Fiber-reinforced composite material and sandwich structure
A fiber-reinforced, composite material technology, applied in the field of fiber-reinforced composite materials, can solve problems such as the decline of mechanical properties, and achieve the effect of light weight and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
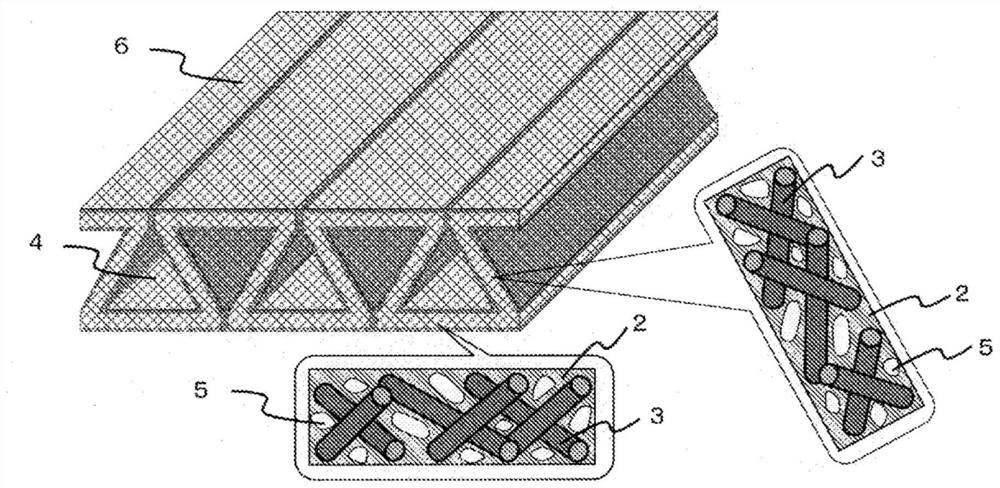
[0135] As the reinforcing fiber base material (B'), the carbon fiber nonwoven fabric produced in the above-mentioned manner is prepared to be folded into a Figure 10 The weight per unit area obtained from the cross-sectional structure shown is 100 g / cm 2folded substrate. At this time, when the prepreg is produced, in the pair of folds 8 adjacent to the reinforcing fiber base material (B'), the linear distance (Lr) between the pair of adjacent folds is 0 mm, that is, the contact is made Folding is carried out, and the distance (Lf) between the adjacent pair of folds along the carbon fiber nonwoven fabric is 10 mm, and one fold of the adjacent pair of folds is used as the starting point until it exists on the opposite side of the pair of folds. Fold it so that the straight-line distance (Ls) to the other crease in the direction becomes 5 mm. In addition, it folded so that the composition ratio 9 of a pair of folds that were close when the front and back surfaces of the folded...
Embodiment 2
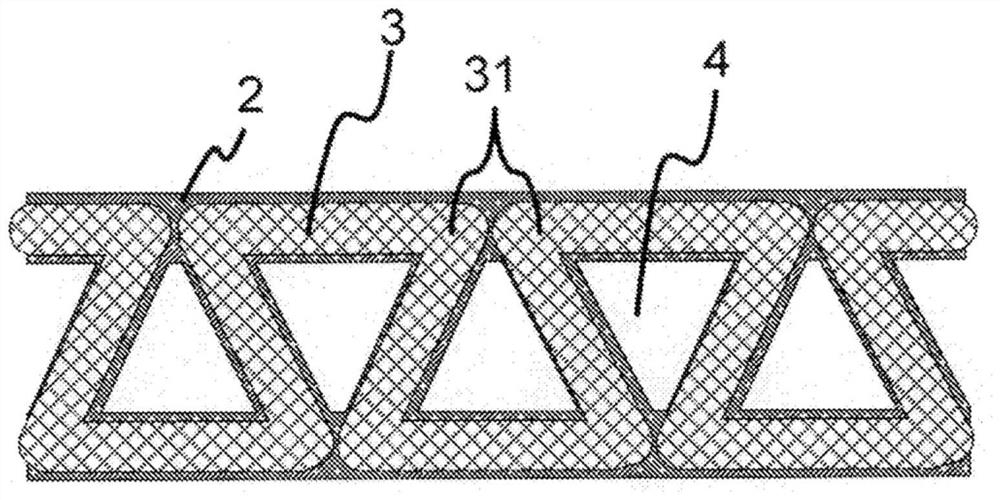
[0138] As the reinforcing fiber base material (B'), except that the configuration of the folded base material was changed so that Lr was 1 mm and Lf was 9 mm, processing was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a prepreg and a fiber-reinforced composite material. . The resulting fiber-reinforced composite material has figure 1 The illustrated cross-section surrounded by three sides of the fiber-reinforced structure is a substantially triangular opening. The openings of the cavity are aligned in the in-plane direction. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
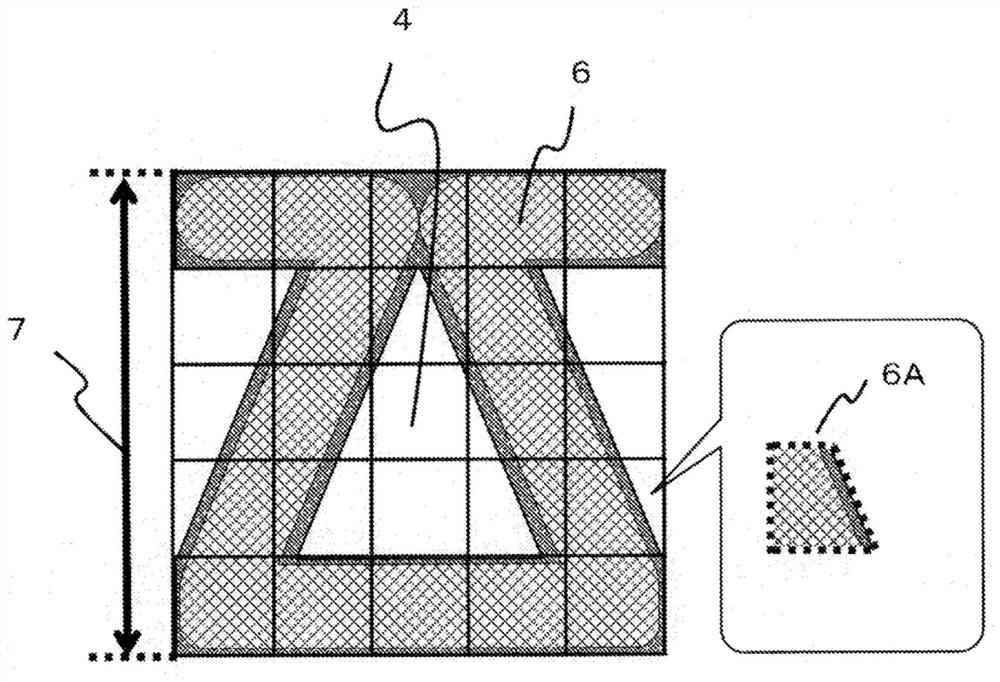
[0140] As the reinforcing fiber base material (B'), except that the configuration of the folded base material was changed so that Lr was 2 mm and Lf was 8 mm, processing was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a prepreg and a fiber-reinforced composite material. . The resulting fiber-reinforced composite material has Figure 13 The cross-section of the three sides of the fiber-reinforced structural portion as shown is a substantially trapezoidal opening. The openings of the cavity are aligned in the in-plane direction. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number average fiber length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap