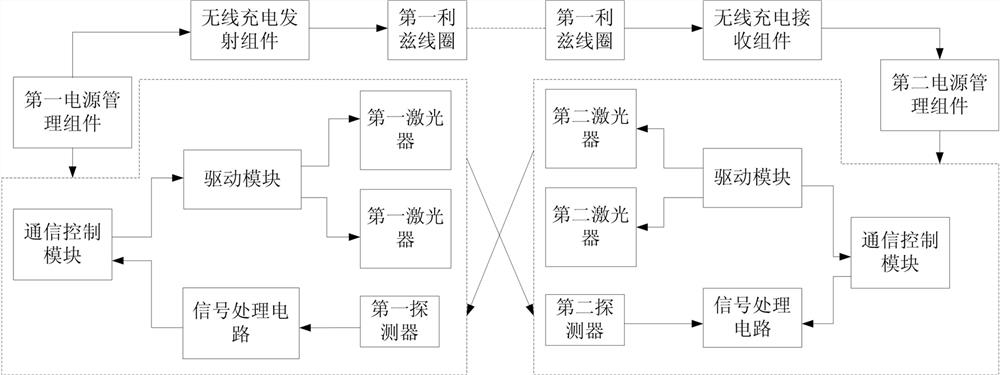
Wireless passive bidirectional laser communication module
A laser communication, wireless passive technology, applied in the direction of optical fiber radio, optical fiber transmission, electromagnetic wave transmission system, etc., can solve the problems of low security, easy interference, difficult equipment parameters, etc. Effects of Stability and Reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example
[0057] Experimental example: the laser distance is l=12mm, and the detector diameter is d=1.2mm. L=100-2.7 (relative position of the laser)-3 (relative position of the detector)=94.3mm, the number of simulated rays is 100 for each laser, and the number of analysis rays is 100,000. The parameter of the laser light source is 35mW, and the half divergence angle is 8°. The sensitivity is -69.6dBm (estimated in the manual), and finally according to the ZEMAX simulation, the received optical power of the detector is 0.64mW (about -2dBm), such as Figure 10 shown. Calculated by formula (2)|δ| =10.6mm.
[0058] When the Y direction of the single-sided laser module is 18mm, the received optical power is 0.0232mW (about -16.3dBm), such as Figure 11 shown. Far greater than the detection sensitivity of the detector, meeting the design requirements. When the X-direction offset of the single-sided laser module is 10.6mm, the received optical power is 0.0351mW (about -14.5dBm), such as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com