Low-altitude flight gridding management method
A management method and low-altitude flight technology, which is applied in the field of grid-based low-altitude flight management, can solve problems such as easy confusion, unintuitive management interface, and altitude and latitude response to aircraft flight conditions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A low-altitude flight grid management method is implemented through the following steps;
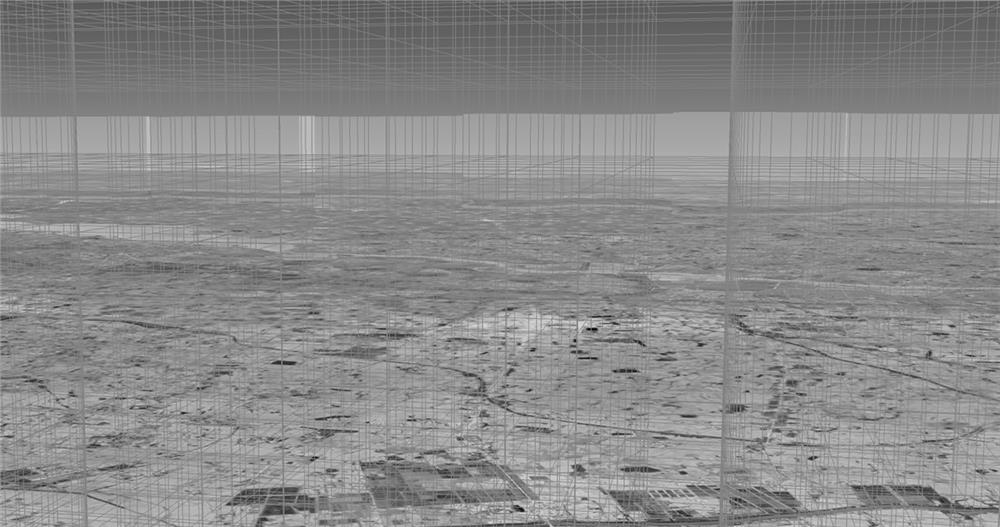
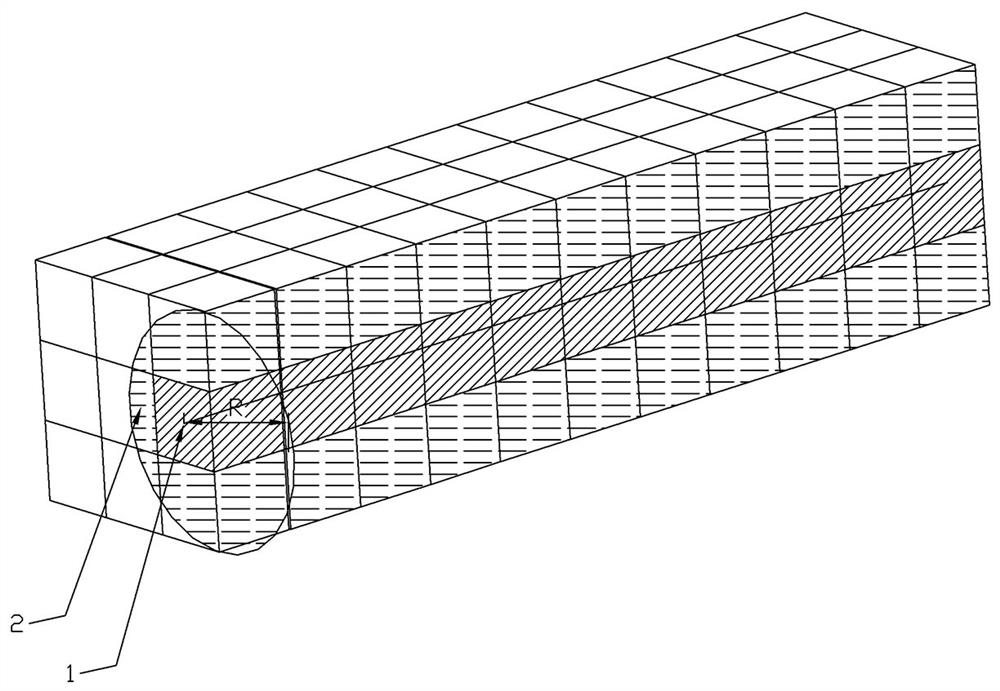
[0028] S1 is based on a three-dimensional geographic information system, and divides the management airspace into several continuous three-dimensional spatial grids; each grid has different grid characteristics; the grid characteristics include grid length, width and height; such as figure 1 shown;
[0029] S2 obtains the longitude, latitude and elevation information of the first UAV's expected flight path 1, and superimposes it with the gridded three-dimensional space;
[0030] S3 marks the grid with the first color 2 that overlaps the expected flight path.
[0031] The length, width and height of the grid can be set according to the type of UAV. The length, width and height of the grid (ie the difference in longitude, latitude, and elevation) can limit the spatial range contained in each grid. , so that after obtaining the longitude, latitude and elevation information of each ...
Embodiment 2
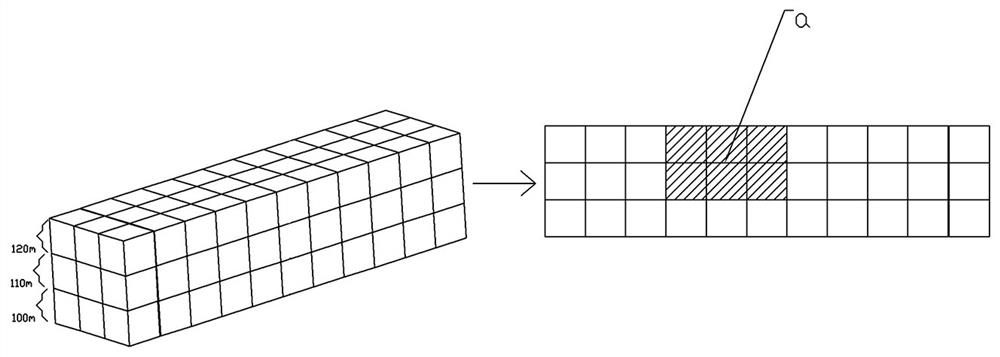
[0049] On the basis of Embodiment 1, further, the three-dimensional space grid is divided into several height layers from bottom to top according to the type of UAV, each height layer has different grid features, and the grid features include grid Length, grid width and grid height.
[0050] Each different altitude layer can correspond to different types of UAVs. The larger the load, speed and volume of the UAV, the higher the flight height should be, and the corresponding grid management space should also be set larger.
[0051] Further, the grid features also include speed limit and UAV type; real-time acquisition of UAV real-time position information, type information and speed information, while taking the speed limit and UAV type as constraints, if there is no one. If the aircraft type information does not match the UAV type attribute of the grid, or the flight speed exceeds the limit speed, the grid will be highlighted with a color mark and an early warning will be issue...
Embodiment 3
[0053] On the basis of Embodiment 1, further, in step S3, after obtaining the expected flight path of the first UAV, first perform a flight rehearsal in the grid space, and the rehearsal steps include:
[0054] S31 obtains UAV type information, flight speed, expected flight period, and expected flight path, and overlaps the expected flight path with the grid space, and counts the grids covered by the flight path;
[0055]S32, according to the number of covered grids and the expected flight period, calculate the time period during which the drone occupies the grid, and mark the grid with a time attribute;
[0056] S33 detects whether there are duplicate grids with other drones' expected flight paths;
[0057] S34 If there are duplicate grids, determine whether the difference between the estimated arrival times of multiple UAVs passing through the same grid is greater than the first threshold; if it is less than or equal to the first threshold, re-planning the path.
[0058] li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com