Anti-hemagglutinin antibodies and methods of use thereof
A hemagglutinin and antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, chemical instruments and methods, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0176] Preparation of human antibodies
[0177] Methods for producing human antibodies in transgenic mice are known in the art. Any such known method can be used in the context disclosed herein to produce human antibodies that specifically bind to influenza B HA. An immunogen comprising any of the following can be used to generate antibodies against influenza B HA. In certain embodiments, the antibody is derived from a full-length native influenza B HA (see, eg, GenBank Accession Nos. AAA43697.1 or ACA33493.1), or with a live attenuated or inactivated virus, or with an encoded protein or fragment thereof DNA was obtained from immunized mice. Alternatively, influenza B HA protein or fragments thereof can be produced using standard biochemical techniques, modified and used as an immunogen. In some embodiments, the immunogen can be a recombinantly produced influenza B HA protein or a fragment thereof. In certain embodiments, the immunogen can be an influenza virus vaccine. I...
Embodiment 1
[0261] Example 1: Generation of Human Antibodies to Influenza B Hemagglutinin (HA)
[0262] exist Human antibodies to influenza hemagglutinin, which contain DNA encoding the variable regions of human immunoglobulin heavy and kappa light chains, are raised in mice. Mice were immunized with a combination of vectors expressing influenza A and B hemagglutinin, then infected and recovered with influenza A and B strains, followed by administration of a booster containing a cocktail of recombinant hemagglutinin proteins. Antibody immune responses were monitored by an influenza HA specific immunoassay. Anti-influenza B HA antibodies were isolated directly from antigen-positive mouse B cells that were not fused to myeloma cells as described in US Patent 7,582,298, which is specifically incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. Using this method, fully human anti-influenza HA antibodies (ie, antibodies with human variable domains and human constant domains) were obtained.
...
Embodiment 2
[0264] Example 2: Heavy and Light Chain Variable Region Amino Acid and Nucleotide Sequences
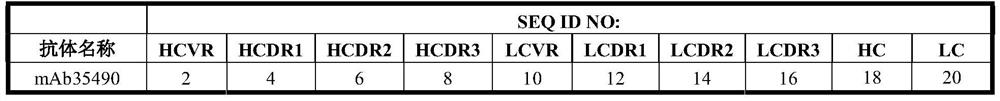
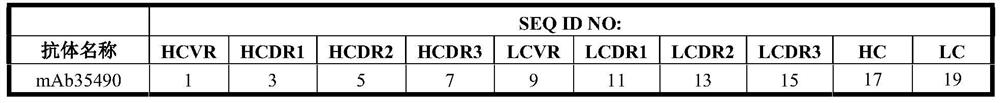
[0265] Table 1 lists the heavy and light chain variable regions and CDRs and amino acid sequence identifiers for the heavy and light chain sequences of exemplary anti-influenza B HA antibodies. The corresponding nucleic acid sequence identifiers are listed in Table 2.
[0266] Table 1: Amino Acid Sequence Identifiers
[0267]
[0268] Table 2: Nucleic acid sequence identifiers
[0269]
[0270] The antibodies disclosed herein have fully human variable regions, but may have mouse constant regions (eg, mouse IgG1 Fc or mouse IgG2 Fc (a or b isotype)) or human constant regions (eg, human IgG1 Fc or human IgG4 Fc). As understood by one of ordinary skill in the art, an antibody with a particular Fc isotype can be converted into an antibody with a different Fc isotype (eg, an antibody with mouse IgGl Fc can be converted into an antibody with human IgG4, etc. ), but in any case the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com