Multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming
A technology of reinforcement learning and logic programming, applied in machine learning, biological models, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to explain strategies, unusable, limited access rights, etc., achieve good explainability and improve collaborative behavior
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
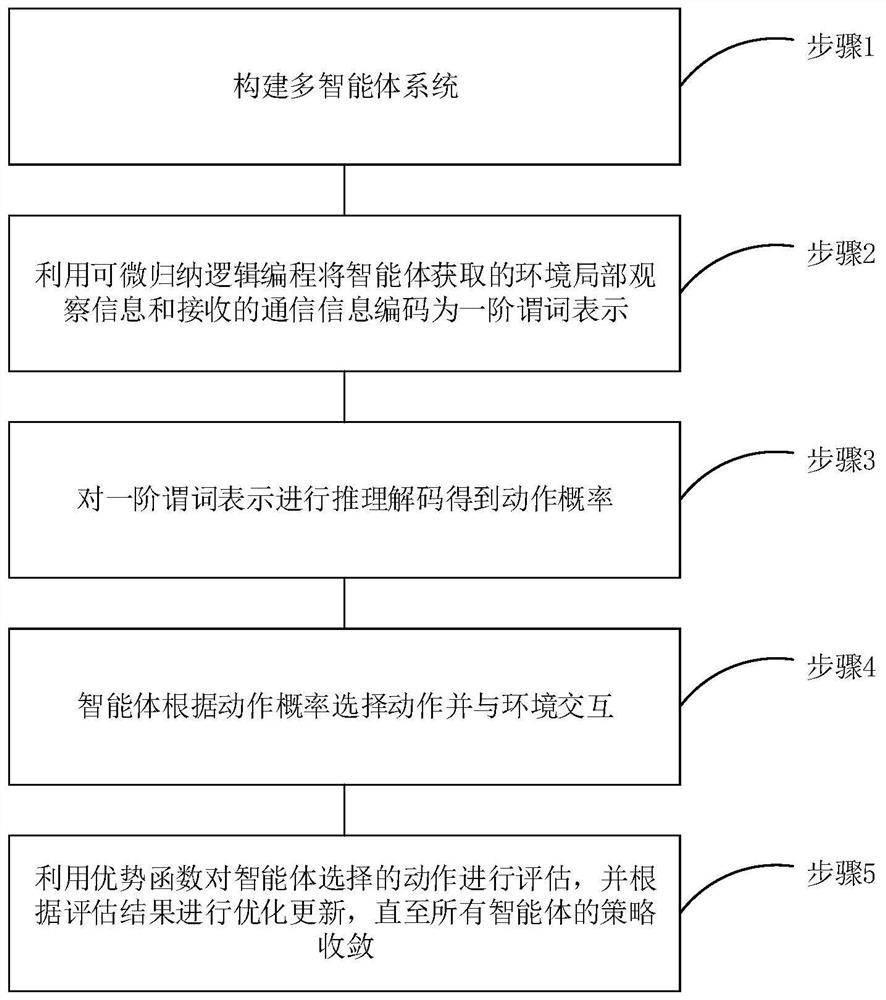
[0063] See figure 1 , figure 1 This is a schematic diagram of a multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming in this embodiment includes:
[0064] Step 1: Build a multi-agent system;
[0065] In this embodiment, the multi-agent system includes a reinforcement learning environment and multiple agents that interact with the environment. Where multiple agents work cooperatively in an environment to achieve a goal, the scenario can be defined as a partially observable Markov game with N agents.
[0066] In a multi-agent system, there is an environmental state S that describes the configuration of all agents, and an observation set (O) corresponding to the agent. 1 ,…,O N , and the action set (A 1 ,…,A N ), N represents the number of agents, where,
[0067] Each agent chooses an action...
Embodiment 2
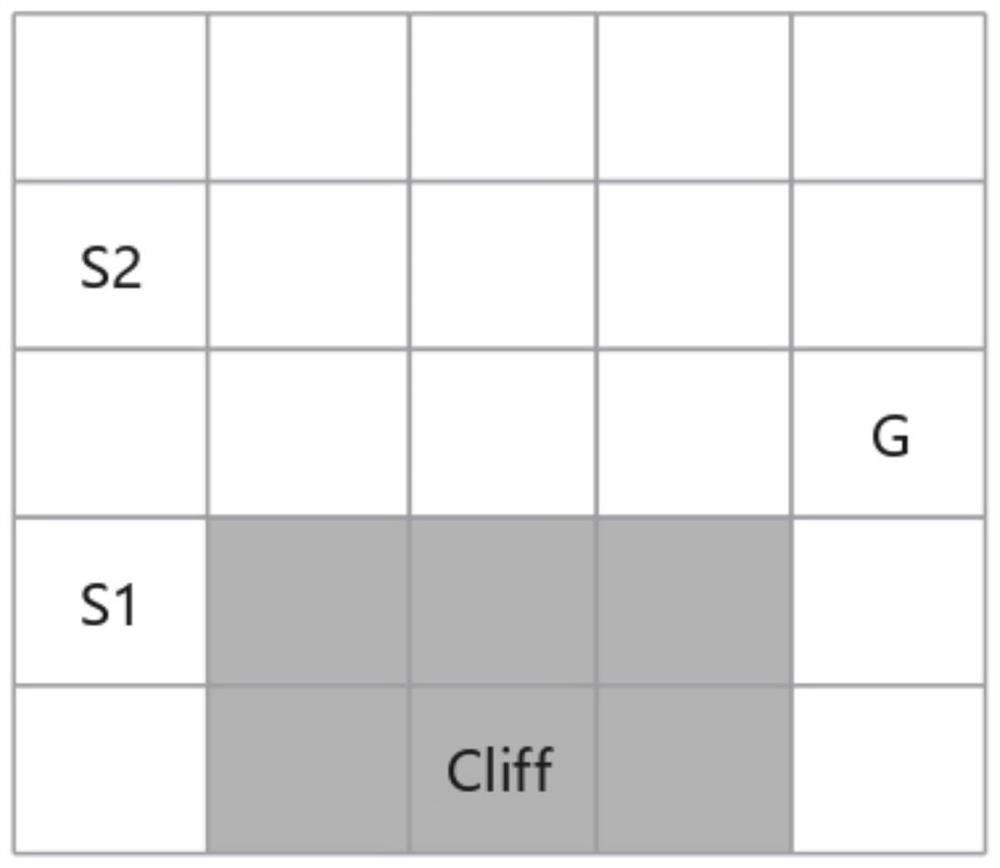
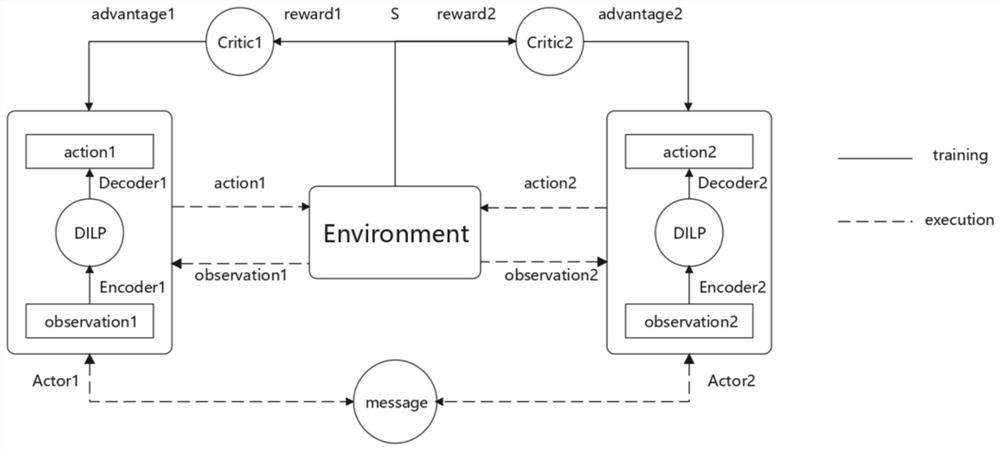
[0124] In this embodiment, the application principle of the multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming of the first embodiment is described in detail through test experiments. Please refer to figure 2 and image 3 , figure 2 It is an experimental environment diagram of a multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming provided by an embodiment of the present invention; image 3 It is an architecture diagram of the multi-agent reinforcement learning method based on inductive logic programming provided by the embodiment of the present invention.
[0125] This example uses the well-known grid world environment in reinforcement learning as a testbed for the algorithm. like figure 2 As shown, the environment consists of a 5×5 grid. The two agents represented by S1 and S2 start from different positions and move towards a single goal represented by G. Each agent can take an action by choosing to move up, down...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com